adv diagnosis - exam 1 desiree study guide
1/232
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
233 Terms
imaging in US physical therapy practice is increasing but inconsistent
describe the current state of imaging within the respect to physical therapists practice within the united states
most state practices do not have the same language - some are silent, others restrictive. a few states (maryland, colorado, and wisconsin) now allow PTs to refer or order imaging with specific training
do most states within the US have the same practice act language regarding a physical therapist practice and imaging referral
almost all state practice acts include a "duty to refer", making it a legal responsibility for PTs to refer patients when findings are beyond our scope
do all, or at least most state practice acts include the "duty to refer" as a legal duty and responsibility of a physical therapist
our role is to recognize when imaging is not needed, integrate imaging findings into our PT POC, understand the image/report to gather PT relevant information, knowing what tissues that is at fault to know what modality to use, and how to communicate imaging information with the radiologist, physician, and especially the patient
list the physical therapist role relative to imaging. what do you need to know, integrate, understand, and communicate
false
true or false: imaging should be conducted for every patient who presents with musculoskeletal complaints
its not always warranted. many injury locations/types have their own set of rules on how to rule the need for imaging in or out
why is "imaging should be conducted for every patient who presents with musculoskeletal complaints" a false statement
true
true or false: imaging should only be considered when the provider expects the results to influence decision making and plan of care
"imaging is indicated when the information yielded would change the treatment plan"
why is "imaging should only be considered when the provider expects the results to influence decision making and plan of care" a true statement
true
true or false: knowing when a patient should have imaging is a responsibility of a physical therapists
in most cases there are subsets of criteria where PTs should be able to rule in or out especially with direct access patients
why is "knowing when a patient should have imaging is a responsibility of a physical therapists" a true statement
