Reconstructing Phylogenies and Gene Evolution
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What is phylogeny?
Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of relationships among organisms or their genes, represented in a diagram called a phylogenetic tree.
What does each split or node in a phylogenetic tree represent?
Each split or node represents the point at which lineages diverged.
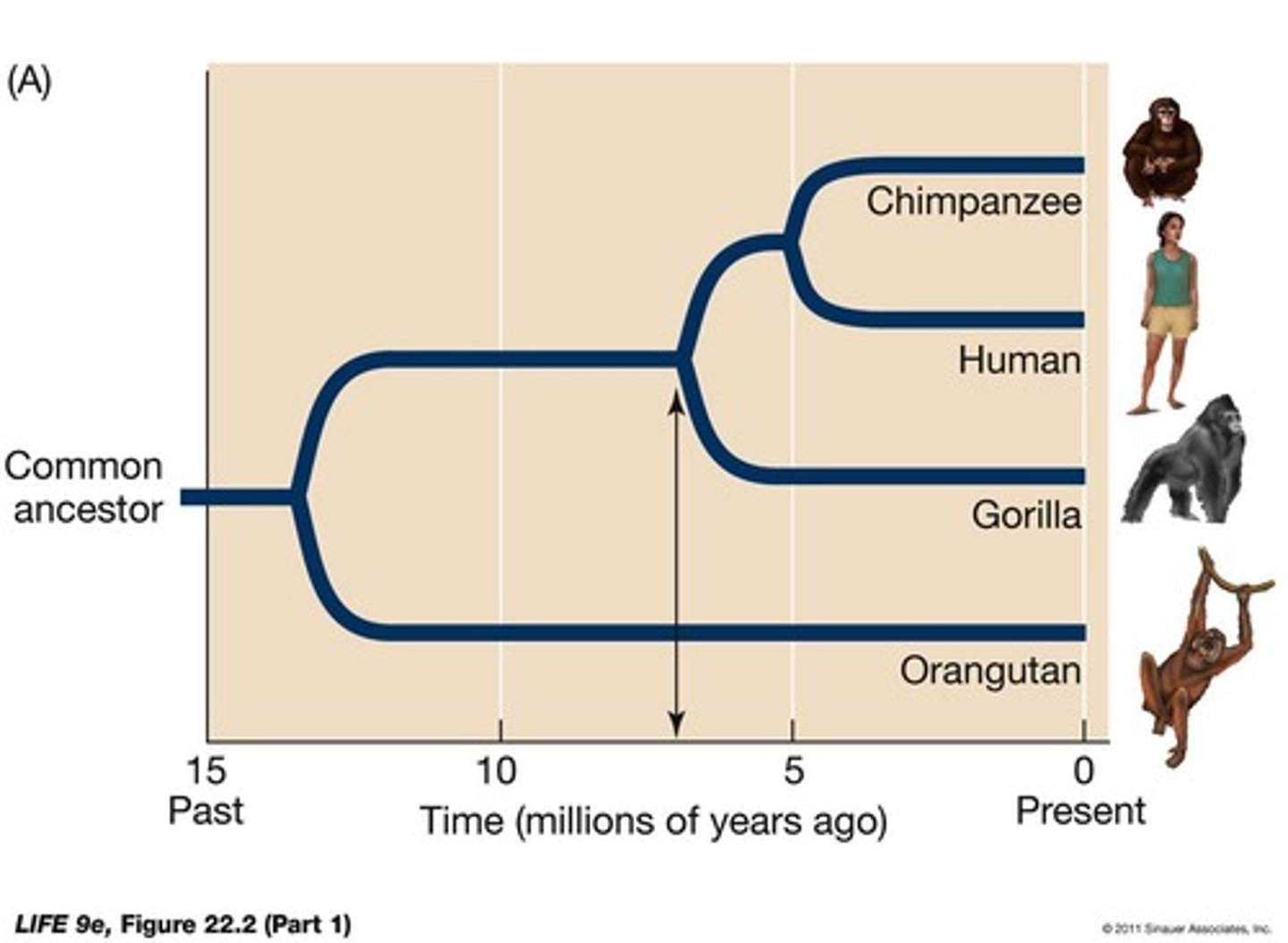
What is the root of a phylogenetic tree?
The root is the common ancestor of all organisms in the tree.
How is the timing of divergences shown on a phylogenetic tree?
The timing of divergences is shown by the position of nodes on a time or divergence axis.
What is a molecular clock?
A molecular clock is a method that uses the rate of evolution of certain genes or proteins to help set the time scale of a phylogenetic tree.
What is the significance of homologous traits in phylogenetics?
