Chapter 8: Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Red marrow of bones
provides a site for blood cell formation
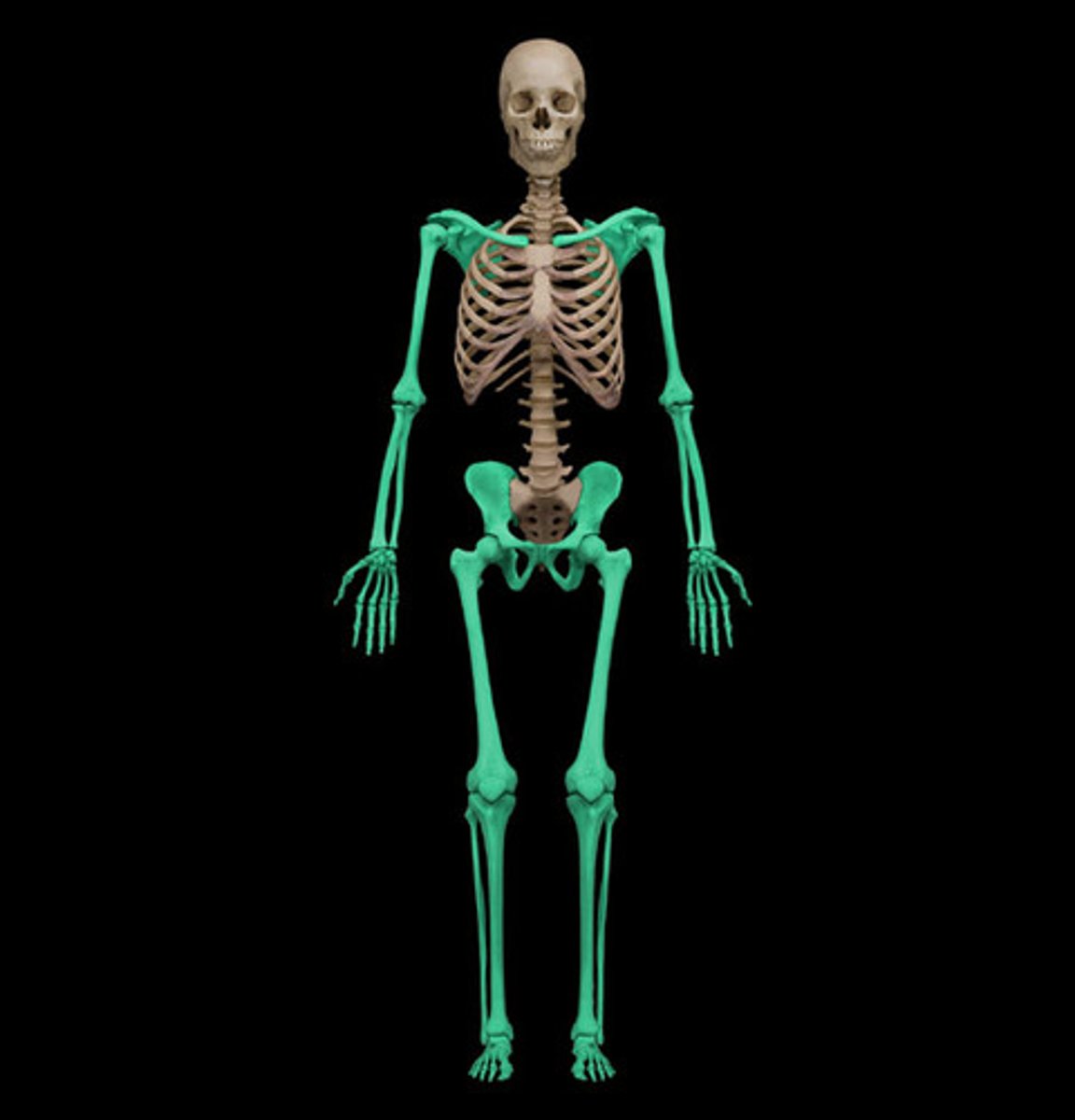
appendicular skeleton
Bones of the limbs and limb girdles that are attached to the axial skeleton
illium
hip bone
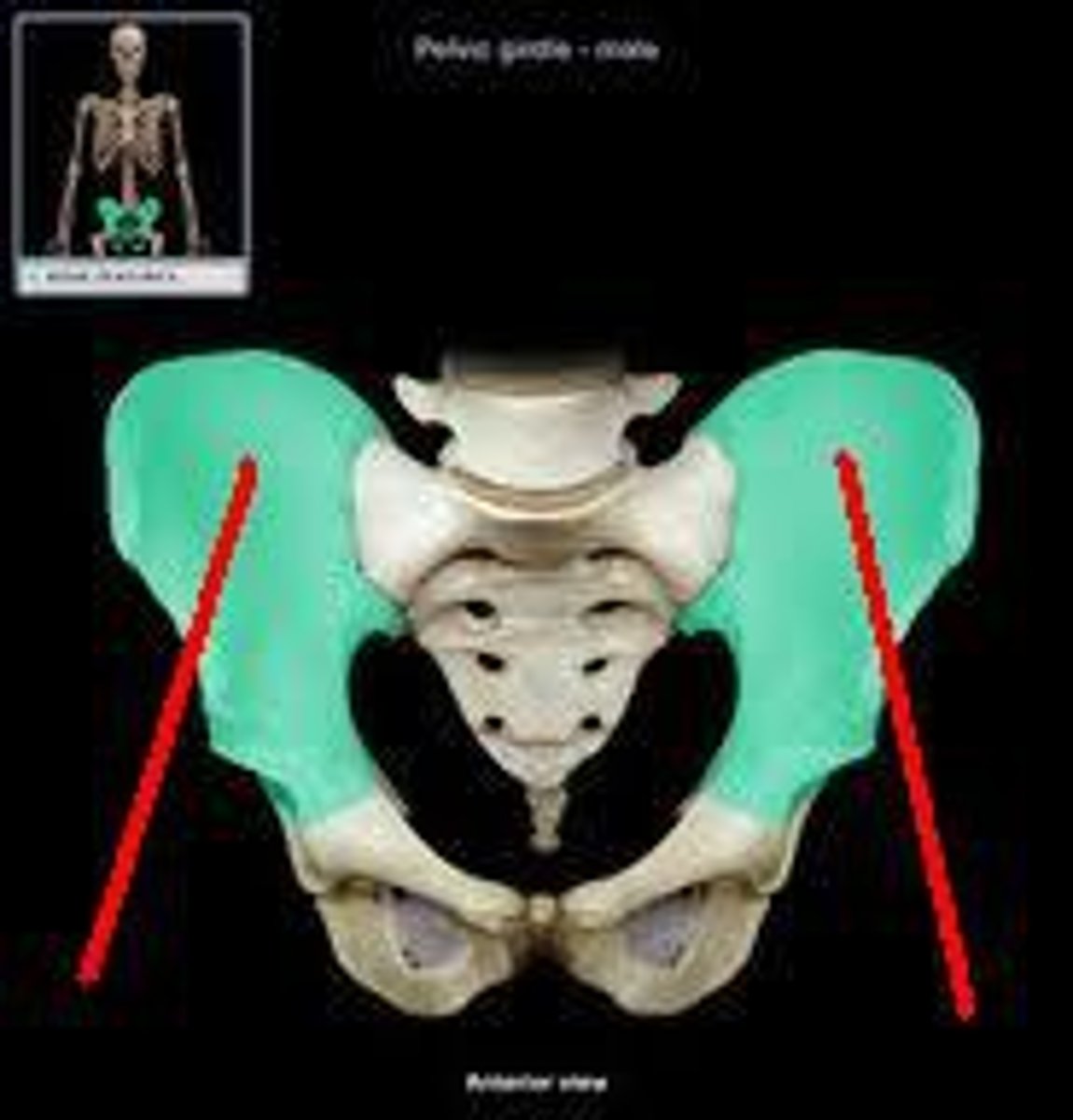
ischium
the curved bone forming the base of each half of the pelvis.
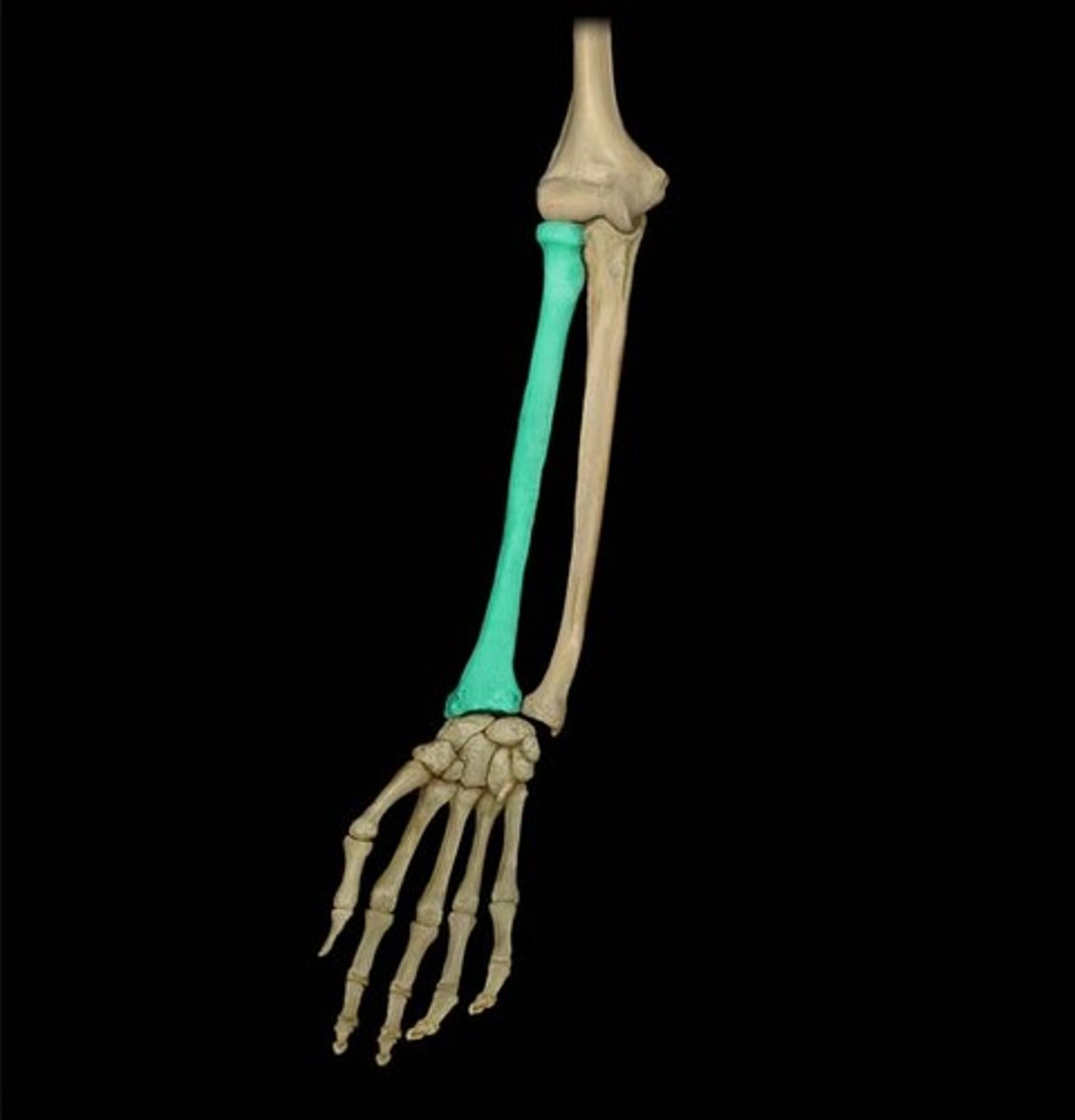
Radius
lateral bone of the forearm
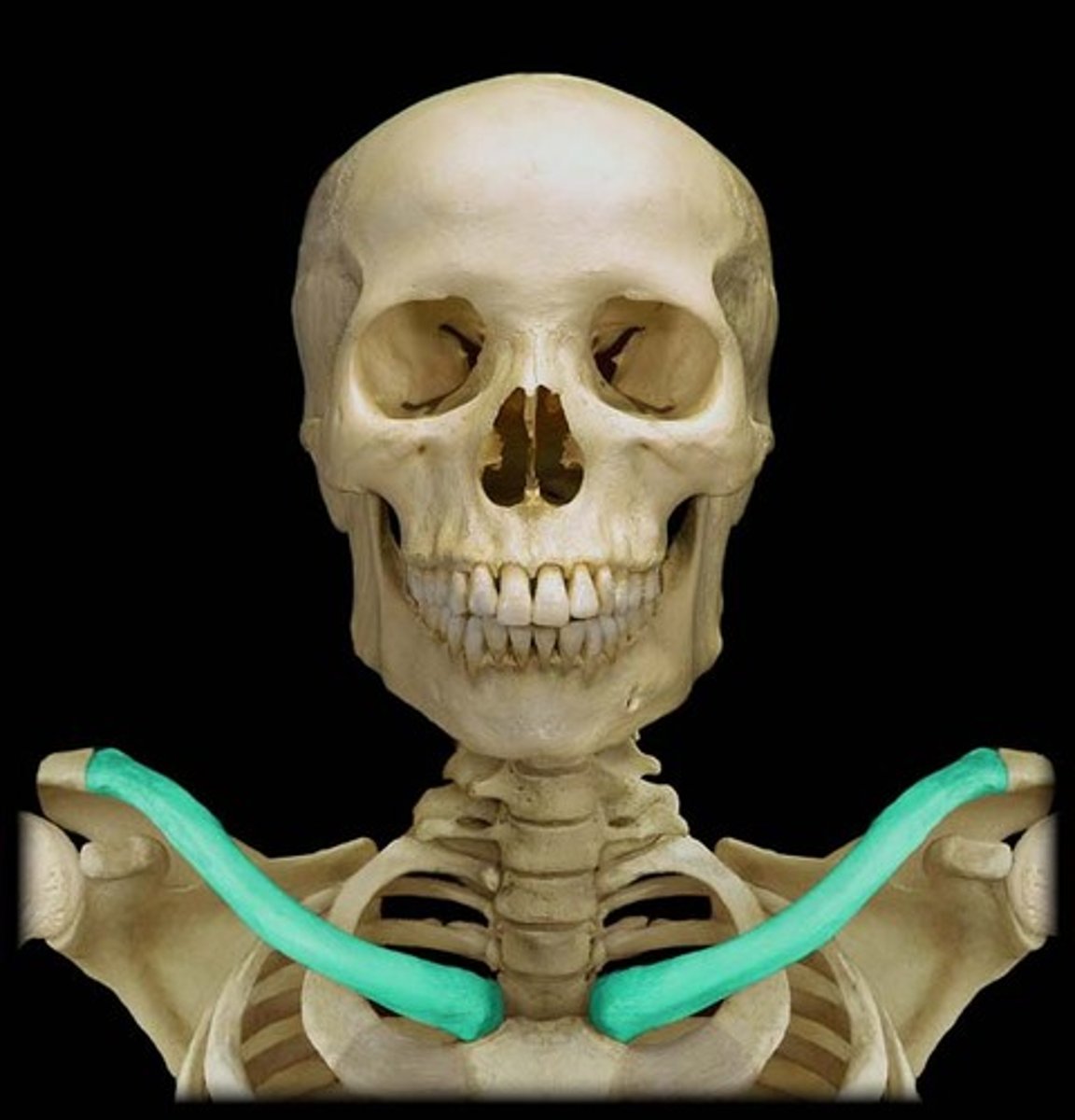
Clavicle
collar bone
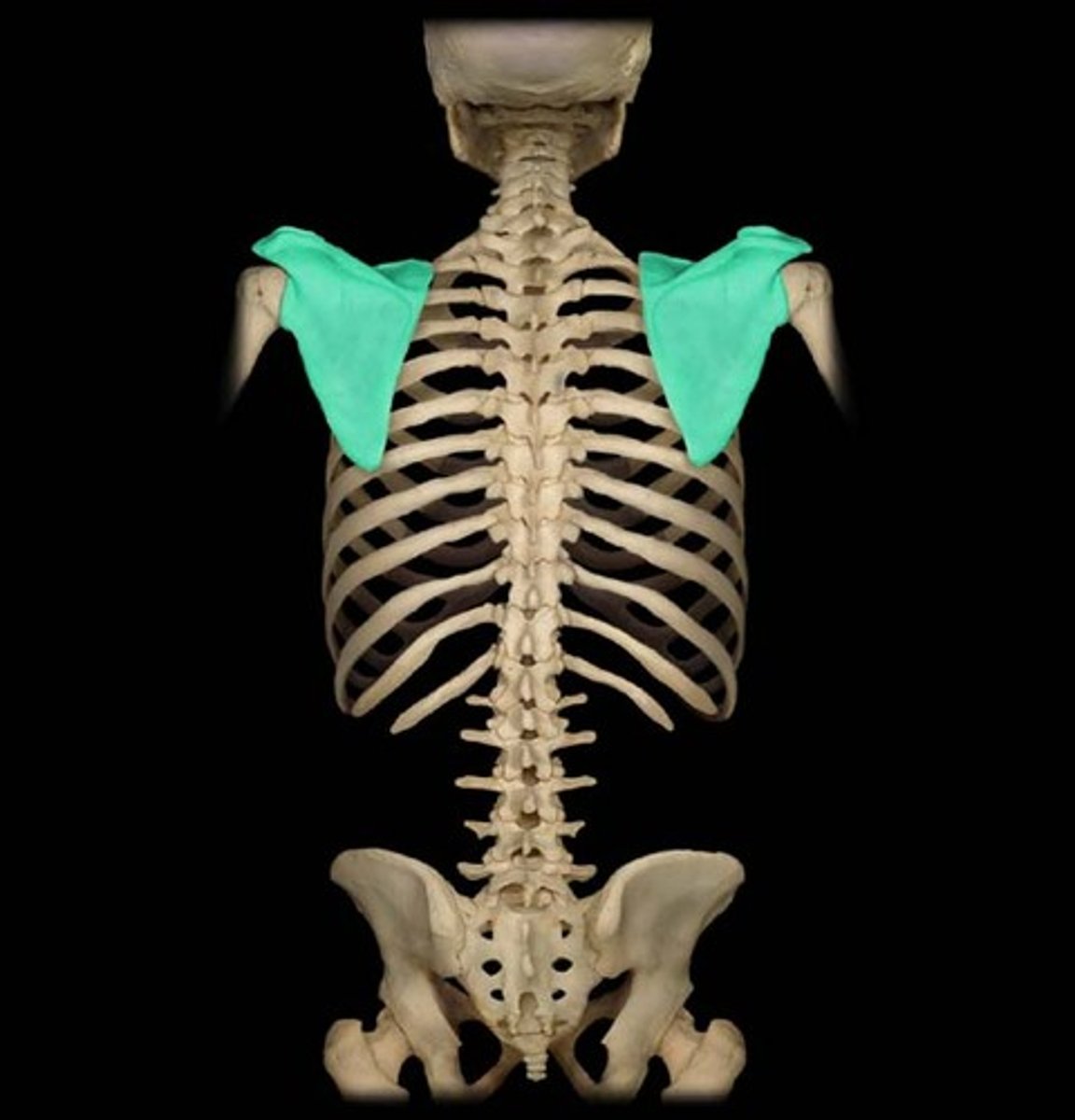
Scapula
shoulder blade
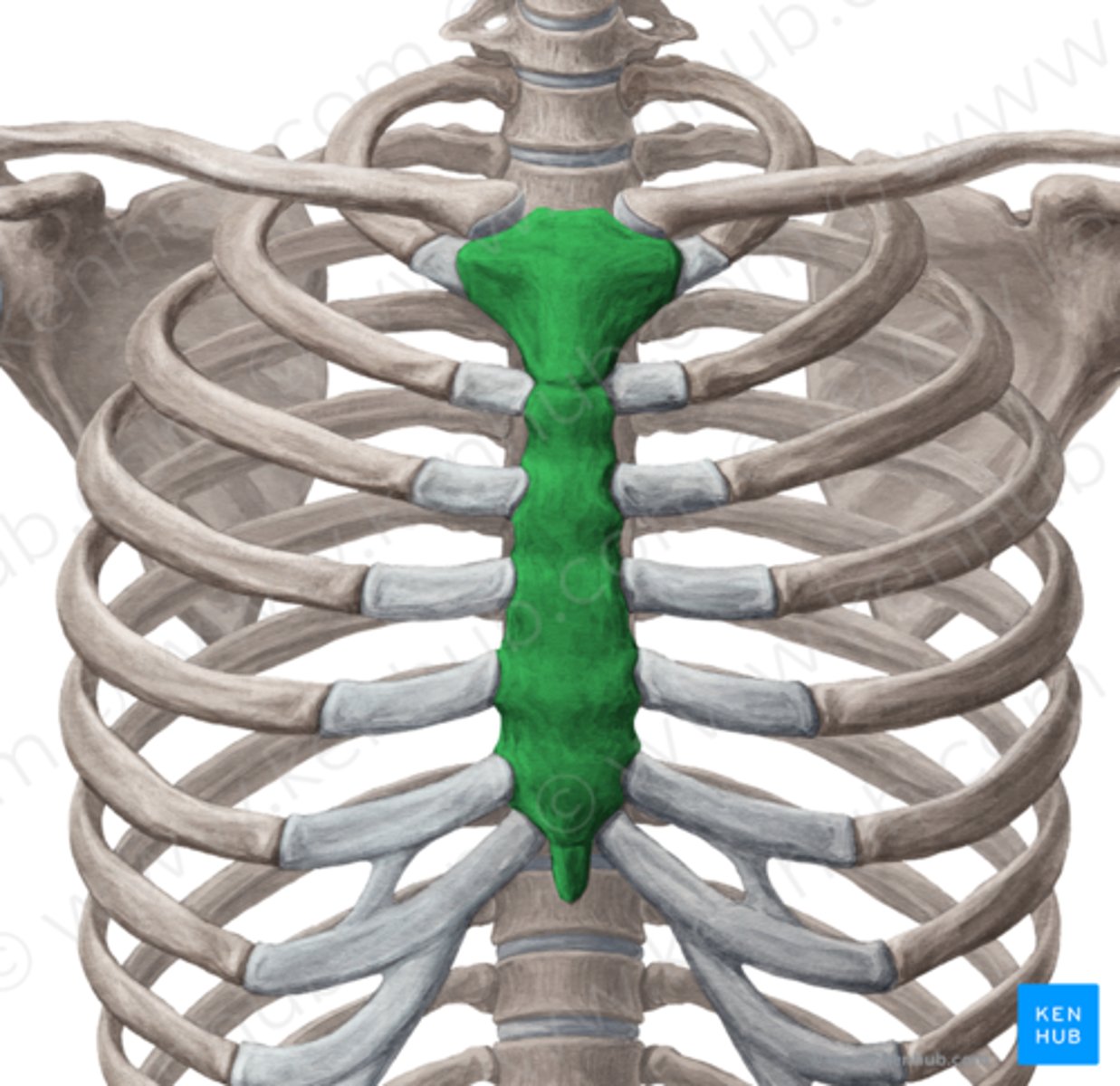
Strenum
breastbone
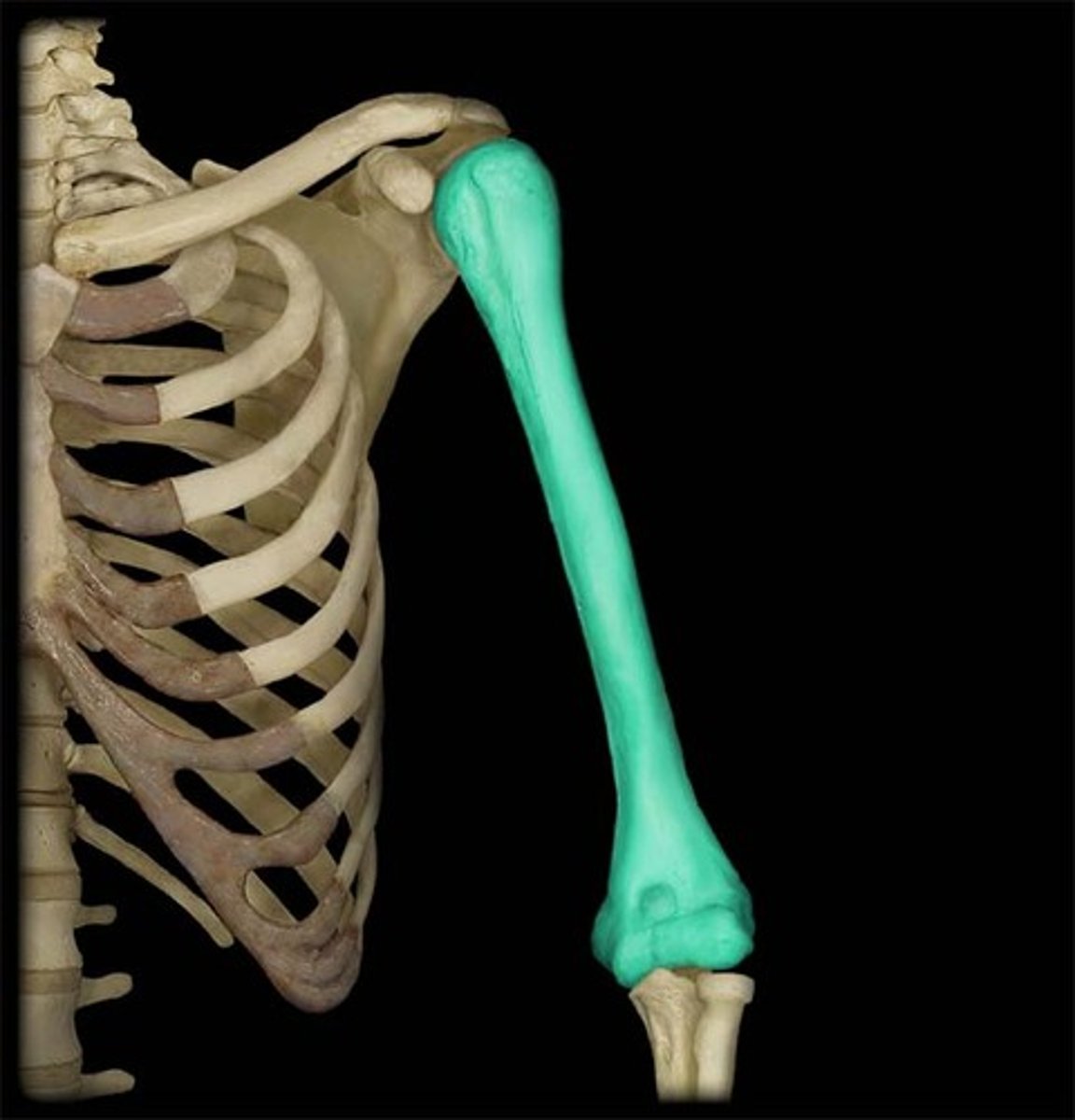
Humerus
upper arm bone
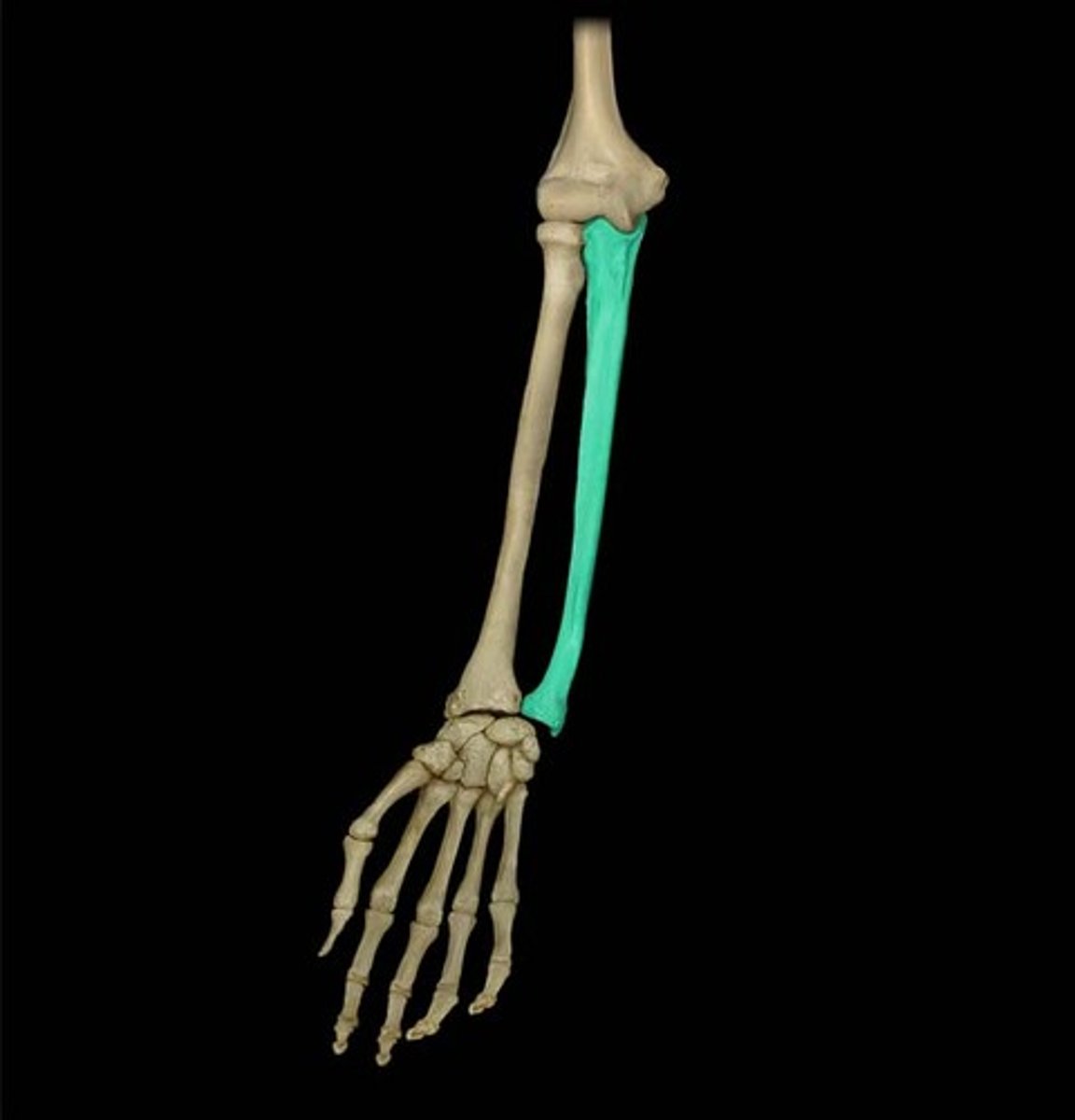
Ulna
medial bone of the forearm
