Water and Carbon Cycles in AQA Geography A-Level
1/276
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
277 Terms
Inputs
Where matter or energy is added to the system
Outputs
Where matter or energy leaves the system
Stores
Where matter or energy builds up in the system
Flows
Where matter or energy moves in the system
Boundaries
Limits to the system (e.g. watershed)
Open systems
Systems that receive inputs and transfer outputs of energy or matter with other systems.
Closed systems
Systems where energy inputs equal outputs.
Dynamic equilibrium
When inputs equal outputs despite changing conditions.
Positive feedback
A chain of events that amplifies the impacts of the original event.
Negative feedback
A chain of events that nullifies the impacts of the original event, leading to dynamic equilibrium.
Local scale
Refers to the carbon and water cycles being open systems.
Global scale
Refers to the carbon and water cycles being closed systems.
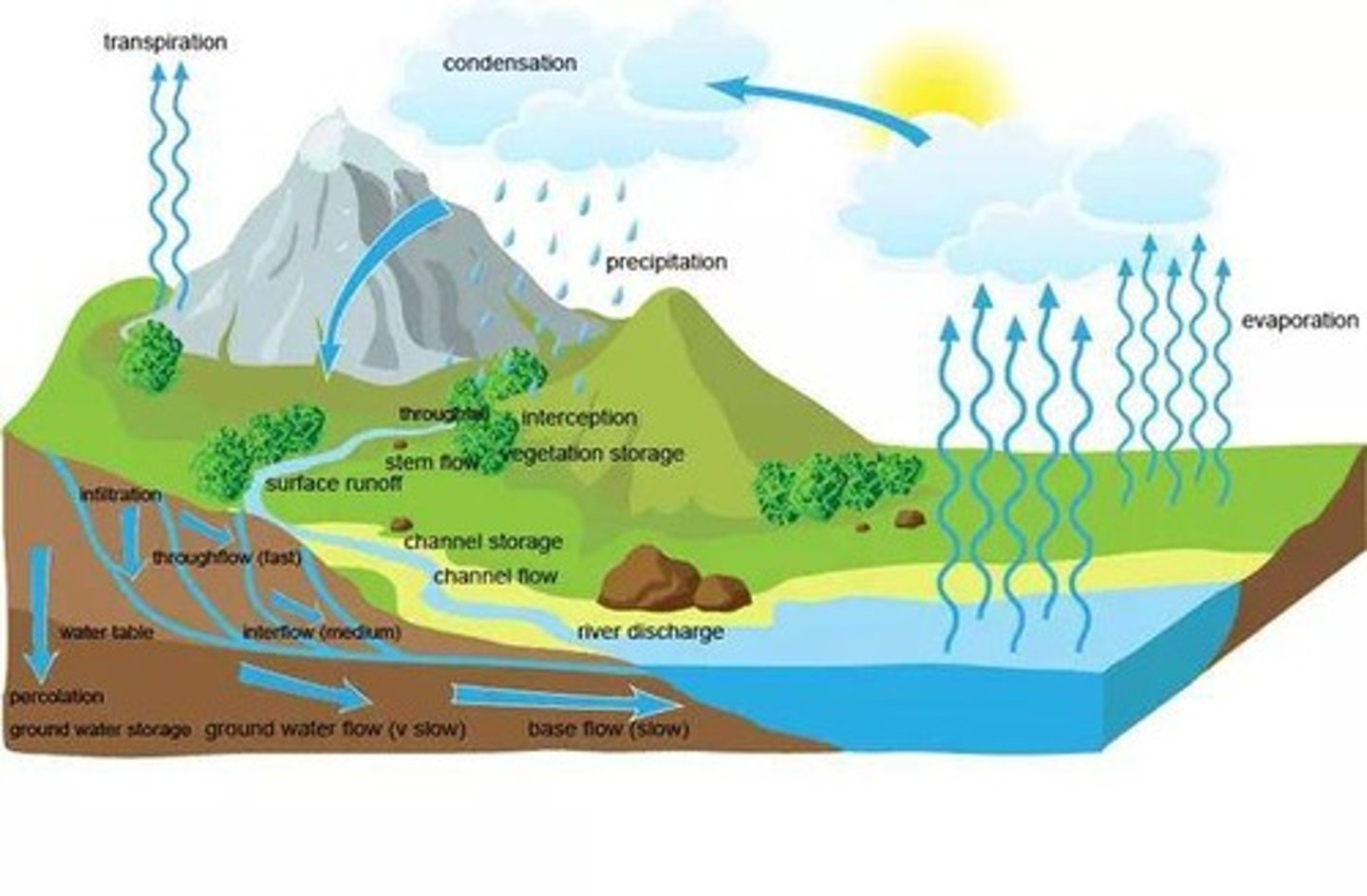
Water Cycle: Local Scale
In a local drainage basin system, water may be lost as an output through evapotranspiration and runoff, but more water may be gained as an input through precipitation.