Homologous traits are features shared by two or more species that were inherited from a common ancestor.
What is the difference between ancestral and derived traits?
An ancestral trait is present in the ancestor of a group, while a derived trait is found in a descendant that differs from the ancestral trait.
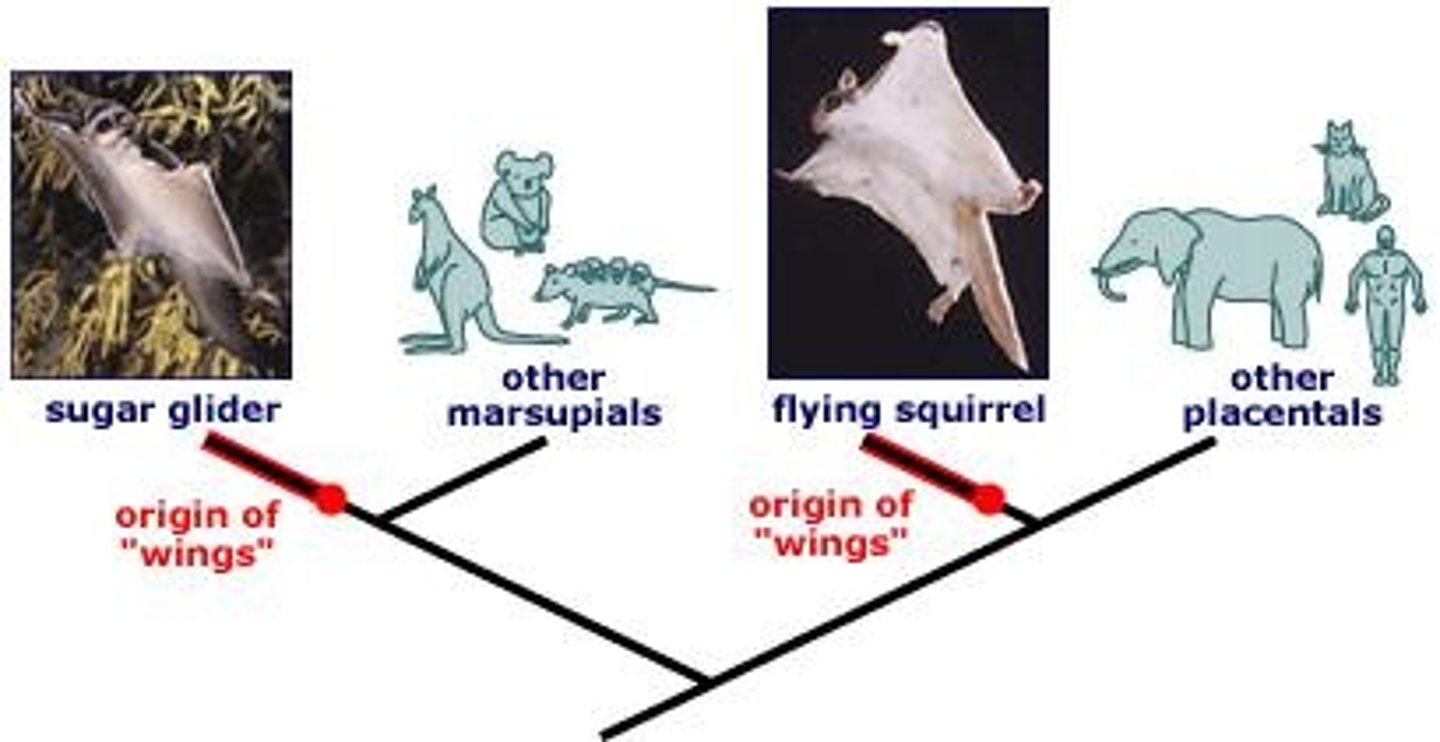
What are analogous traits?
Analogous traits are similar traits that evolve in unrelated groups of organisms, often through convergent evolution.
What is the parsimony principle in phylogenetics?
The parsimony principle states that the simplest explanation of observed data is preferred, minimizing the number of evolutionary changes assumed.
What types of data can be used to construct phylogenetic trees?
Data types include morphological, fossil, developmental, molecular, and behavioral data.
What is morphology in the context of phylogenetic analysis?
Morphology refers to the physical form of organisms, which is one of the easiest pieces of data to use in phylogenetic analysis.
What are the limitations of using morphology in phylogenetic analysis?
Limitations include few morphological differences in some taxa, difficulty comparing distantly related species, and environmental causes of morphological variation.
How do computer programs assist in constructing phylogenetic trees?
Computer programs analyze traits and construct trees based on the data provided.