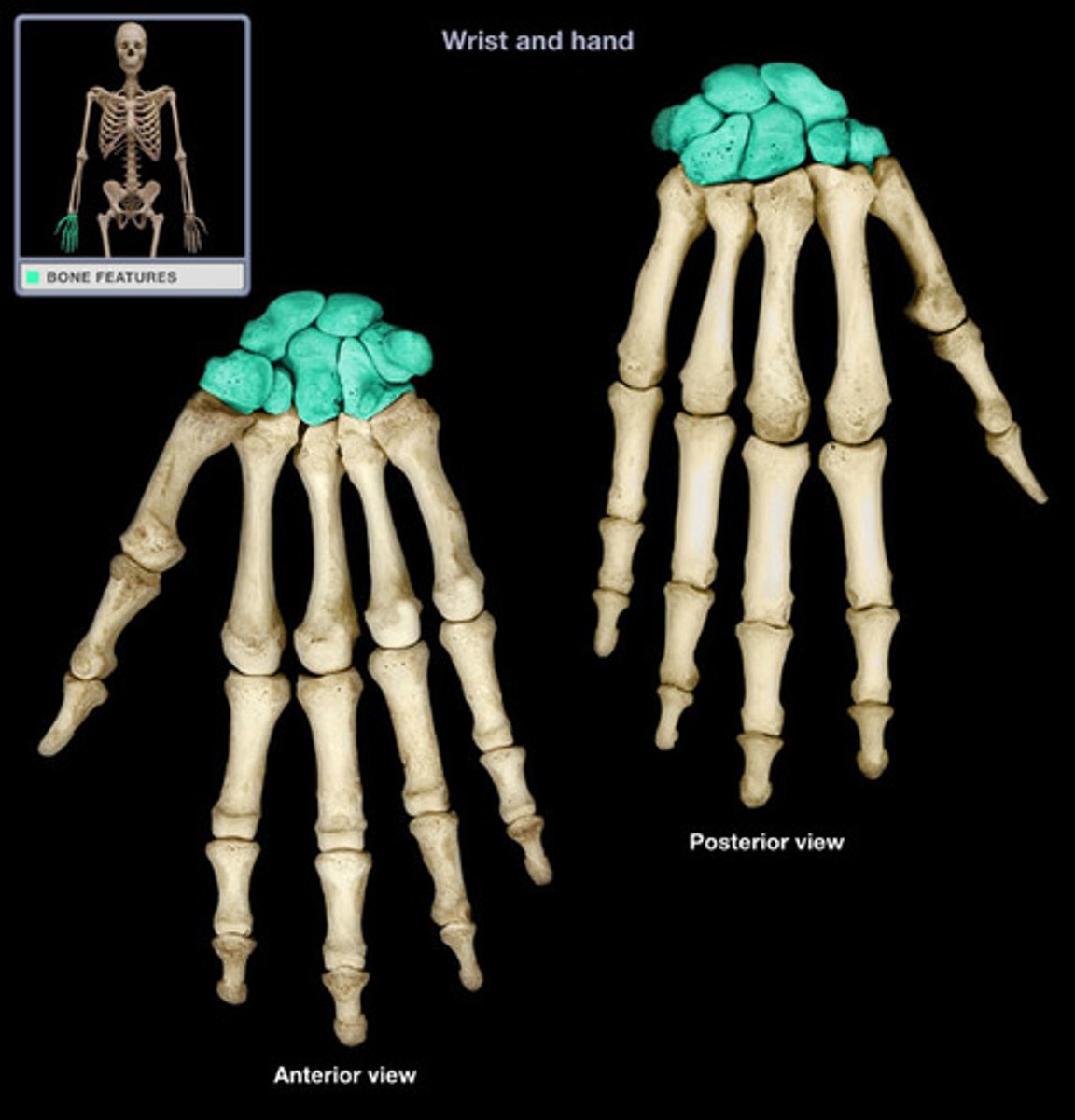
Carpals
wrist bones
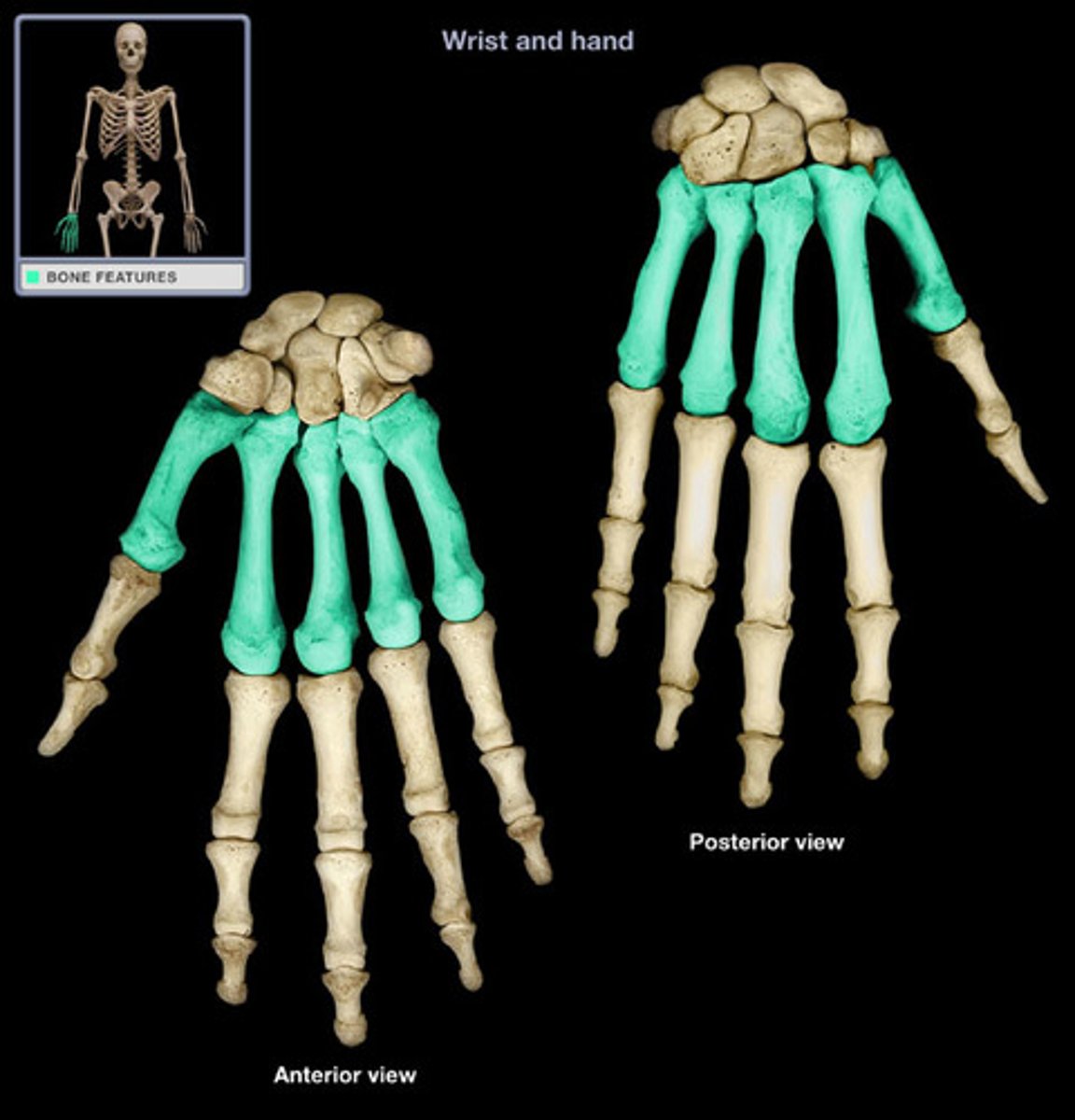
Metacarpals
hand bones
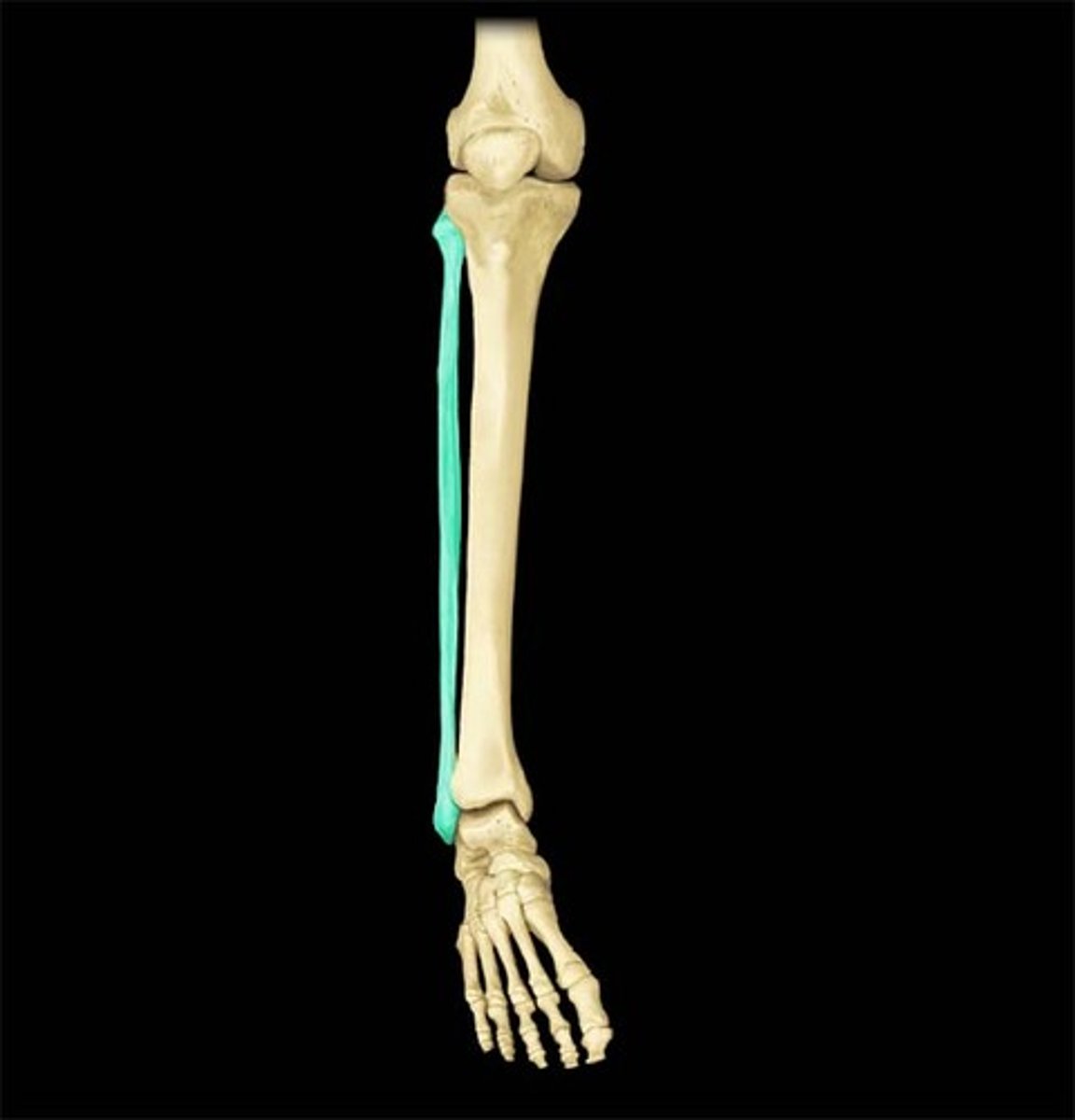
Fibula
calf bone
Tarsals
ankle bones
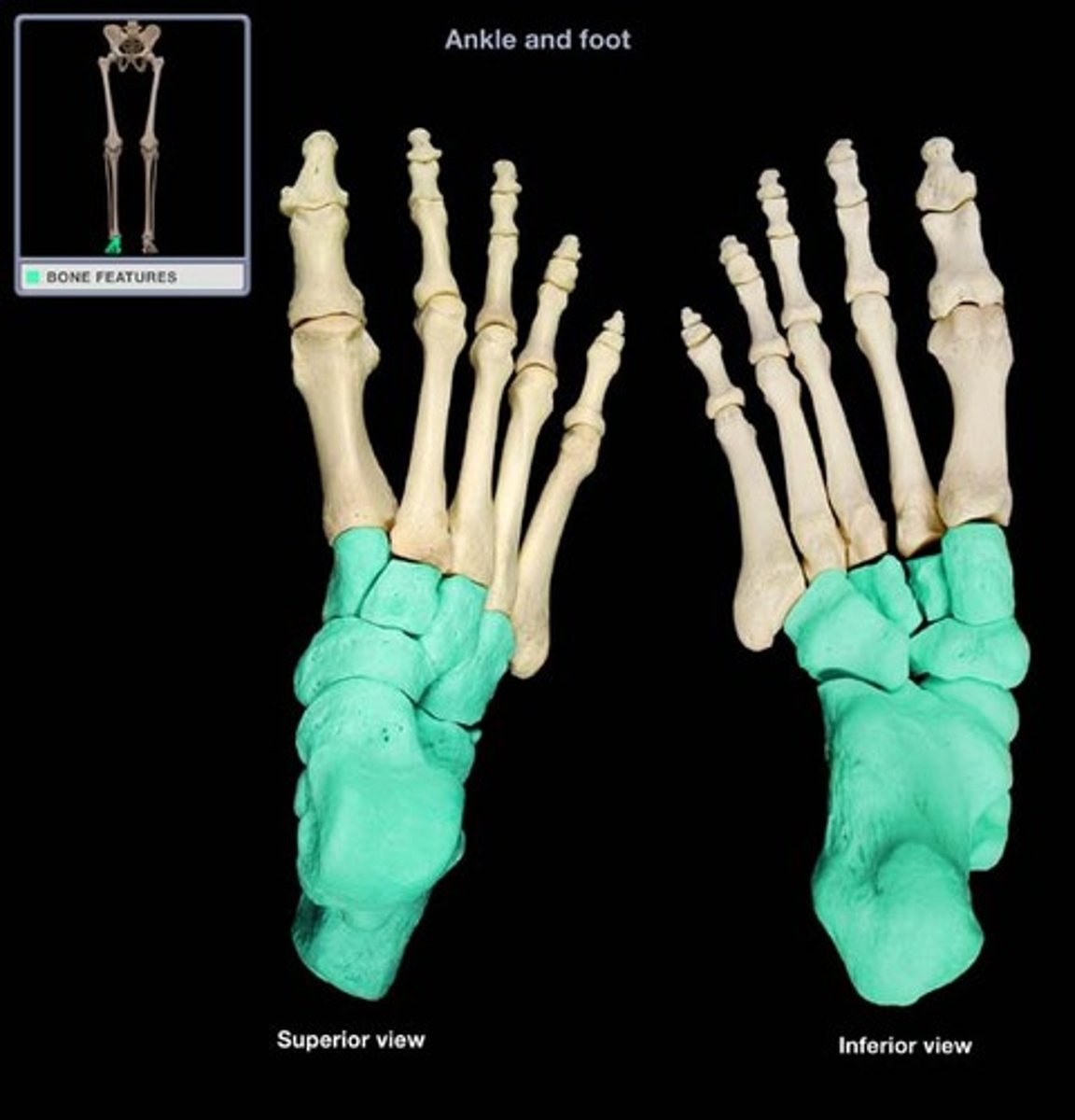
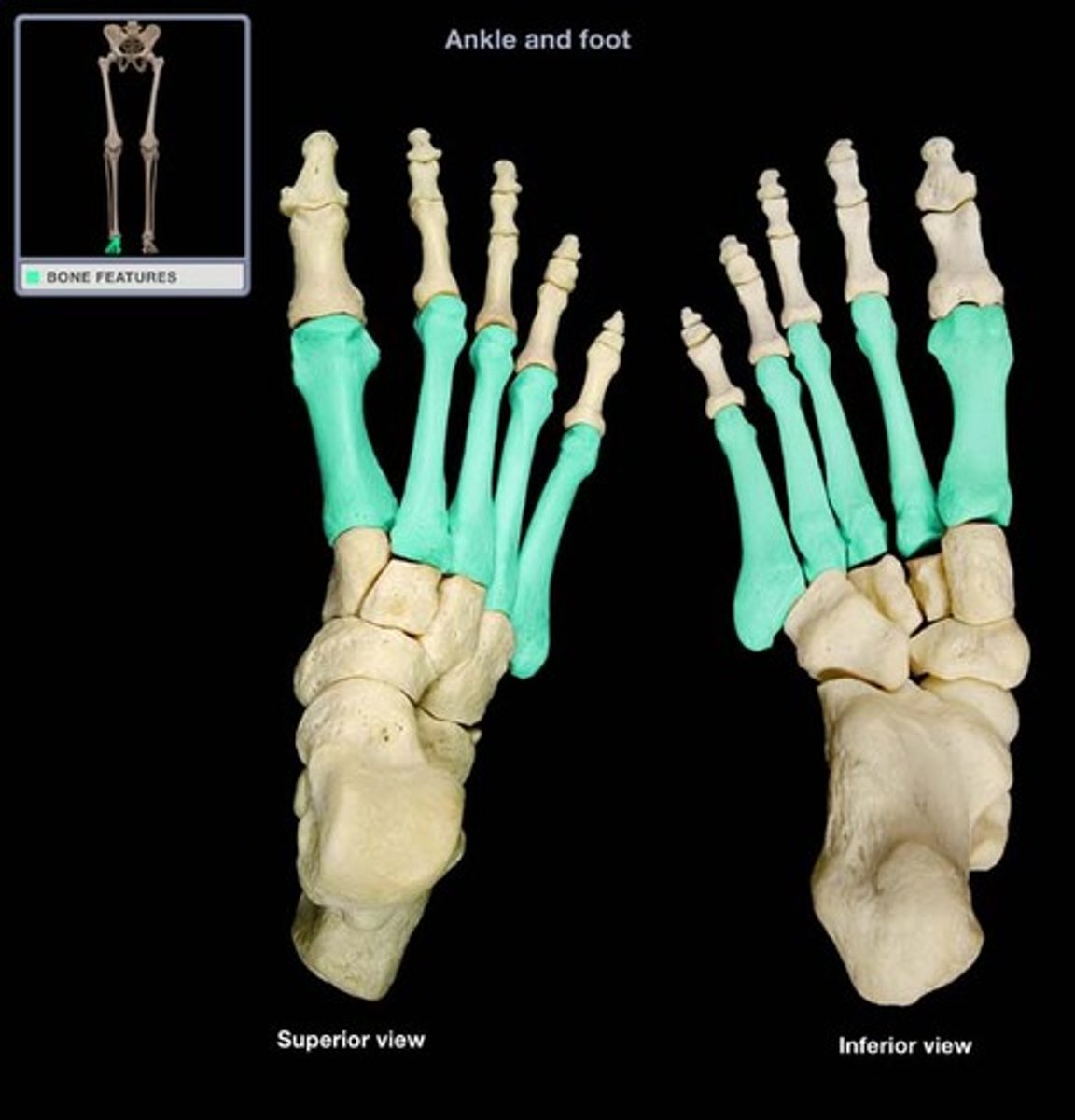
Metatarsals
foot bones
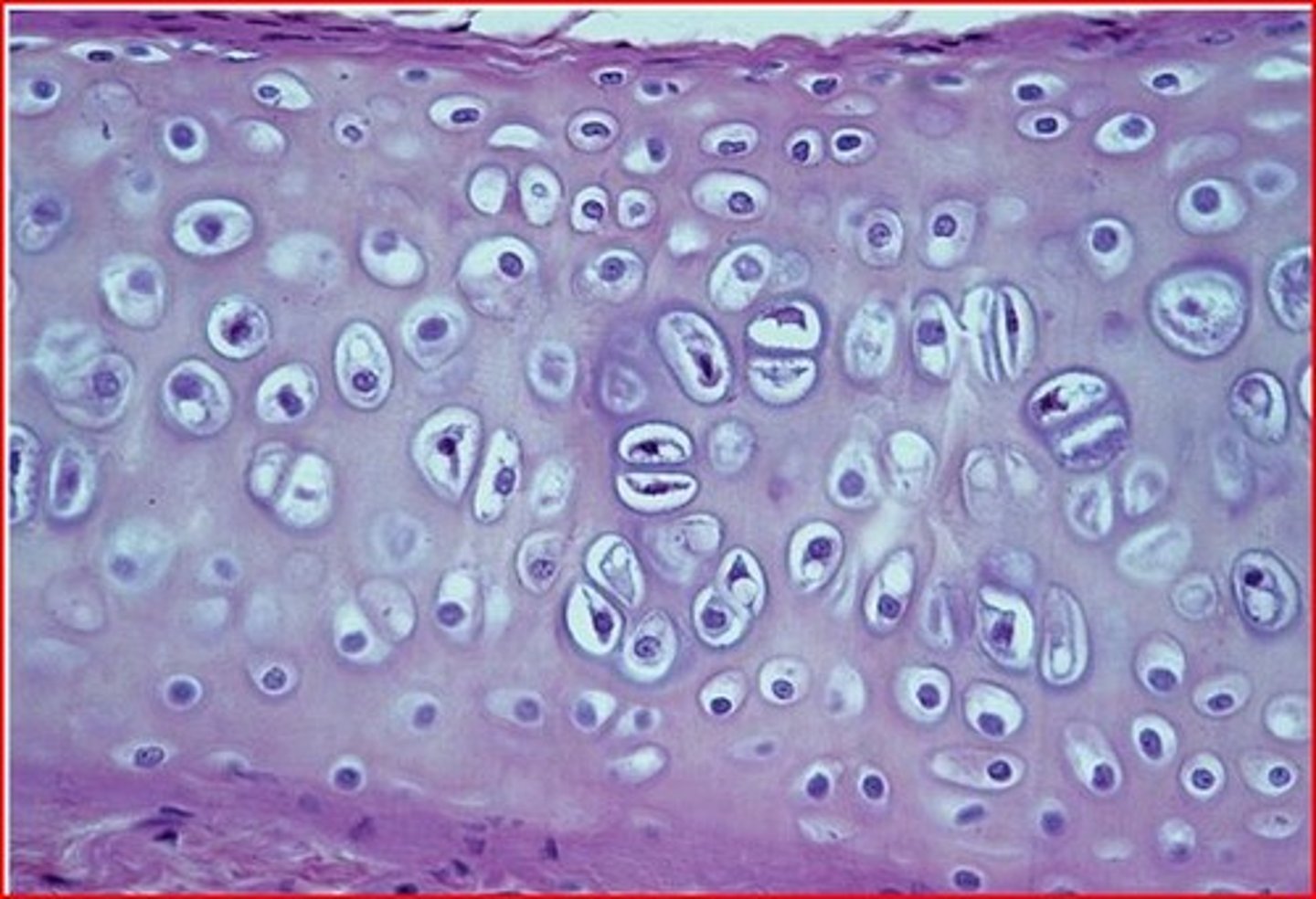
Hyaline
most common type of cartilage
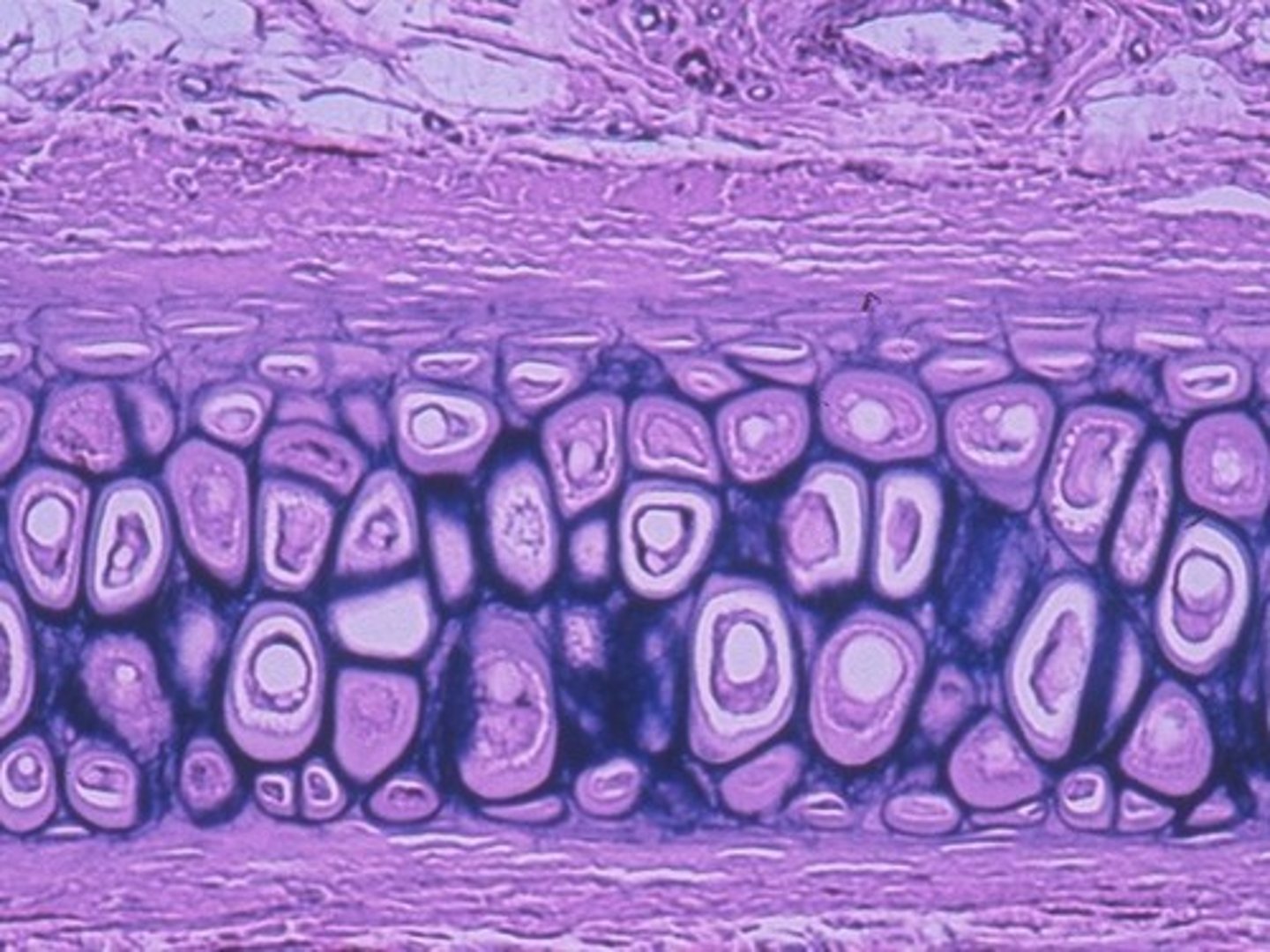
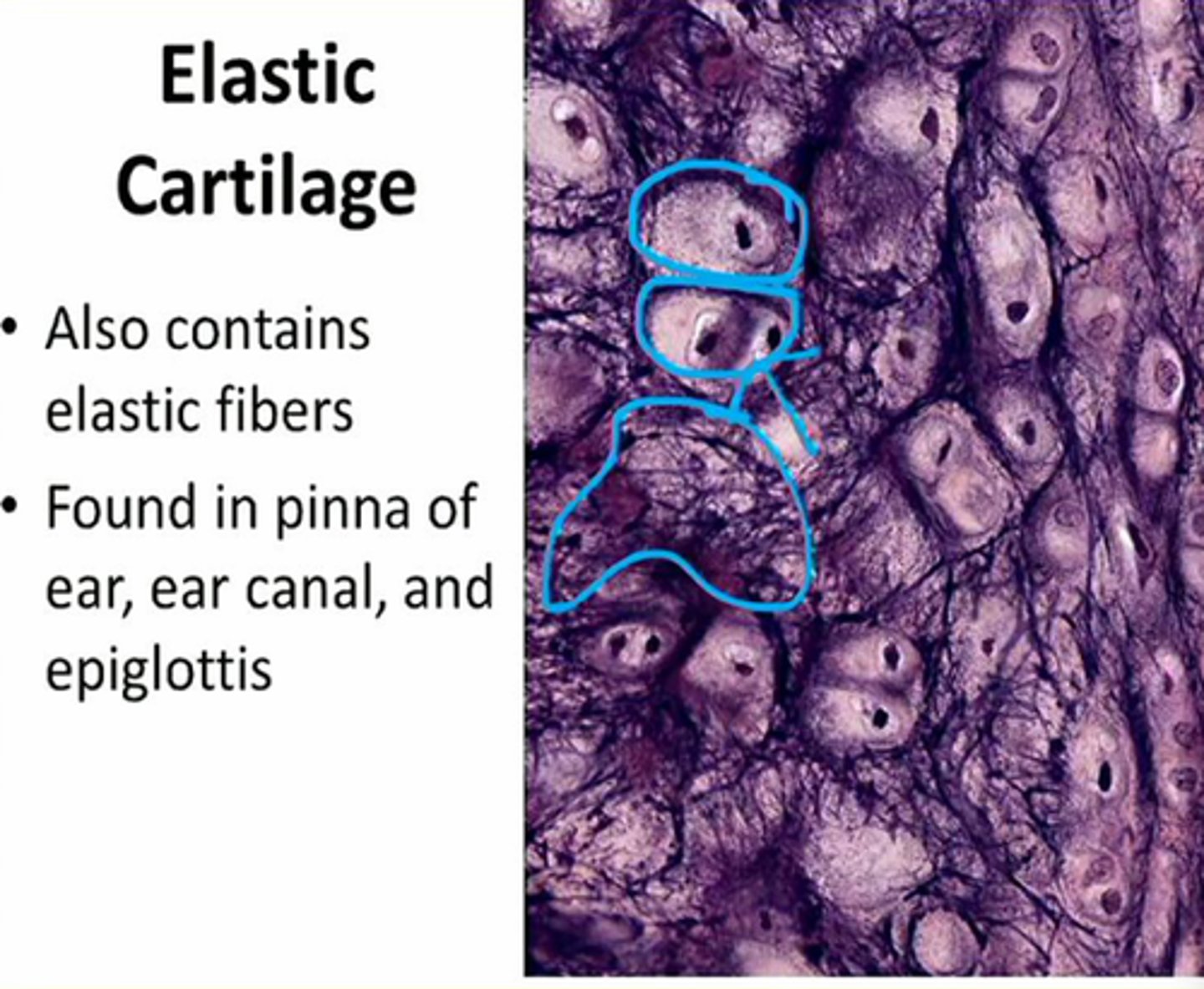
elastic cartilage
cartilage with abundant elastic fibers, flexiable
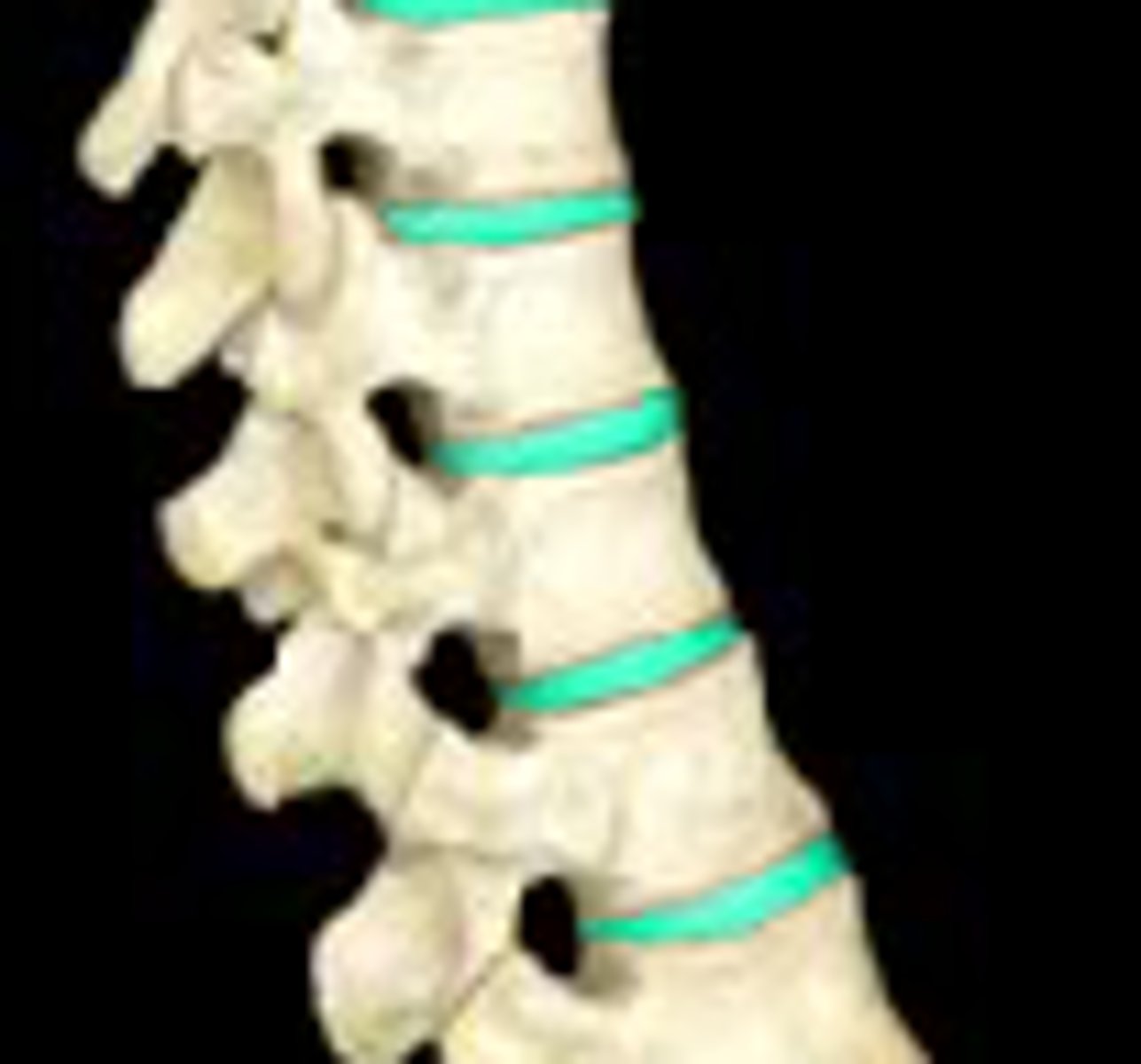
Fibrocartilage
Pads between vertebrae that are shock absorbers
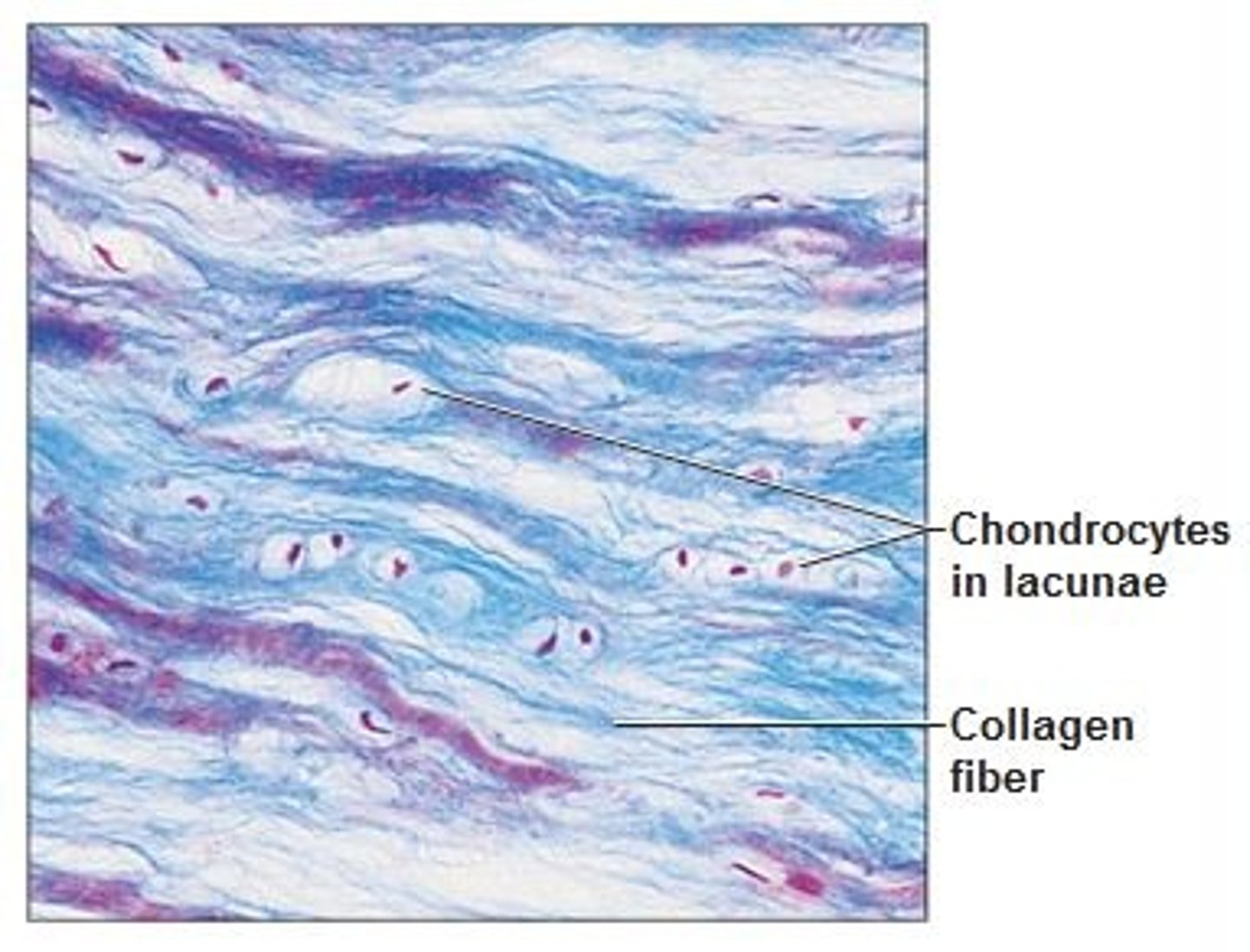
Cartilage
A connective tissue that is more flexible than bone and that protects the ends of bones and keeps them from rubbing together.