Precipitation
Any water that falls to the surface of the earth from the atmosphere including rain, snow and hail.
Convectional rainfall
Due to heating by the sun, warm air rises, condenses at higher altitudes and falls as rain.
Relief rainfall
Warm air is forced upward by a barrier such as mountains, causing it to condense at higher altitudes and fall as rain.
Frontal rainfall
Warm air rises over cool air when two bodies of air at different temperatures meet, condensing at higher altitudes and falling as rain.
Evapotranspiration
Comprised of evaporation and transpiration.
Evaporation
Occurs when water is heated by the sun, causing it to become a gas and rise into the atmosphere.
Transpiration
Occurs in plants when they respire through their leaves, releasing water they absorb through their roots.
Streamflow
All water that enters a drainage basin will either leave through the atmosphere or through streams.
Infiltration
The process of water moving from above ground into the soil.
Infiltration capacity
Refers to how quickly infiltration occurs.
Grass crops and tree roots
Create passages for water to flow through from the surface into the soil, increasing the infiltration capacity.
Overland flow
Occurs when precipitation falls at a greater rate than the infiltration capacity.
Percolation
Water moves from the ground or soil into porous rock or rock fractures.
Percolation rate
Dependent on the fractures that may be present in the rock and the permeability of the rock.
Throughflow
Water moves through the soil and into streams or rivers.
Flow speed in clay soils
Slower flow rate due to high field capacity and smaller pore spaces.
Flow speed in sandy soils
Drains quickly because they have a lower field capacity, larger pore spaces, and natural channels.
Surface Runoff (Overland flow)
Water flows above the ground, as sheetflow or in rills.
Groundwater Flow
Water moves through the rocks, ensuring water in rivers after dry periods.
Streamflow
Water that moves through established channels.
Stemflow
Flow of water intercepted by plants or trees, down a stem, leaf, branch, or other part of a plant.
Soil Water
Water stored in the soil which is utilized by plants.
Groundwater
Water that is stored in the pore spaces of rock.
River Channel
Water that is stored in a river.
Interception
Water intercepted by plants on their branches and leaves before reaching the ground.
Surface Storage
Water stored in puddles, ponds, lakes, etc.
Water table
The upper level at which the pore spaces and fractures in the ground become saturated.