true
true or false: knowing when the results of imaging would impact the physical therapist's plan of care and physical therapist's management of a patient is the responsibility of the physical therapist
there are clinical decision aids available once this decision is made such as: evidence based clinical decision rules, ACR, west australia diagnostic imaging pathways, and discussion with PCP or radiologist
why is "knowing when the results of imaging would impact the physical therapist's plan of care and physical therapist's management of a patient is the responsibility of the physical therapist" a true statement
clinical decision rules
american college of radiology appropriateness criteria (ACR)
western australia diagnostic imaging pathways
discussion with PCP or radiologists
list the type of clinical decision aids that are available to help determine if imaging is indicated
evidence based
determine risk level to not miss serious conditions
clinical decision rules
evidence based consensus
IDs high and low values studies based on clinical variants
american college of radiology appropriateness criteria (ACR)
pathways based on suspected diagnoses
western australia diagnostic imaging pathways
acute cervical trauma - canadian C spine rules
acute ankle injury/ottawa ankle rules
acute knee trauma/ottawa knee rules
lumbar guidelines (ACR criteria)
shoulder dislocation
suspected compression fracture
elbow extension sign (elbow fracture)
acute radial wrist fracture (scaphoid fracture)
recall the following clinical decision rules related to imaging
purpose: decide if C-spine x-ray is needed after trauma
imaging needed if: high risk factor (age ≥65, dangerous mechanism, or paresthesias in extremities), unable to actively rotate neck 45 degrees left and right
no imaging: low-risk factors present (simple rear-end crash, sitting in ED, ambulatory, delayed pain, no midline tenderness) and can rotate 45 degrees bilaterally
acute cervical trauma - canadian C-spine rules
purpose: determine needed for ankle/foot x-rays after trauma
imaging needed if: pain in malleolar or midfoot zone and bone tenderness at posterior edge/tip of lateral or medial malleolus, base of 5th metatarsal or navicular, or unable to bear weight immediately and in ER (4steps)
acute ankle injury/ottawa ankle rules
purpose: decide if knee x-ray is required