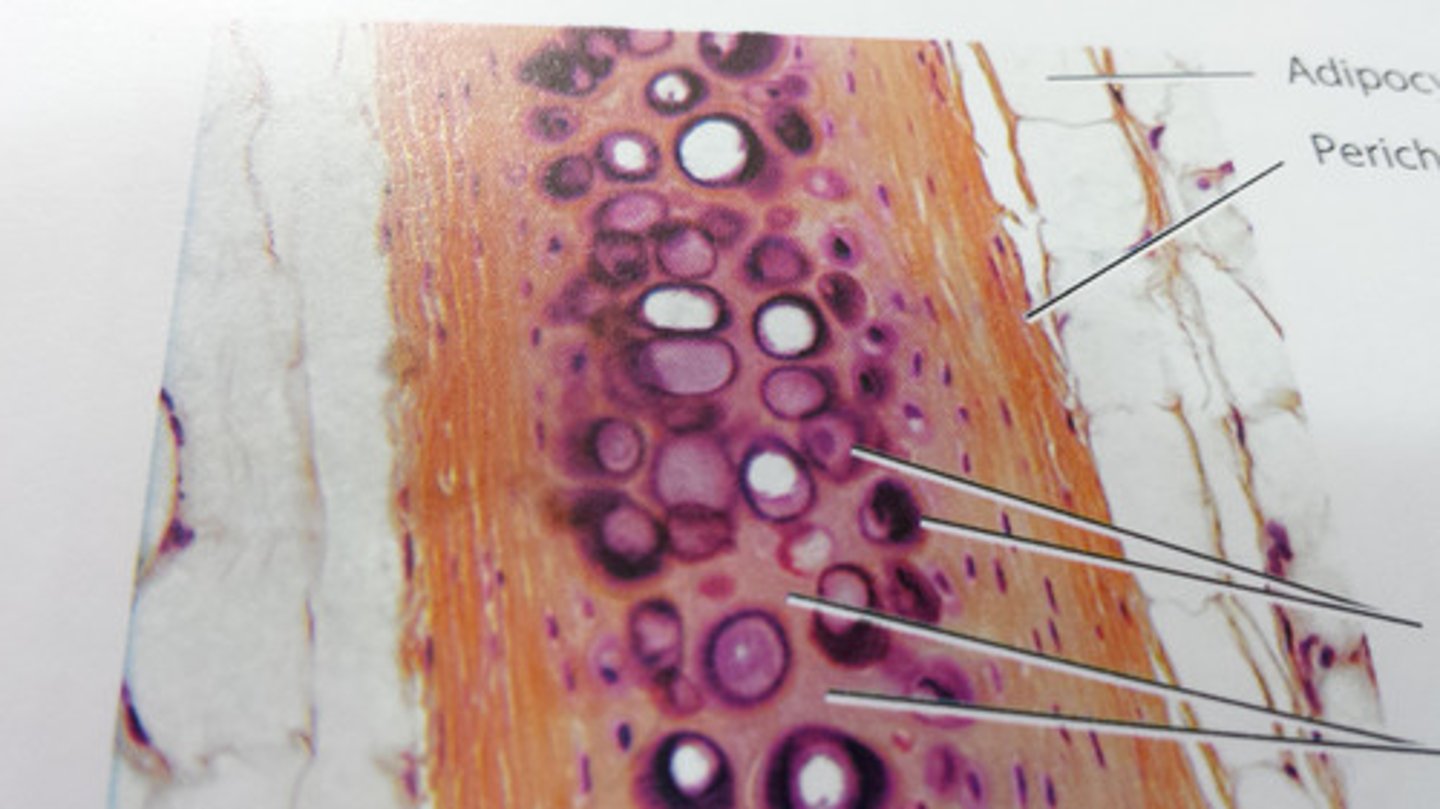
Perichondruim
membrane that covers cartilage
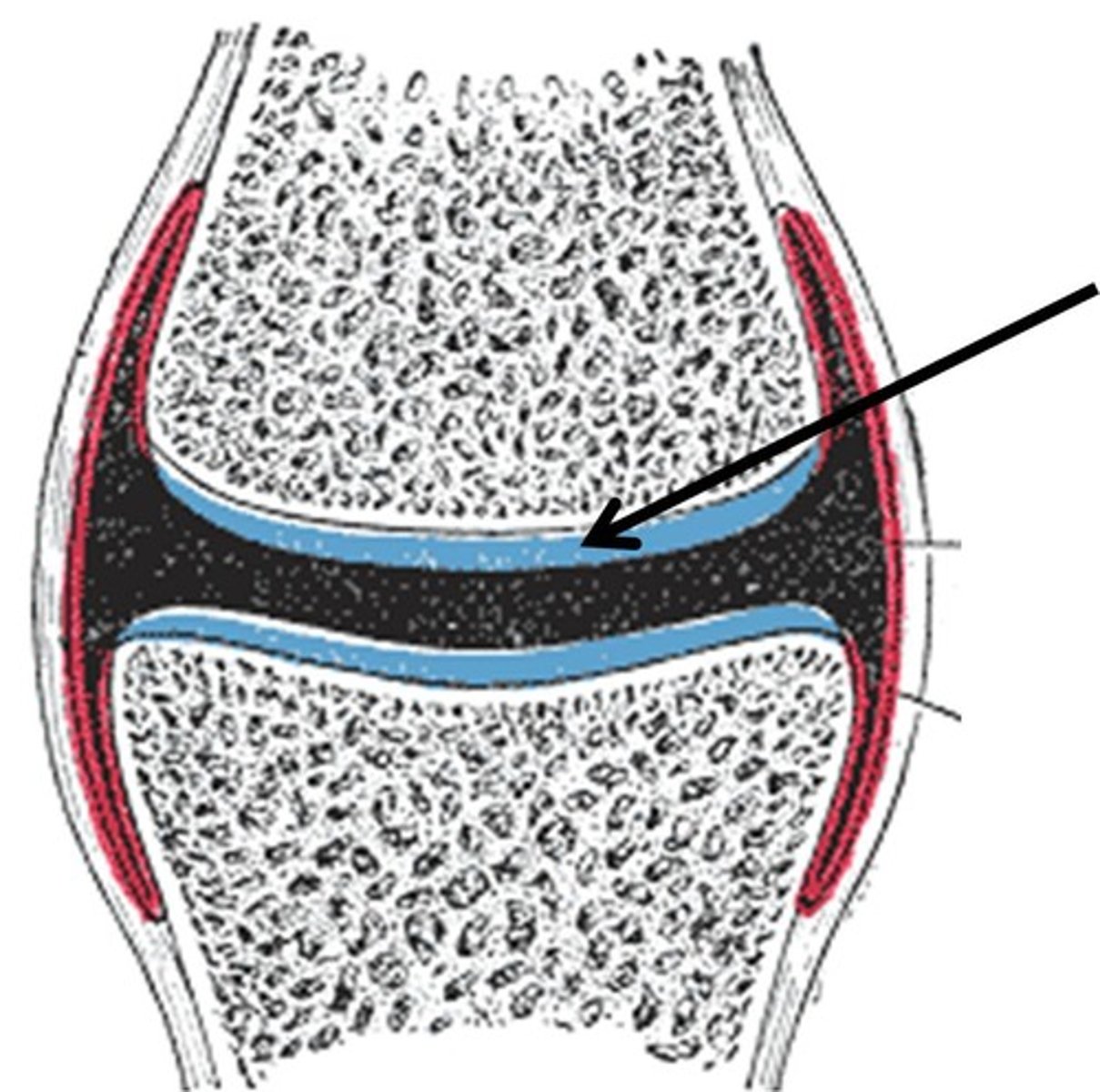
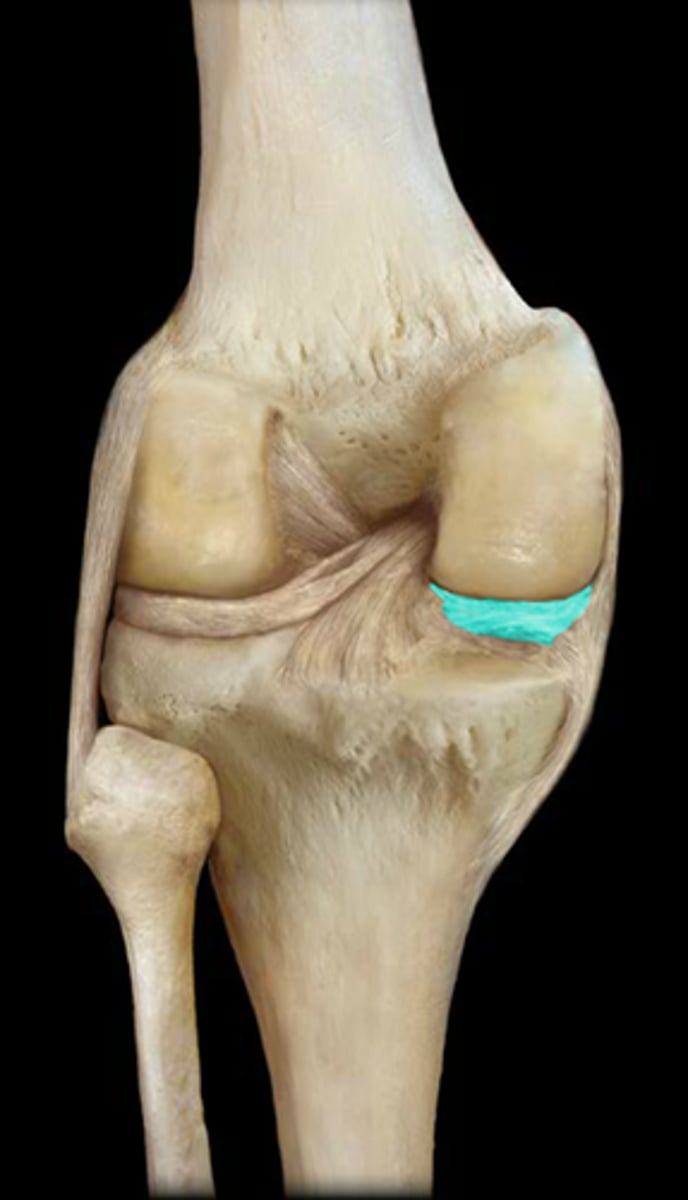
articular cartilage
covers the surfaces of bones where they come together to form joints
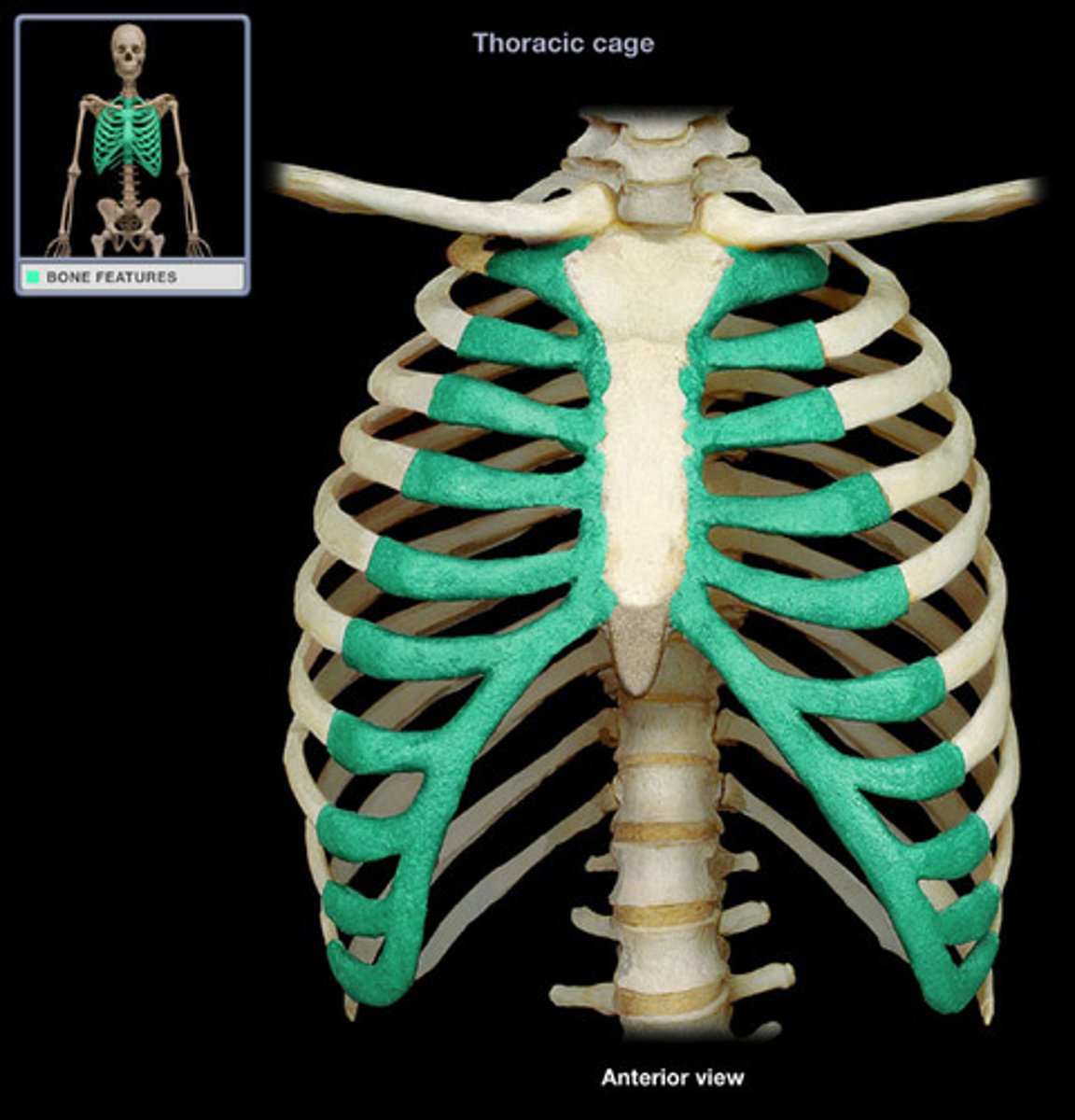
Costal cartilages
connect the ribs to the sternum
Respiratory cartilages
form the skeleton of the larynx and reinforce other respiratory passageways
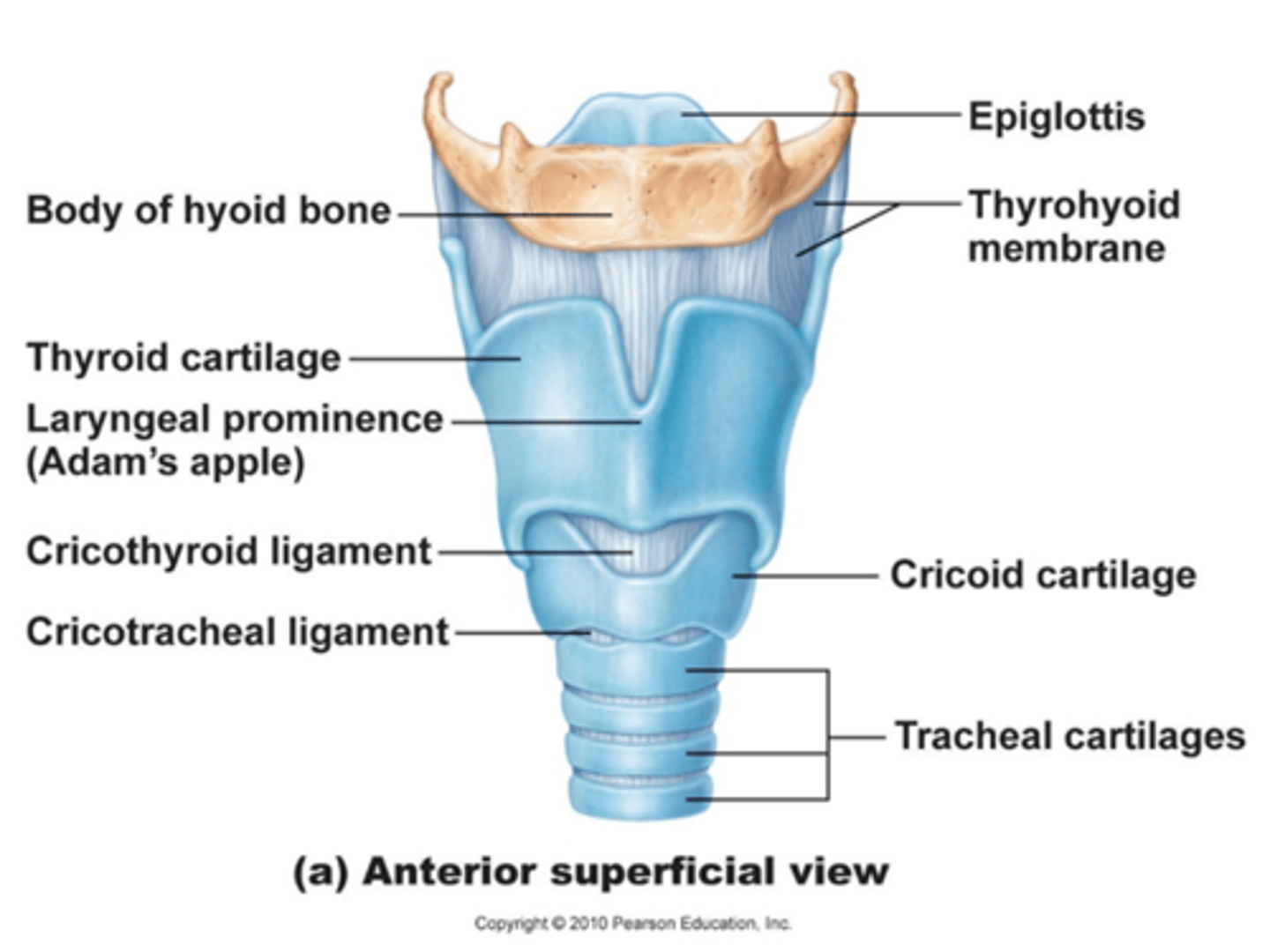
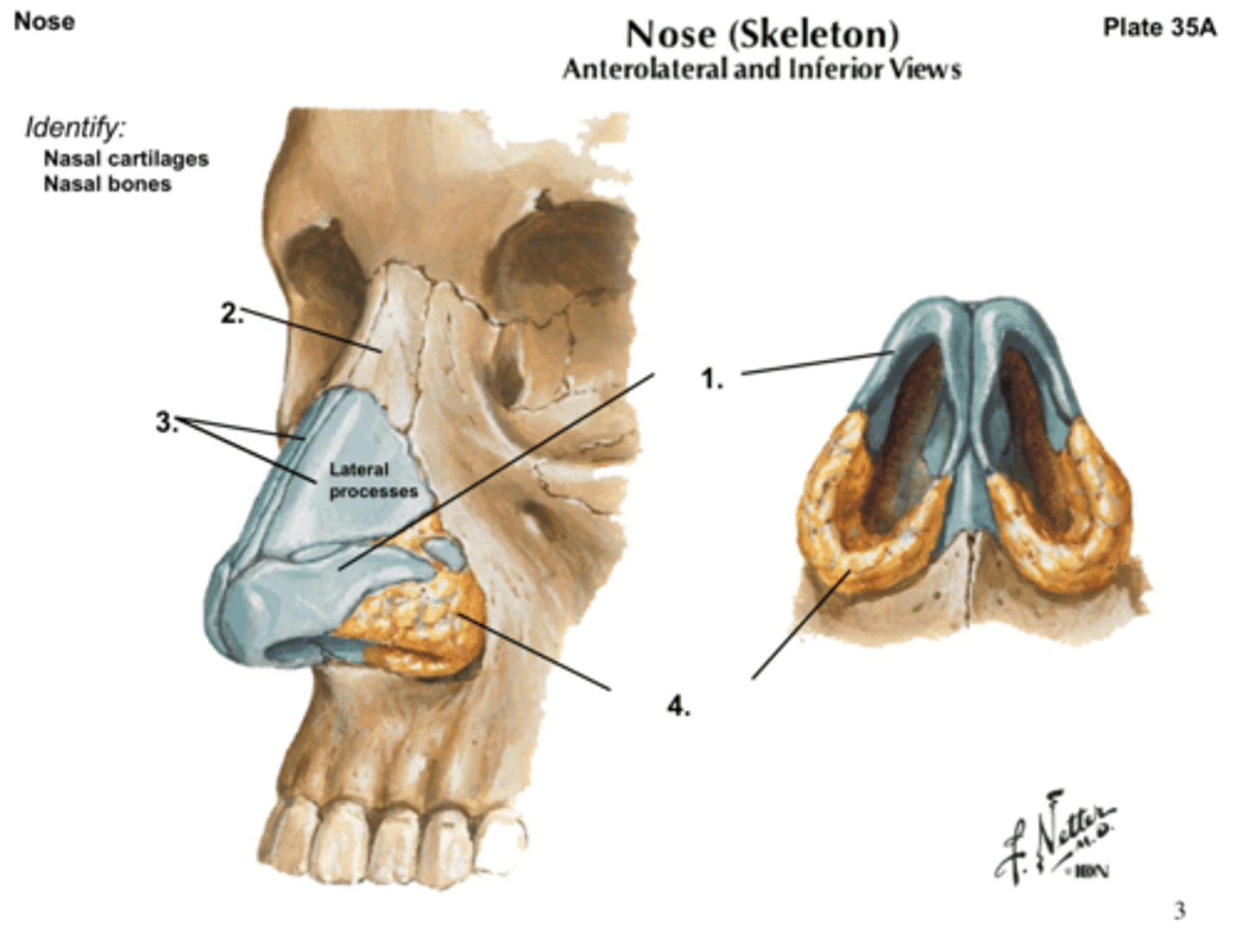
nasal cartilages
support the external nose
Where can elastic cartilage be found
external ear, epiglottis
intervertebral discs
fibrocartilage pads that separate and cushion the vertebrae
Menisci
pads located in the knee joint
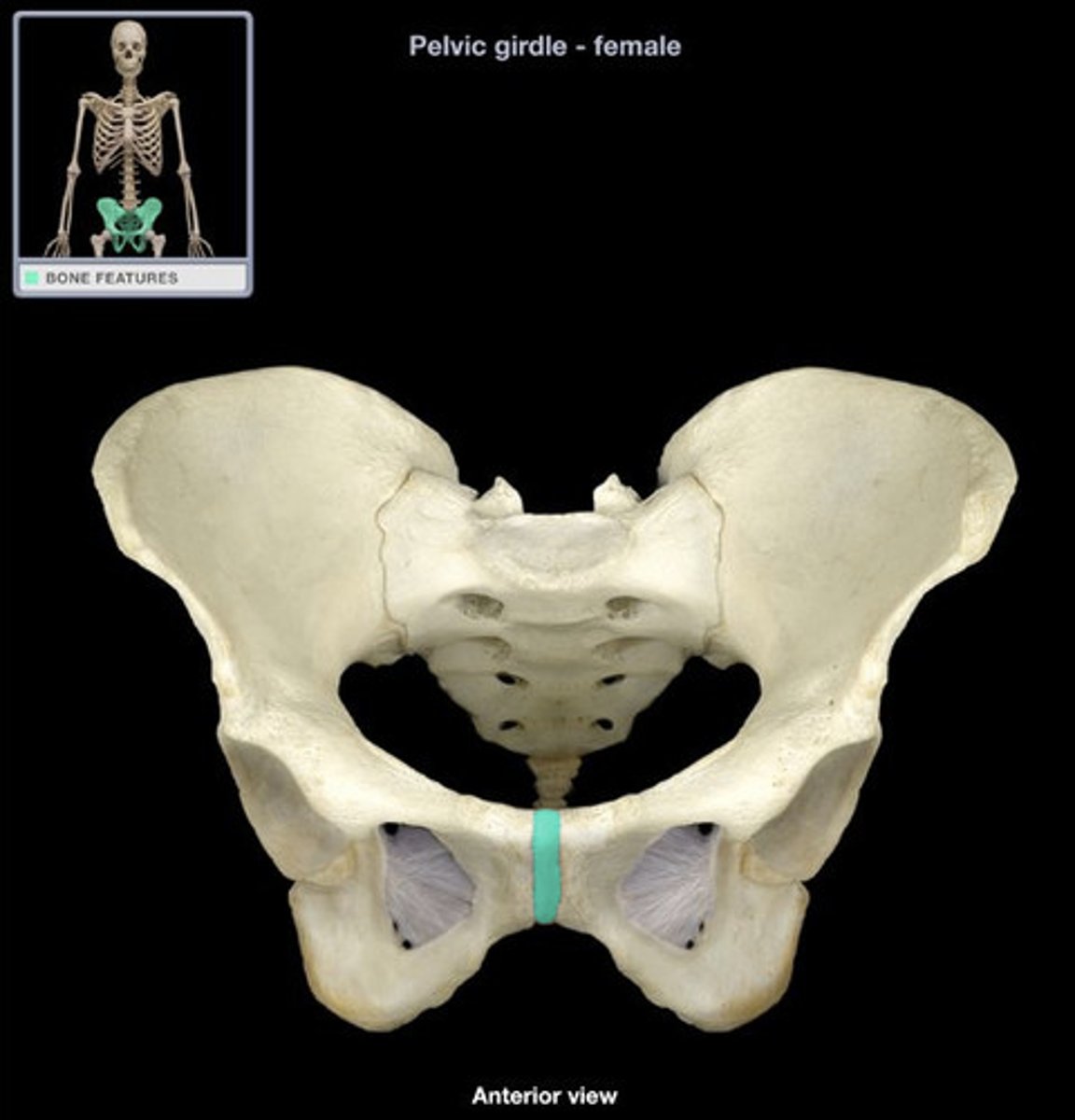
pubic symphysis
cartilaginous joint at which two pubic bones fuse together
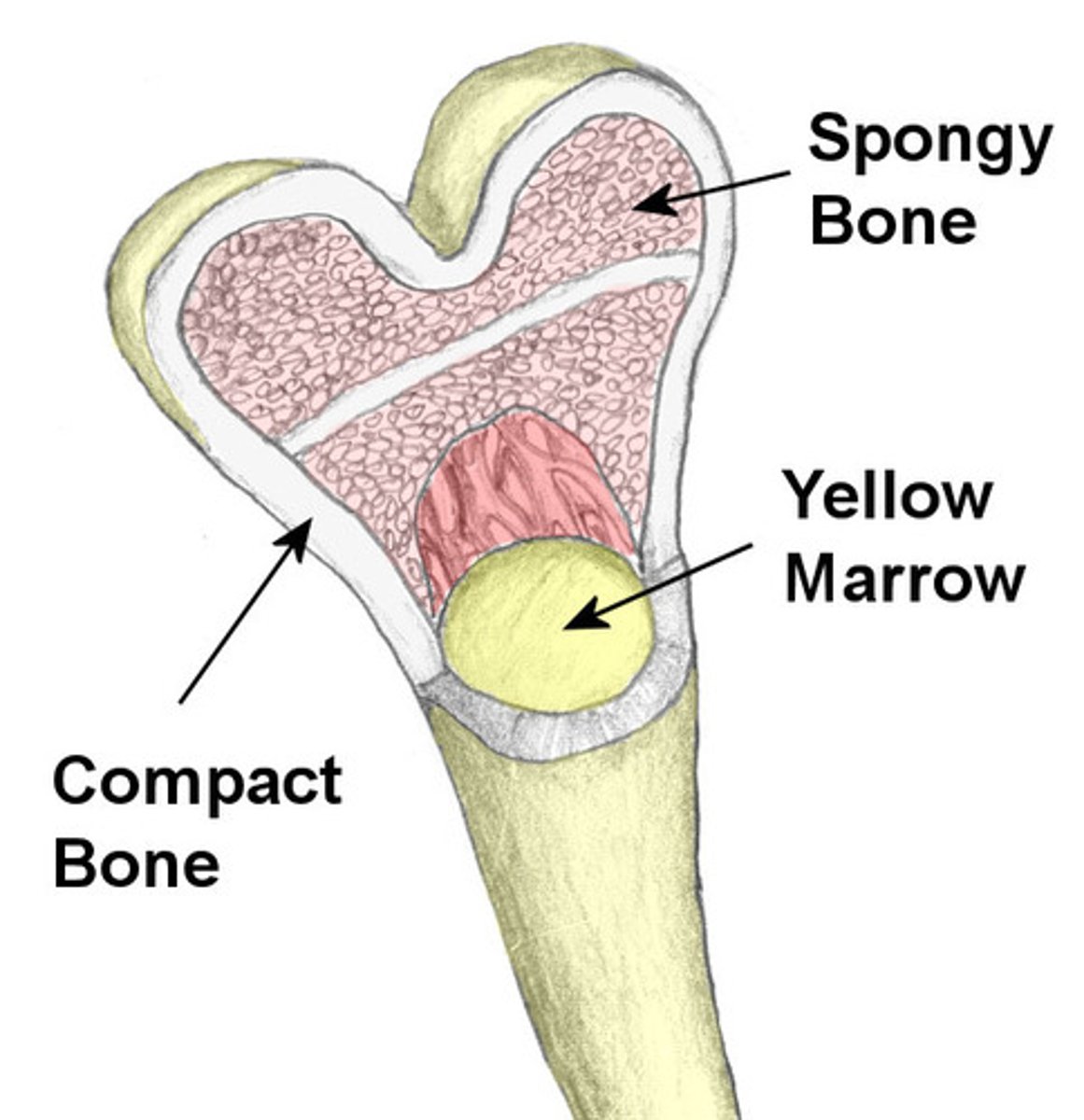
Compact bone