What is the tree of life?
The tree of life is the complete evolutionary history of life, illustrating how all life is connected through evolutionary history.
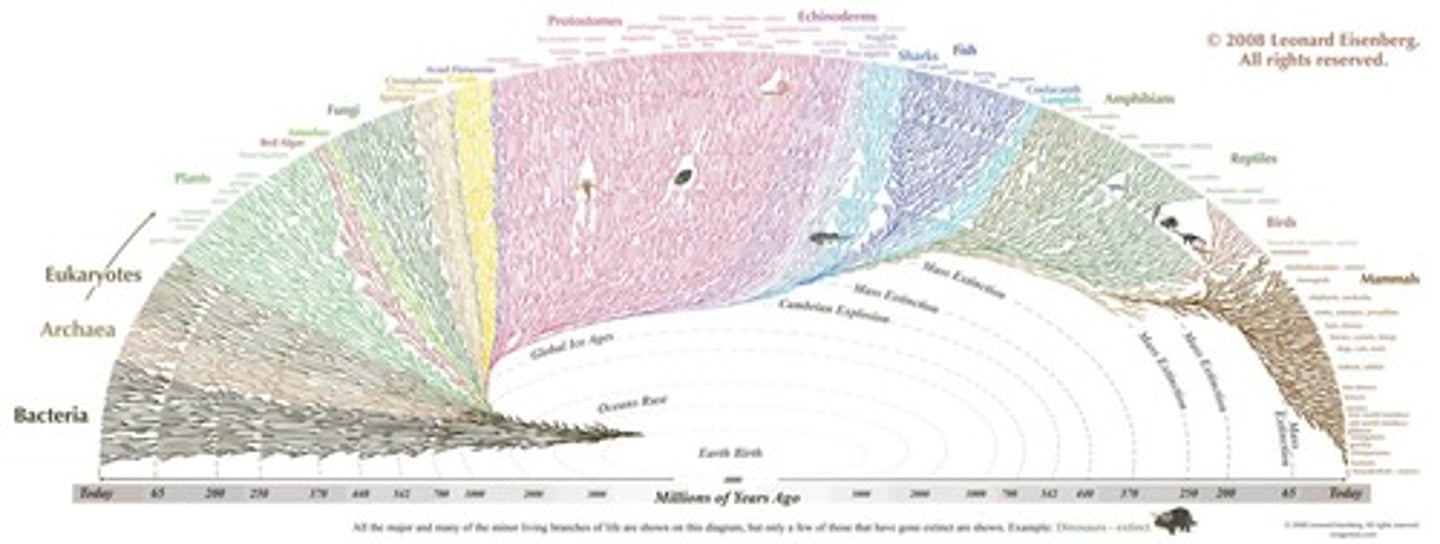
Why is knowledge of evolutionary relationships essential in biology?
It is essential for making comparisons in biology and understanding the connections between different organisms.
What is convergent evolution?
Convergent evolution is the process where independently evolved traits in unrelated organisms become superficially similar due to similar selection pressures.
What role do fossils play in determining phylogeny?
Fossils provide historical data that can help establish the timing and relationships of evolutionary divergences.
What is the importance of using multiple data types in phylogenetic analysis?
Using multiple data types increases the accuracy of the constructed phylogenetic tree.
How can developmental similarities reveal evolutionary relationships?
Similarities in developmental patterns may indicate evolutionary relationships between different organisms.
What is one example of analogous traits?
Flying squirrels and sugar gliders are examples of organisms with analogous traits.
How can traits that differ within a group of interest be used in phylogenetic analysis?
Biologists determine these traits to ascertain when they evolved and to understand the relationships between species.
What is the significance of the vertical order of taxa in a phylogenetic tree?
The vertical order of taxa is largely arbitrary, as lineages can be rotated around nodes without changing the relationships.
What is the role of fossils in paleontology?
Fossils provide information about the morphology of past organisms, their locations, and the times they lived. They help determine derived and ancestral traits and when lineages diverged.
What are the limitations of the fossil record?
The fossil record is fragmentary and missing for some groups.
How can behavior influence phylogenetic trees?
Behavior can be inherited or culturally transmitted; for example, bird songs are often learned and may not be useful for phylogenies, while frog calls are genetically determined and can be used.
What types of data are used to construct phylogenetic trees?
DNA sequences, including mitochondrial, chloroplast, and nuclear DNA, as well as gene product information like amino acid sequences.
What predictions can phylogenetic trees help make?
They can predict characteristics of fossils, the evolution of complex features, poorly-studied species, the order of evolution, and the evolution of diversity.
