Immunology 26 | Immune Assays
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Which test counts the numbers of RBCs and WBCs?
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
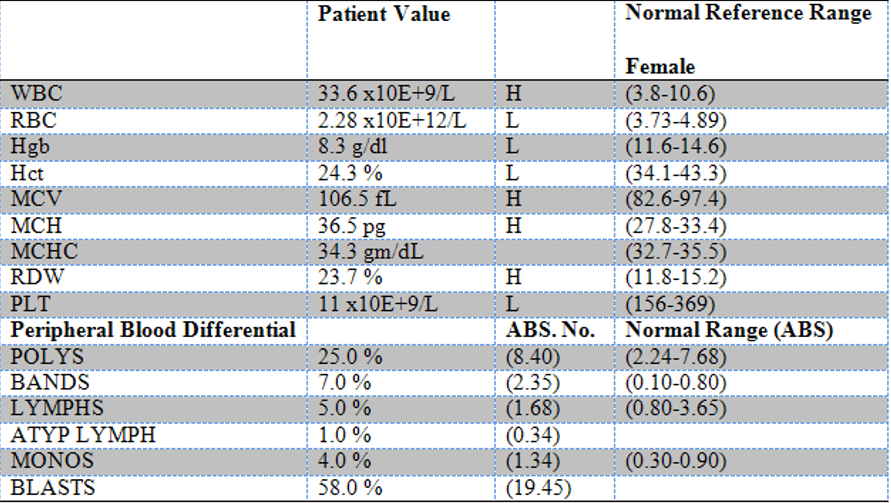
Which test determines the percentages of white blood cells?
CBC with differential
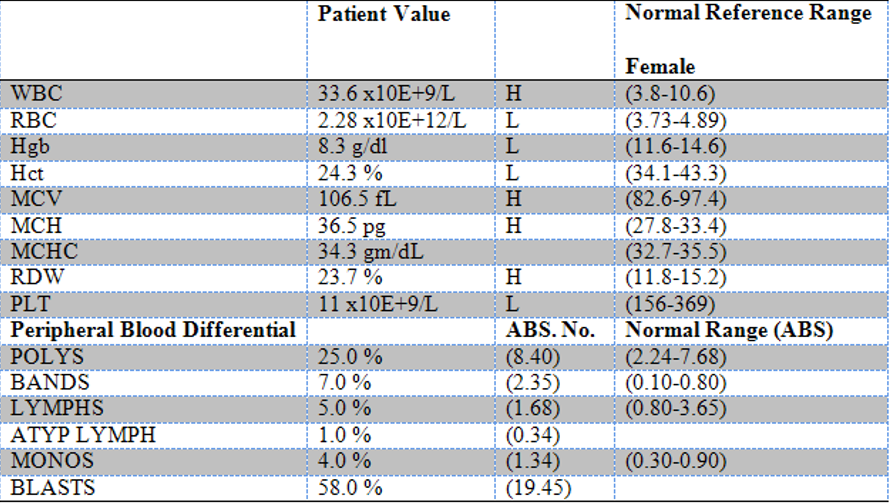
How are serum proteins like immunoglobulins (antibodies), detected?
Via the lab technique, serum electrophoretogram that separates blood proteins into different peaks based on their size and charge.
Each peak corresponds to a specific group of proteins, which can help diagnose various health conditions.
