1.2 Discharge Relationships within drainage basins
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Annual hydrographs/river regimes
Shows the variation in the flow of a river over the course of a year
Why does Stream flow occur
Result of runoff, groundwater springs from lakes and from melt water in mountains or sub polar environments
What is streamflow influenced by
Amount and nature of precipitation
Local rocks - porosity and permeability
Shape or morphology of the drainage basin, area and slope
Amount of type and vegetation cover
Amount and type of soil cover
Flood hydrographs
Shows how the discharge of a river varies over a short time, referring to an individual storm or group of storms of not more than a few days in duration.
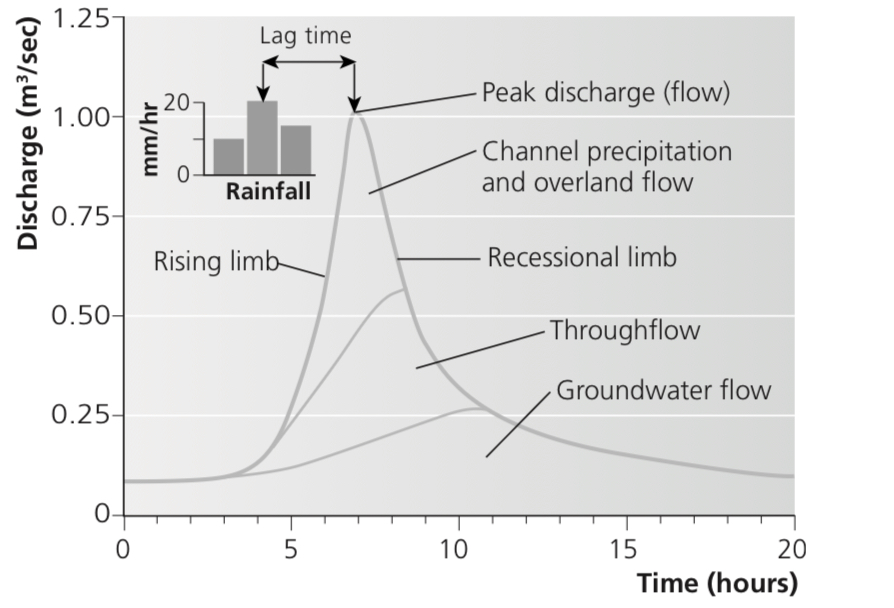
explain each aspect of the flood hydrograph
Rising limb - shows how quickly floodwaters begin to rise
Falling limb - the speed with which the water level in the river declines after the peak
Peak flow - the maximum discharge of the river as a result of the storm
Lag time - the time between the peak of the storm and the maximum flow in the river
Through flow - water flowing through the soil in natural pipes and percolines
Groundwater flow - subsurface water flow - lakes
Drainage density
The measure of how many stream channels exist in a given area
How does precipitation type and intensity influence flood hydrographs
High intensity rainfall produces runoff, steep rising limb, high peak flow
Low intensity rainfall infiltrates into the soil and percolates slowly into the rock, increasing lag time, reducing peak flow
Precipitation such as snow sits on the ground until it melts, sudden melting can cause flooding and lead to high runoff and high peak flows
How does temperature and evapotranspiration influence flood hydrographs
Temperature affects type of precipitation and evapotranspiration rate (high temp, high EVT, less water into rivers)
Warm air holds more water, potential for high peak flows in hot areas is raised
How does antecedent moisture influence flood hydrographs
If it has been raining previously the ground is saturated - rainfall with quickly produce surface runoff - leading to high peak flow and short lag time
How does drainage basin size and shape influence flood hydrographs
Smaller drainage basins respond more quickly to rainfall conditions - peak of the flood can occur soon after peak of the storm
Larger drainage basins respond more slowly, as it takes a longer time for the water to travel down stream from the uppercourse.
Circular basins respond more quickly than linear basins- where the response is more drawn out.
How does drainage density influence flood hydrographs
Basins with a high drainage density, such as urban basins with a network of sewers and drains, respond very quickly.
Networks with a low drainage density have a very long lag time
How does porosity and impermeability influence flood hydrographs
Impermeable surfaces cause surface runoff. Leads to greater peak flows. Usually in urban areas
Rocks such as chalk and gravel are permeable, water can be infiltrated and percolate - reduces peak flow and increases lag time.
How do slopes influence flood hydrographs
Steeper slopes create more surface runoff, shorter lag time, higher peak flow
How does vegetation type influence flood hydrographs
Broad-leafed vegetation intercepts more rainfall, reduces surface runoff and peak flow, and increases lag time.
In winter, trees lose their leaves, so they intercept less
How does land use influence flood hydrographs
Land uses that create impermeable surfaces/reduce vegetation reduce interception and increase surface runoff
More drainage channels are built - water is carried to rivers quickly, increasing peak flow and reducing lag time.