imaging needed if: age ≥ 55, tenderness at fibular head, isolated patellar tenderness, inability to flex knee to 90 degrees, unable to bear weight 4 steps immediately and in ER
acute knee trauma/ottawa knee rules
purpose: imaging only when serious pathology suspected or persistent symptoms
imaging needed if: red flags (severe/progressive neuro deficits, cauda equina signs, cancer history, infection, fracture risk, trauma, unexplained weight loss)
no red flags: try conservative management for 6 weeks before imaging
lumbar guidelines (ACR criteria)
imaging needed if: first time dislocation or traumatic event, suspicion of fracture (especially hill-sachs or bankart lesion), persistent pain, deformity, or instability after reduction
shoulder dislocation
imaging needed if: trauma in older adult or osteoporotic patient, midline spinal tenderness or sudden severe back pain, prolonged corticosteroid use or known osteoporosis
suspected compression fracture
purpose: quick rule out test
imaging needed if: unable to fully extend elbow after injury
if full extension = fracture very unlikely (sensitive rule)
elbow extension sign (elbow fracture)
imaging needed if: snuffbox tenderness, pain with axial thumb compression or wrist extension, swelling over scaphoid after fall on outstretched hand (FOOSH)
if negative x-ray but high suspicion -> immobilize and re-image in 10-14 days
acute radial wrist fracture (scaphoid fracture)
conventional radiograph (X-ray)
most of the time, what is the initial imaging modality that is used
if there is a fracture and/or any need for surgery, the patient may have weightbearing precautions where their TRX will be delayed
list some examples of when imaging results would change your plan of care
clinical hypothesis, who's writing the order, will results change, POC, cost, radiation exposure, contraindications or fear
considerations for making a recommendation for imaging or directly ordering images
age, MOI, signs and symptoms, other test results (neuro/special test), modality requested, RL side specified, your hypothesis, contact number for if results are urgent
information needed for radiology orders
ASAP: contact PCP/specialist when the findings align with - neoplasms, complete contractile ruptures, posterolateral corner injury, high ankle sprains, lisfranc sprain
indicate when a discussion when a patient's primary care physician or physician specialist would be appropriate prior to ordering or referring for image
