Video Production Final
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
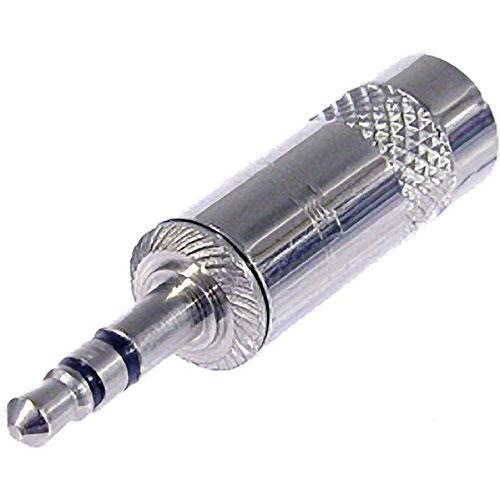

3.5mm (mini 1/8”)
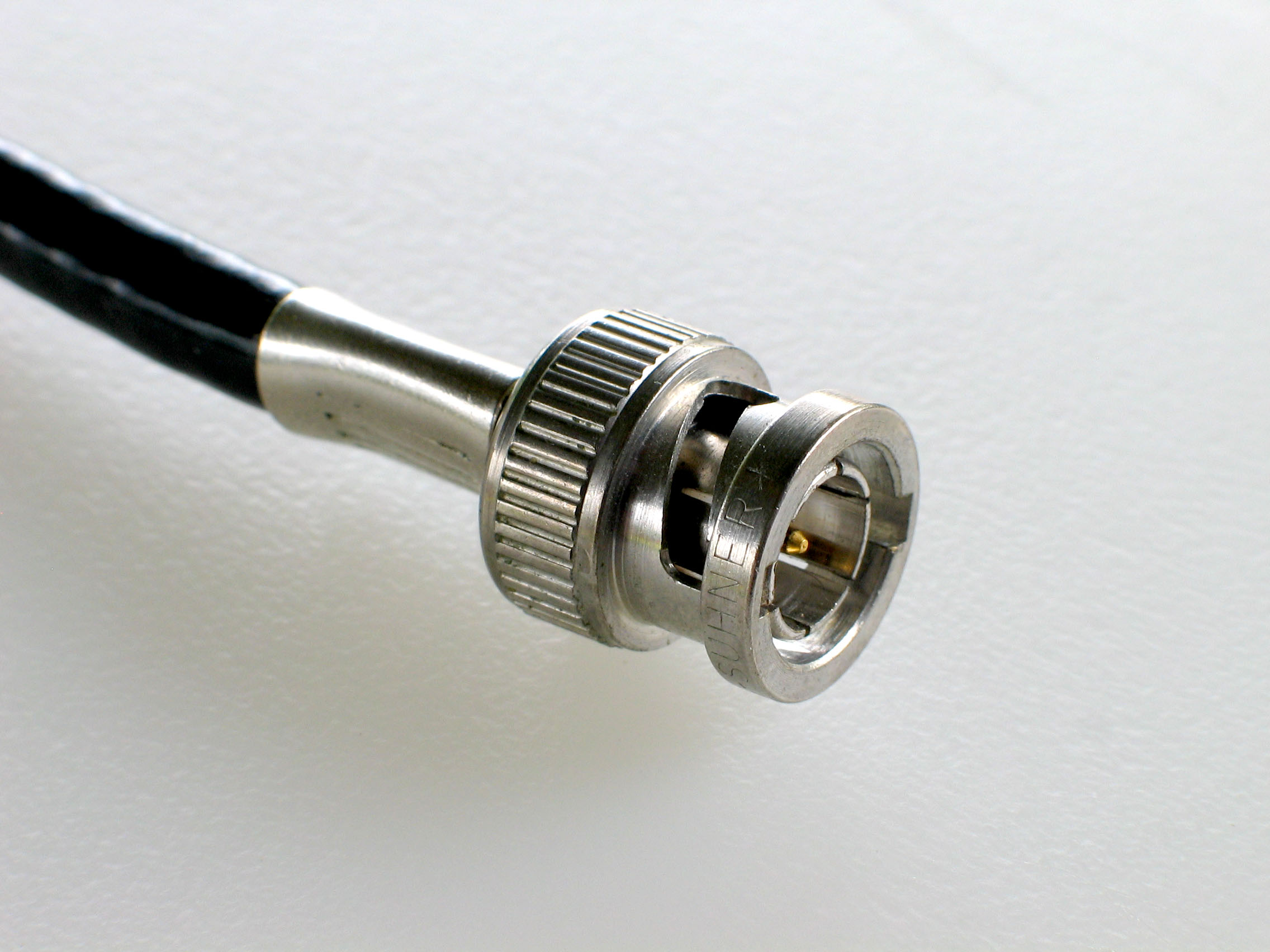
BNC

dvi

Firewire
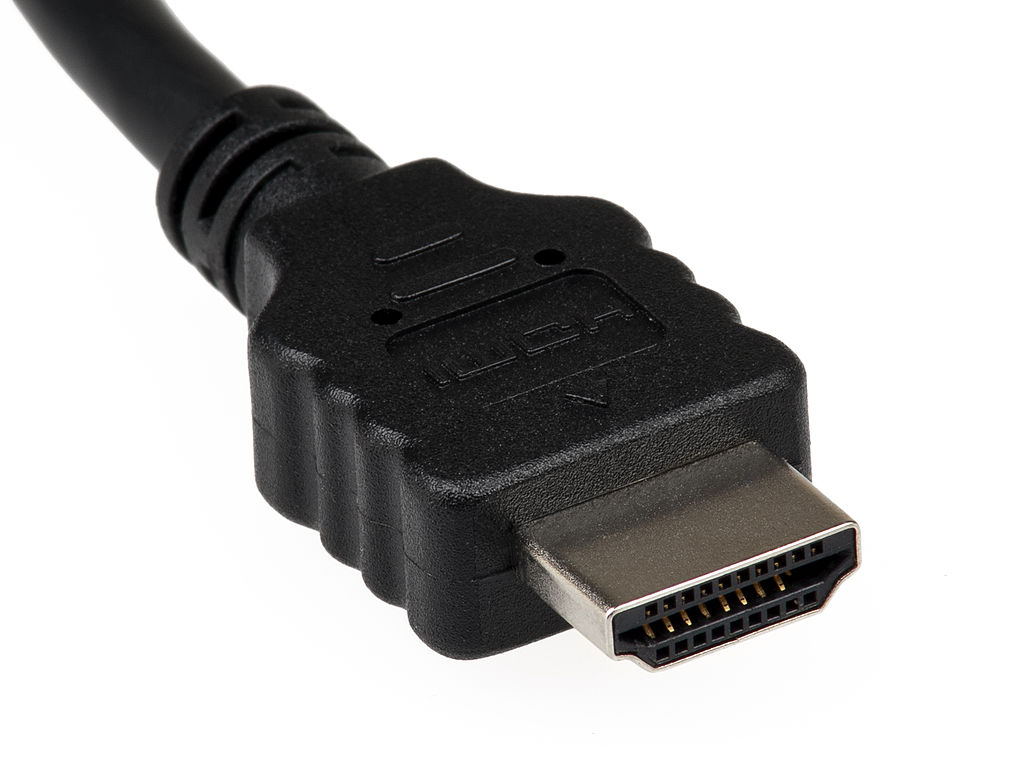

HDMI

Quarter Inch Connector

RCA

RF
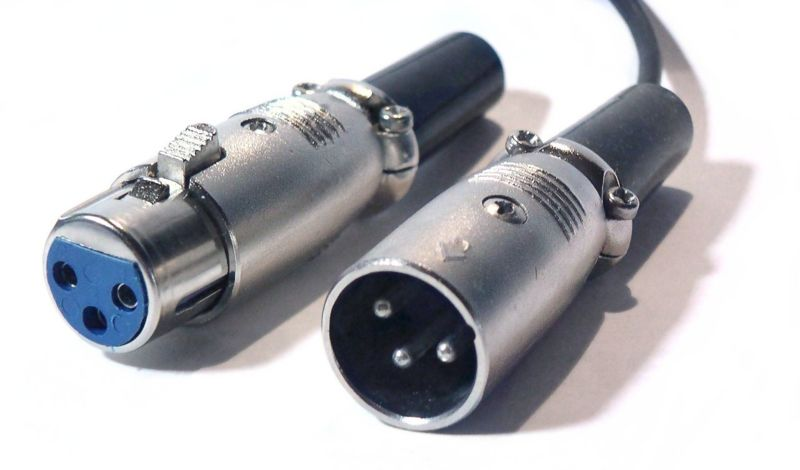

XLR
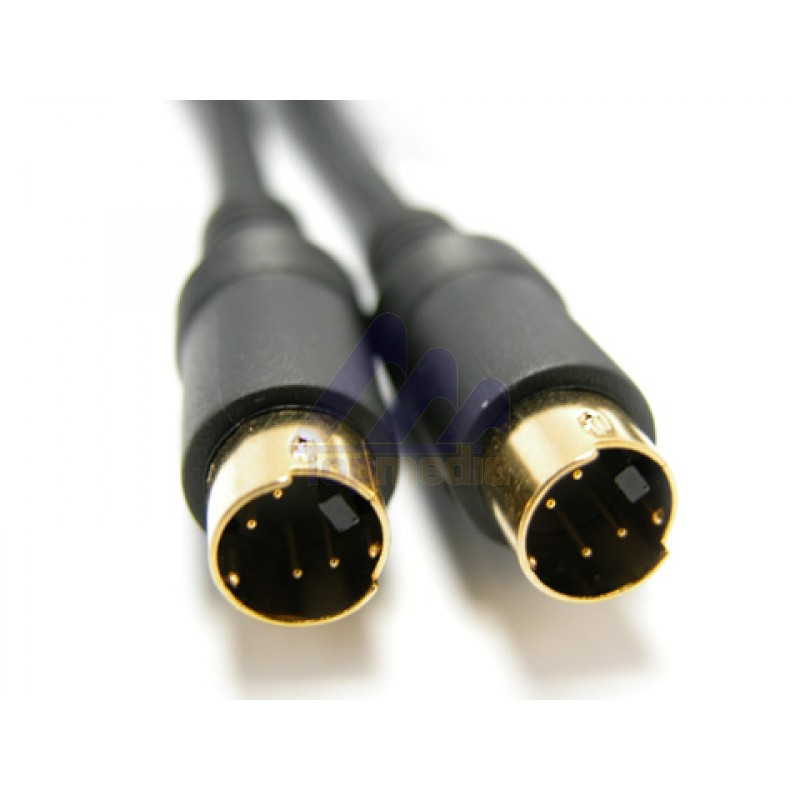

SVHS
Video gain control
Gain increases the signal from the image sensor (CMOS/CCO) to adjust brightness without changing f-stop or shutter speed
High gain → brighter image but adds noise/grain.
Low gain → darker blacks, but color saturation may fluctuate.
Color temperature
Variations in the quality of what appears to be white light, measured in degrees Kelvin (K).
Standard television lights operate at 3200 degrees K.
Light with a higher color temperature appears bluish and light with a lower color temperature appears reddish.
White balance
White balance = color balance. It tells the camera what “true white” looks like. Ensures all colors are recorded and displayed correctly, since white light is the sum of all colors.
Incorrect white balance shows up as pictures with orange or blue tints
Microphone pickup pattern
the directions in which it is sensitive to incoming sound
(Microphones cannot discriminate what sound they pick up)
Omni-directional microphone
sensitive in all directions. They are used to record where sound comes from many directions or when people are seated around a table. used in video field production
Omni uses - meetings, press conferences, wide open spaces where audio is needed.
Cardioid
microphones that a heart-shaped pickup pattern. They are extremely sensitive out front but less sensitive to the sides and back. used in video field production
used for when you want to record the sound only near the source such as on a podium
Supercardioid
microphones that exaggerate the sensitivity in front of the mic. used in video field production
used when you want to record a sound coming from a small area some distance away. Recording bird songs for example.
Shotgun microphones