How did biologists use phylogenetic trees in drug discovery?
They used phylogeny to predict that close relatives of the Pacific Yew might produce similar compounds, leading to the discovery of a related compound in the European Yew for efficient Taxol production.
Who started the biological classification system?
The biological classification system was started by Swedish biologist Carolus Linnaeus in the 1700s.
What is binomial nomenclature?
Binomial nomenclature gives every species a unique, unambiguous name consisting of a genus name and a species name.
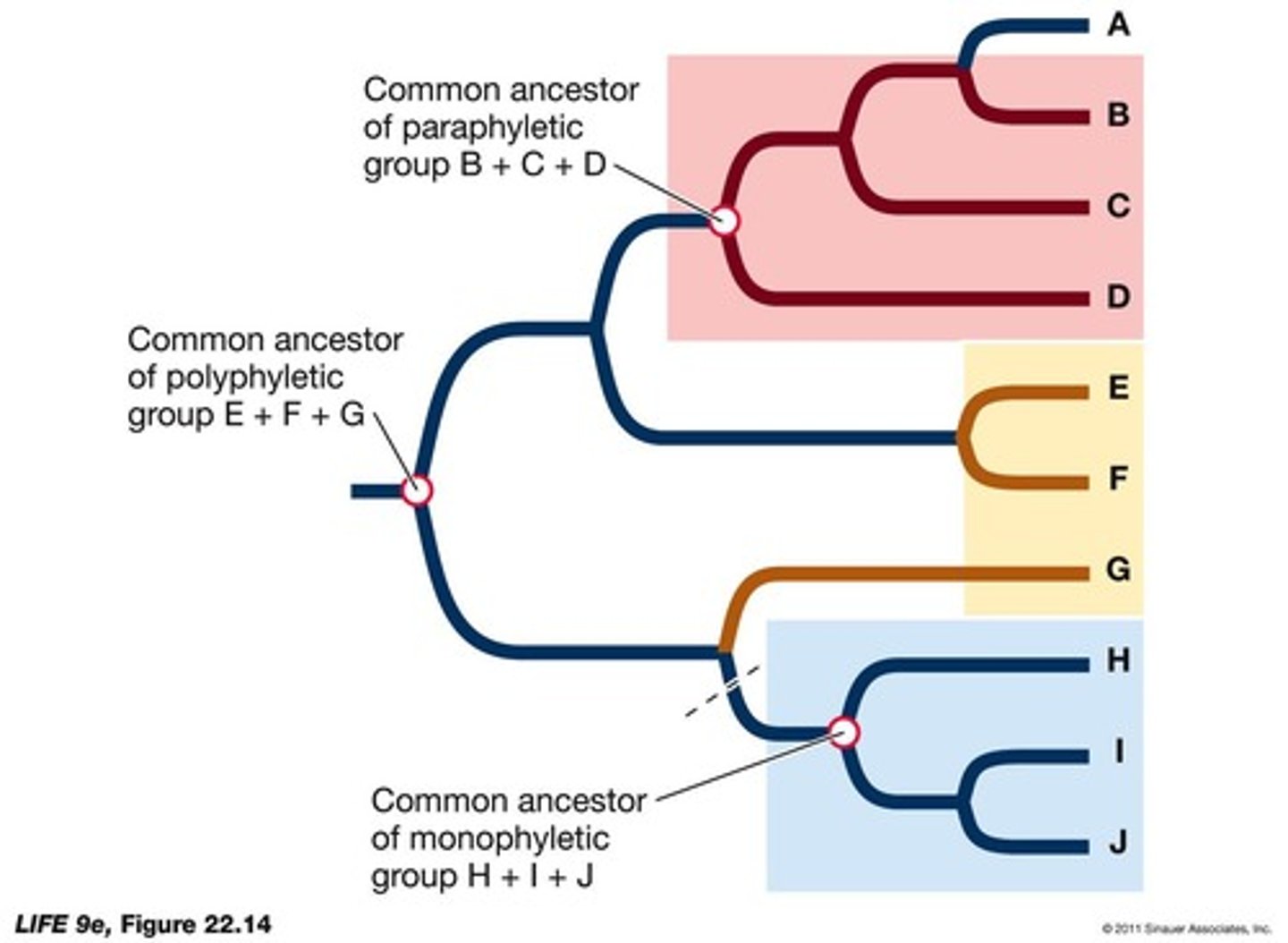
What is a clade in phylogenetics?
A clade represents all the descendants of a common ancestor and is expected to be monophyletic.
What is a taxon?
A taxon (plural, taxa) is any group of organisms treated as a unit, such as a genus or vertebrates.