accuracy for ordering imaging when it is needed: PT's were 74%, ortho surgeons 80%, but non-ortho doctors were at 35%
what was the summary of the Moore et al 2005 study
PT's especially when board certified in determining when imaging is necessary are 3x more likely to have accuracy agreement between diagnosis and imaging results, PTs average visits before ordering MRI, percent of orders complying with ACR = 83.2%, (great accuracy of PTs deciding appropriately when imaging is needed)
what was the summary of the Crowell et al 2016 study
1st ordered diagnostic study, little risk, time effective, cost effective
why are conventional radiographs the most common imaging modality
the image is produced on a sensitive plate or film using x-rays, gamma rays, or other type of similar radiation. the radiation passes through the patient where there is attenuation (meaning where it is changed or blocked depending on the density of the tissue). the remnant radiation incepted by receptor to create a visual image
describe how standard radiograph creates a visual image
where the radiation is changed or blocked by pathologic tissue
define the term attenuation
on density of the tissue
what does attenuation depend on
harm is done when using radiation. it affects neural atoms gains/loses of electrons, disrupts composition of matter, disrupts life processes. you must use shielding/diagnostic yield to protect patient from the harm of radiation
indicate the effects of ionizing radiation
energy that is deposited in patients
define absorbed dose
absorbed dose that is adjusted for harmful effects
define equivalent dose
equivalent dose that is adjusted for the harm that is causes to different tissues
define effective dose
single chest x-ray
single mammogram
full body CT scan
rank single mammogram, fully body CT scan, and single chest x-ray from low to high in terms mSV (radiation)
0.1 msV
what is a safe level of radiation for single chest x-ray
3 mSV
what is a safe level of radiation for single mammogram
10 mSV
what is a safe level of radiation for full body CT scan
true
true or false: radiation exposure is cumulative
false
true or false: all body tissues absorb radiation equally
physical qualities of an object that determine how much radiation it absorbs (composition, thickness). the greater the atomic number, the volume density and/or thickness, the greater this is