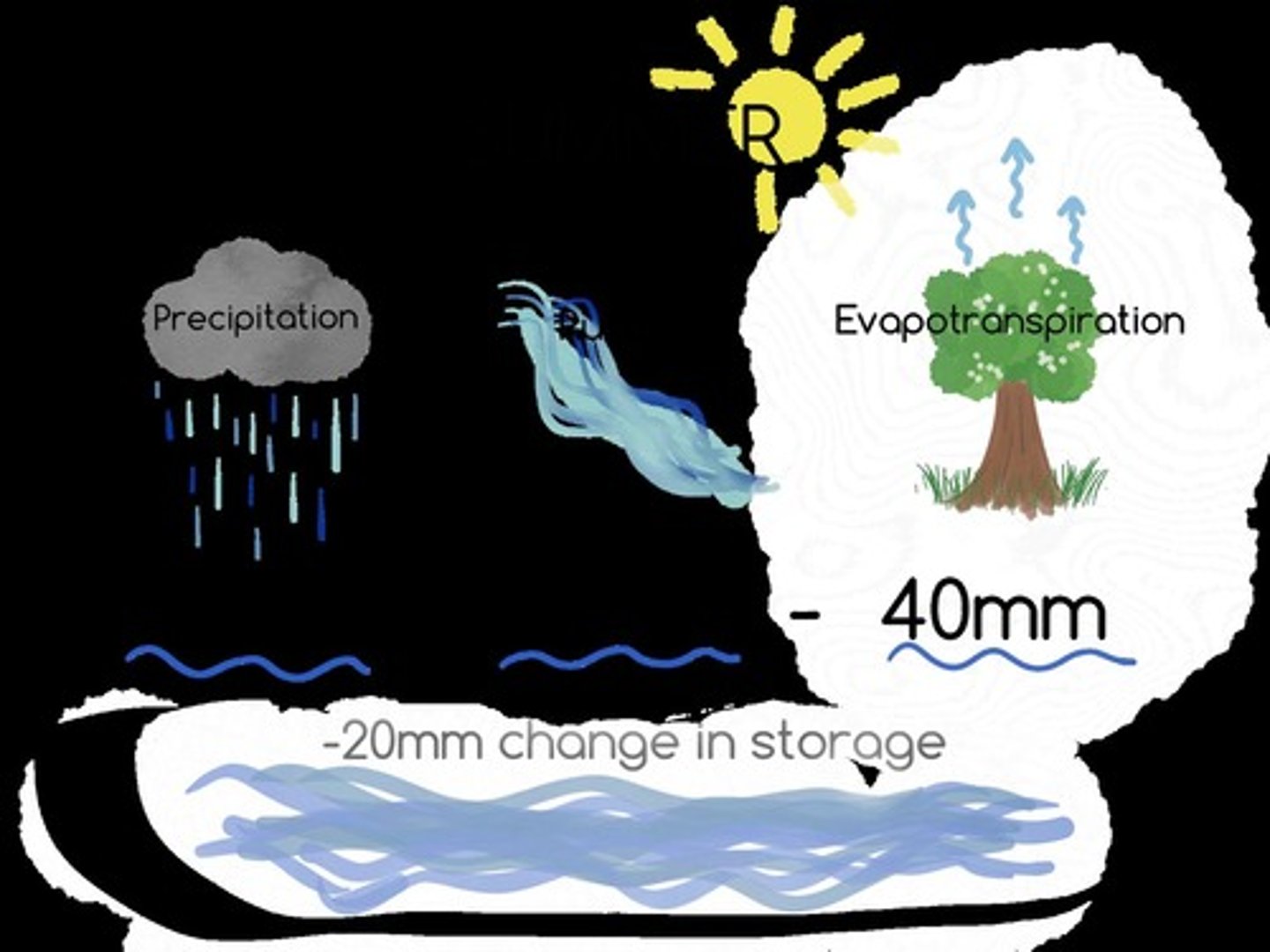
Water balance
Expresses the process of water storage and transfer in a drainage basin system.
Water balance formula
Precipitation = Total Runoff + Evapotranspiration +/- (change in) Storage.
Impact of deforestation
Less interception by trees increases surface runoff and decreases soil water storage.
Impact of storm events
Large amounts of rainfall quickly saturate the ground to its field capacity.
Field capacity
The maximum amount of water soil can hold before excess water drains away.
Evapotranspiration
The sum of evaporation and plant transpiration from the Earth's surface to the atmosphere.
Seasonal variations
Changes in water balance affected by temperature and precipitation fluctuations.
Change in storage
Affected by the amount of precipitation in comparison with the amount of runoff and evapotranspiration.
Storm Events
Large amounts of rainfall quickly saturate the ground to its field capacity. No more water can infiltrate the soil, increasing the surface runoff.