What are the three types of taxonomic groups based on monophyly?
Monophyletic (includes ancestor and all descendants), paraphyletic (does not include all descendants), and polyphyletic (does not include the common ancestor).
What is the hierarchical classification of Panthera pardus?
Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Animalia, Phylum: Chordata, Class: Mammalia, Order: Carnivora, Family: Felidae, Genus: Panthera, Species: pardus.
What governs the use of scientific names?
Explicit rules ensure there is only one correct scientific name for any taxon, with different rules for zoology, botany, and microbiology.
What is the significance of monophyly in classification?
A taxon is expected to be monophyletic, meaning it contains an ancestor and all its descendants, ensuring accurate representation of evolutionary relationships.
What is the importance of phylogenetic trees in understanding evolution?
Phylogenetic trees help learn about the evolution of complex features and the order of evolution among species.
How can phylogenetic trees aid in studying poorly-studied species?
They allow biologists to generate expectations about the characteristics of organisms that have not yet been studied.
What compound does the Pacific Yew tree produce, and what is its significance?
The Pacific Yew tree produces Taxol, a compound helpful in treating certain kinds of cancer.
Why was it difficult to obtain Taxol from the Pacific Yew tree?
It was difficult and expensive to extract enough of the compound from the tree.
What is the relationship between phylogeny and the evolution of diversity?
Phylogenetic trees can provide insights into how diversity has evolved over time.
What is the role of molecular data in constructing phylogenetic trees?
Molecular data, particularly DNA sequences, have become the most widely used data for constructing phylogenetic trees.