Hard, dense bone tissue that is beneath the outer membrane of a bone
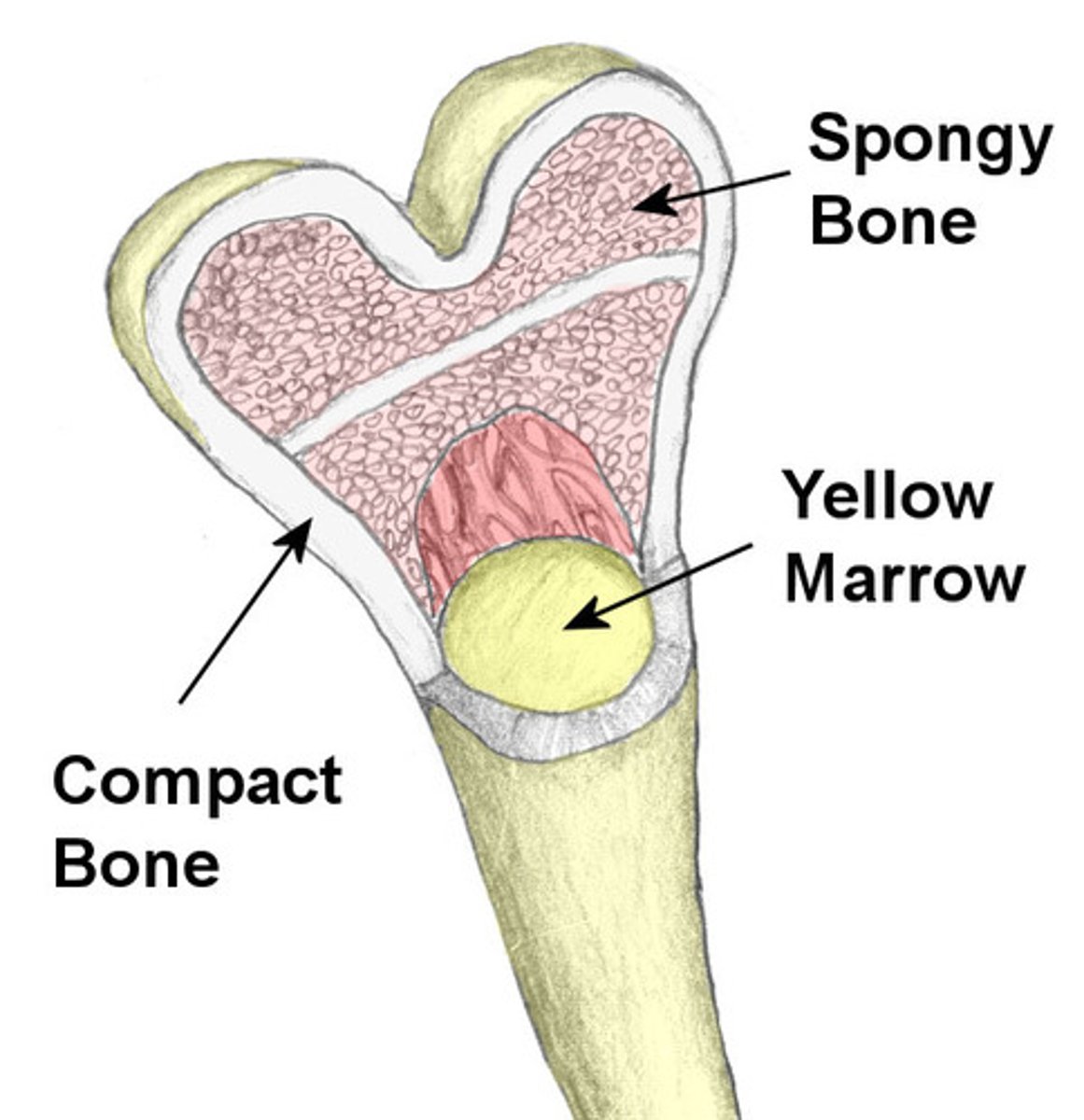
Spongy bone
Layer of bone tissue having many small spaces and found just inside the layer of compact bone.
Long bones
longer than they are wide
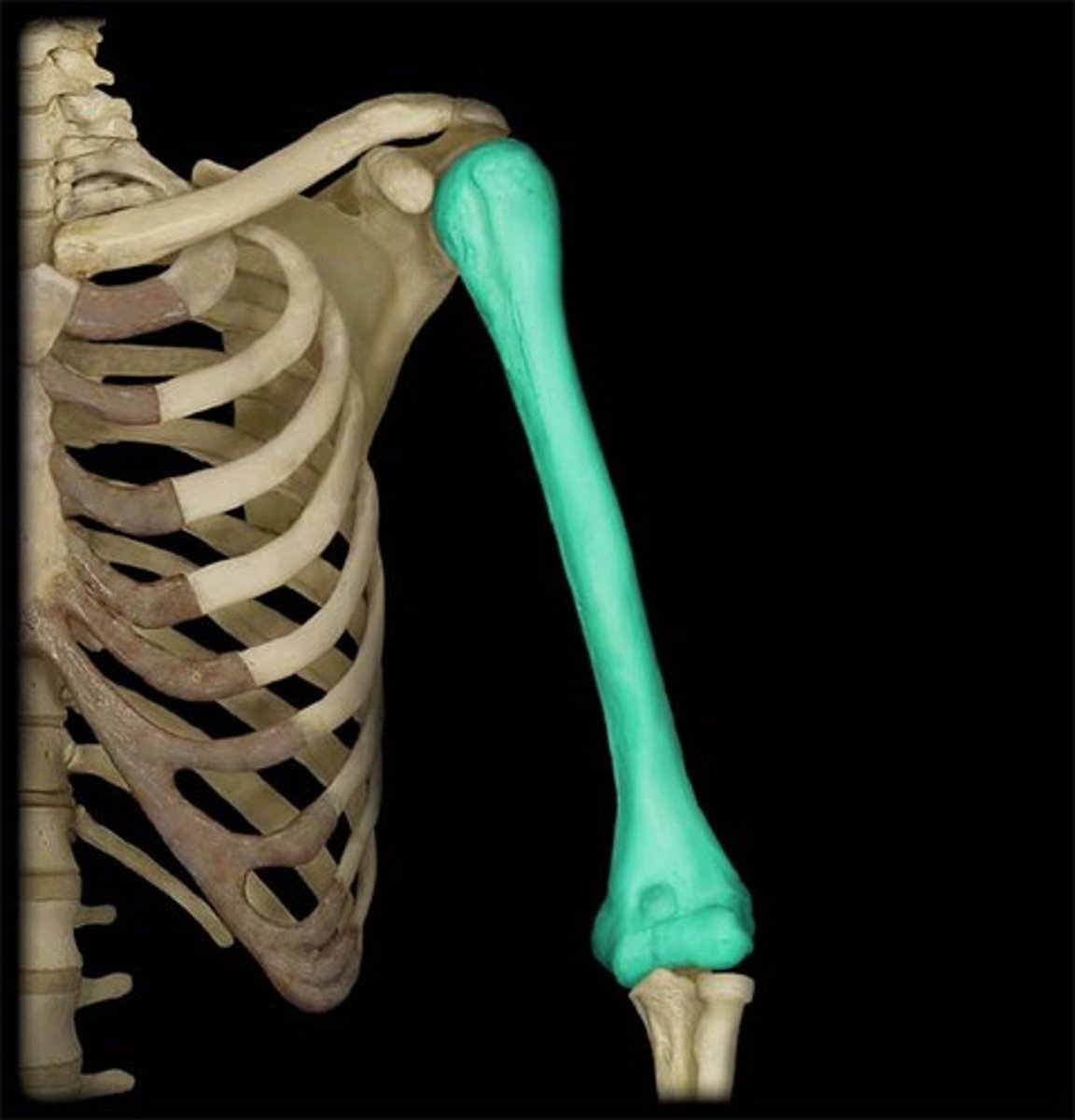
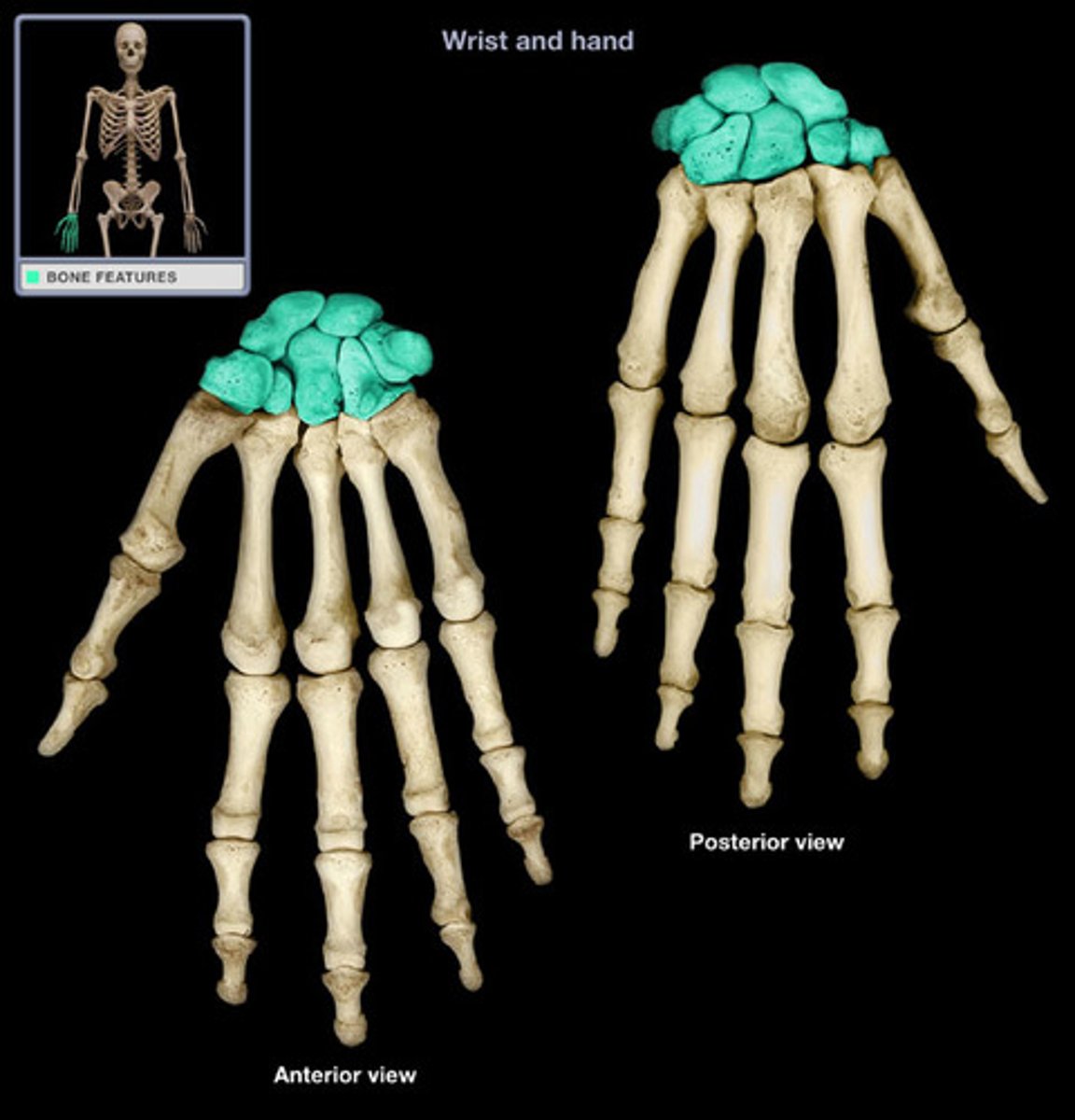
Short bones
carpals and tarsals
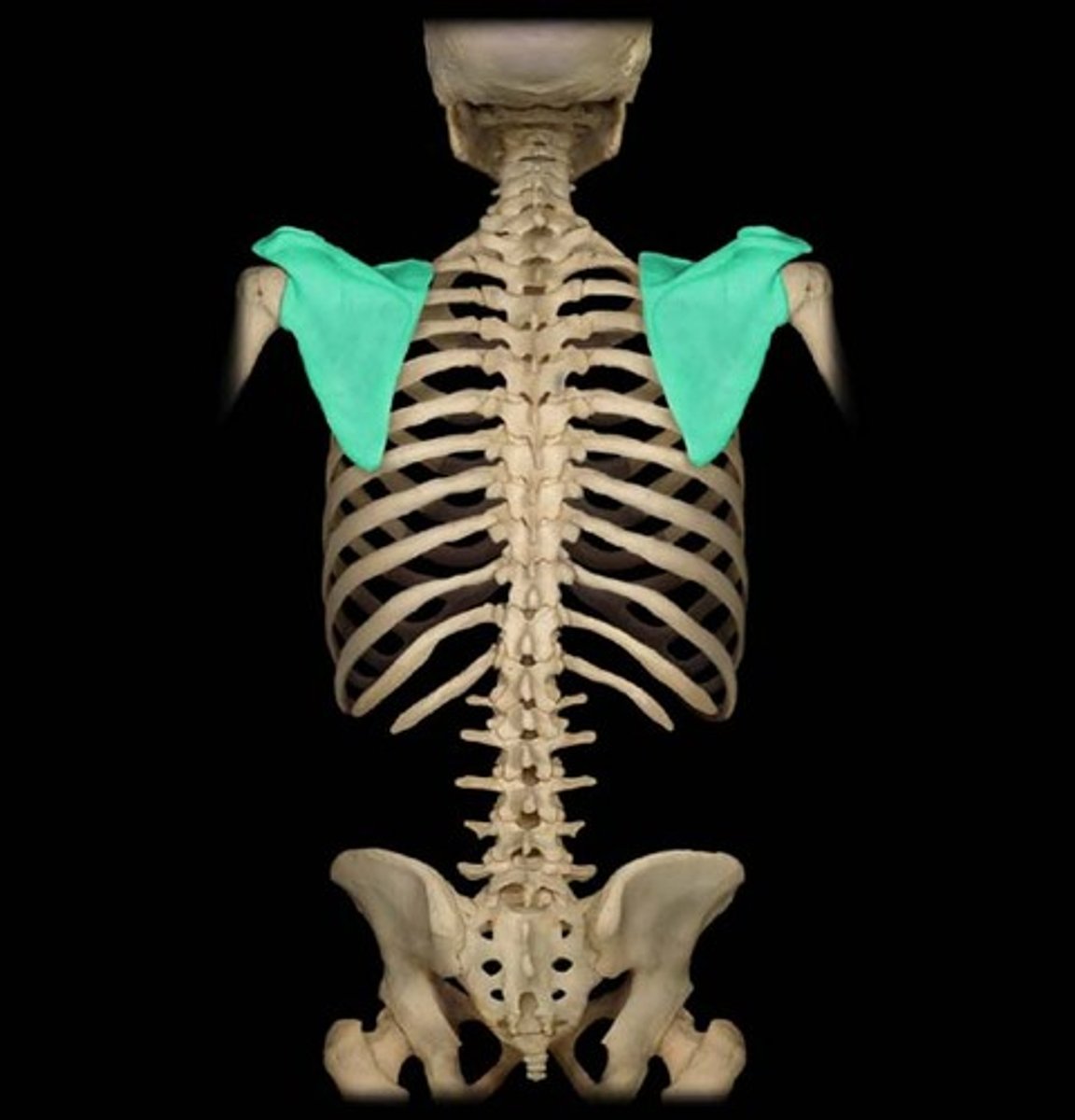
Flat bones
thin, flattened, and usually curved
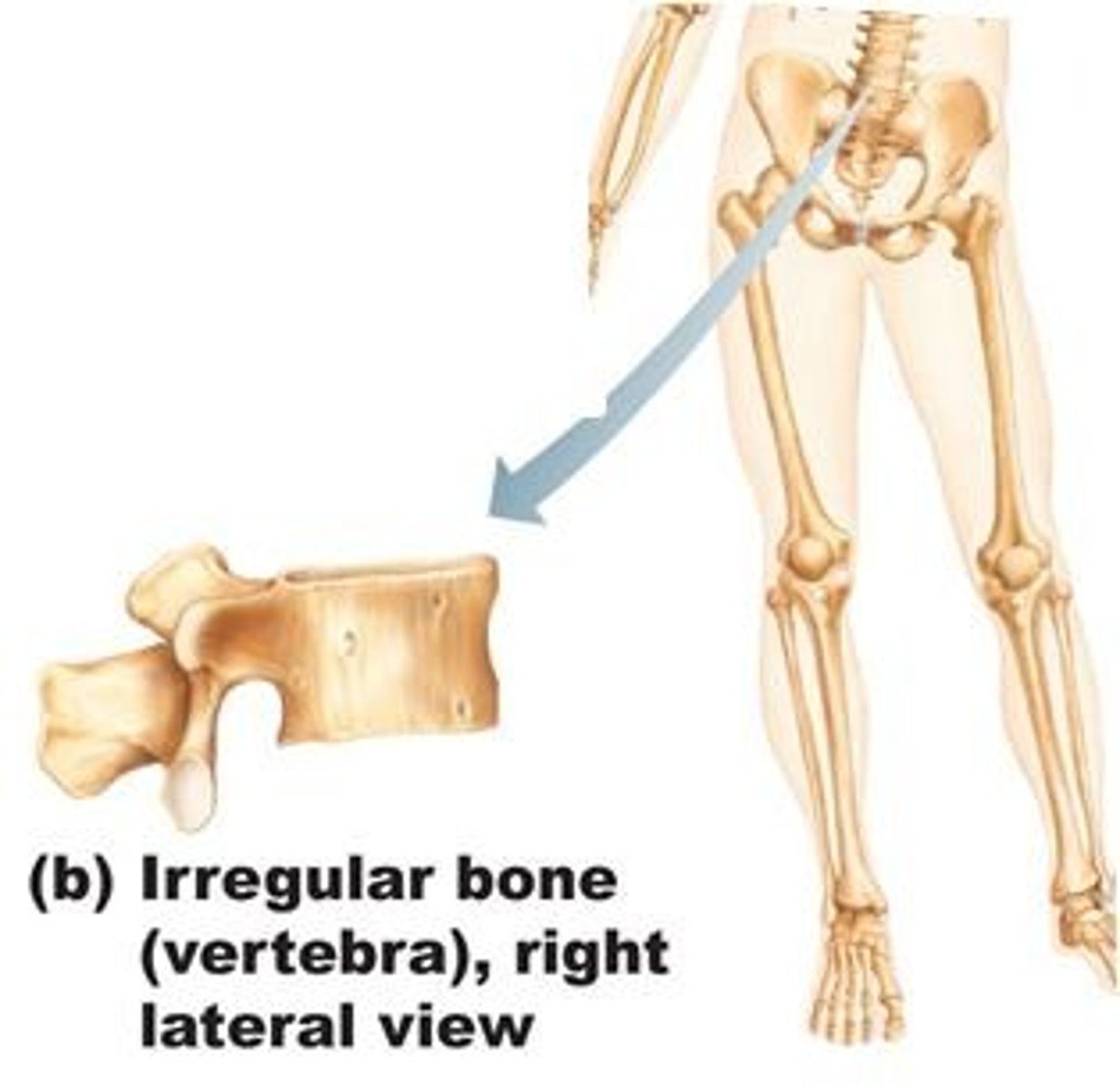
Irregular bones
vertebrae
Sesamoid bones
round bones found near joints (e.g., the patella)
sutural bones
tiny bones between cranial bones
Bone markings
reveal where muscles, tendons, and ligaments were attached and where blood vessels and nerves passed
Tuberoisty
large rounded projection
Crest
Narrow ridge of bone
Trochanter
large, rough projection
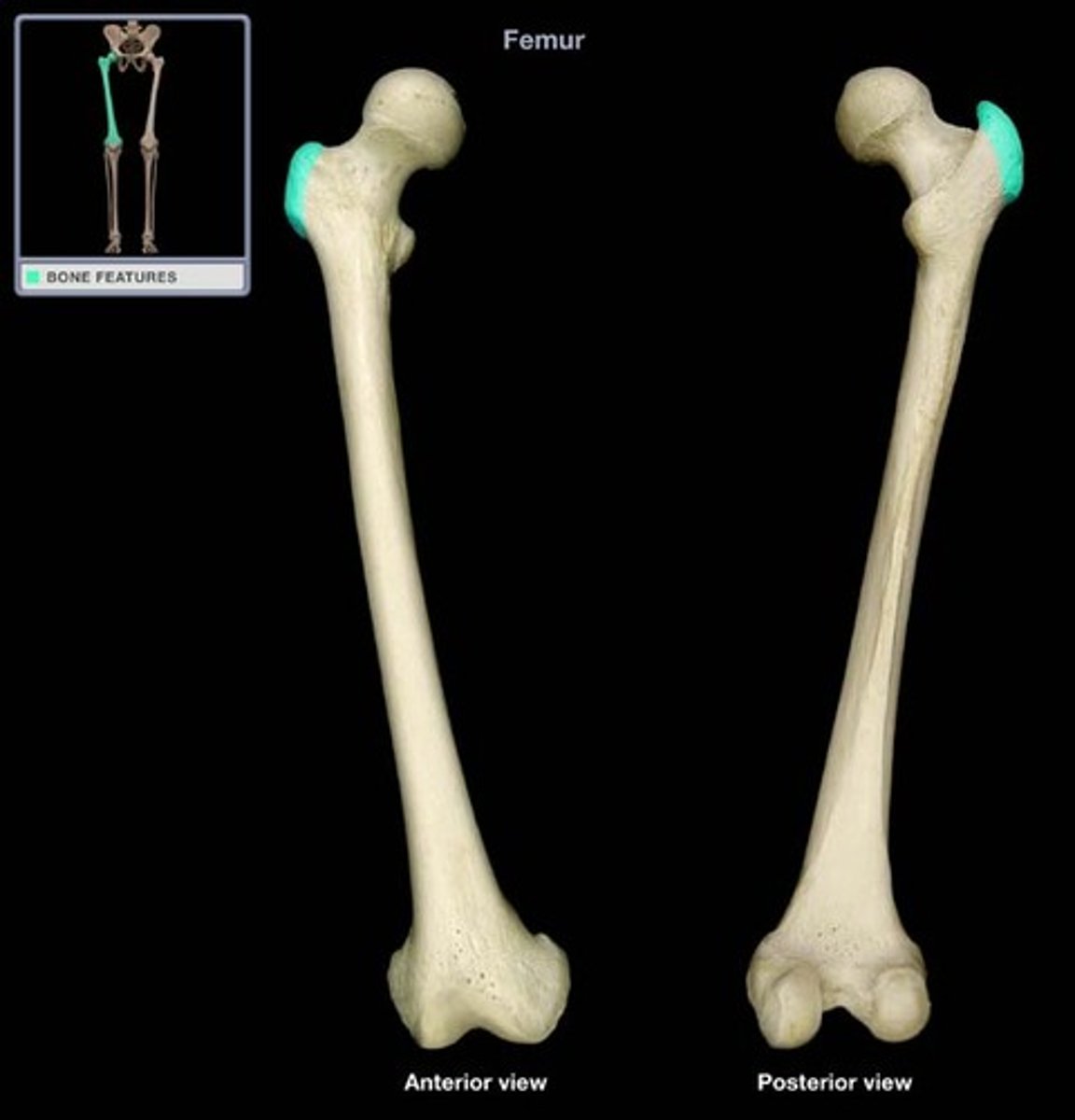
Line
Narrow ridge of bone; less prominent than a crest
Tubercle
small rounded projection