define radiodensity
minimal absorption of radiation = show up as black
define radiolucent
air
what would be an example of something that is radiolucent
whiter color more absorption gets through
define radiopaque
heavy metals in joint replacement
what would be an example of something that is radiopaque
composition and thickness
what factors influence an objects radiodensity
air
fat
water
bone
metal
place in order air, fat, water, bone, metal from lowest radiodensity (most radiolucent) to highest radiodensity (most radiopaque)
air
fat
water
bone
metal
place in order air, fat, water, bone, metal as how the substance would appear on radiography from the darkest to lightest
true
true or false: the greater the radiodensity of objective, the greater the amount of radiation will be absorbed resulting in less of the x-ray beam reaching the film
true
true or false: an object or tissue that has greater radiodensity will be more radiopaque and will appear whiter (lighter) on radiograph
lead, bone
examples of things that have higher radiodensity and more radiopaque
true
true or false: an object or tissue that has lower radiodensity will be more radiolucent and will appear darker (blacker) on a radiograph
air
examples of things that have lower radiodensity and more radiolucent
lighter
does bone appear darker or lighter on a radiograph compared to air or fatty tissues
more radio dense
why does bone appear lighter/more white on radiograph than air and fat
frontal plane (beam located above supine lying patient)
what plane and how is a person situated for an anterior to posterior view
frontal plane (beam located above prone lying patient)
what plane and how is a person situated for a posterior to anterior view
sagittal plane (lateral projecting beams)
what plane and how is a person situated for lateral to medial view
transverse plane (depends on what is being imaged)
what plane and how is a person situated for an axial view
oblique plane (beams aligned 45 or 0 degree angle for better anatomic visualization)
what plane and how is a person situated for oblique view
true
true or false: imaging reveals pathology, but the history and physical exam provides relevance
highly specific
when generally describing the psychometric properties of radiographs, radiographs are best described as being highly specific or highly sensitive
all the way across
define complete fracture
not all the way across