Surface Runoff
Water that flows over the ground surface when the soil is saturated and cannot absorb any more water.
Prolonged Rainfall
Rainfall that occurs over an extended period, allowing for better infiltration and groundwater recharge.
Infiltration
The process by which water enters the soil from the surface.
Percolation
The movement of water through the soil layers into groundwater stores.
Groundwater Stores
Underground reservoirs of water that are replenished by rainfall and surface water.
Seasonal Changes
Variations in environmental conditions and processes that occur in different seasons.
Spring Vegetation Growth
Increased plant growth leading to more interception of rainfall by vegetation.
Summer Rainfall
Typically less rain in summer, leading to harder, more impermeable ground.
Autumn Rainfall
Seasonally more rainfall occurs with less vegetation growth, leading to less interception.
Winter Ground Conditions
Frozen ground may be impermeable, encouraging runoff, while snow discourages runoff and slows water cycle processes.
Pastoral Farming
Agriculture related to livestock, which can reduce soil infiltration due to trampling.
Arable Farming
Agriculture related to crops, where ploughing increases infiltration but drainage ditches can increase runoff.
Hillside Terracing
A farming technique that increases surface water storage and decreases runoff.
Irrigation
The movement of water by human intervention, which can lead to groundwater depletion.
Urbanisation
The development of roads and buildings with impermeable surfaces that reduce infiltration and increase surface runoff.
Green Roofs
Vegetative roofs that help reduce impermeable surfaces and tackle urban flooding.
Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems (SUDS)
Systems designed to manage surface water runoff in urban areas using natural processes.
Soil Water Budget
The annual balance between inputs and outputs in the water cycle and their impact on soil water storage.
Field Capacity
The maximum possible level of storage of water in the soil, beyond which flooding may occur.
Water Surplus
A condition where there is greater input from precipitation than output from evapotranspiration.
Deciduous Trees
Trees that lose their leaves seasonally, affecting photosynthesis and soil moisture levels.
Evapotranspiration
The combined process of evaporation and transpiration from the land and plants.
Soil Permeability
The ability of soil to transmit water, which affects infiltration and runoff.
Potential evapotranspiration
The amount of water that could evaporate and transpire from a given area, depending on the temperature and humidity.
Water surplus
A condition where the amount of water available exceeds the amount of water being used or evaporated.
Water deficit
