[BIO 111] CH 5 - Biological Molecules
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
4 classes of biological molecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
Macromolecules
large, complex molecules that have unique properties due to their arrangement of atoms
Polymers
long chains of monomers
Monomers
building blocks that make up polymers
Enzymes
specialized proteins that speed up reactions
Dehydration reaction
two monomers bond through the loss of water
Hydrolysis
water molecules break down large molecules into smaller units
Carbohydrates
simple sugars and polymers of sugars
Carbohydrate monomer
monosaccharides
Carbohydrate polymer
polysaccharides
Monosaccharides
molecules that follow the general formula CH2
What is the most common monosaccharide?
glucose C6H12O6
How are monosaccharides classified?
location of carbonyl group and number of carbons in skeleton
Aldose
molecules with a carbonyl group attached at the end of carbon skeleton
Ketose
molecules with carbonyl group attached within of carbon skeleton
What do monosaccharides serve as?
major fuel source for cells and raw building blocks for molecules
Disaccharide
two monomers joined together by glycosidic linkages
Glycosidic linkage
covalent bonds between 2 monosaccharides
What role do polysaccharides serve?
serve as storage and structural roles
4 types of polysaccharides
starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin
Starch
primary carb in plants composed of glucose monomers
Where are starches stored in plants?
Chloroplast granules
What is the simplest starch?
amylose
Glycogen
primary carb in animals
Where is glycogen stored in animals?
Liver and muscles
Cellulose
primary carb in plants that makes up cell walls
Chitin
primary carb found in fungi and exoskeletons of arthropods
Lipids
fatty compounds
What is largest and most diverse class of biological molecules?
lipids
What are lipids considered?
hydrophobic and nonpolar
Polymer of lipids
none
Fats
large molecules made up of glycerol group and 3 fatty acid chains
Glycerol
3 carbon alcohol with 3 hydroxyl groups attached to each carbon
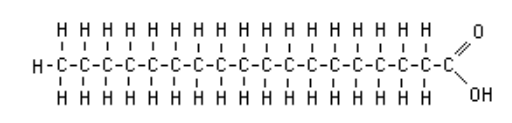
Fatty acid
long carbon chain with carboxyl group attached at the end
What is the major function of fats?
energy storage
Triglyceride
3 fatty acids chains attached to glycerol
Saturated fatty acid
fatty acid with no double bonds present
Unsaturated fatty acid
fatty acid with one or more doubles bonds that cause a kink/bend to form
Which type of fat is solid at room temperature and is found in most animal fats?
Saturated fats
Which type of fat is liquid at room temperature and is found in most plant and fish fats?
unsaturated fats
Trans fats
hydrogenated veggie oils with trans double bonds
Phospholipids
2 fatty acids chains and phosphate attached to a glycerol group
What do phospholipids do in water?
self assemble in bilayers with hydrophobic tails pointing inward
Steroid
lipids characterized by carbon skeleton consisting of 4 fused rings
Cholesterol
type of steroid that is the base of all other steroids
Hormonal proteins
coordinate organisms activities
Storage proteins
storage of amino acids
Catalyst
something that speeds up chemical reactions
Proteins
biological molecules made up of amino acid chains
Monomer of proteins
amino acids
Polymers of proteins
polypeptides
Amino acids
organic molecules made up of a carboxyl and amino group
Peptide bonds
covalent bonds between amino acids that hold polypeptide chains together
How is a protein’s function determined?
unique shape given by its folding, twisting, and coiling
What are the 4 levels of structure of proteins?
Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary
Primary structure
unique sequence of amino acids
Secondary structure
coils and folds in polypeptide chains
What are the coils called in a protein’s secondary structure?
alpha helix
What are the folds called in a protein’s secondary structure?
beta pleated sheets
Tertiary structure
loops and folds that give proteins its 3D shape that occur from the interactions between R groups within its chains
Quaternary structure
two or more polypeptide chains form a protein
Denaturation
a protein’s loss of its native structure which makes it inert
What causes denaturation?
extreme changes in pH, salt [], temp, or other enviro factors
Gene
amino acid sequence of a polypeptide
Nucleic acids
molecules composed of nucleotides
Monomers of nucleic acids
nucleotides
Polymers of nucleic acids
polynucleotides
Gene expression
DNA directs synthesis of mRNA which controls protein synthesis
DNA —> RNA
transcription
RNA —> protein
translation
What are nucleotides consist of?
phosphate group, pentose sugar, and nitrogenous base
Pyrimidines
cytosine, thymine, uracil — single 6 sided ring
Purines
adenine and guanine — 6 sided ring fused to 5 sided ring
How are nucleotides held together?
phosphodiester linkages
Phosphodiester linkages
phosphate group covalently bonds pentose sugars in nucleotides
How are nitrogenous bases paired in RNA?
thymine with uracil and guanine with cytosine