CHEM 107 - EXAM 2
1/111
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Number of Electron Groups: 2
Lone Pairs: 0
Ideal Bond Angle: ?
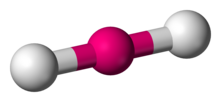
Linear, 180
Number of Electron Groups: 3
Lone Pairs: 0
Ideal Bond Angle: ?
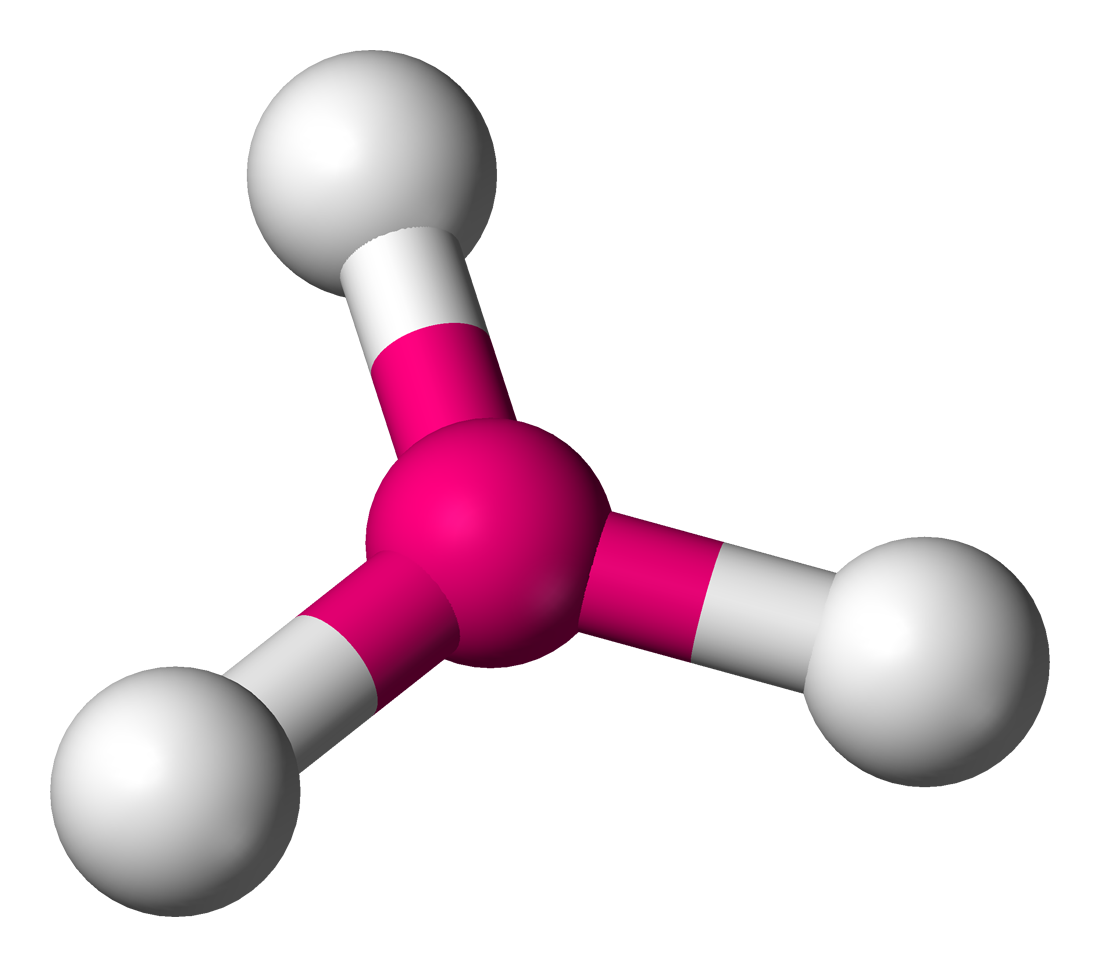
Trigonal Planar, 120
Number of Electron Groups: 3
Lone Pairs: 1
Ideal Bond Angle: ?
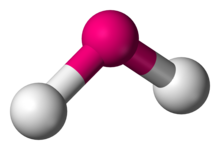
Bent, 120
Number of Electrons Groups: 4
Lone Pairs: 0
Ideal Bond Angle: ?