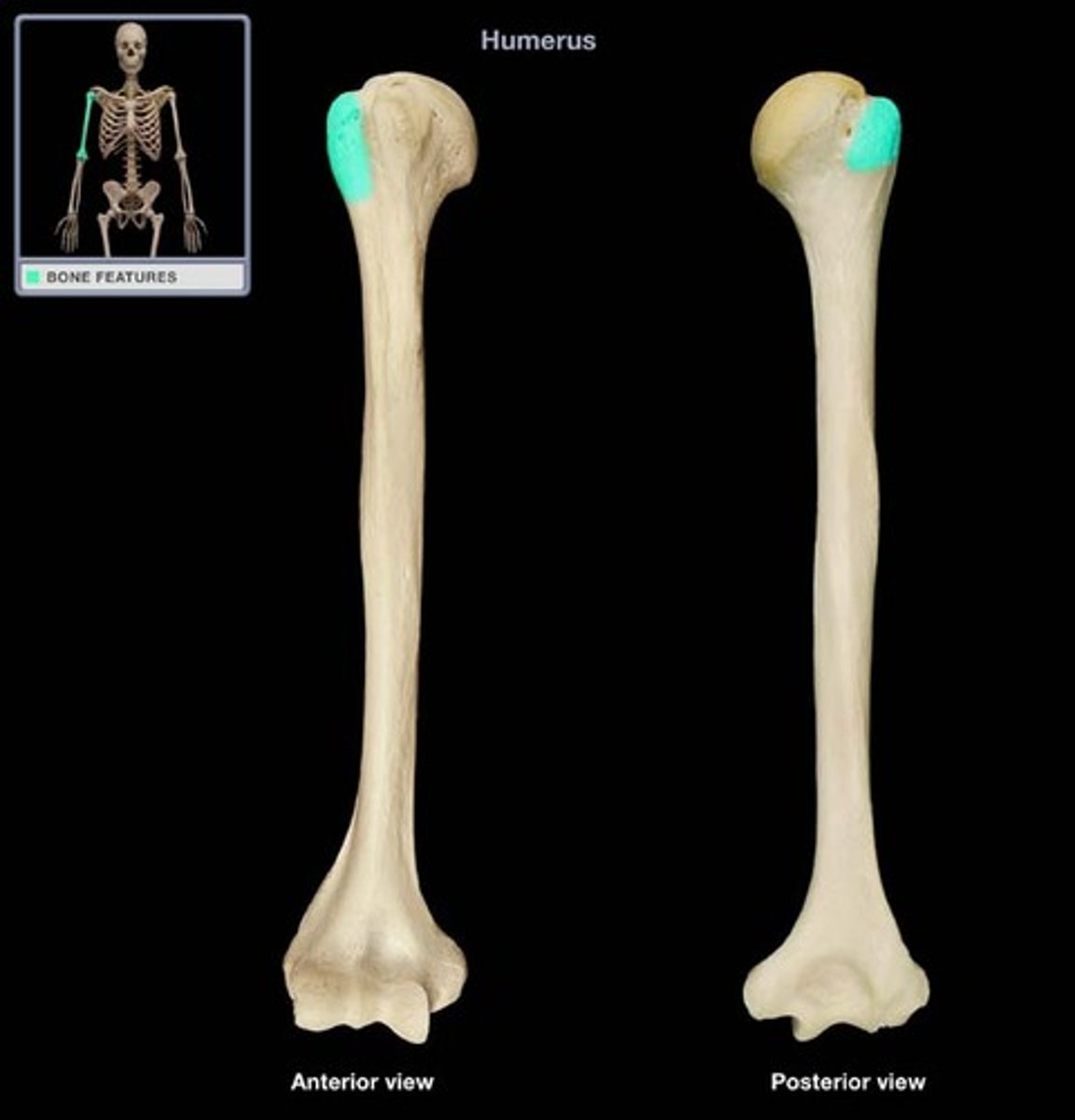
Epicondyle
Raised area on or above a condyle
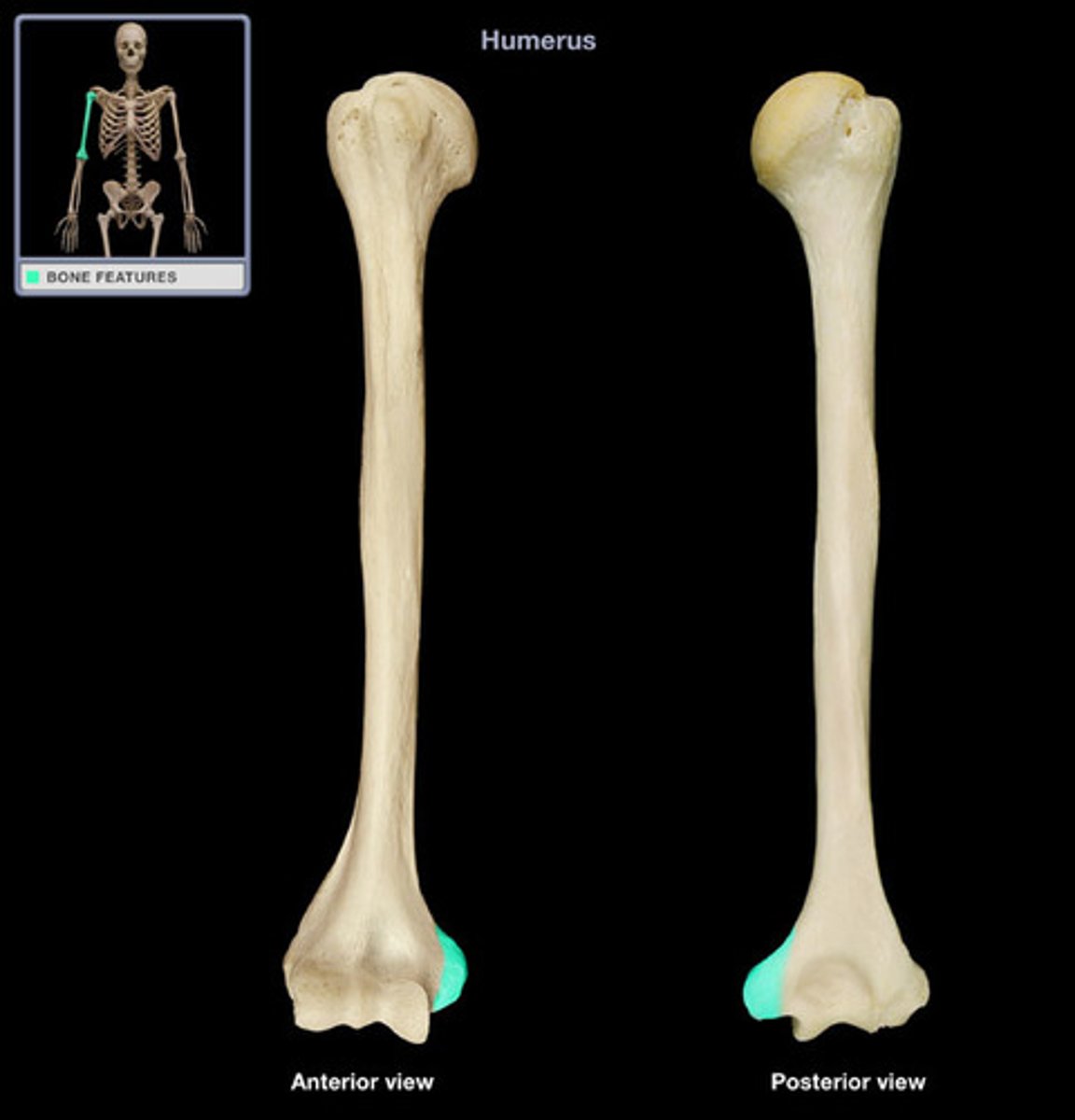
Spine
sharp, slender, often pointed projection
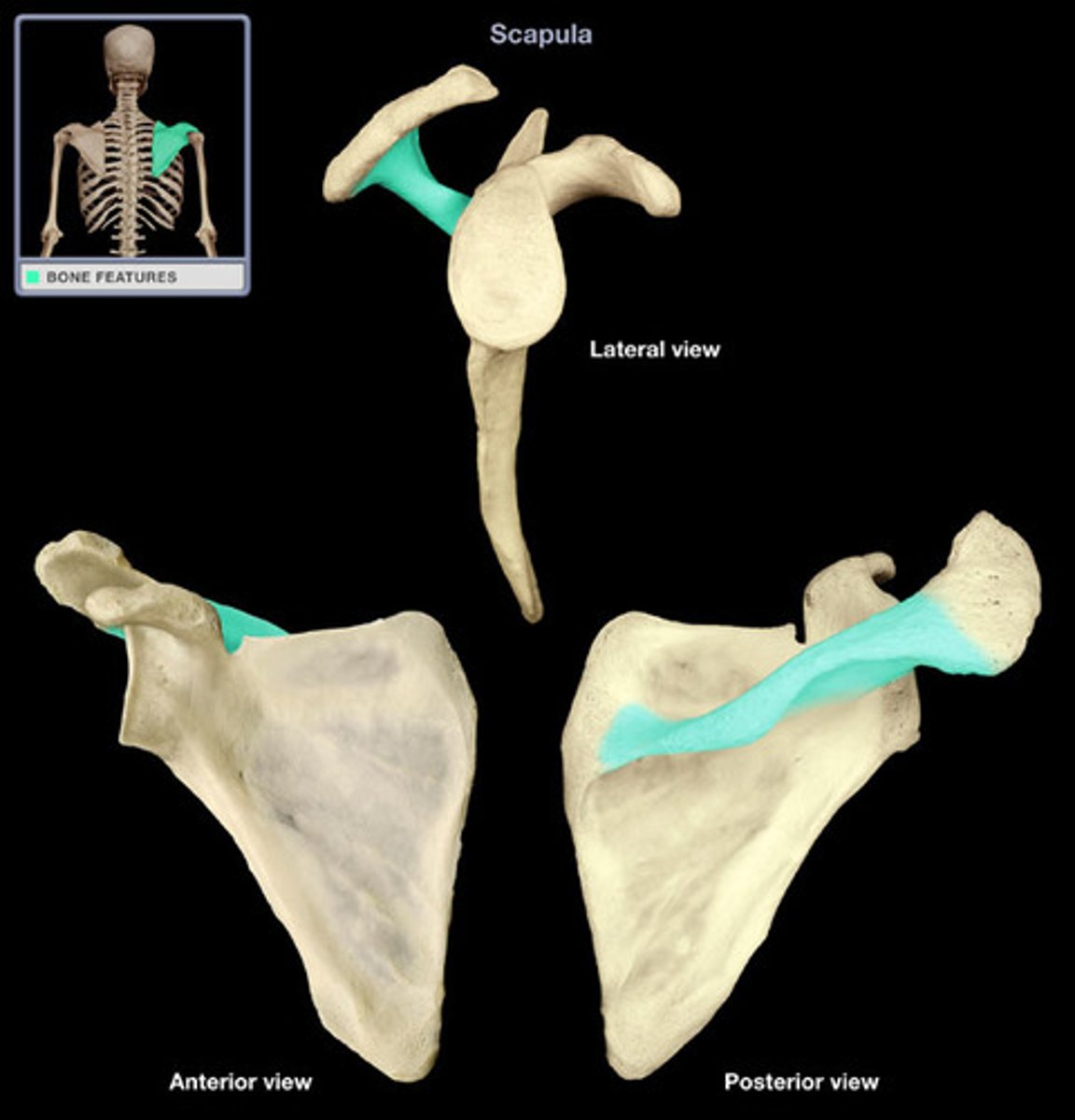
Process
any bony prominence
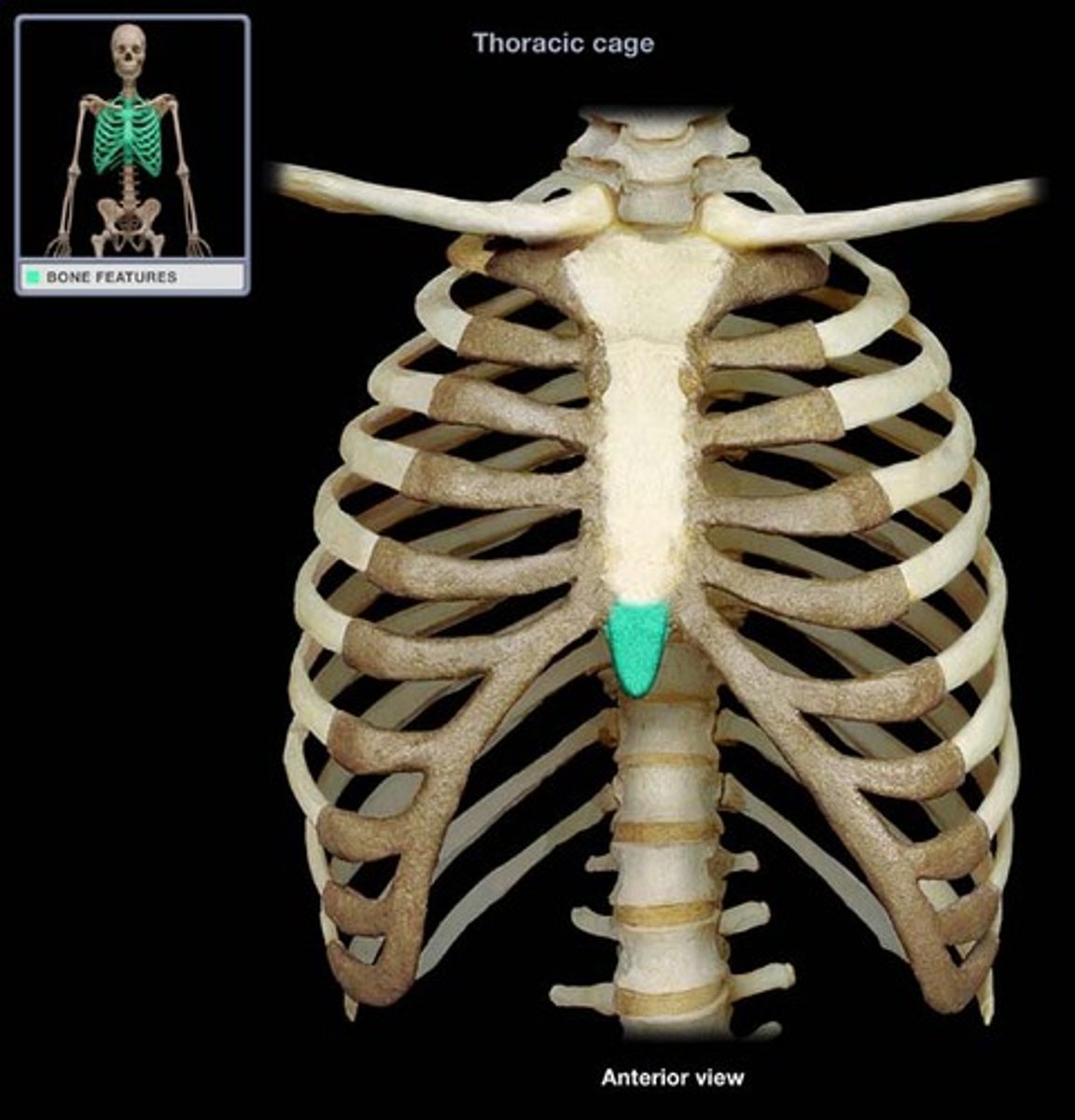
Head
bony expansion carried on a narrow neck
Facet
smooth, nearly flat articular surface
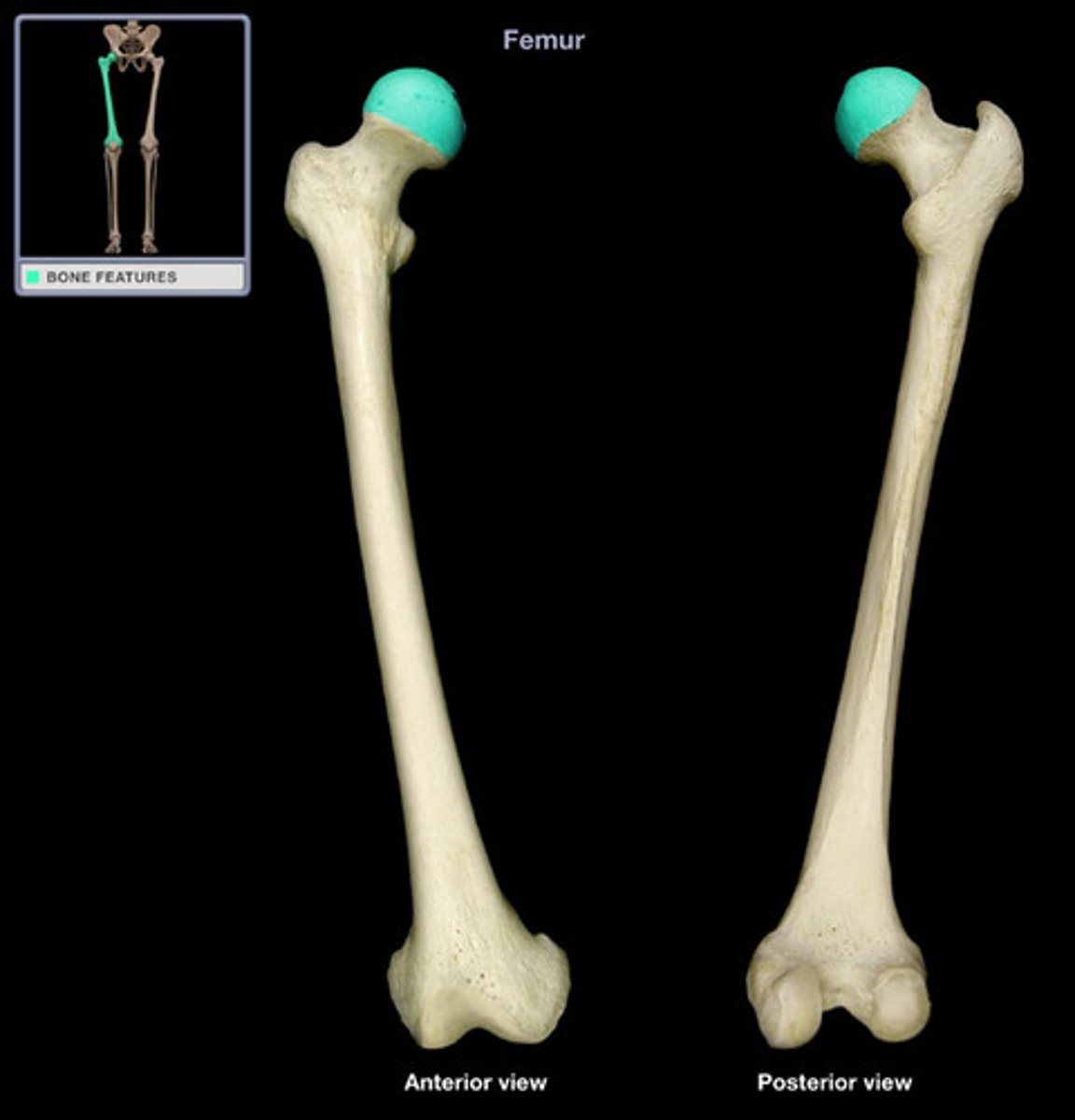
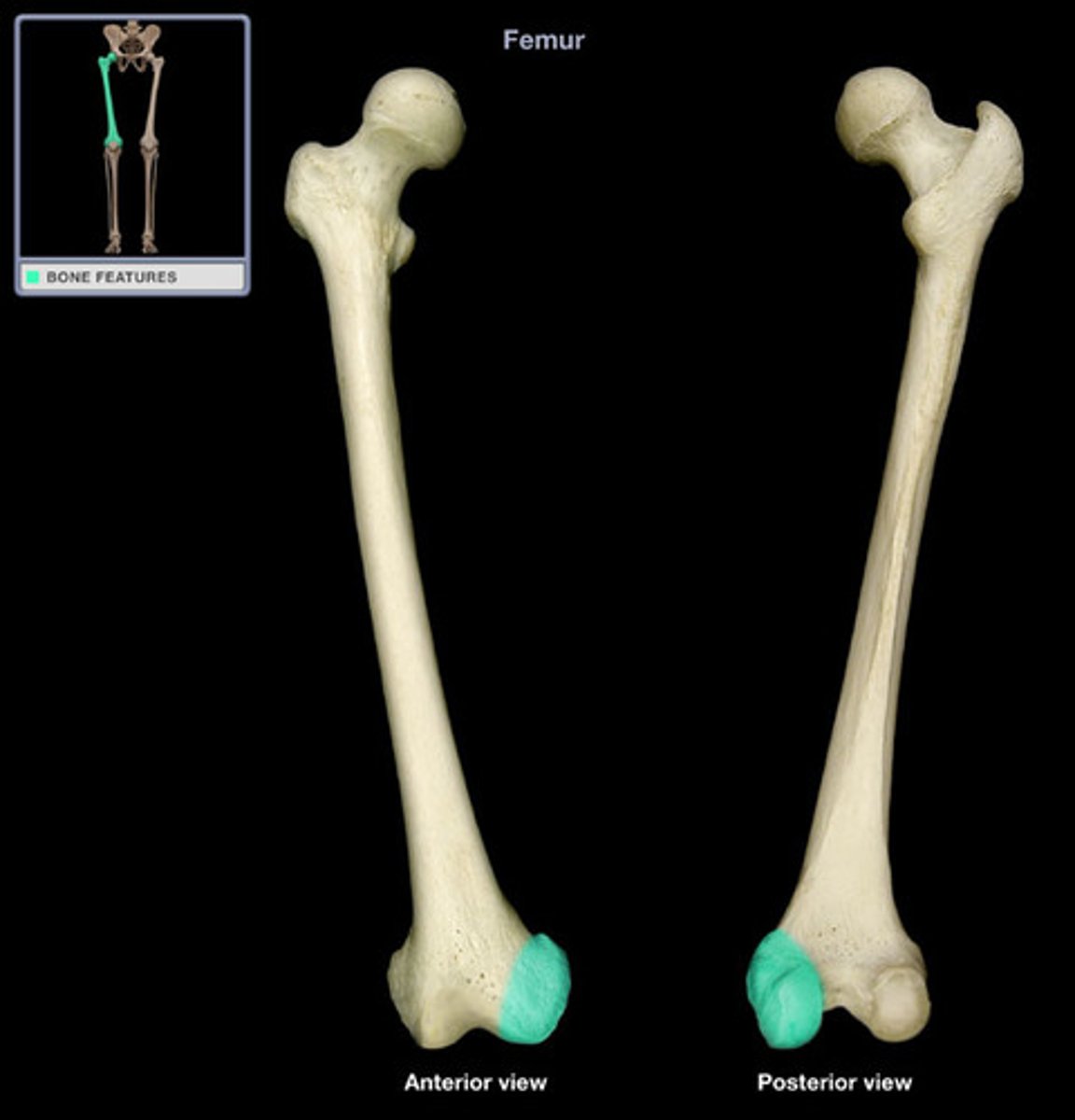
Condyle
rounded articular projection
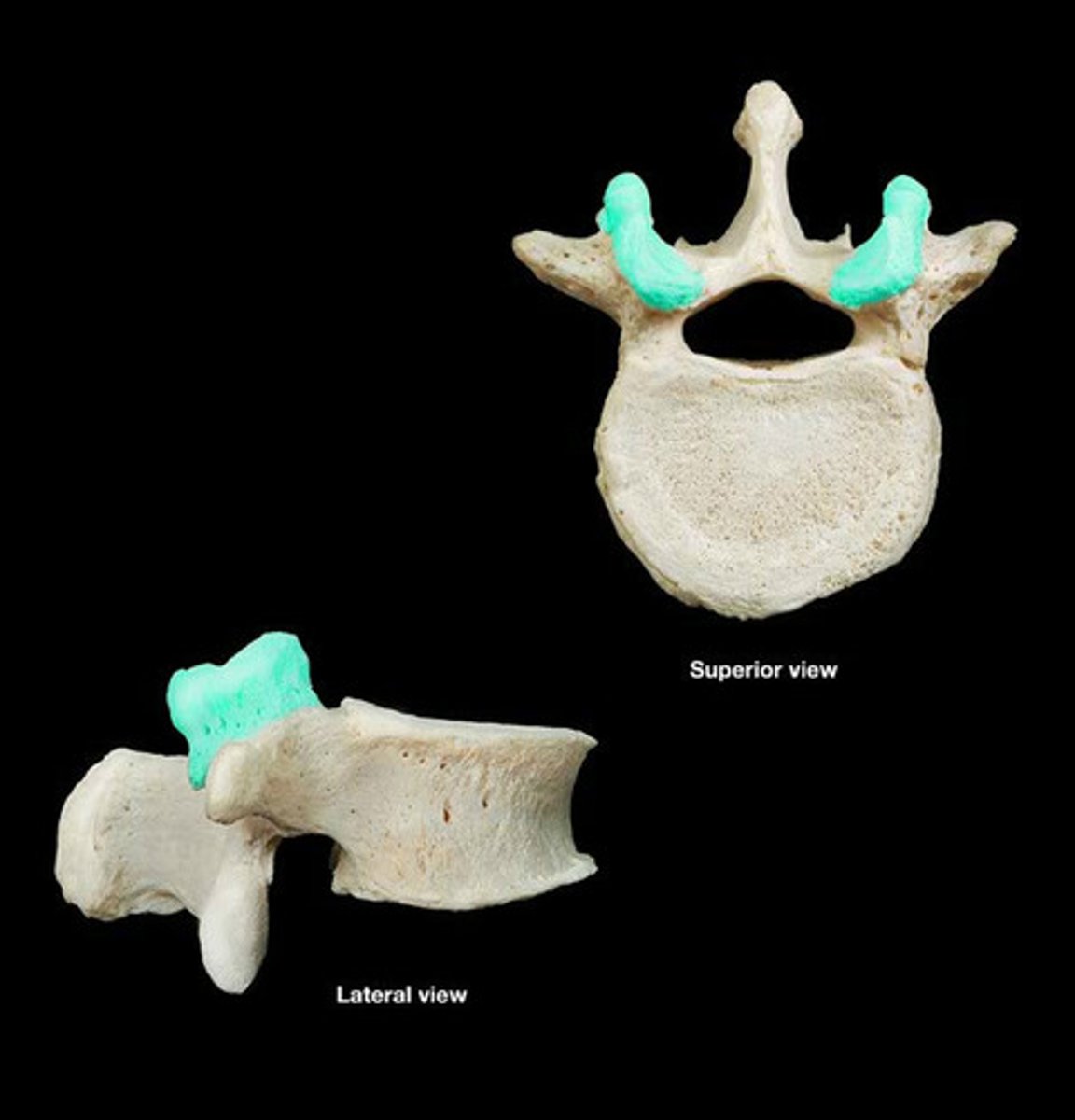
Ramus
armlike bar of bone
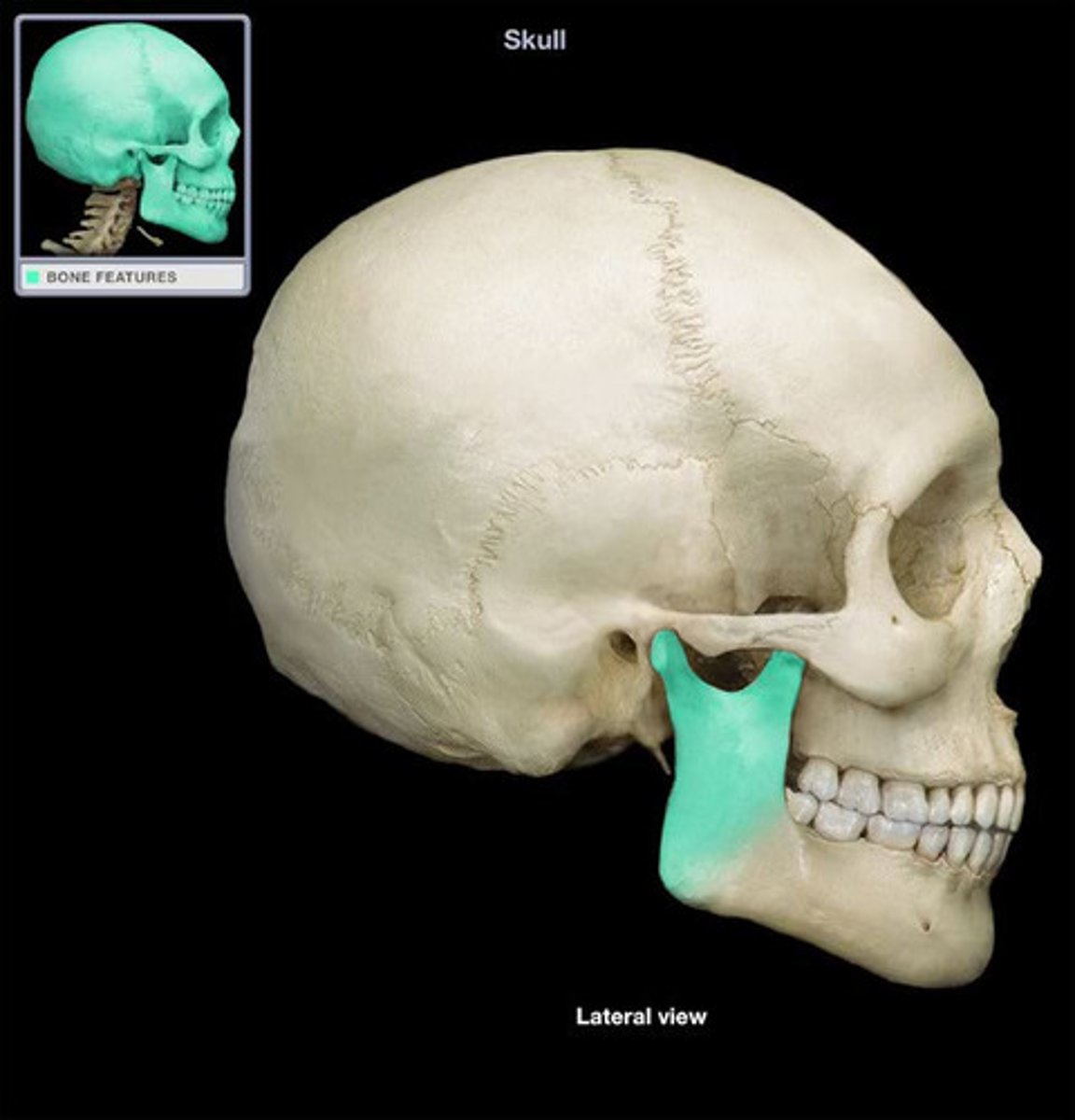
Fissure
Narrow, slitlike opening
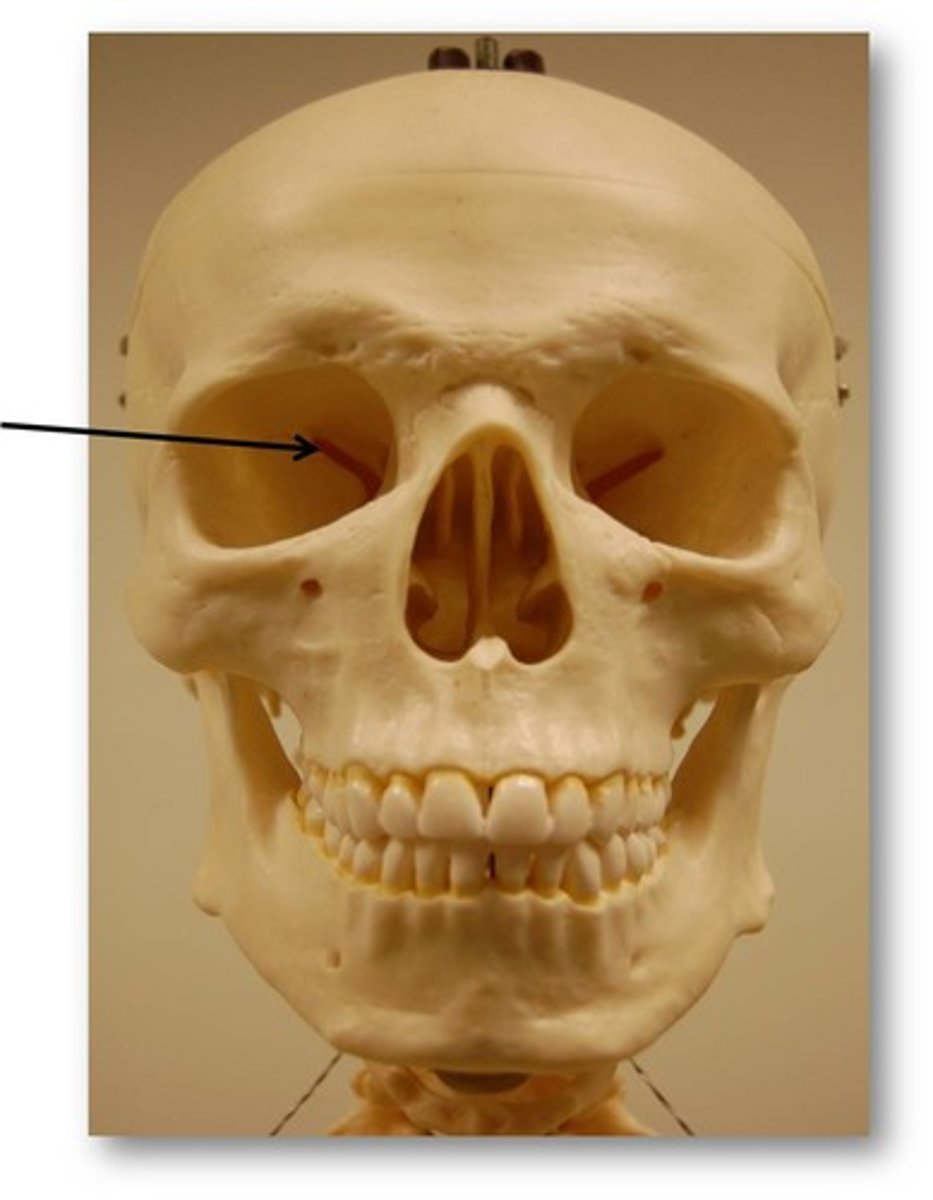
Notch
indentation at the edge of a structure
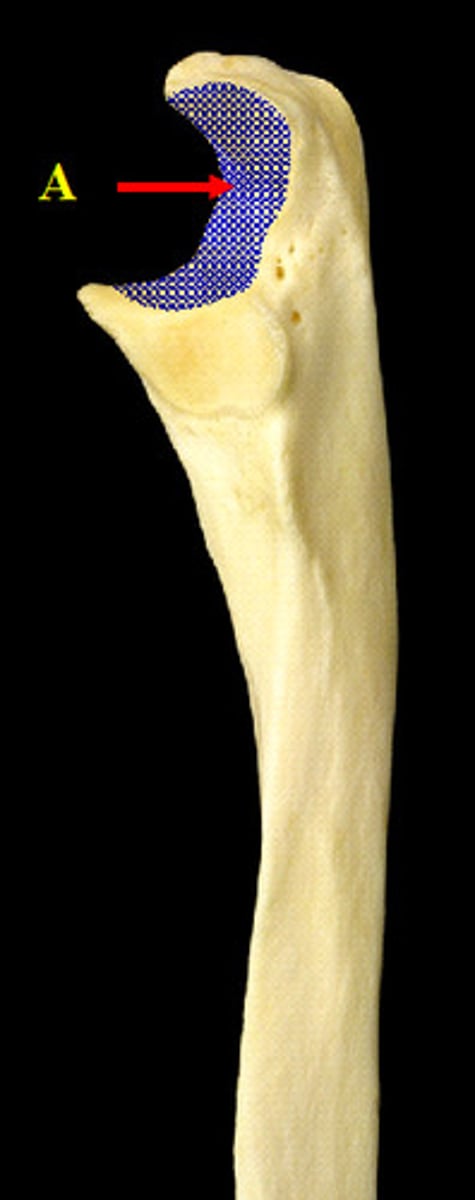
Foraman
hole in a bone
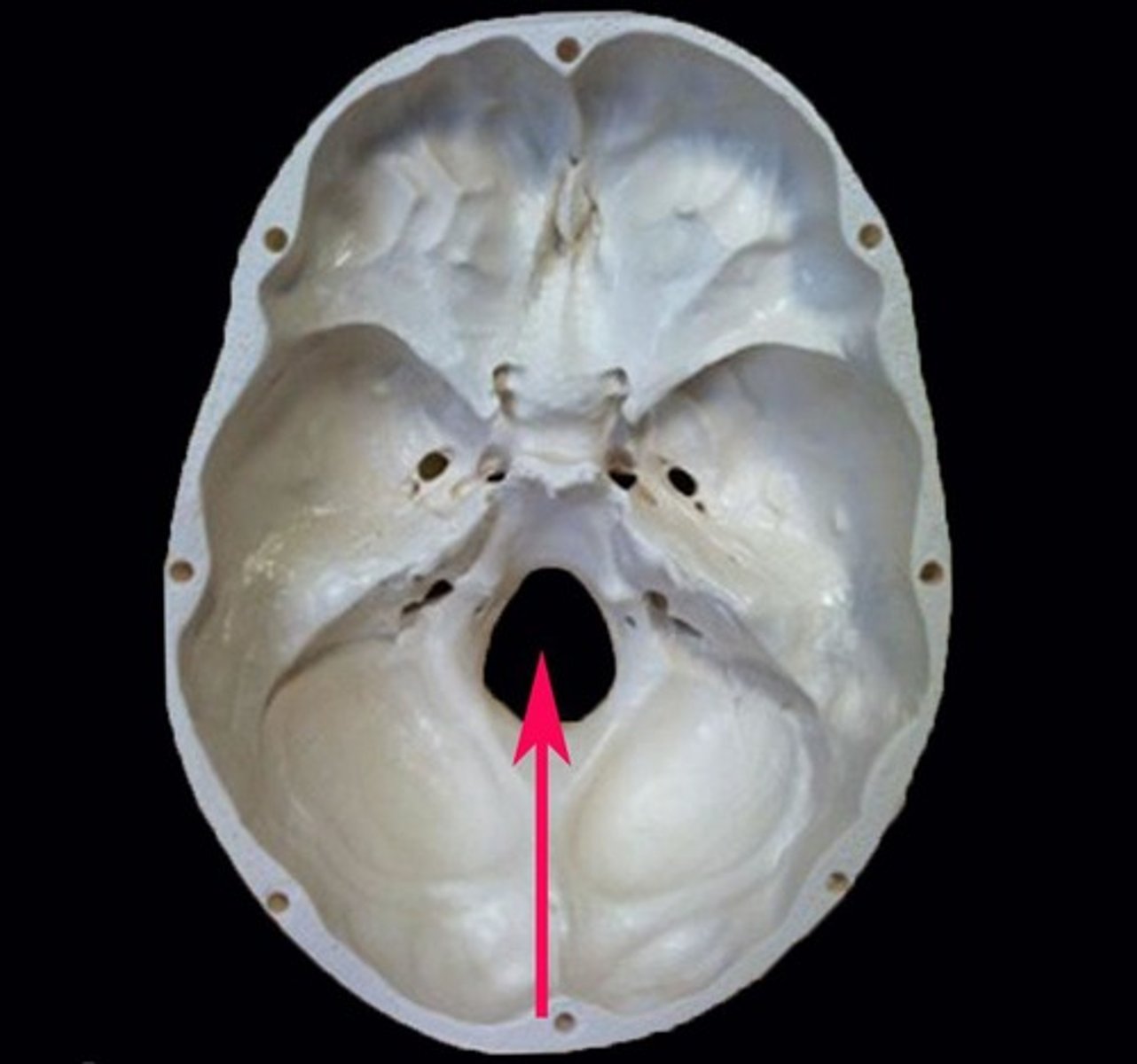
Meatus
canal-like passageway
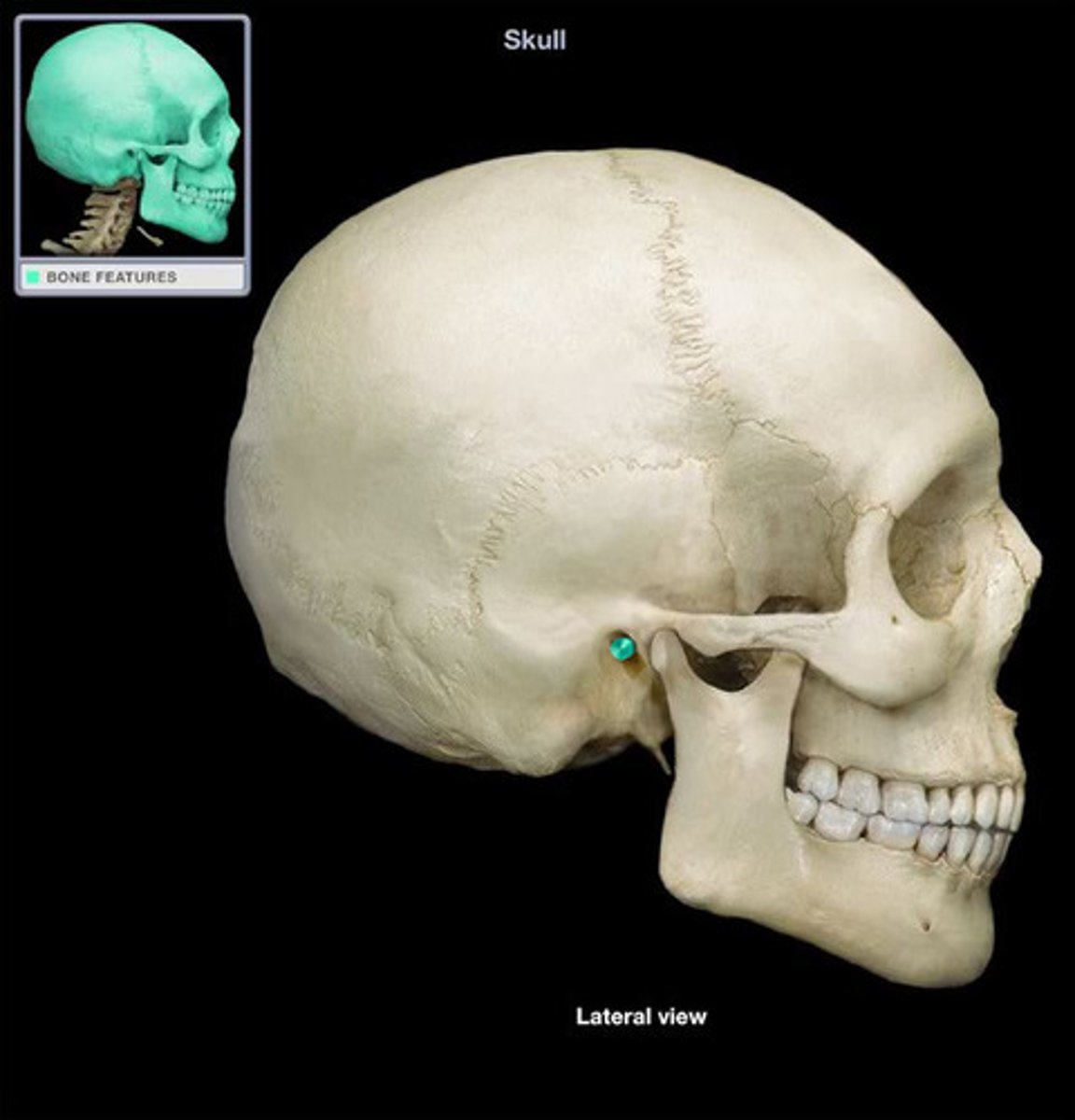
Sinus
cavity within a bone
