Honors Biology Final Study Guide - Unit 6
Biogeography
the study of where organisms live now and where they and their ancestors lived in the past
Patterns in biogeography
1. A pattern in which closely related species differentiate in slightly different climates. 2. A pattern in which very distantly related species develop similarities in similar environments.
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Biogeography
the study of where organisms live now and where they and their ancestors lived in the past
Patterns in biogeography
1. A pattern in which closely related species differentiate in slightly different climates. 2. A pattern in which very distantly related species develop similarities in similar environments.
Darwin's theory and biogeography
To Darwin, the biogeography of Galápagos species suggested that populations on the island had evolved from mainland species.
Age of Earth
Earth is about 4.5 billion years old - plenty of time for evolution by natural selection to take place.
Radioactive dating
Geologists use radioactivity to establish the age of certain rocks and fossils.
Evidence from fossils
Recently, researchers have found more than 20 related fossils that document the evolution of modern whales from ancestors that walked on land.
Imperfection of the geological record
Darwin struggled with what he called the 'imperfection of the geological record.'
Basilosaurus
A fossil with a streamlined body and reduced hind limbs, suggesting it spent its entire life swimming in the ocean.
Homologous structures
Structures that are shared by related species and that have been inherited from a common ancestor.
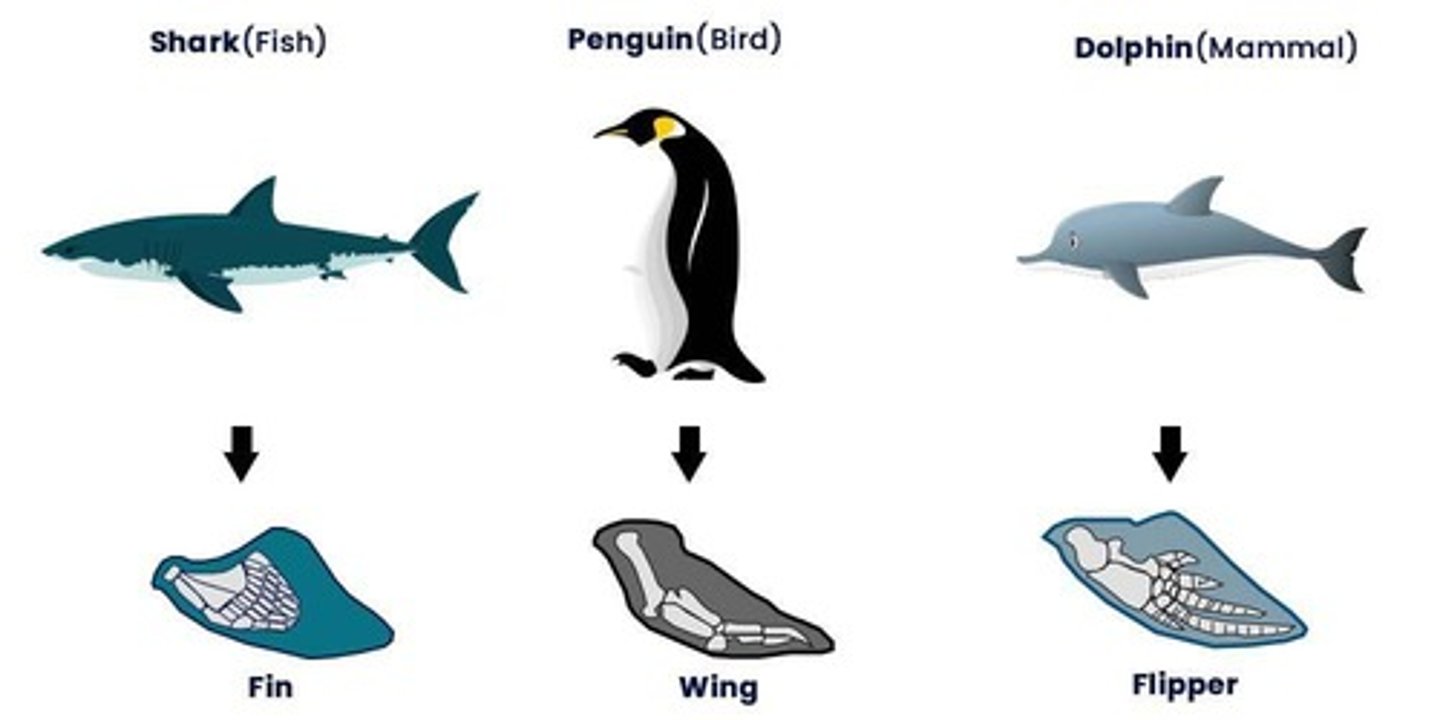
Descent with modification
Evolutionary theory explains the existence of homologous structures adapted to different purposes as the result of descent with modification from a common ancestor.