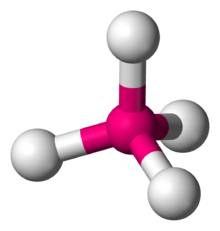
Tetrahedral, 109.5
Number of Electrons Groups: 4
Lone Pairs: 1
Ideal Bond Angle: ?
Trigonal Pyramidal, 109.5
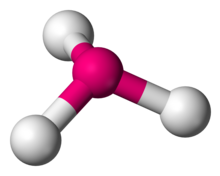
Number of Electrons Groups: 4
Lone Pairs: 2
Ideal Bond Angle: ?
Bent, 109.5
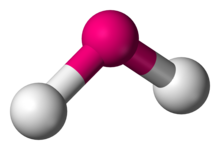
Number of Electron Groups: 5
Lone Pairs: 0
Ideal Bond Angle: ?
Trigonal Bipyramidal, 90 and 120
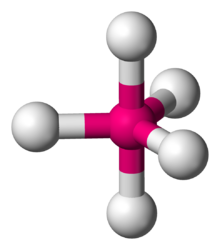
Number of Electron Groups: 5
Lone Pairs: 1
Ideal Bond Angle: ?
See-saw, 90 and 120
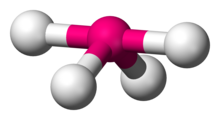
Number of Electron Groups: 5
Lone Pairs: 2
Ideal Bond Angle: ?
T-shaped, 90
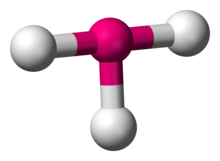
Number of Electron Groups: 5
Lone Pairs: 3
Ideal Bond Angle: ?
Linear, 180
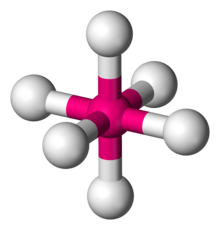
Number of Electron Groups: 6
Lone Pairs: 0
Ideal Bond Angle: ?
Octahedral, 90
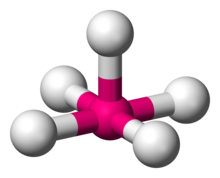
Number of Electron Groups: 6
Lone Pairs: 1
Ideal Bond Angle: ?
Square Pyramidal, 90
Number of Electron Groups: 6
Lone Pairs: 2
Ideal Bond Angle: ?
Square Planar, 90
What measurement for gasses is used?
Volume
What is the resultant from molecular collisions between gas molecules and container walls?
Pressure
What is the weight of air per unit of area?
Atmospheric pressure
What measures the atmospheric pressure?
Barometer
One atm
760 mmHg
1 mmHg
1 torr
Which law states that both pressure and volume are inversely proportional?
Boyle’s Law
Which law states that both pressure and temperature are directly proportional?
Gay Lussac’s Law
Which law states that both volume and temperature are directly proportional?
Charles’ Law
P1V1 / T1 = P2V2 / T2
Combined Gas Law
Which law states that volume and moles are directly proportional?
Avogadro’s Law
PV = nRT
Ideal Gas Law
What is the constant-R equal to?
0.0821 L atm mol-1 K-1
At STP, what does one mole of gas contain?
22.4 L
An atom with its electrons in their lowest energy locations are in what?
Ground State
When an atom is promoted to a higher energy, an atom is in a what?
Excited State
What is the arrangement of electrons in the space around the nucleus of the atom?
Electron Configuration
What are three levels for electron configuration?
Shells, subshells, orbitals
Each orbital has two electrons which in a property known as what?
Spin
Two electrons occupying the same orbital must have opposite spins is defined in what?
Pauli’s Exclusion Principle
What is the range of visible light?
400-800 nm
What is the outermost electron shell of an atom?
Valence Shell
Which electrons are the most loosely bound and responsible for chemical reactivity of elements?
Valence Electrons
List all exceptions and their noble gas electron configuration
Chromium [Ar] 4s1 3d5
Copper [Ar] 4s1 3d10
Molybdenum [Kr] 5s1 4d5
Silver [Kr] 5s1 4d10
Which periodic property increases from up to down in a group and decreases left to right in a period?
Atomic Size
What is the energy required to remove an outermost electron from a gaseous atom, forming a cation?