A condition where the amount of water available is less than the amount needed, often due to prolonged dry conditions.
Global water cycle
The continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
Oceans
The largest store of water, containing 97% of global water.
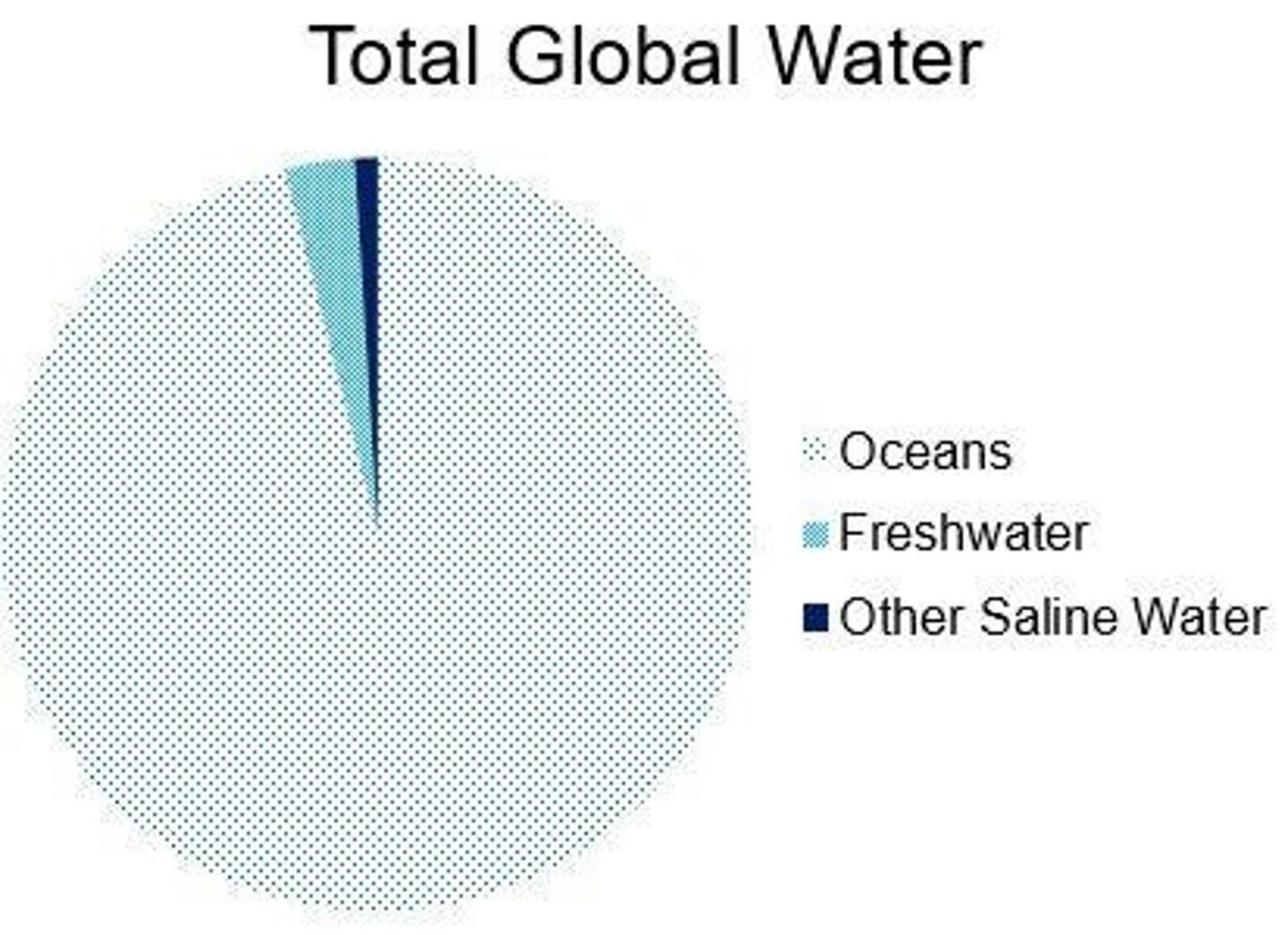
Freshwater
Water that has low concentrations of dissolved salts, making up only 2.5% of global water stores.
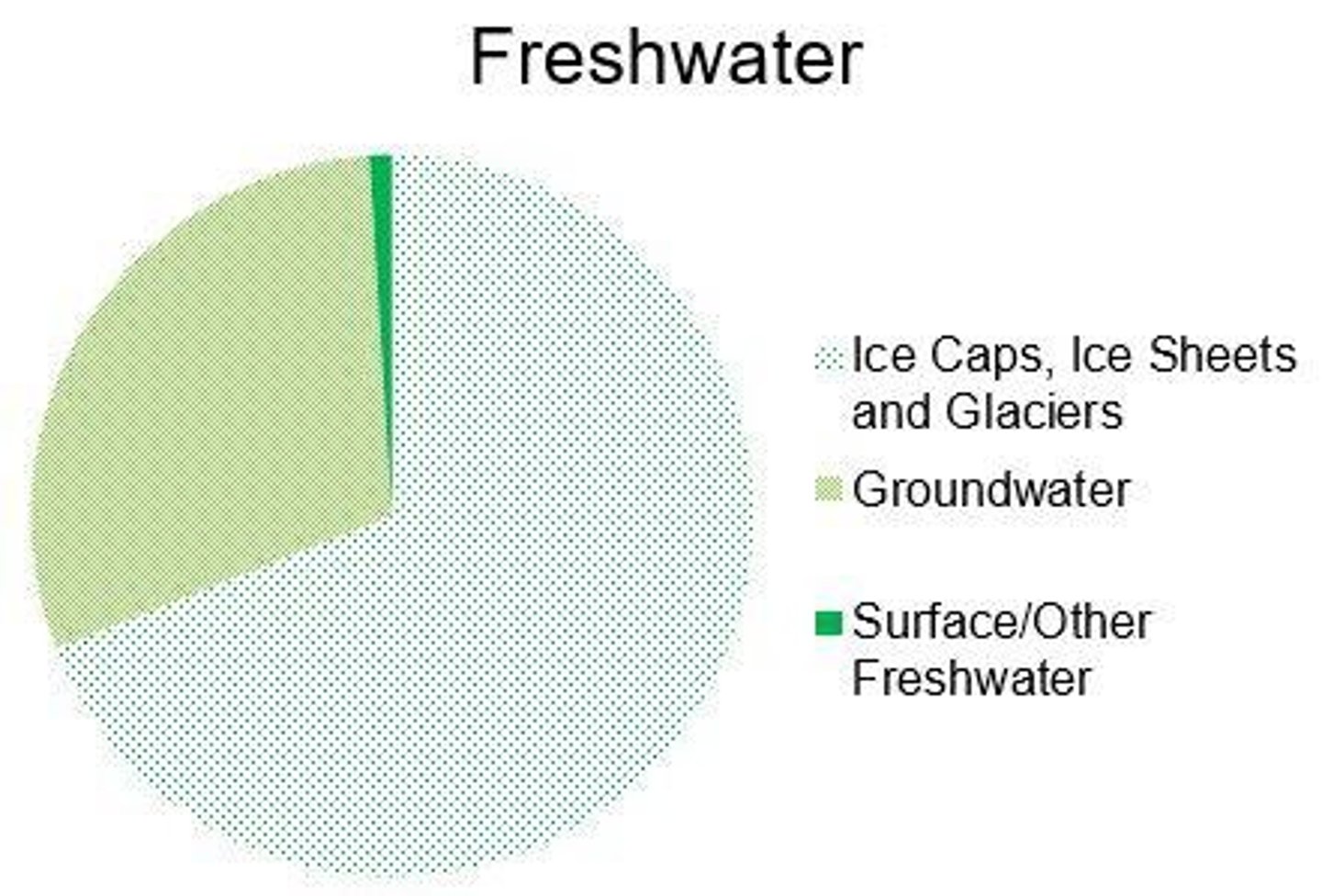
Glaciers, ice caps, and ice sheets
These make up 69% of the freshwater available on Earth.
Groundwater
Water that is stored underground, accounting for 30% of the Earth's freshwater.
Surface freshwater
Only accounts for around 1% of global water stores, including lakes, rivers, and wetlands.
Hydrosphere
Any liquid water on Earth, including oceans, rivers, and lakes.
Lithosphere
Water stored in the Earth's crust and upper mantle.
Cryosphere
Any water that is frozen, including glaciers and ice caps.
Atmosphere
Water vapor present in the air.
Aquifers
Underground water stores that are unevenly distributed globally.
Shallow groundwater aquifers
Can store water for up to 200 years.
Fossil aquifers
Deeper aquifers that may last for 10,000 years, formed during wetter climatic periods.
Glaciers
May store water for 20-100 years.
Lakes
Can store water for 50-100 years.
Seasonal snow cover
Stores water for 2-6 months.
Soil water
Acts as a temporary store, holding water for 1-2 months.