when supercardioids are placed in long barrels they are referred to as shotgun microphones.
Frequency response
refers to the ability to accurately reproduce a wide range of frequencies.
No microphone can reproduce all sounds which range from 16 Hz to 16,000 Hz and above.
also depends on the placement of the microphone. Reflected sound appears different than sound going directly into the microphone.
Fishpole
a metal pole that extends out to allow placement of the microphone close to the sound source. Allows the microphone to get into close proximity of the sound and still be off camera
Microphone (Mic) level
a very weak signal that is produced by a microphone. Approx. -40 dB
Line Level
signals that are much stronger than microphone levels. Typically they are found on cd players, tape decks, DVD players, etc. Their output level is usually around -10 dB to +4 dB.
Preamp/Preamplifier
the function of a preamp is to amplify a low-level signal to line-level. A preamplifier (preamp), or control amp in some parts of the world, is an electronic amplifier which precedes another amplifier to prepare an electronic signal for further amplification or processing
Key light
The main light on a subject.
Camera Control Unit (CCU)
Control over the video signal is the job of the camera control unit (CCU). The CCU contain components that regulate the sensitivity of the image sensor, iris, level of video gain, etc.
External CCU's are used in large studio cameras or in set ups where the camera is quite a distance from the switcher. The external CCU allows the operator to make adjustments without having to have the camera next to him/her.
Internal CCU's are common on portable cameras and lower level industrial products. Internal controls operate the same functions as an external but the controls are located on the camera itself.
Baselight
refers to the amount (or intensity) of light that is required to make the camera function properly
Backlight
A light which is generally mounted behind a subject to light the subject's hair and shoulders without illuminating a subject's front