Analogous structures
Body parts that share common function, but not structure.
Example of analogous structures
A bird's wing and a horse's front limb have different functions but similar structures.
Vestigial structures
Inherited from ancestors but have lost much of original function due to different selection pressures acting on the descendant.
Lamarck's Theory
Lamarck was a French biologist best known for his Theory of Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics, first presented in 1801.
Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics
Lamarck believed that evolution was the 'acquired traits' of a species that is inherited by its offspring.
Lamarck's view on organism change
Lamarck's theory suggests that organisms can change during their lifetimes in response to their environment and that these changes are inherited by their offspring.
Example of Lamarck's theory
If a short-nosed elephant was continually stretching out its trunk to try to reach the leaves high up in trees, its trunk would stretch and become longer over time, and any babies that it had would be born with longer trunks.
Lamarck on unused body parts
Lamarck believed that when body parts were not being used, they disappear.
Darwin's Theory of Evolution
Theory that explains how species evolve over time through natural selection.
Natural Selection
Mechanism of evolution where organisms with traits better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Survival of the Fittest
Concept that organisms best adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Variation
Differences in physical and behavioral features within a species.
Overproduction
The phenomenon where organisms produce more offspring than can survive.
Competition
The struggle between organisms for limited resources in their environment.
Speciation
The process by which new species arise from existing species.
Ecology
Study of how organisms interact with each other and their environment.
Biotic
Things that are living.
Abiotic
Things that are NOT living.
Niche
A job or role for an organism in an ecosystem.
Habitat
Where an organism lives in an ecosystem.
Ecosystem
Biotic and abiotic factors interacting in a specific location.
Autotrophs
Organisms that capture energy from nonliving sources and store it for other organisms.
Primary Producers
Organisms that produce energy available to other organisms, primarily autotrophs.
Photosynthesis
Process where algae and plants use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and carbohydrates.
Chemosynthesis
Process where some bacteria use chemical energy from inorganic molecules to produce carbohydrates.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that cannot capture energy directly from sunlight or inorganic sources and acquire energy by consuming other organisms.
Consumers
Organisms that obtain energy by eating other organisms.
Carnivores
Consumers that eat other animals.
Herbivores
Consumers that eat plant leaves, roots, seeds, and fruits.
Omnivores
Consumers that eat both plants and animals.
Scavengers
Consumers that eat carcasses of dead animals.
Decomposers
Organisms that break down organic matter, producing detritus.
Detritivores
Organisms that chew or grind detritus into smaller pieces.
Food Chain
A series of organisms in which energy is transferred from one organism to another.
Short Food Chain Example
In a short food chain, a plant is eaten by a herbivore, which is eaten by a carnivore.
Primary Producers in Ocean
Usually tiny floating algae called phytoplankton.
Food Web
A network of feeding interactions, through which both energy and matter move.
Food Web Definition
A network that includes all the food chains in an ecosystem.
Decomposition
Releases matter in the form of nutrients that can be used by primary producers.
Trophic Level
Each step in a food chain or food web.
Ecological Pyramids
Models of trophic levels in a food chain or a food web.
Biomass
The amount of living tissue in a trophic level.
Biomass Determination
The amount of biomass in a trophic level is determined by the amount of energy in that level.
Compounds in Organisms
All organisms contain the compounds water, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
Elements in Compounds
These compounds are mainly made of the elements oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Matter Flow
Matter flows from one trophic level to another and is recycled within and among ecosystems.
Biogeochemical Cycles
Cycles of elements and compounds in ecosystems.
Biological Processes
Activities done by organisms, such as photosynthesis.
Geological Processes
Processes that occur in the geosphere, including volcanoes, earthquakes, and formation of rock.
Chemical and Physical Processes
Processes that mostly occur in the hydrosphere or atmosphere, including the formation of precipitation and the flow of water.
Human Activities Impact
Activities such as burning fossil fuels and forests that affect cycles of matter on a global scale.
Water Cycle
The process where water enters the atmosphere as vapor, condenses into droplets, and returns to the surface as precipitation.
Carbon Cycle
The cycle involving carbon as a major component of organic compounds and its exchange between the atmosphere and living organisms.
Respiration
A process that returns CO2 to the atmosphere.
Human Activity in Carbon Cycle
When humans burn fossil fuels, they return carbon stored over millions of years to the atmosphere in a very short time.