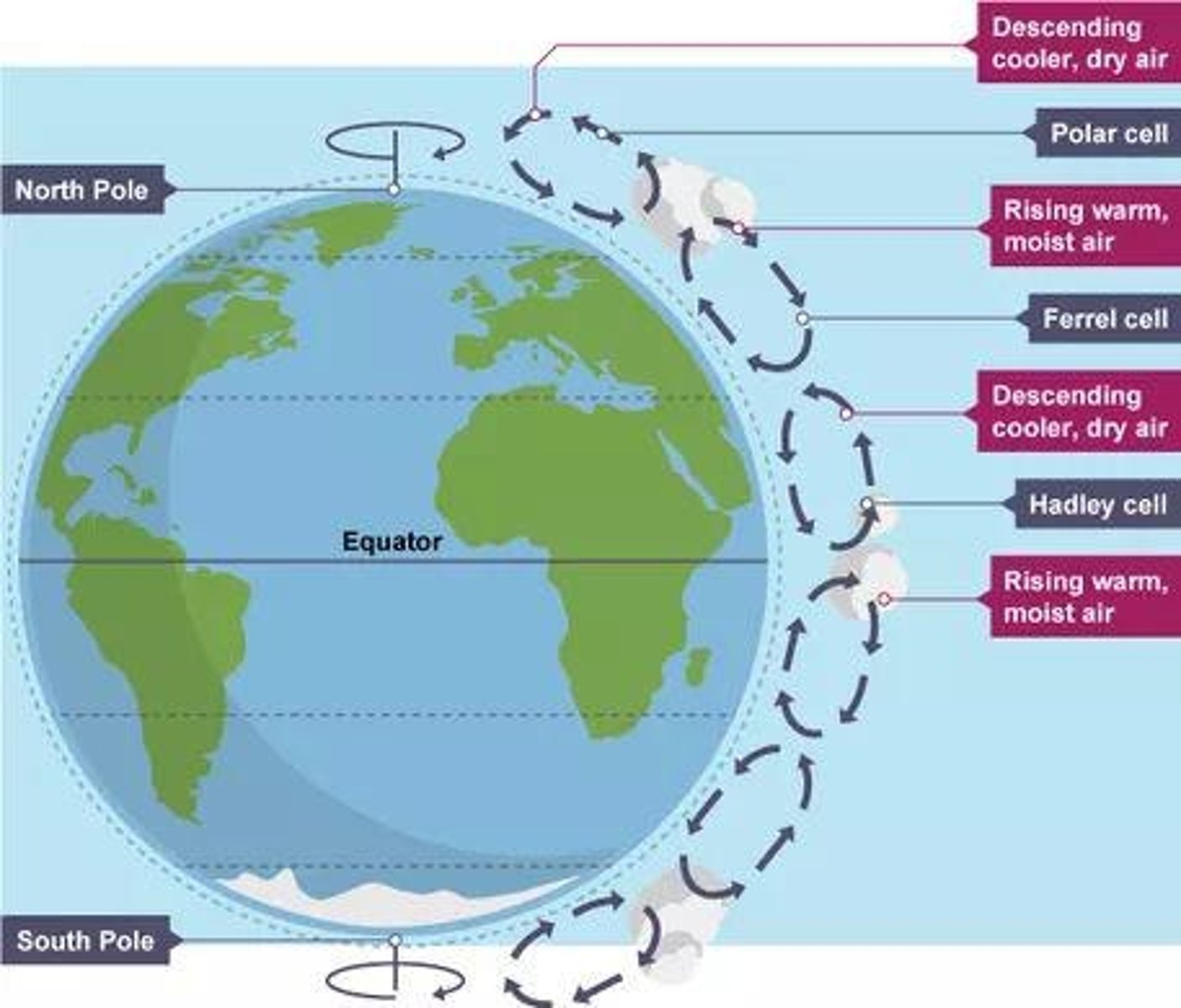
Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)
A low pressure zone on the equator that has very heavy rainfall and is responsible for monsoons.
Convectional rainfall
Rainfall that occurs due to the rising of warm air, leading to precipitation.
Jet-stream
A fast flowing air current that influences weather patterns.
Seasonal changes in the water cycle
Include less precipitation and more evapotranspiration in summer due to higher temperatures.
Storm events
Cause sudden increases in rainfall, leading to flooding and replenishment of some water stores.
Droughts
Lead to depletion of major water stores and decreased activity of flows in the water cycle.