Passive mixer
a mixer that simply combines a number of different inputs into one output without amplifying the signal. They do not require power.
• They are popular in field production for set ups requiring two microphones.
Active mixer
give you control over the amplification of each of the audio sources. Each channel on the mixer has its own level control and the mixer has a master control. Active mixers are the types used in control rooms, concerts, lecture halls, and so on. They require power of some sort to operate.
Sampling rate
Sampling rate (or frequency) = number of samples taken per second from a continuous signal to create a discrete signal. Expressed in hertz (Hz).
Sampling period/interval = time between samples.
Higher sampling rate → more accurate reproduction of the original signal.
Timeline (Avid/Adobe editing)
A chronological display of an edited sequence in an editing system. A visual representation of a movie over time, consisting of video clips laid horizontally across the screen. This is a common interface in video editing applications such as Final Cut Pro and Avid Media Composer
Teleprompter
An electronic device for displaying text to be read, often used in television or public speaking
Video switcher
A video switcher is a hardware device used in video production to switch between different video or audio sources. This allows the producer to mix video and also add in special effects or footage captured on a secondary source.
Routing switcher
A device used to direct the path of one or more signals into one or more devices.
Producer
big-picture management
Oversees all aspects of production: idea development, cast hiring, shoot supervision, fact-checking.
Responsible for overall quality and survivability of the show
Director
technical and creative execution during production.
Supervises technical elements: camera placement (blocking), lighting, microphones, props.
In dramatic productions, acts like a film director—gives cues to actors and controls recording.
Varies depending on live or recorded performance