Ionization Energy
If an electron is more strongly held to an atom, what happens to Ionization Energy (Increases/Decreases)?
Increases
If atomic size increases, what happens to Ionization Energy (Increases/Decreases)?
Decreases
What is the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom?
Electron Affinity
If electron affinity is greater (more negative), what happens to the stability of the anion (Increases stability/Decreases stability)?
Increases stability
Why does H and He not follow the Octet Rule?
Stable at two valence electrons
Which element is an exception to the Octet Rules and has less than 8 valence electrons?
Boron
Which elements are an exception to the Octet Rule and have more than 8 valence electrons?
Phosphorus, Sulfur
Which elements are an exception to the Octet Rule and located in the d-block?
Transition Elements
Which bond is the electrostatic attraction of ions?
Ionic Bond
Which bond shares electrons?
Covalent Bond
What are metal atoms bonded to several other atoms?
Metallic Bond
What is the formation of ionic bonds, in terms of energy?
Exothermic
What is the equal or near-equal sharing of electrons within a bond?
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
What is the unequal sharing of electrons within a bond?
Polar Covalent Bond
Which periodic trend increases from left to right and decreases top to bottom?
Electronegativity
What happens to a bond if electronegativity increases?
Polarity Increases
Electronegativity difference of 0 - 0.4 is classified as…?
Nonpolar Covalent
Electronegativity difference of 0.4 - 2 is classified as…?
Polar Covalent
Electronegativity difference of 2 and higher is classified as…?
Ionic
“Like dissolves like” means what?
Polar dissolves Polar, Nonpolar dissolves nonpolar
Which melting and boiling points are higher, Polar or Nonpolar?
Polar
What is the resultant of compound with a nonmetal and metal?
Ionic
What is the resultant of compound with nonmetals only?
Covalent
The strength of the covalent bond is equivalent to what?
Pairs
What does VSEPR (Valence-shell electron-pair repulsion) do?
Predicts the shapes of molecules and polyatomic ions
What happens to electrons in the electron-sea model?
Delocalized throughout the whole crystal structure
Metallic bond strength increase with what properties?
Decreasing atomic size and Increasing number of valence electrons
How are carbon atoms in diamond joined?
Covalent bonds in a tetrahedral geormetry
How are carbon atoms in graphite bonded?
Sheets
What is the electron-sea model?
A “sea” of positive ions and electrons encompassing ions
How does the electron-sea model contribute towards metals?
Makes electricity possible
When a force is applied to a model, what happens to the electrons?
The flow of electrons maintains the bonding
The band populated by valence electrons is the what?
Valence band
The empty band above the valence band is the what?
Conduction band
The energy difference between the bands is the what?
Band Gap
How does current work?
Electrons move from the valence band to the conductor band
What is doping?
Adding trace amounts of an element to a substance to modify its properties
What can doping modify?
Semiconductors
How is N-type prepared?
Doping with a valence electron rich element
What is the resultant of N-type doping?
Increases electrical properties
What is the resultant of P-type doping?
Decreases electrical properties
How is P-type prepared?
Doping with a valence electron deficient element
What are P-type and N-type required for?
Transistors
What are Intramolecular Forces?
The bonds within molecules
What are Intermolecular Forces?
The bonds between molecules
What is strongest Intermolecular Force?
Hydrogen Bonding
Which elements can cause Hydrogen Bonding to occur?
Fluorine (F), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N)
Why does the density of water decreases when it is a solid?
Molecules expand outward due to Hydrogen Bonding
What requires energy to break for water molecules, in order to achieve a state of matter?
Intermolecular Forces
What molecules have dipole-dipole attractions?
Polar molecules
What does London Dispersion Forces depend on?
Molecular size
If the LDFs increases, then the molecular size (increases/decrease)
Increases
Energy is the ability to do what?
Work and transfer heat
Energy used to cause an object that has a mass to move is called what?
Work
Energy used to cause the temperature of an object to rise is called what?
Heat
What is the SI unit of energy?
Joules
What is the non-SI unit of energy that is commonly used?
Calorie
What is defined as the energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by one Celsius?
1 Calorie
1 cal is equivalent to what?
4.184 Joules
1000 cal is equivalent to what?
1 food Cal
Thermochemistry is the study of what?
Energy transformations involved within a chemical reaction