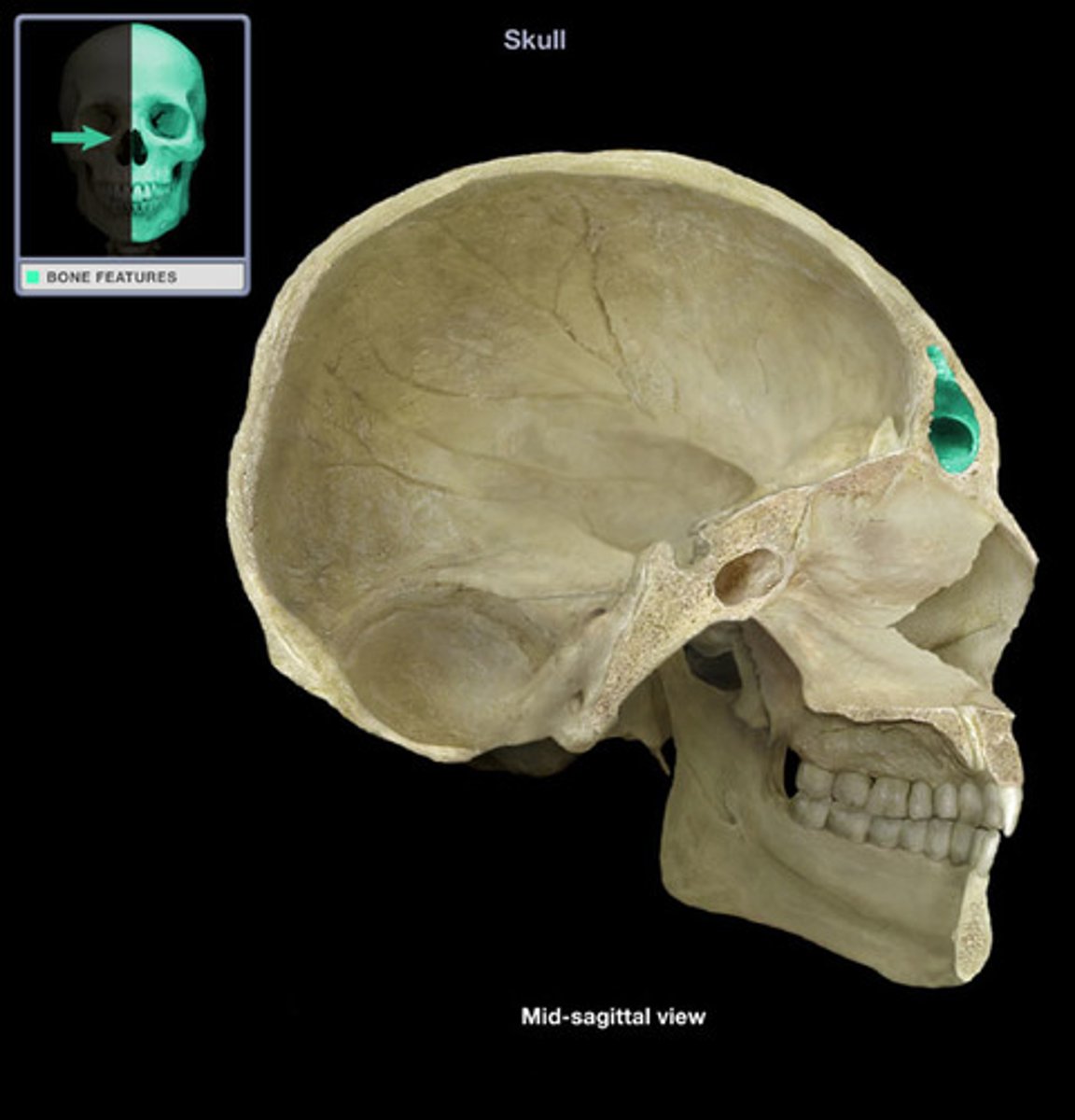
Fossa
Shallow, basinlike depression in a bone, often serving as an articular surface
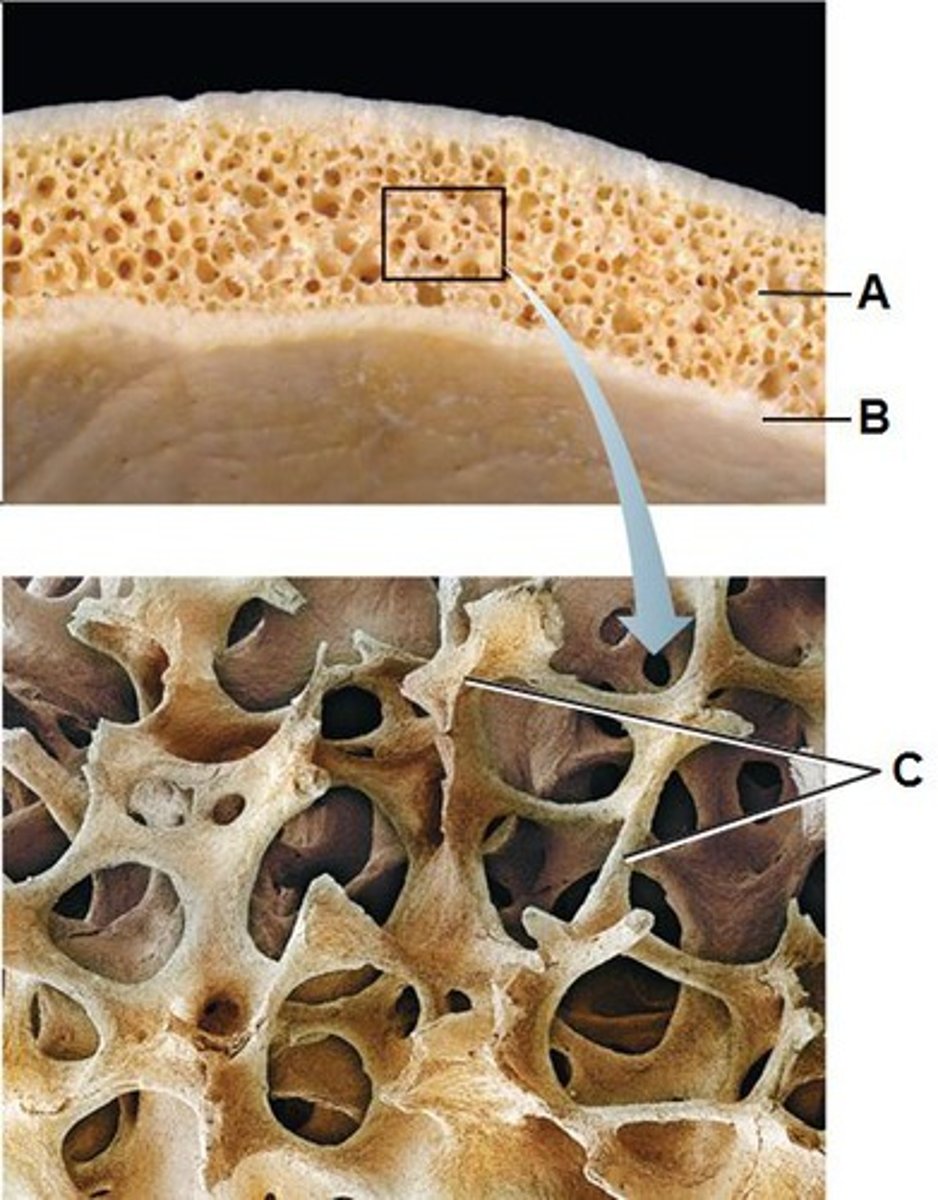
Trabeculae
supporting bundles of bony fibers in cancellous (spongy) bone
Central canal
A tiny channel found within the spinal cord and inferior medulla oblongata
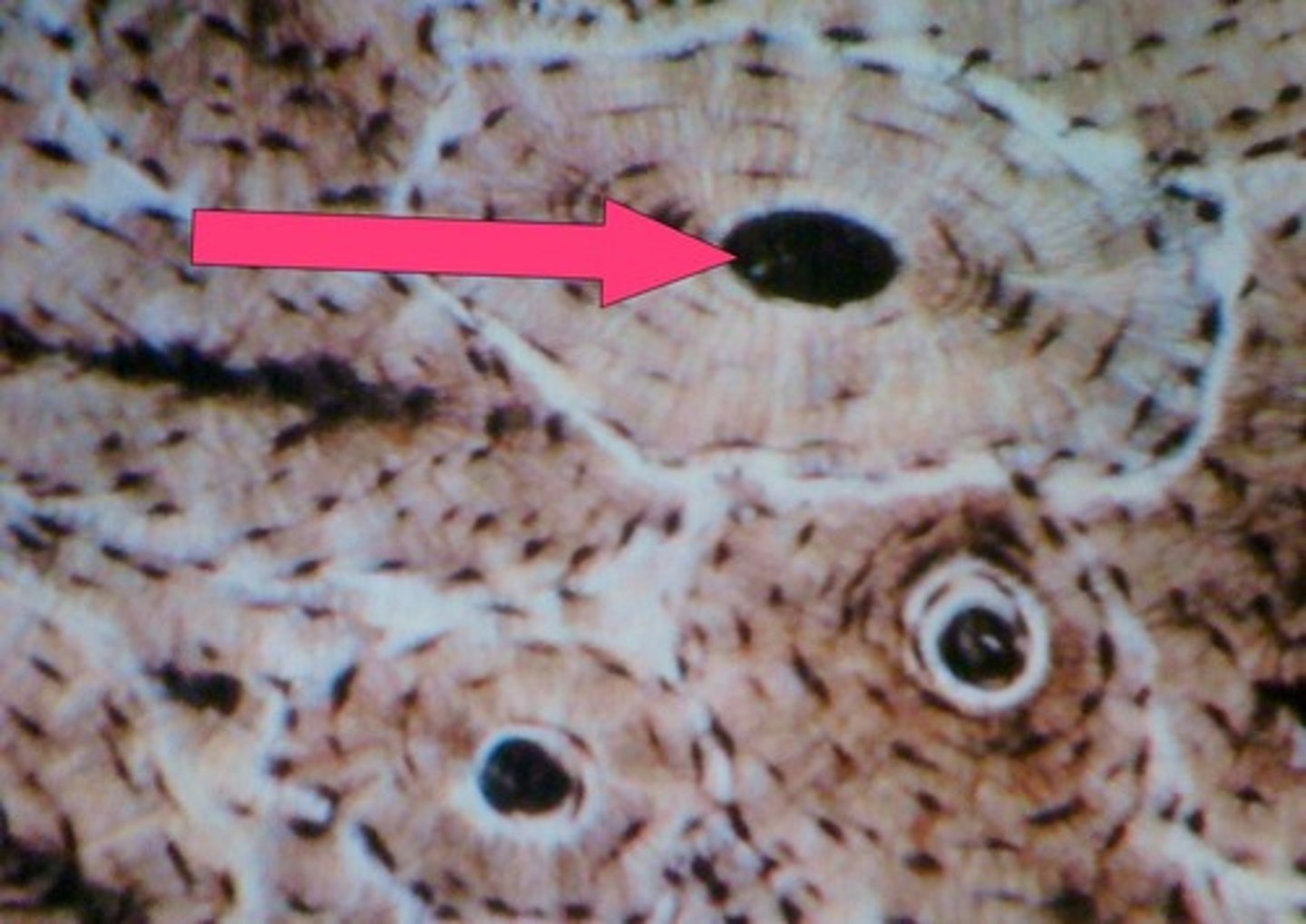
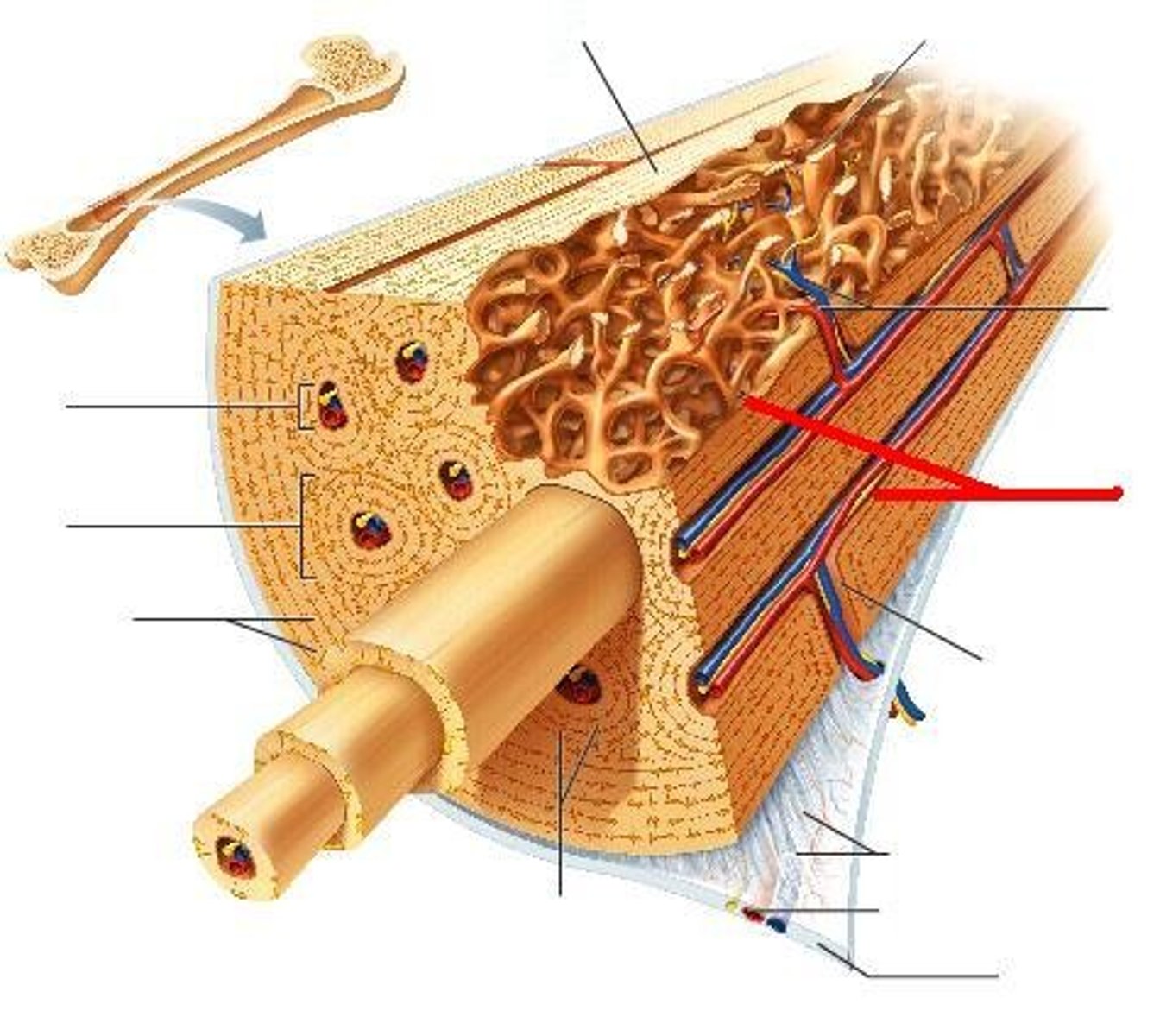
Osteon
structural unit of compact bone
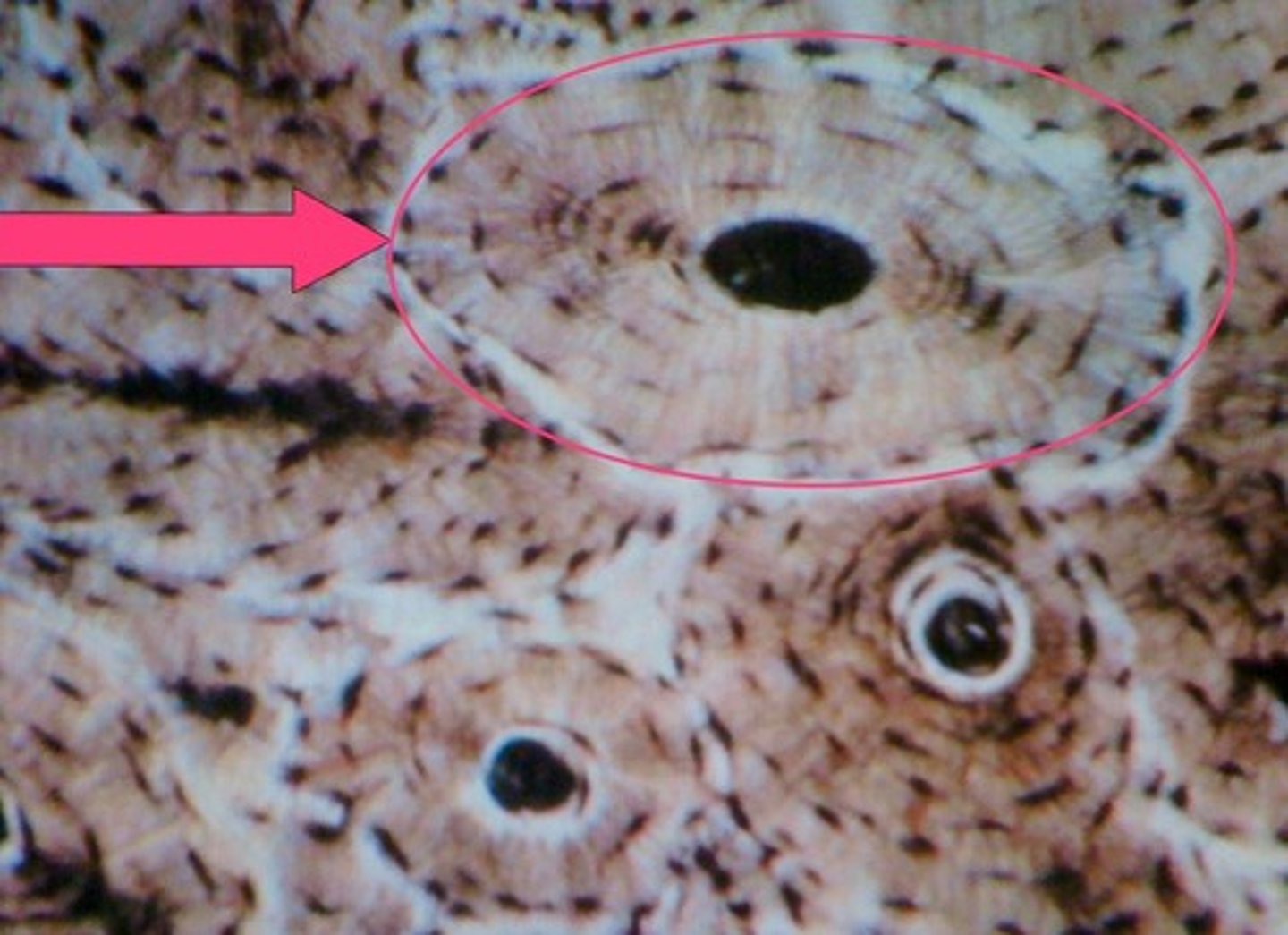
circumferential lamellae
fill outer region of dense bone
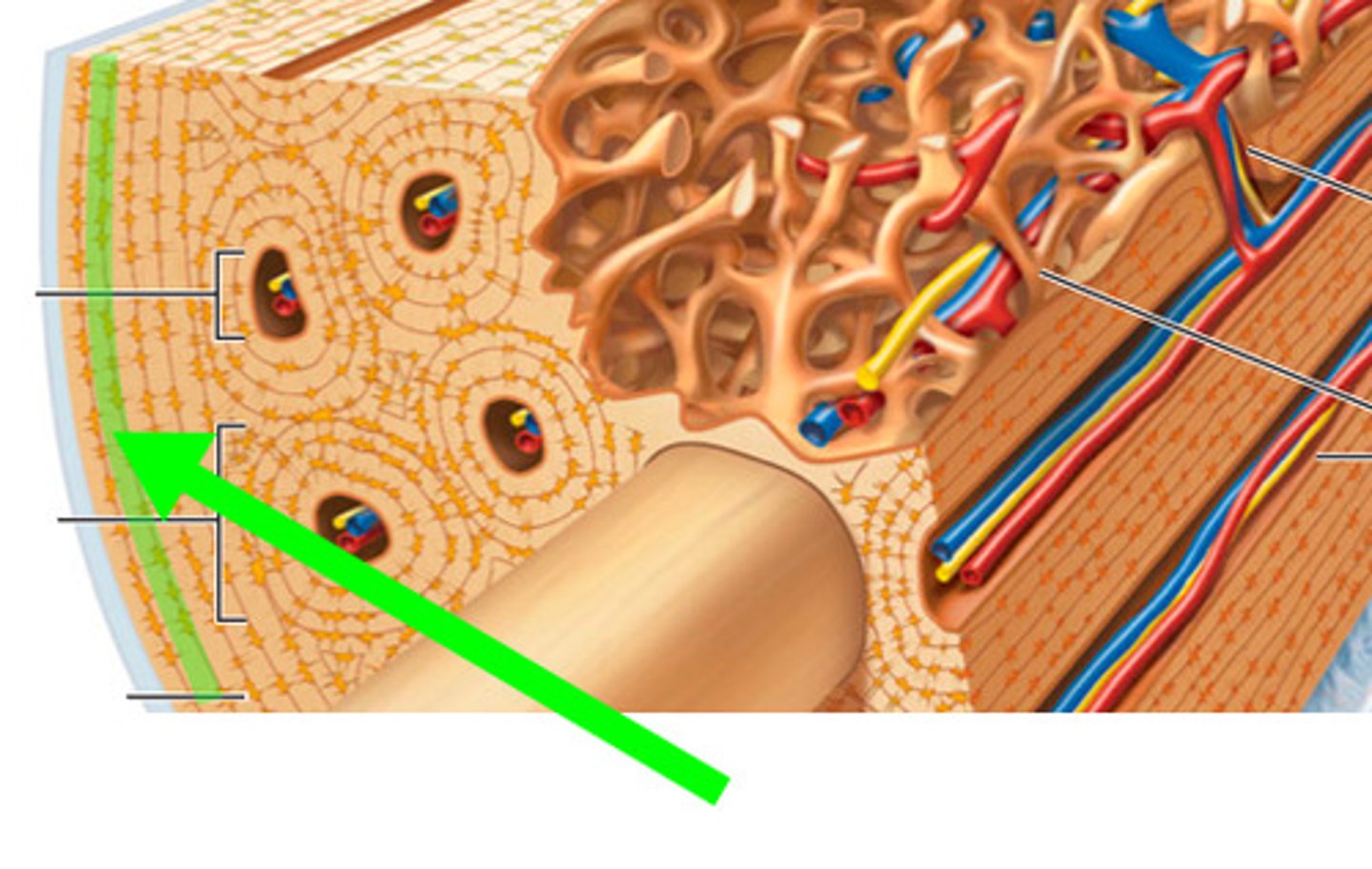
Osteoctyes
mature bone cells
Lacunae
small cavities in bone that contain osteocytes
Concentric lamellae
layers of bony matrix around a central canal
Canaliculi (compact bone)
Hairlike canals that connect lacunae to each other and the central canal
perforating canals
Carry blood vessels into bone and marrow
Endochondral ossification
Process of transforming cartilage into bone.