Technical Director
often the vision mixer, working under the supervision of the television director.
Manually switches video sources.
Performs edits and overlays titles as directed.
Operates production equipment while the director coordinates overall decisions.
How do you manually set a camera’s white balance, and why is it necessary? (Short answer)
Ensures accurate color reproduction under different lighting conditions
Press the white balance button/switch.
Use correct filter (filter wheel/add-on filters).
Point camera at a pure white subject (50–80% of frame, matte surface).
Set exposure and focus.
Activate white balance; camera stores current color balance.
Identify common audio connectors and their uses. (Short answer)
Phono/RCA: Line-level inputs/outputs, video transfer, unbalanced.
XLR/Cannon: Mic & line-level signals, professional quality, balanced.
Mini/1/8": Microphones & headphones, unbalanced.
Phone/1/4": Headphones, mics, speakers, unbalanced.
Identify common video connectors. (Short answer)
Phono/RCA
3.5mm / Mini/1/8"
BNC
F-connector/RF cable
FireWire
HDMI
Where would you use omni, cardioid, and supercardioid microphones? (Short answer)
Omni: Meetings, press conferences, wide open spaces.
Cardioid: Podium, recording sound near the source.
Supercardioid: Narrow area at a distance (e.g., bird songs).
Describe a typical three-point lighting setup. (Short answer)
Key Light: Main illuminator, determines overall design.
Fill Light: Side angle, softer, balances shadows.
Back Light (Rim/Hair/Shoulder): Behind subject, separates from background.
Identify five types of microphones used in video production. Short answer)
Handheld Microphone
Lavalier Microphone
Surface-Mounted Microphone
Shotgun Microphone
Contact Microphone
(Bonus: Hanging Microphone)
What is the purpose of a submix in audio recording? (Short answer)
Combines multiple inputs into one fader for easier control.
Example: Mics 1–5 → Submix #1; CD player → Submix #2.
Adjusting submix changes levels of all sources in that group.
Purpose: Simplifies sound management in studios.