define incomplete fracture
incomplete (splintering usually Peds)
define greenstick fracture
diagonal across bone
define oblique fracture
straight line across bone
define transverse fracture
break wraps around bone
define spiral/torsional fracture
bone comes through the skin
define compound fracture
partial without skin wound
define simple fracture
bone breaks into 2 or less pieces (complete or incomplete)
define non-comminuted fracture
bone breaks into 3 or more pieces (3, 4, 5 = mild and more than 5 is severely)
define comminuted
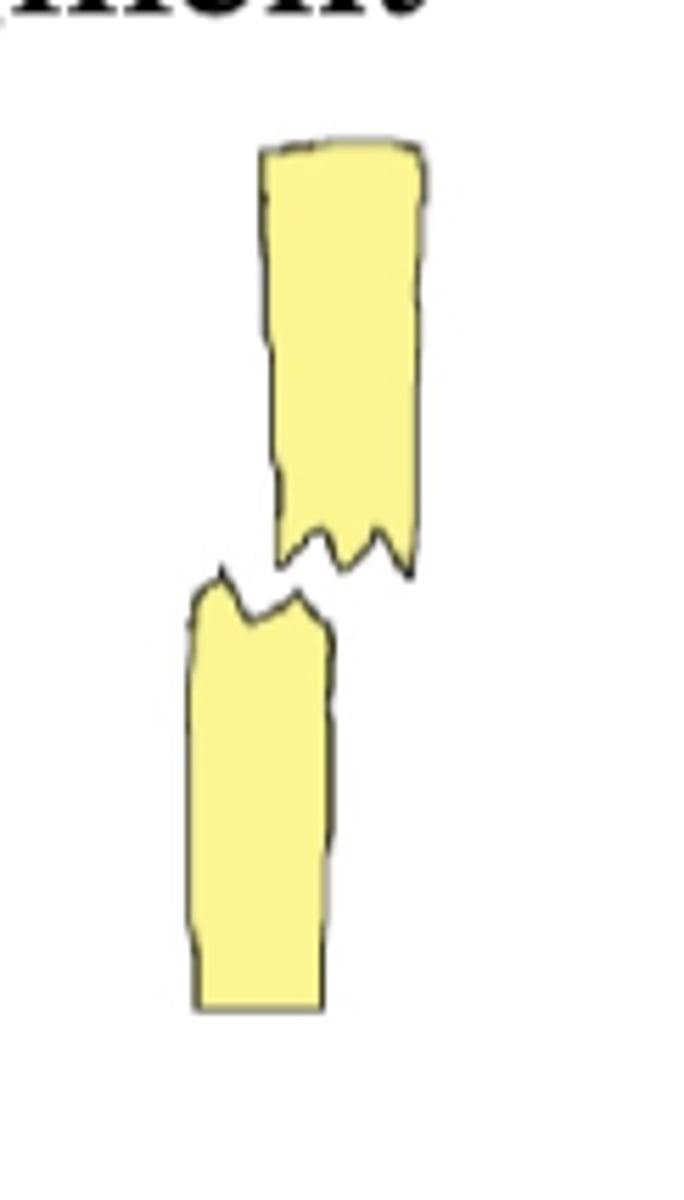
left translated completed fracture
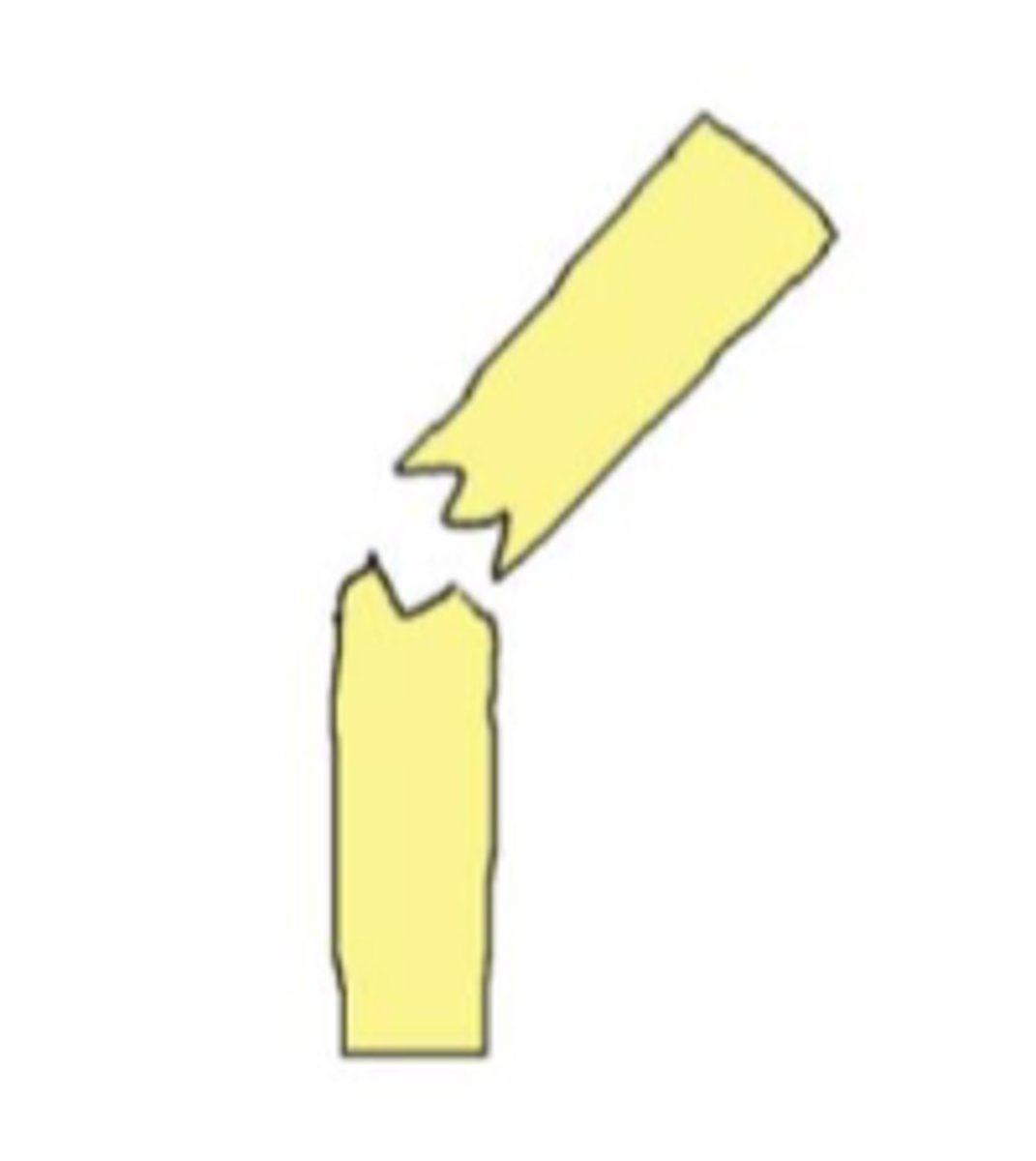
left angulated completed fracture
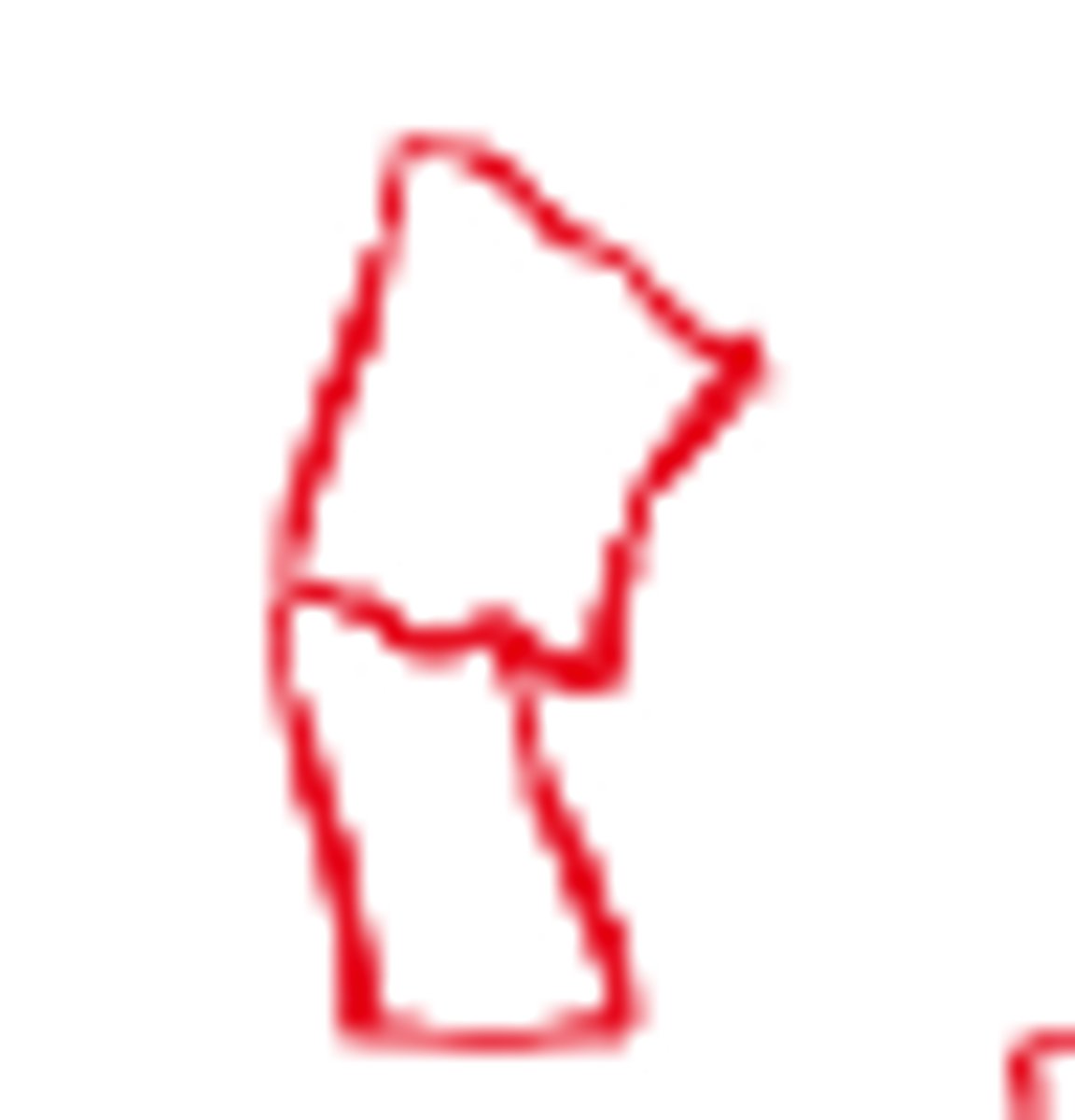
left angulated incomplete fracture
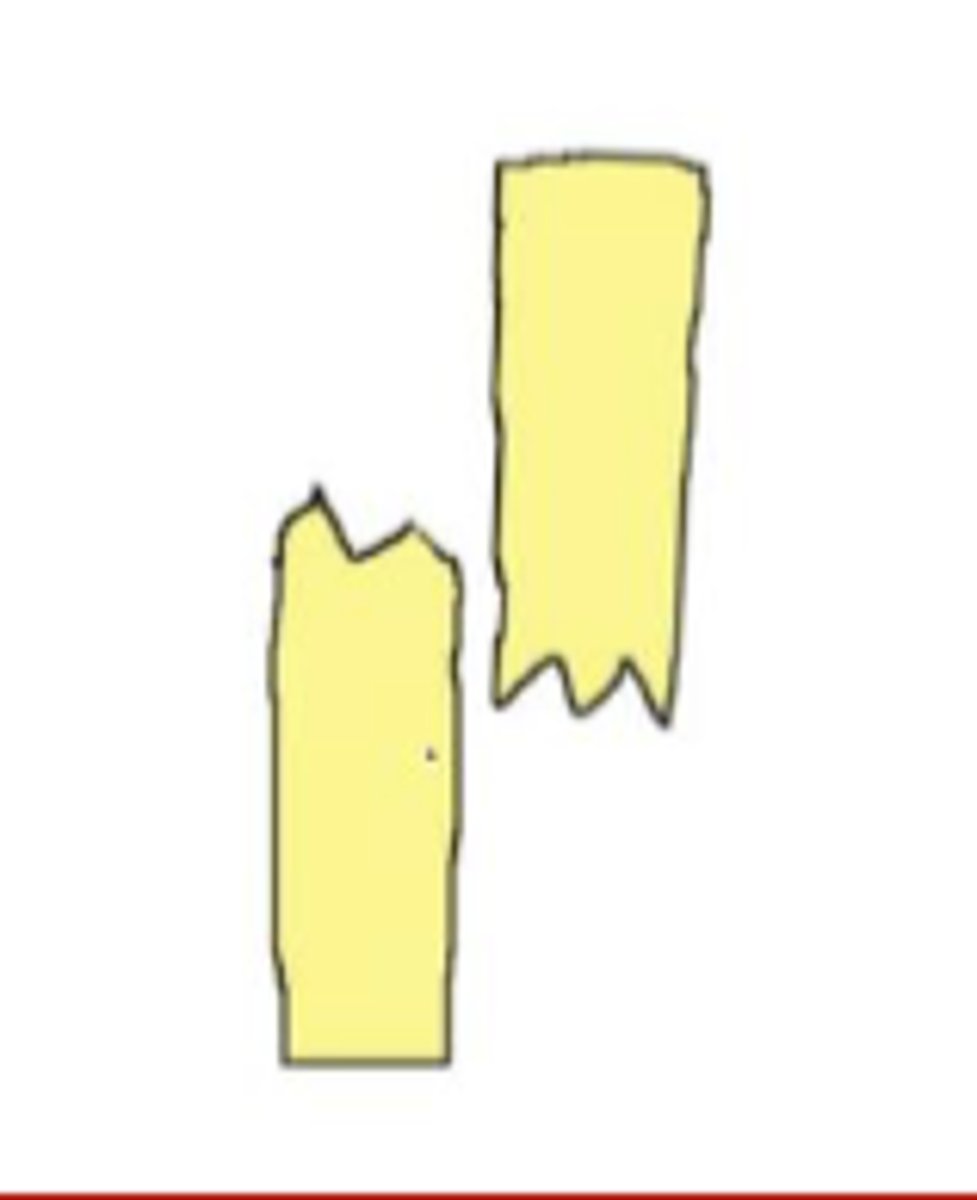
complete fracture with shortening
peds growth plate (physis)
what type of fracture is salter harris fracture
pediatric
who is most likely to get a salter harris fracture
fracture across physis without metaphysical or epiphyseal injury
type 1 salter harris fracture
extends into metaphysis
type 2 salter harris fracture
extends into epiphysis
type 3 salter harris fracture
through metaphysis and epiphysis
type 4 salter harris fracture
crush injury
type 5 salter harris fracture
open fractures
what type of fractures does the gustilo classification apply
skin has been disrupted
what does gustilo classification describe
fracture of anatomic neck, surgical neck, greater tuberosity, or lesser tuberosity - displacement is angulation of more than 45 degrees or more than 1 cm form anatomic position
neer classification relates to what type of fractures
no displacement
neer classification: one part
one displacement
neer classification: two part
two displacements but humeral head in contact with glenoid
neer classification: three part
three or more displacements and dislocation of articular surface
neer classification: four part
validated system on name type of fracture that may be used post op you may see in chart but won't use in clinical practice
muller AO classification
alignment, bone density, cartilage, soft tissue
ABCs of radiographic eval
it accounts for all possible findings and decreases chance for observational error
why is a "search pattern" such as the ABCs system a requirement
observation and interpretation
what is a key reason for errors in interpretation of imaging