Epiphysis
End potions of a long bone
Peristeum
outer layer of bone/ Two membranous sites of osteoprogenitor cells
Diaphysis
shaft of a long bone
Medullary cavity
Contains yellow marrow in adult bones
Epiphysis Line
growth plate
Function of the organic matrix in bone
Flexibility and tensile, strength, bones can bend and twist
the important organic bone components
Collagen fibers and osteocytes
function of the calcium salts
strengthen bones
Collagen
Baking removes ___ from the bone
Calcium/minerals
Bone in acid removes _____
epiphyseal face
cartilage cells at the epiphyseal side are continuing to grow and divide mitotically
diaphyseal face
aging, dying, and then osteoblasts move in to form bones.
Tibia
shin bone
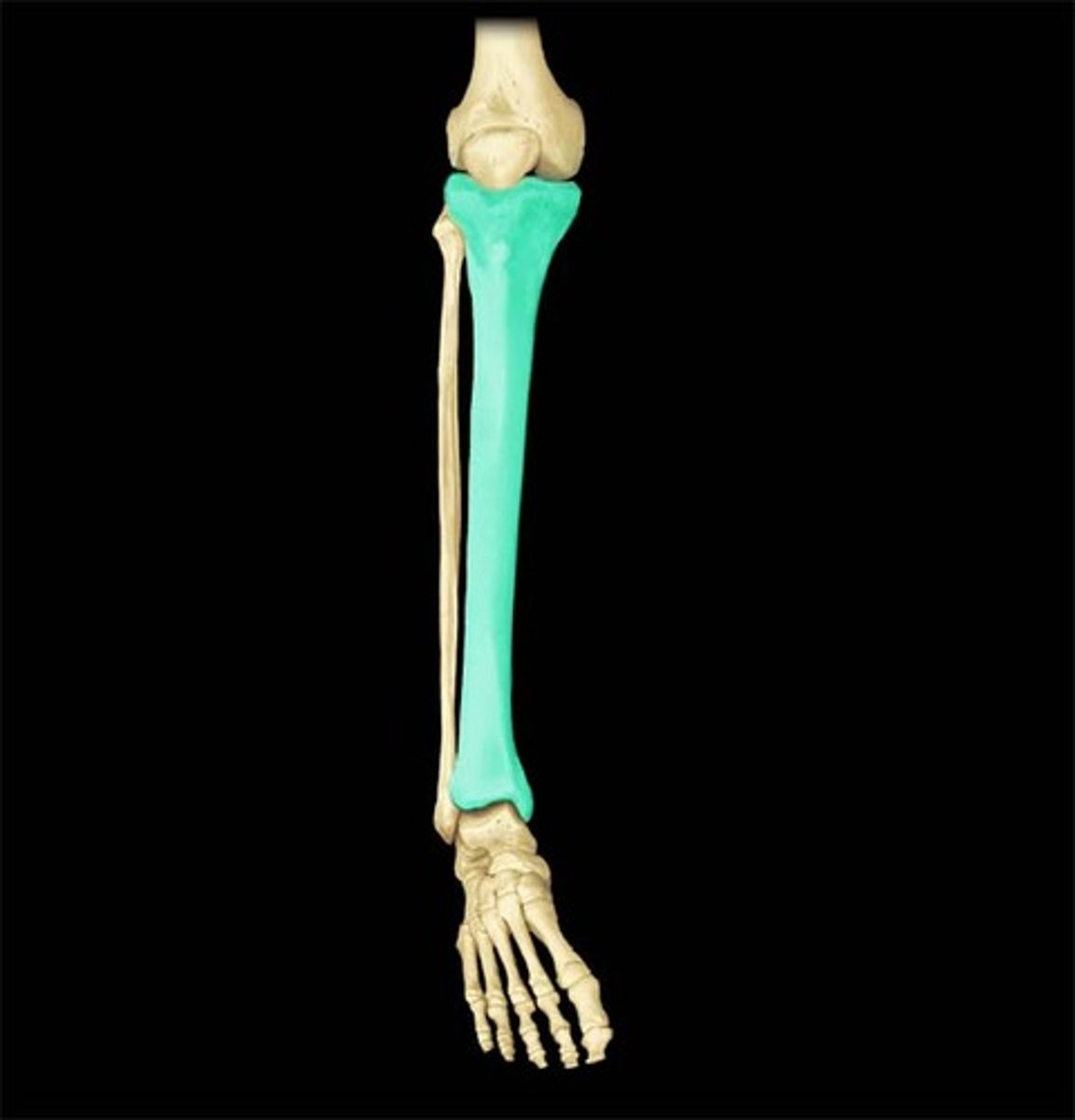
pectoral girdle
clavicle and scapula
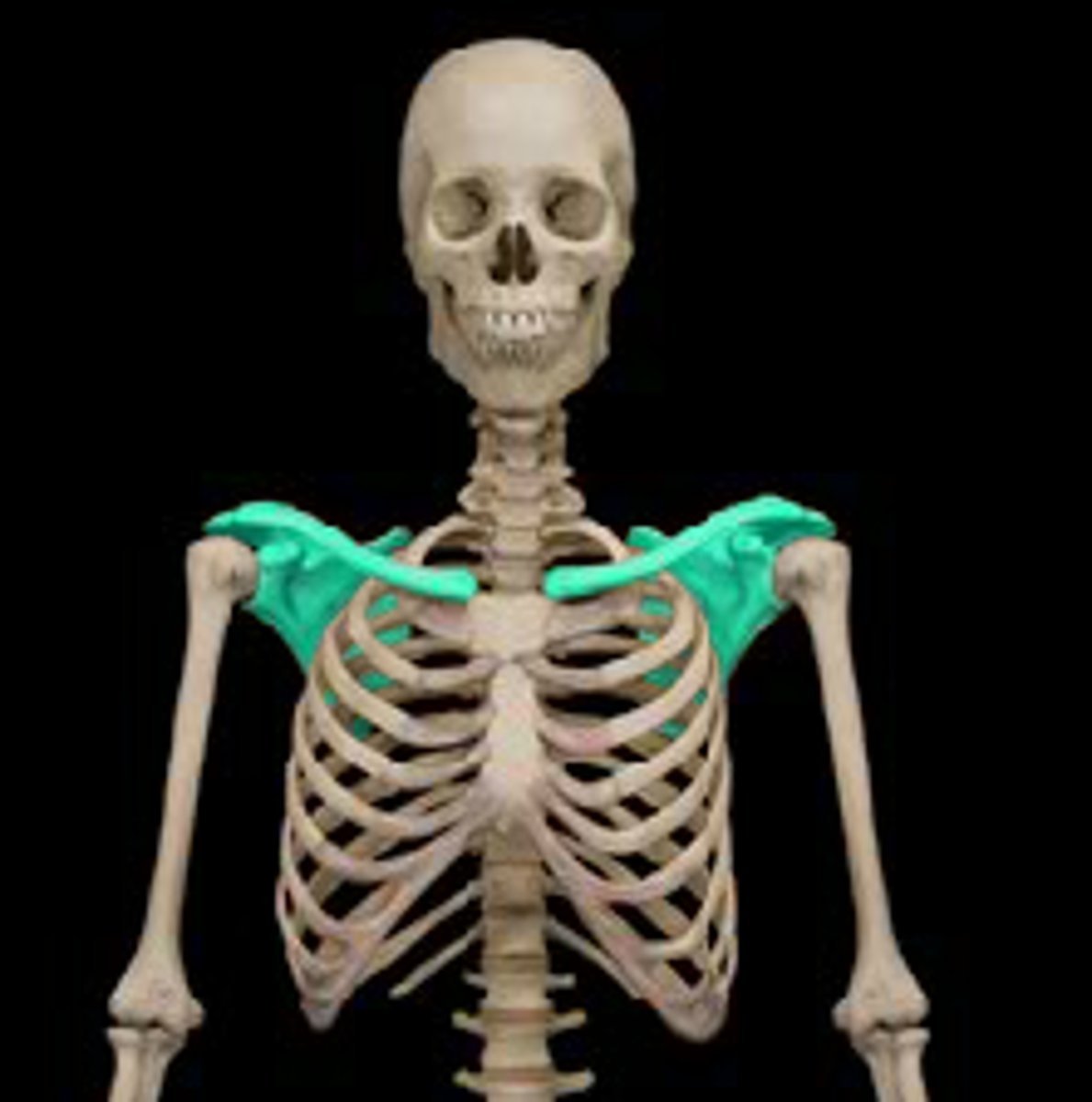
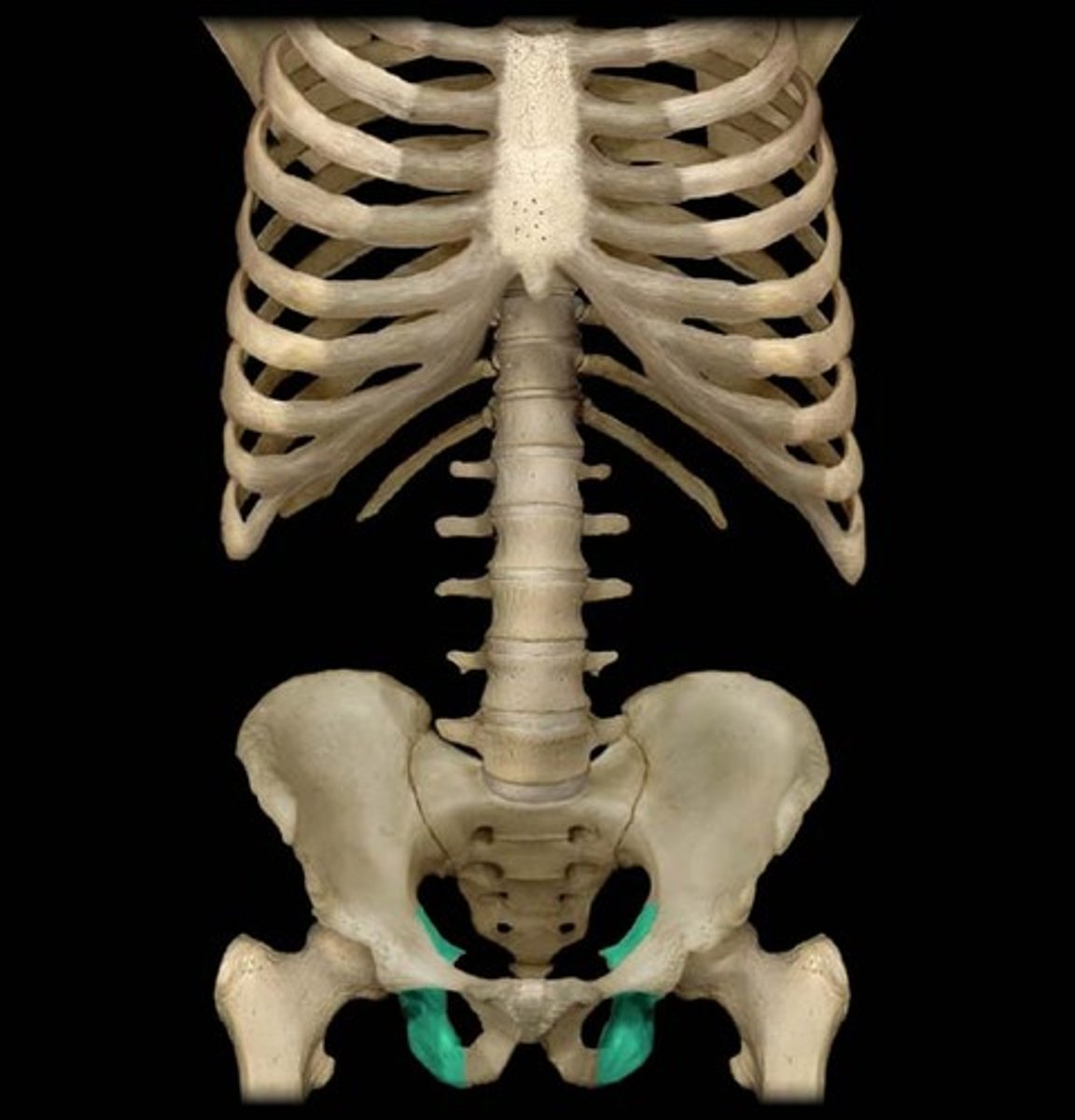
bones of the pelvic girdle
ilium, ischium, pubis
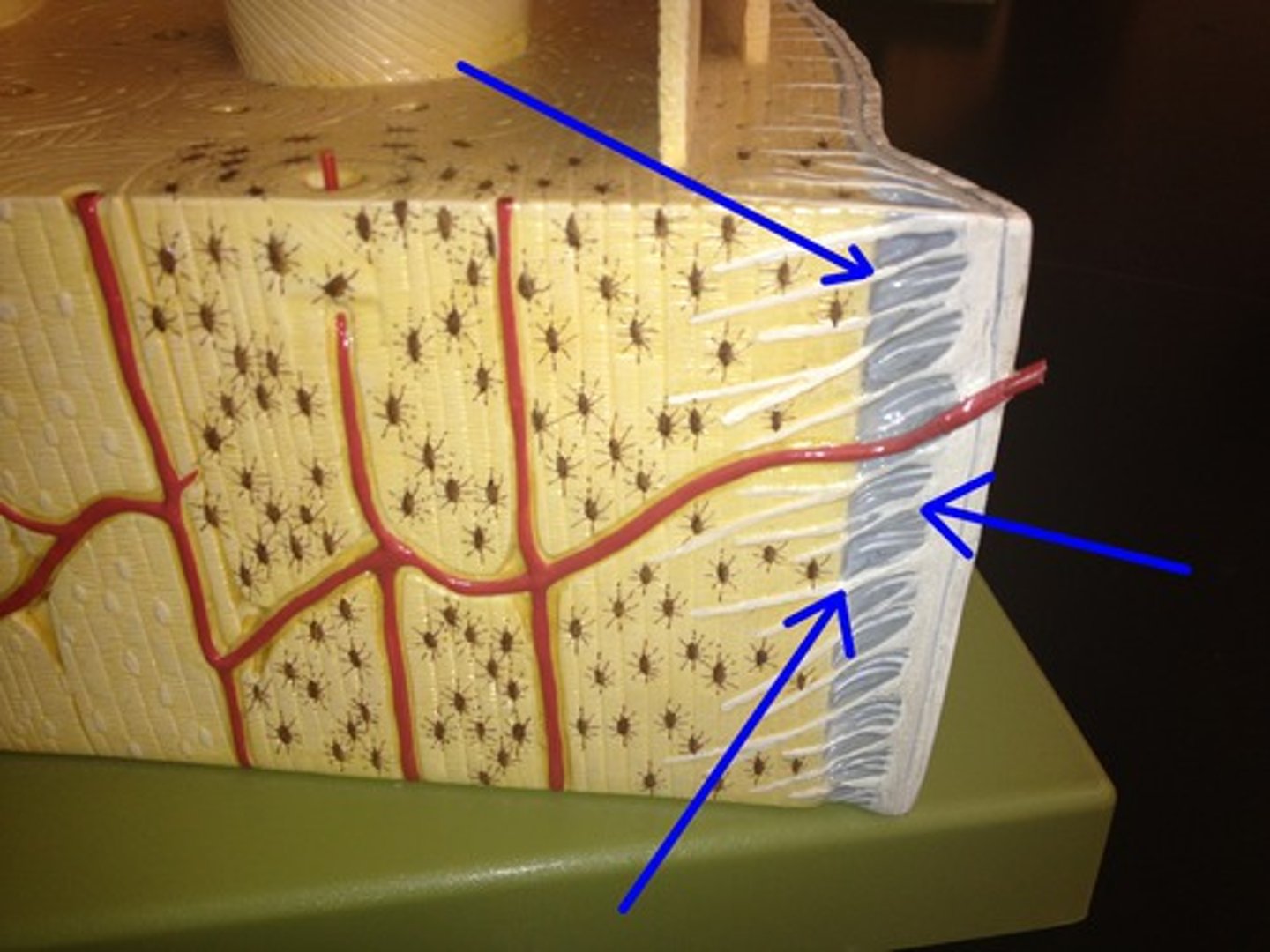
Periosteum
A dense fibrous membrane covering the surface of bones (except at their extremities) and serving as an attachment for tendons and muscles.
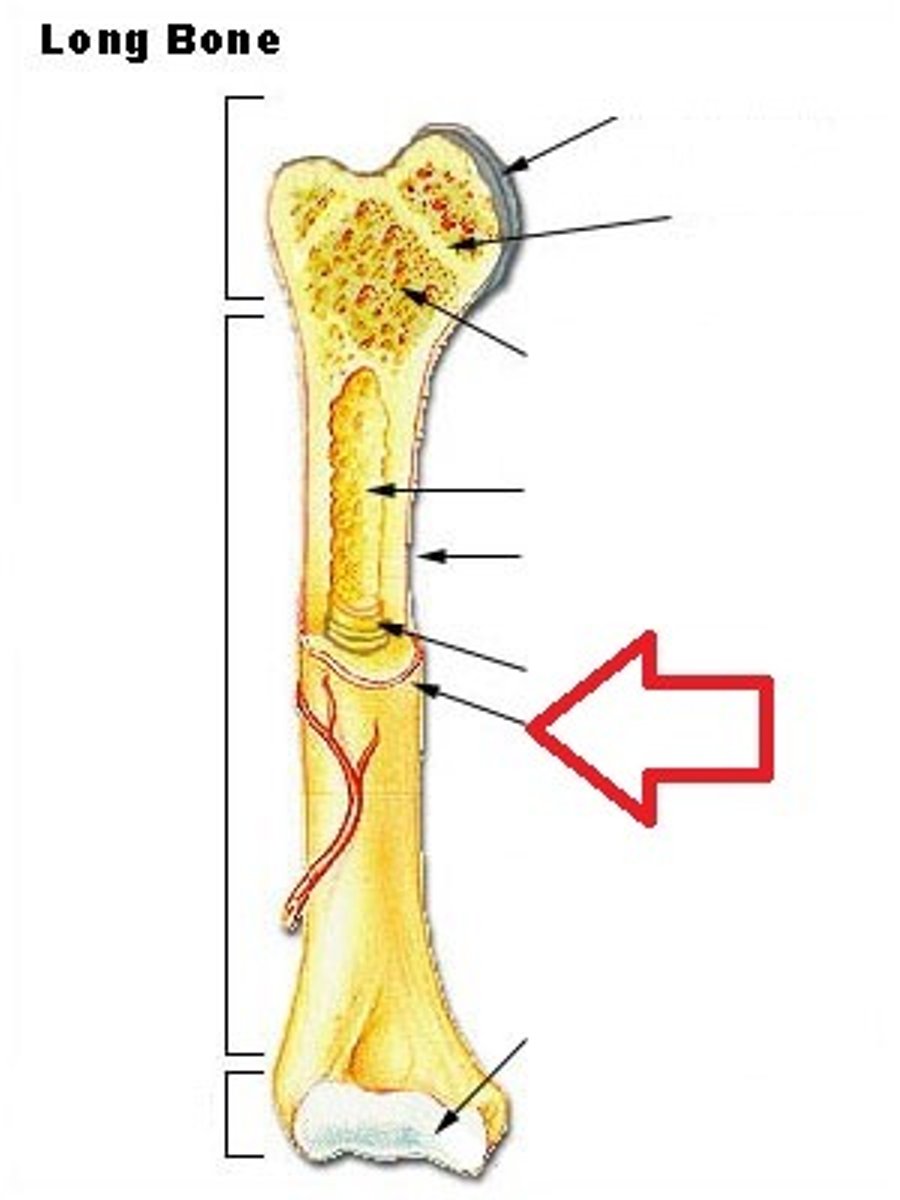
perforating fibers
secure periosteum to underlying bone
proximal epiphysis
the end of the bone located nearest to the midline of the body
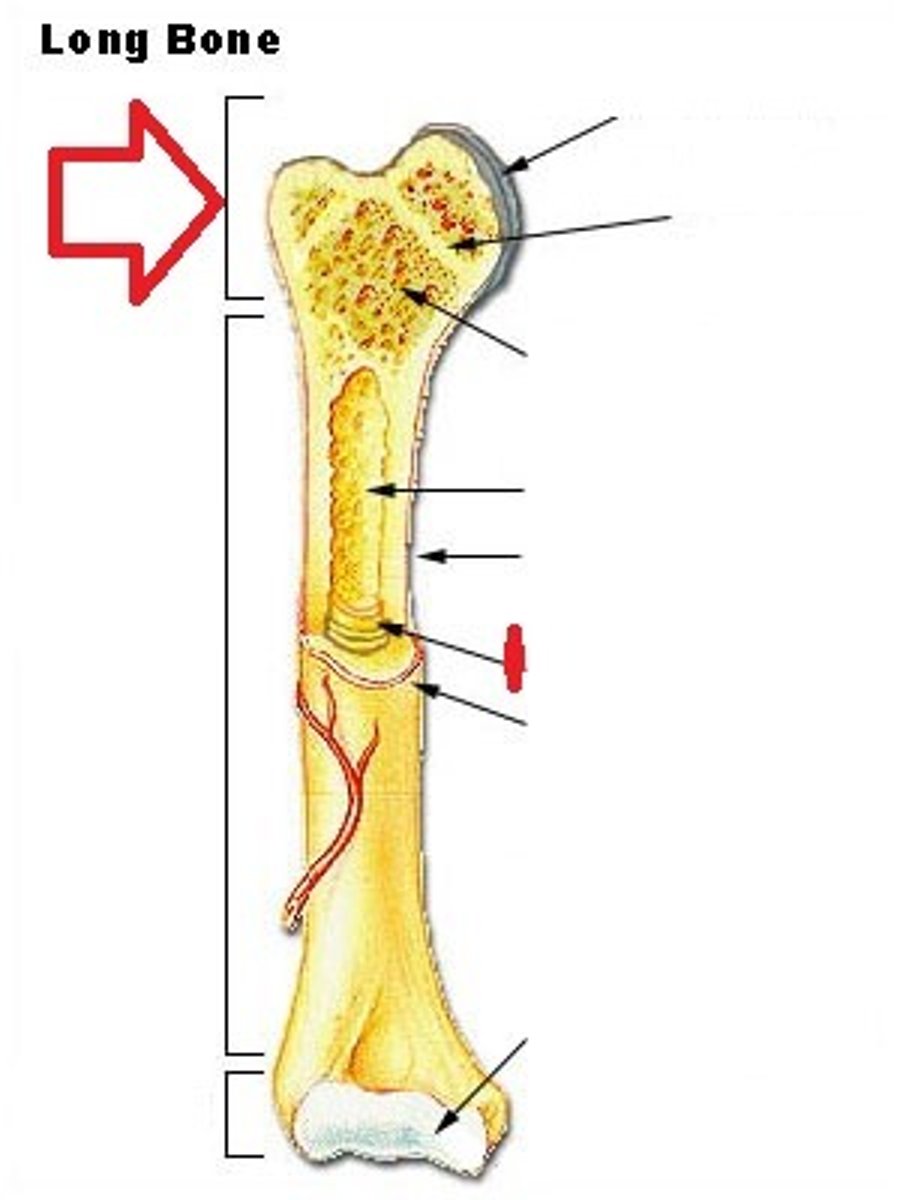
Distal epiphysis
end farthest from trunk
Epiphyseal line