What is the significance of taxonomic rules in biological classification?
Taxonomic rules ensure consistency and clarity in naming species, facilitating communication and understanding in the scientific community.
What is the difference between a paraphyletic and a polyphyletic group?
A paraphyletic group does not include all descendants of a common ancestor, while a polyphyletic group does not include the common ancestor itself.
What is the genome?
The full set of genes plus noncoding regions of DNA (or RNA for some viruses).
How do mutations contribute to evolution?
Mutations, resulting from mistakes in DNA replication, provide the genetic variation necessary for evolutionary change.
What is molecular evolution?
The field that uses molecular variation to reconstruct evolutionary history.
How do genes evolve?
Genes can evolve through nucleotide substitutions, which may result in amino acid replacements and change protein function.
What does comparing nucleotide or amino acid sequences reveal?
The longer two sequences have been evolving separately, the more differences they accumulate.
Why do evolutionary biologists use unicellular organisms or viruses for experimentation?
Because they have short generation times, making it easier to study evolution.
What is sequence alignment in amino acid sequences?
A technique to determine deletions and insertions since two species diverged by adding gaps and aligning sequences.
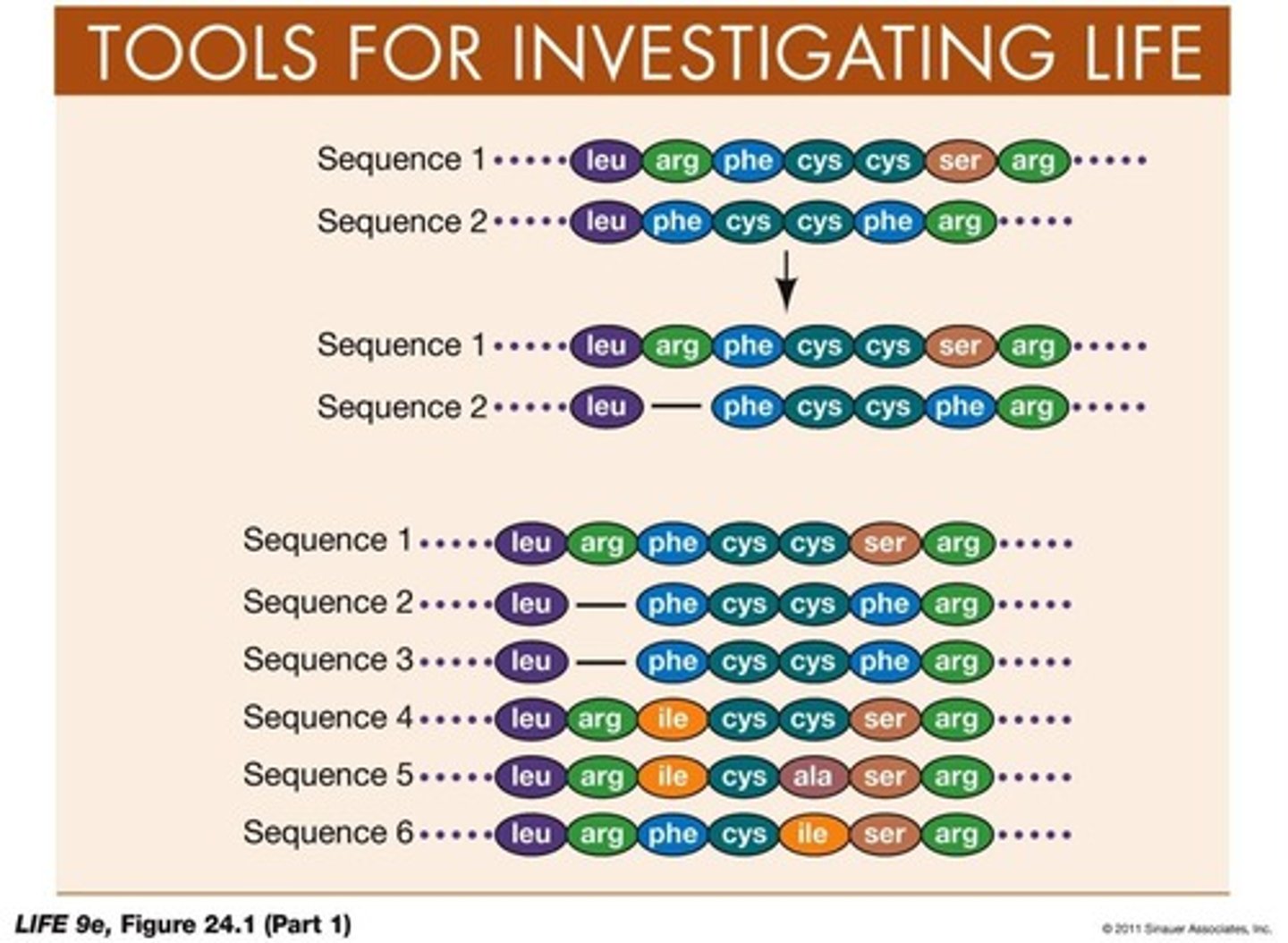
What is a synonymous substitution?
A nucleotide substitution that does not change the specified amino acid.
What is a nonsynonymous substitution?
A substitution that causes a change in the specified amino acid, often harmful but occasionally beneficial.
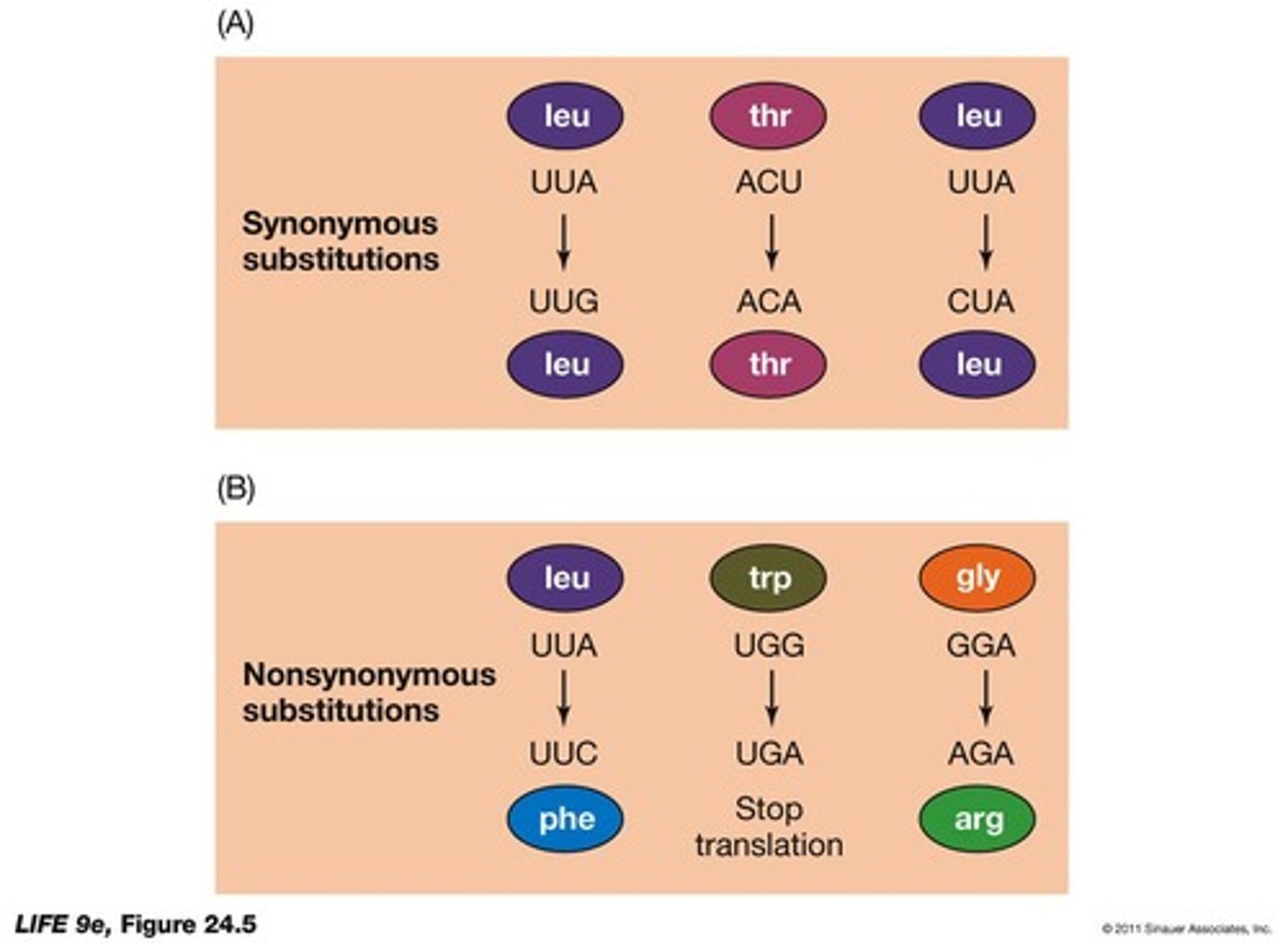
What does the rate of synonymous/nonsynonymous substitutions indicate?
It indicates how fast a gene is evolving.
How does genome size vary among organisms?