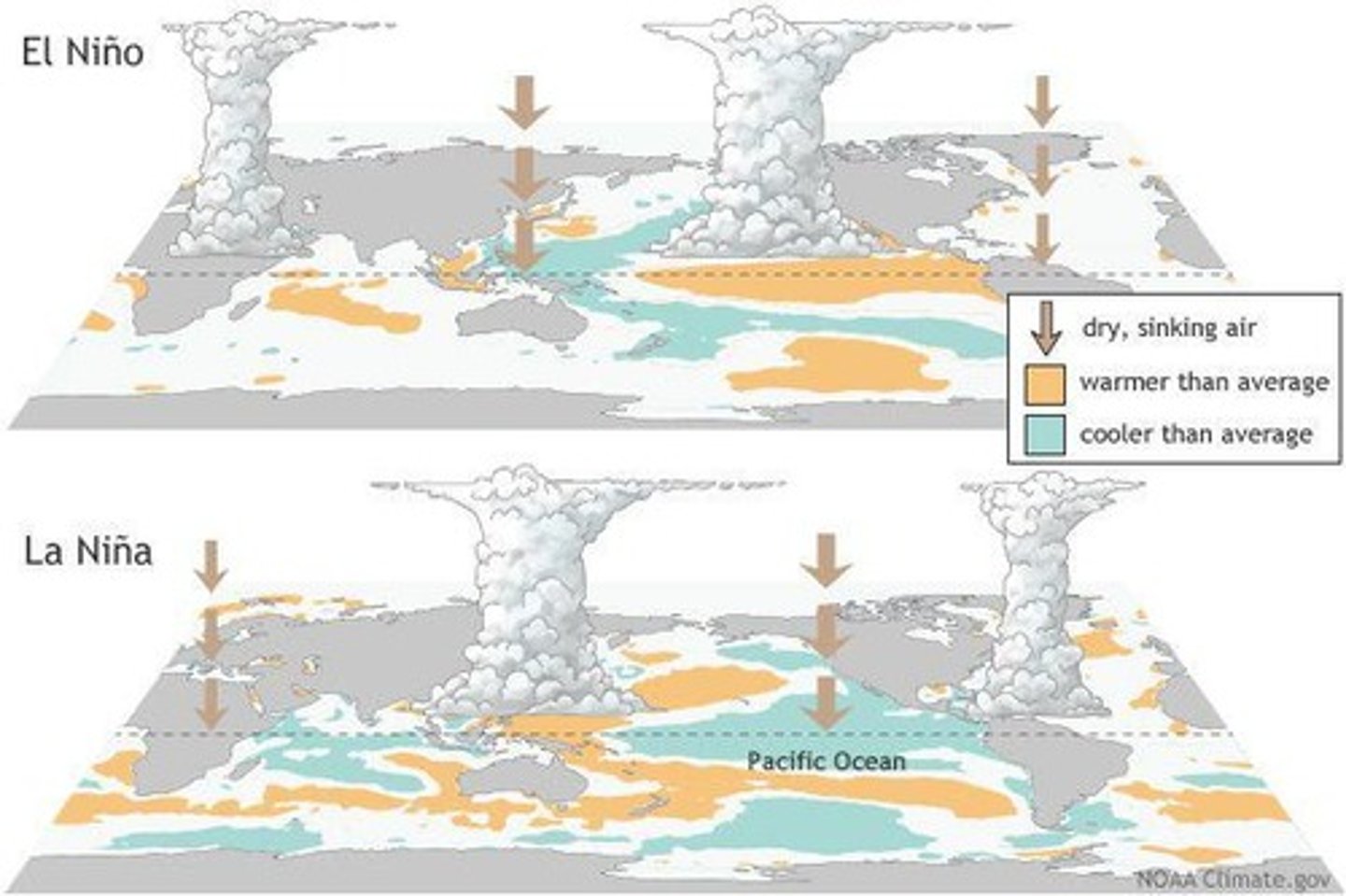
El Niño effect
Occurs every 2-7 years and causes warm temperatures in a predictable way.
La Niña effect
Occurs every 2-7 years and causes cooler temperatures in a predictable way.