growth plate
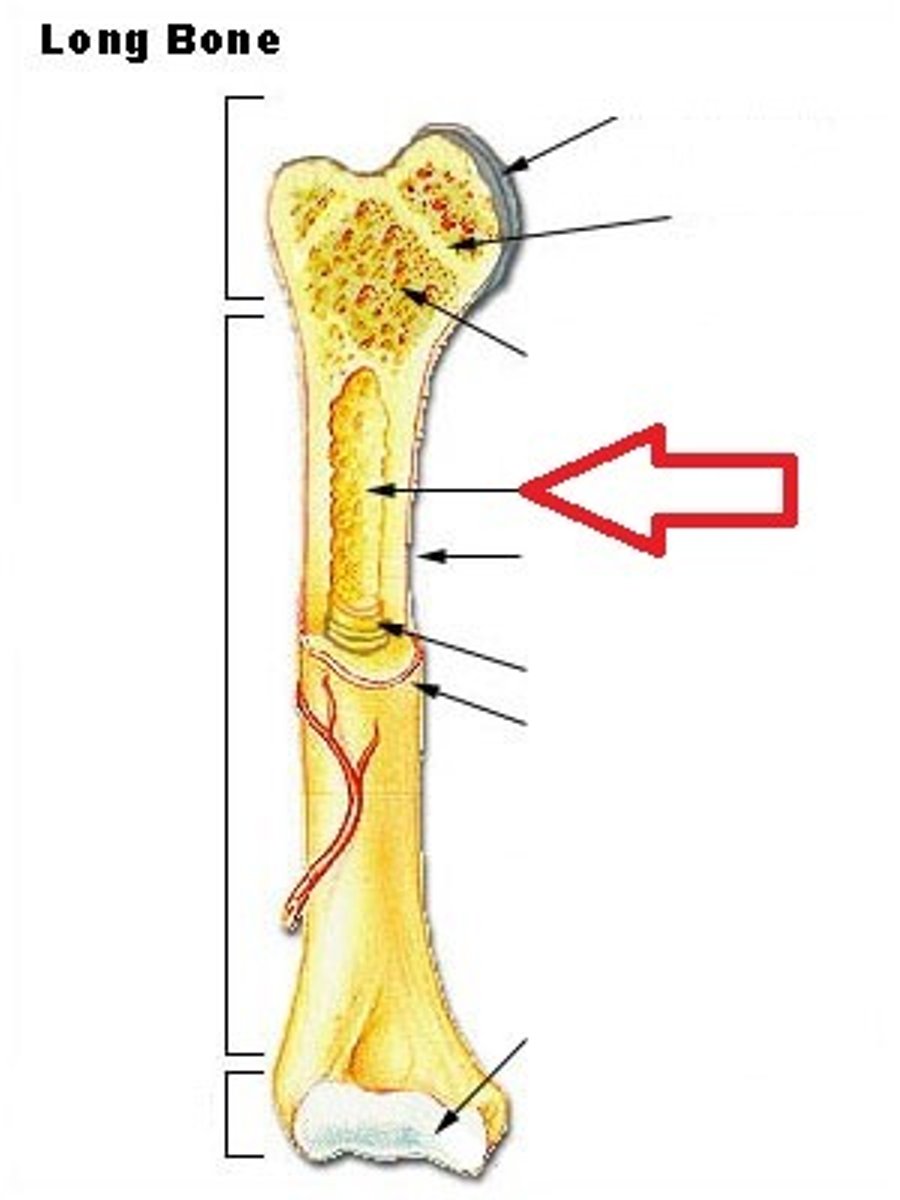
Medullary cavity
cavity within the shaft of the long bones filled with bone marrow
Endosteum
membranous lining of the hollow cavity of the bone
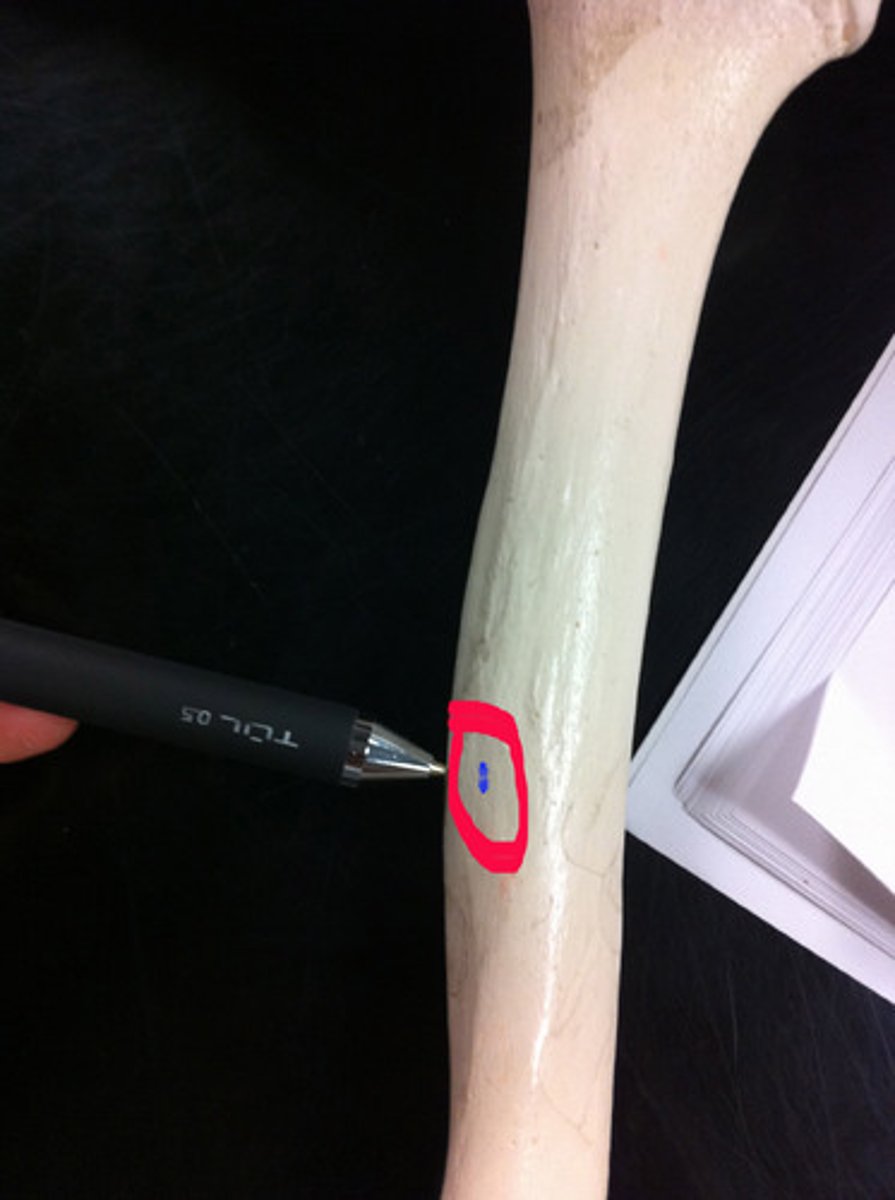
Nutrient foramen
small opening in the middle of the external surface of the diaphysis, through which an artery enters the bone to provide nourishment

Nutrient artery
large artery that enters compact bone near the middle of the diaphysis
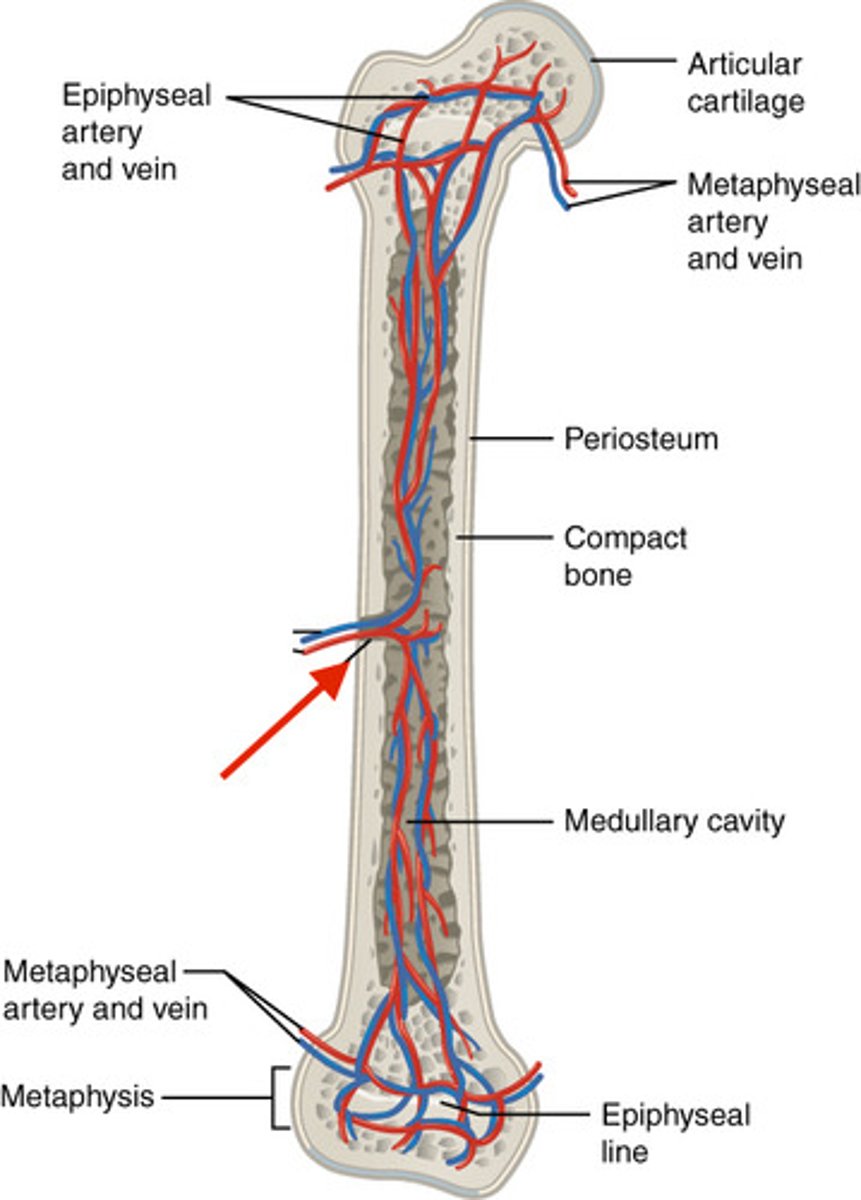
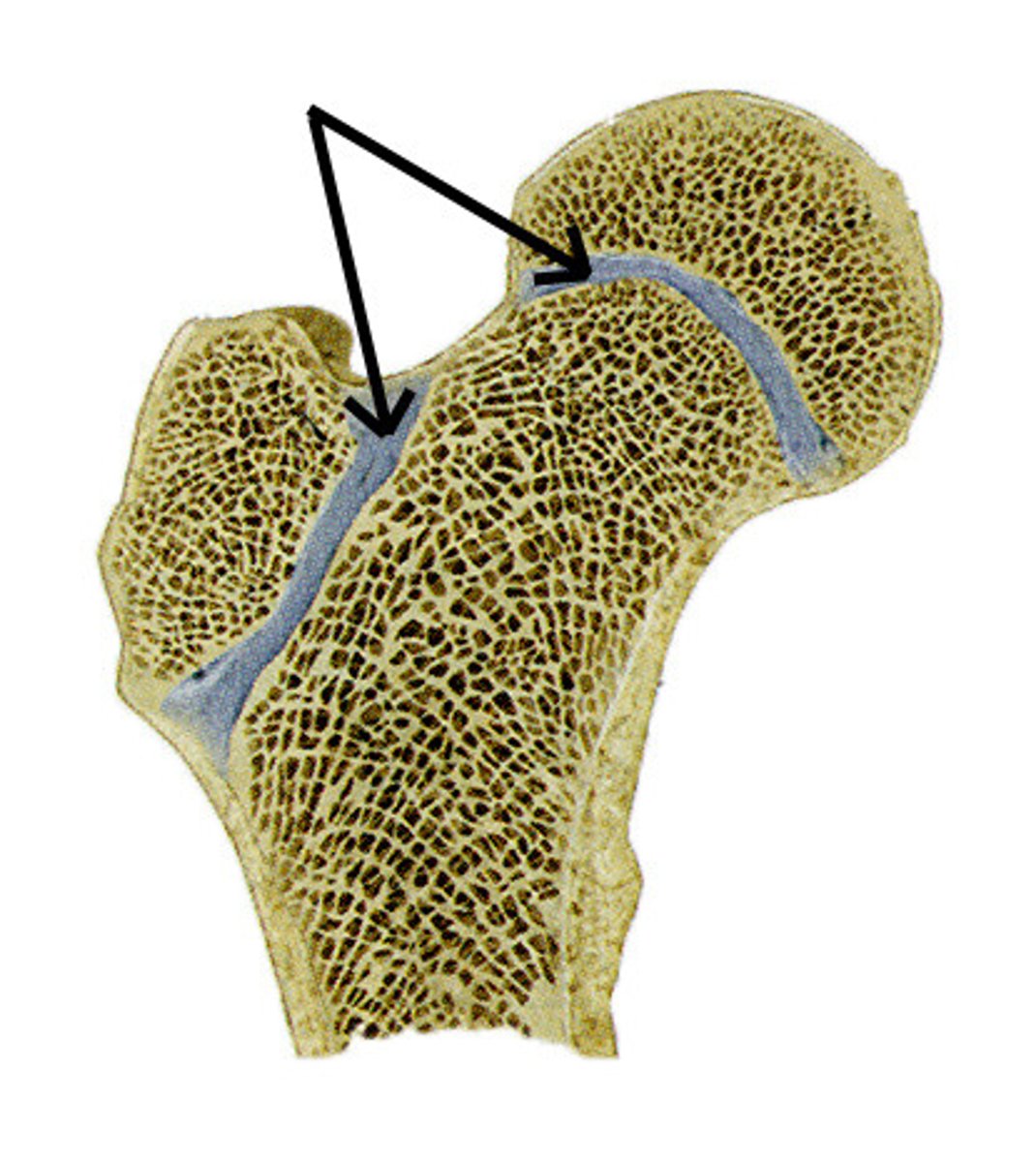
Articular cartilage
covers the surfaces of bones where they come together to form joints
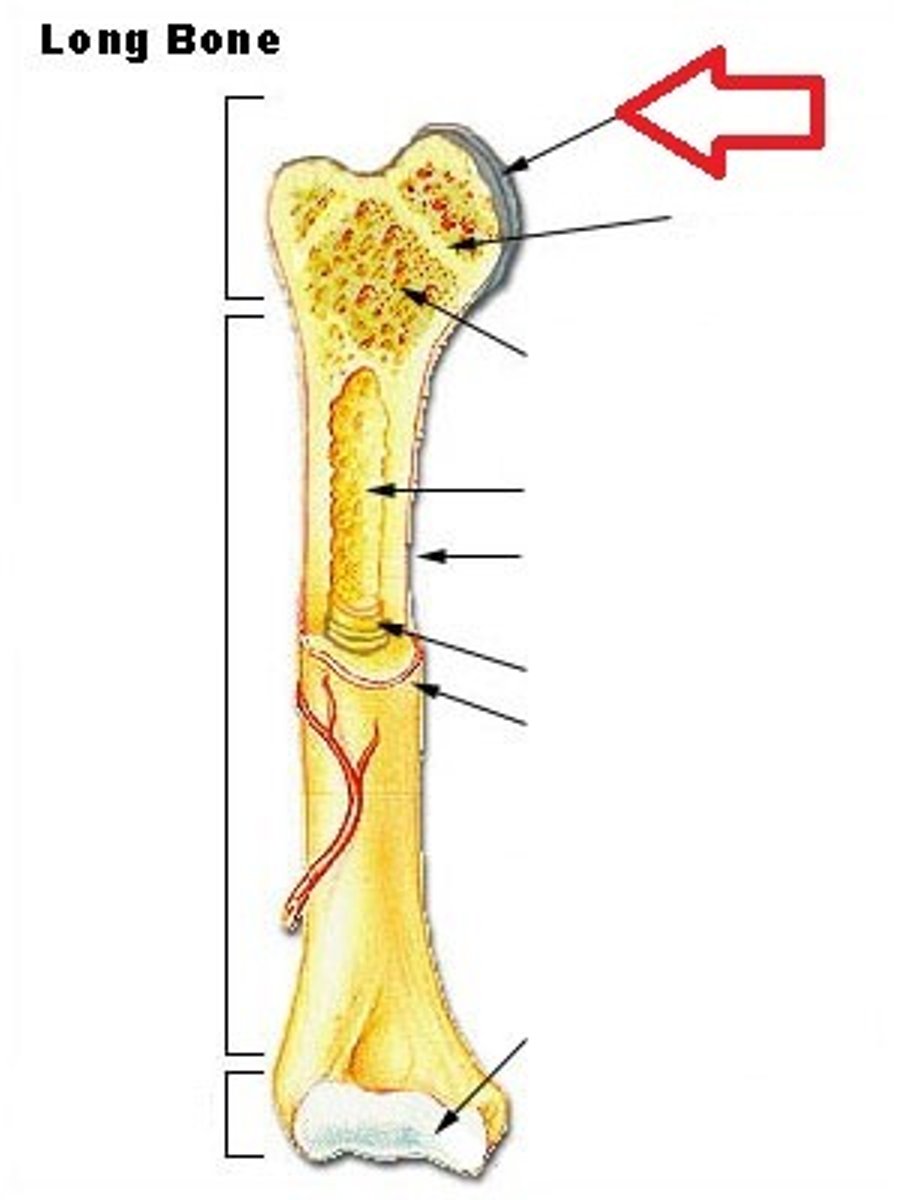
epiphyseal plate
growth plate
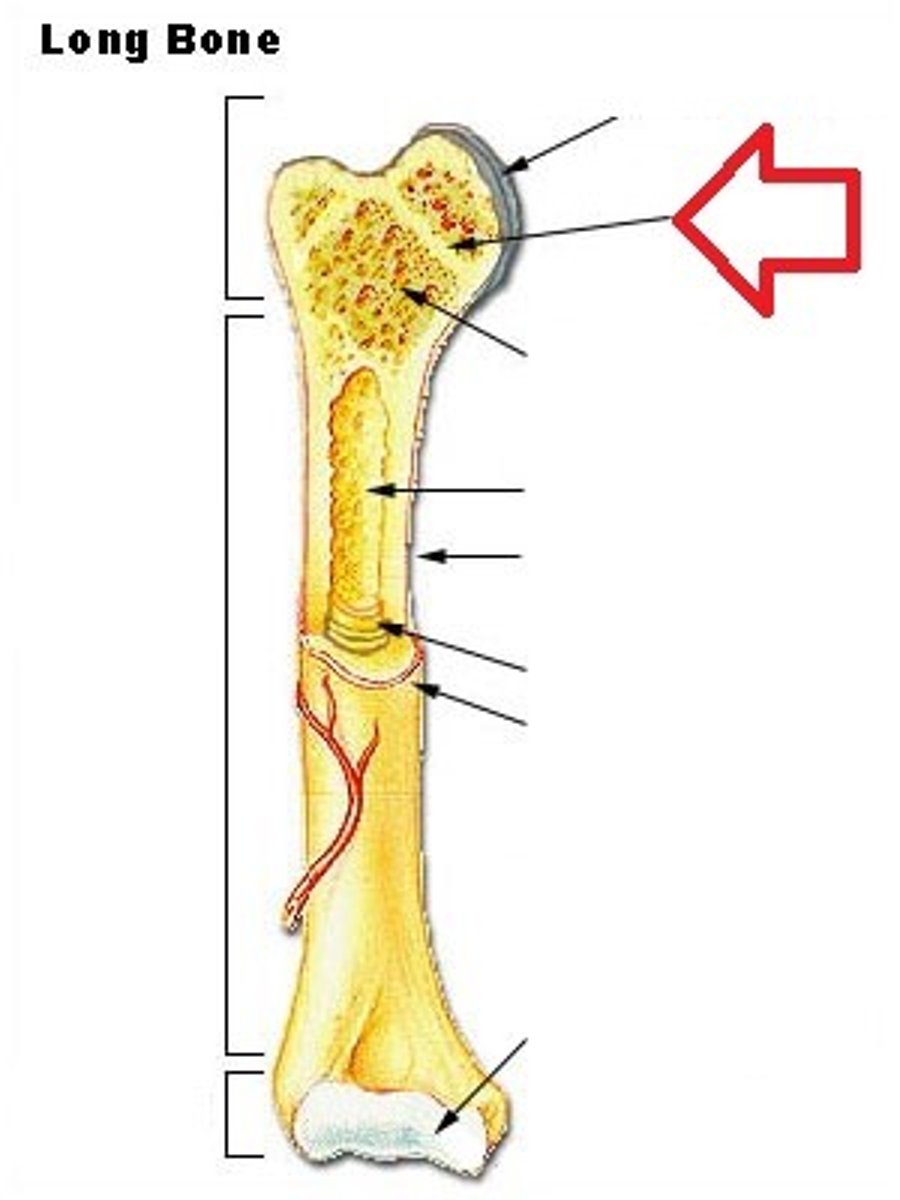
Trabeculae
supporting bundles of bony fibers in cancellous (spongy) bone
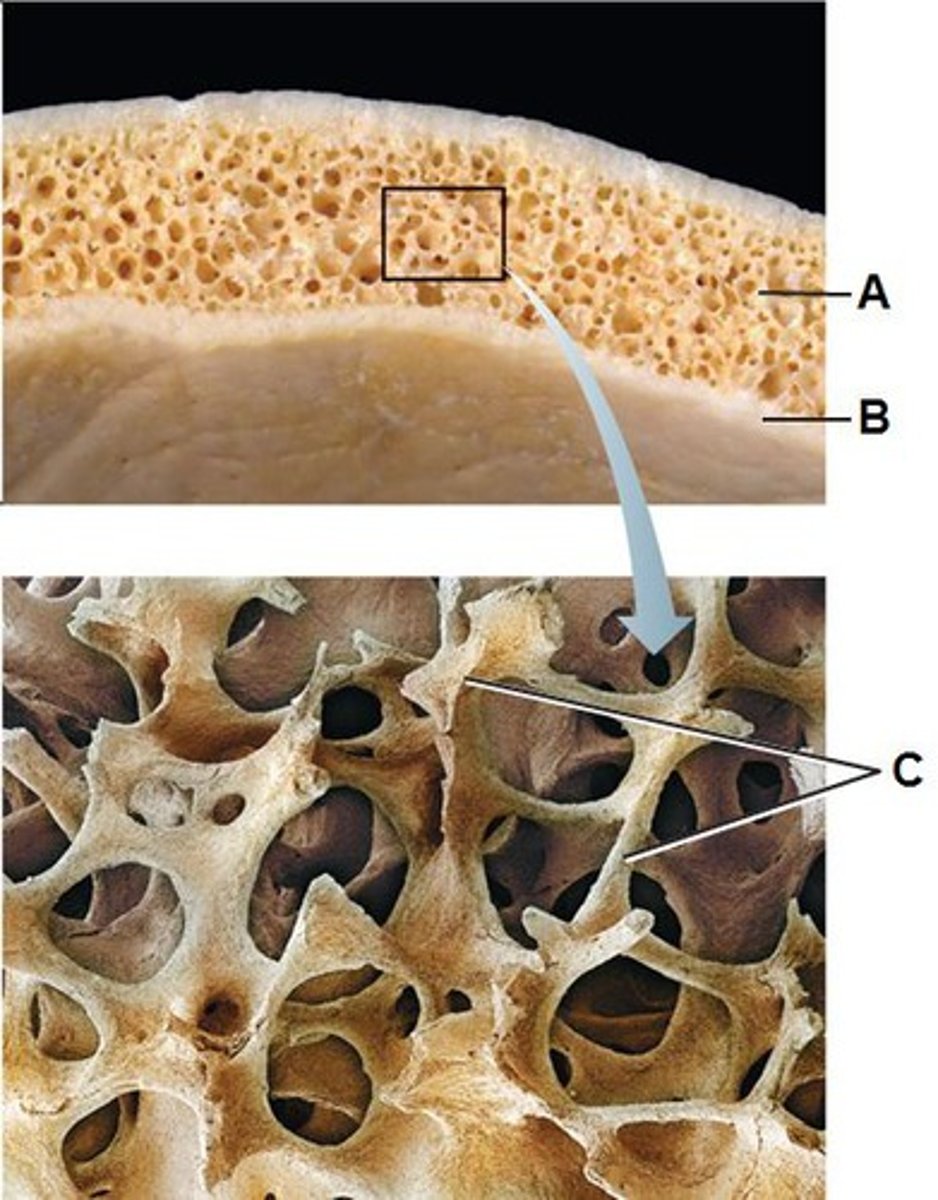
Canaliculi
Hairlike canals that connect lacunae to each other and the central canal
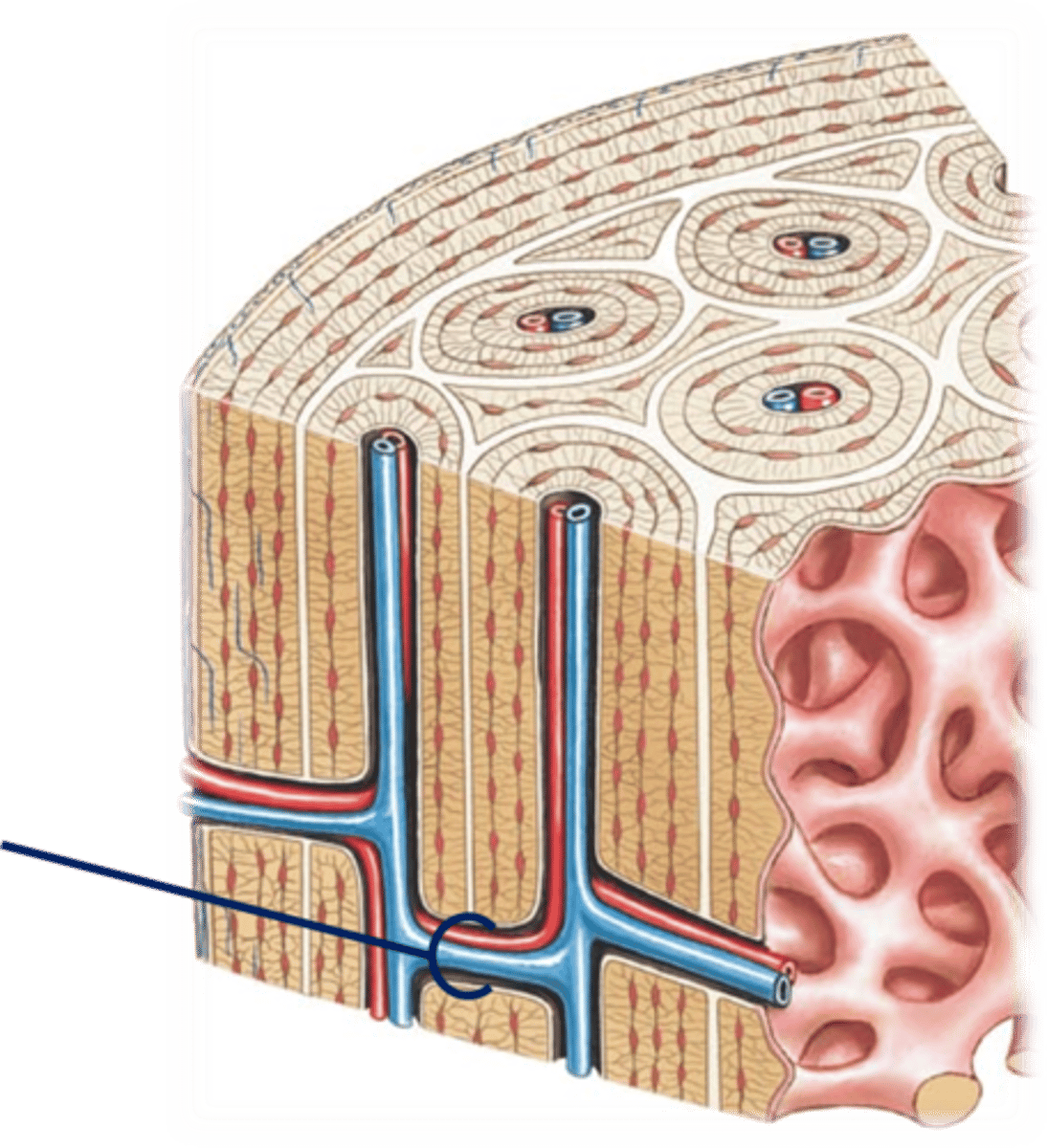
Perforating canals
Perpendicular to the central canal
Carry blood vessels into bone and marrow
Proliferation zone
cartilage cells undergo mitosis
hypertrophic zone
older cartilage cells enlarge
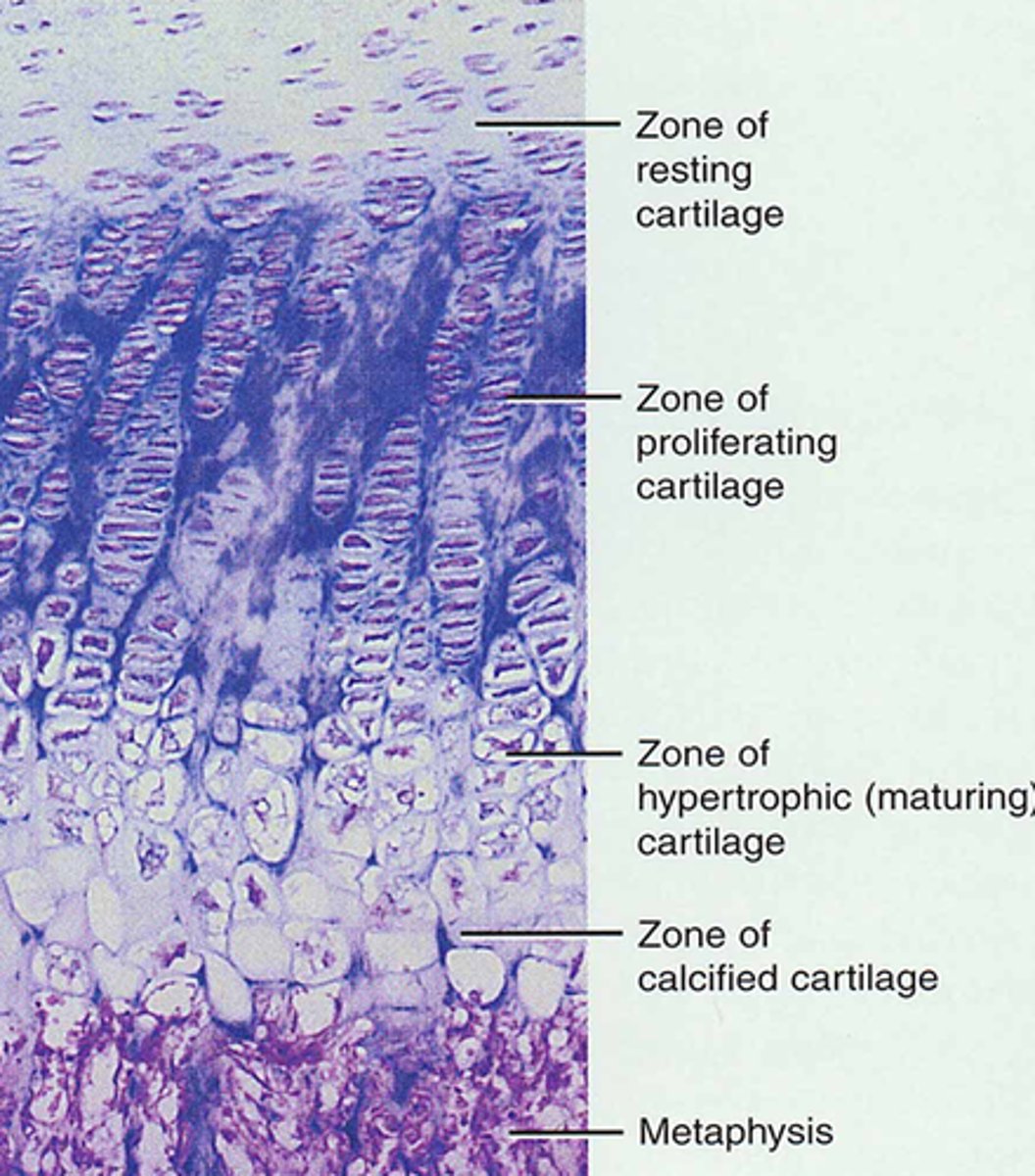
calcification zone
Surrounding cartilage matrix calcifies, chondrocytes die and deteriorate
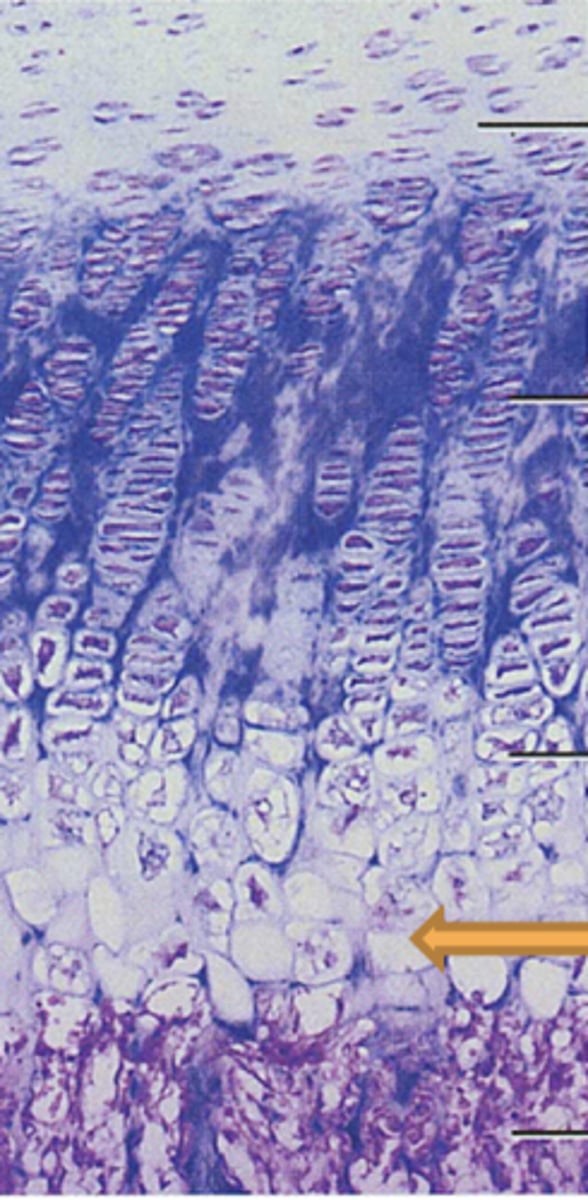
ossification zone
new bone forms