Genome size varies greatly, and there is some correlation between genome size and organism complexity, but a larger genome does not always mean greater complexity.
What is noncoding DNA?
DNA that does not appear to have a function, although some can alter the expression of surrounding genes.
What are parasitic transposable elements?
Mobile genetic elements that can be part of noncoding DNA.
What mechanisms can increase genome size over evolutionary time?
Lateral gene transfer and gene duplication within species.
What is lateral gene transfer?
The horizontal movement of individual genes, organelles, or fragments of genomes from one lineage to another.
How can species acquire DNA fragments from the environment?
Some species can pick up DNA fragments directly from their surroundings.
How can viral genomes contribute to gene transfer?
Genes may be transferred to a new host within a viral genome.
What is hybridization between species?
A process that results in the transfer of many genes between species.
Why is lateral gene transfer advantageous?
It can provide novel genes, such as those conferring antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
What is the significance of genome changes over time?
Genomes are dynamic and evolve, reflecting the evolutionary processes at play.
What are the practical applications of molecular evolution?
Molecular evolution has many applications, including understanding evolutionary relationships and mechanisms.
What is the relationship between genome size and noncoding DNA?
Much of the variation in genome size lies in the amount of noncoding DNA.
What are the four potential fates of gene duplicates?
1. Retain original function (more product could be made). 2. Retain original function but expression diverges in different tissues or at different times. 3. One copy becomes a nonfunctional pseudogene. 4. One copy accumulates substitutions that allow it to perform a new function.
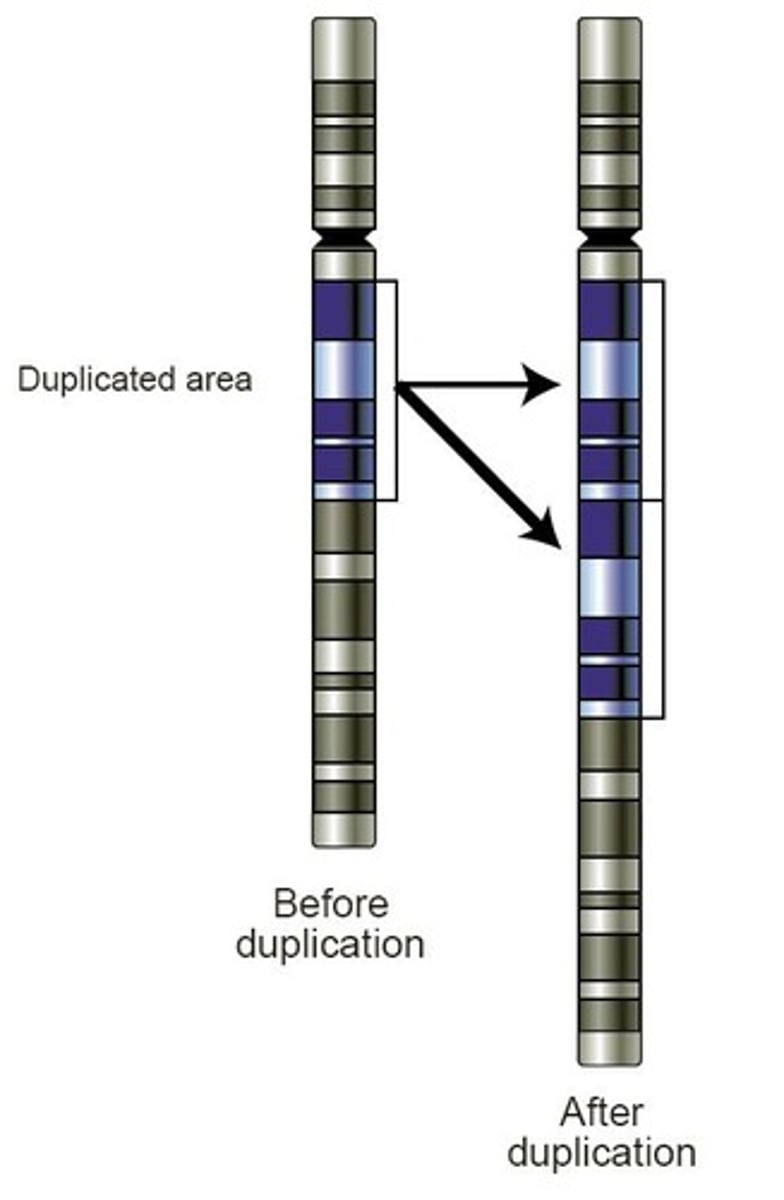
How can gene duplication occur?
Gene duplication can occur through mechanisms such as unequal crossing over during meiosis, where repeated segments can misalign, resulting in one chromosome having more copies and the other having fewer.
What is a gene family and how is it formed?
A gene family is formed through successive rounds of duplication and mutation, resulting in related genes, such as the globin gene family (α-globins, β-globins, myoglobin).
What role do mutations play in genome evolution?
Mutations result in altered gene sequences, contributing to the evolution of physical changes in organisms.
What is lateral gene transfer and its significance?
Lateral gene transfer is a process that contributes to growing genomes and the emergence of new versions of genes, impacting evolution.
How does altering gene expression affect evolution?
Changes in gene expression can dramatically affect morphology and evolution, influencing the development of body forms.
What are Hox genes and their role in development?
Hox genes encode transcription factors that determine cell fate in different segments of an embryo, influencing body structure.
What is the significance of homeotic mutations in understanding Hox genes?
Homeotic mutations, like the Antennapedia mutation, provide clues to Hox gene function by demonstrating how changes in gene expression can alter body structures.
What is heterometry in gene expression?
Heterometry refers to differences in the amount of gene expression, such as how beak size and shape in Galápagos finches are regulated by two regulatory genes.
What is heterochrony in gene expression?
Heterochrony involves changes in the timing of gene expression, exemplified by the differences in neck bone length between giraffes and humans.
What is heterotopy in gene expression?
Heterotopy refers to spatial differences in gene expression, such as the presence of webbing between toes in ducks but not in chickens.
What is a gene tree?
A gene tree illustrates the evolutionary relationships of a single gene across different species or gene families.
How can knowledge of gene evolution aid biologists?
Understanding gene evolution helps biologists comprehend how genes and proteins function.
What is a practical application of studying molecular evolution in viruses?
Studying how viral genes evolve can help predict future changes, aiding in the development of better vaccines.
What is the Engrailed gene and its significance?
The Engrailed gene produces a protein important for development in multicellular organisms and can be represented in a gene tree to show its evolutionary history.
What is the relationship between gene duplication and evolutionary change?
Gene duplication can lead to new functions and increased genetic diversity, driving evolutionary change.
What is the impact of gene expression changes on morphology?
Changes in gene expression can lead to significant morphological variations, influencing evolutionary outcomes.
How does gene expression in Drosophila provide insights into evolution?
The study of gene expression in Drosophila, particularly Hox genes, reveals how genetic changes can lead to diverse body forms.
What are the implications of mutations in Hox genes across animal groups?
Mutations in Hox genes are linked to major structural changes in body plans across different animal groups.
What is the significance of studying molecular evolution in understanding diseases?
By understanding molecular evolution, researchers can gain insights into disease mechanisms and develop targeted therapies.
How do changes in gene expression contribute to evolutionary adaptations?
Changes in gene expression can lead to adaptations that enhance survival and reproduction in changing environments.