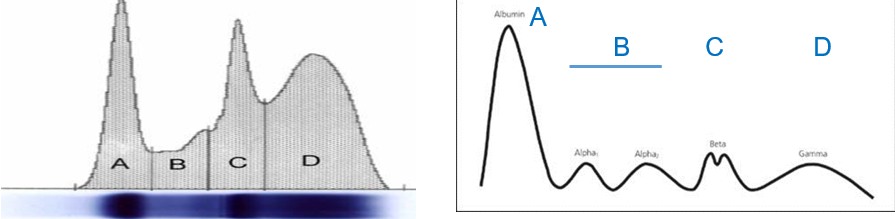
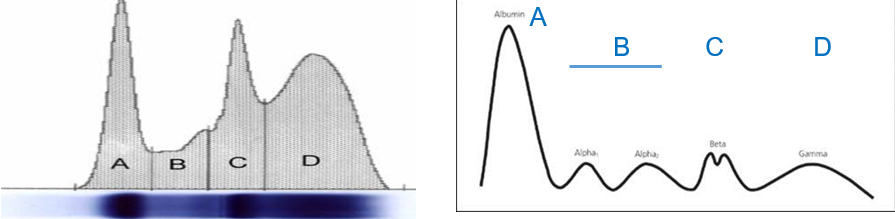
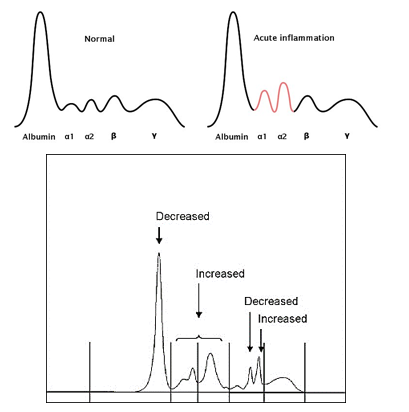
Describe all 4 peaks of serum proteins detected in serum electrophoretograms
First peak (Albumin Peak): Represents albumin, the most abundant protein in the blood. High levels (hyperalbuminemia) may indicate dehydration, while low levels (hypoalbuminemia) suggest that other proteins, such as antibodies, are elevated or that albumin production is reduced.
Second peak (α peak): Represents acute phase proteins, which increase during early stages of inflammation as part of the body’s response to injury or infection.
Third peak (β peak): Mainly represents IgM, an antibody produced in the early stages of an immune response. Some acute phase proteins may also be included here.
Fourth peak (γ peak): Mainly represents IgG, an antibody produced in later stages of the immune response, indicating a more established immune reaction.
Note: Remember that the second peak encompasses both α1 and α2
What are positive and negative acute phase proteins
Positive and negative acute phase proteins are types of proteins whose levels in the blood change in response to inflammation.
Positive acute phase proteins: Their levels increase in response to inflammation. They are produced by the liver as part of the body's response to injury or infection. Examples include C-reactive protein (CRP) and fibrinogen. These proteins help the body fight infection and repair tissues.
Negative acute phase proteins: Their levels decrease during inflammation. These proteins are usually produced in the liver but their production is reduced when inflammation is present. Examples include albumin and transferrin. Their decrease can help the body redirect resources to fight inflammation.
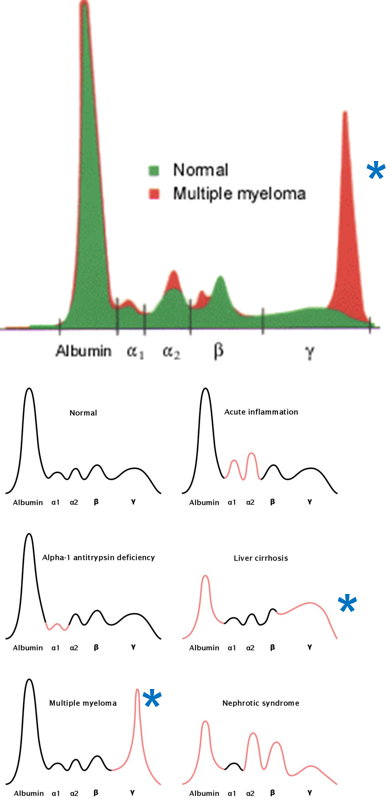
What could an elevated γ peak indicate in an abnormal serum electrophoretogram of an acute phase response?
An elevated γ peak indicates an increase in IgG, which may suggest the immune system has switched to producing IgG antibodies due to re-exposure to an antigen.
This rise in IgG could also be related to autoimmune diseases, where the body produces excess IgG antibodies that attack its own tissues.
Also in multiple myeloma, abnormal plasma cells produce large amounts of a single type of antibody, often IgG, leading to a pronounced elevation in the γ peak. This overproduction of IgG is a hallmark of the disease.
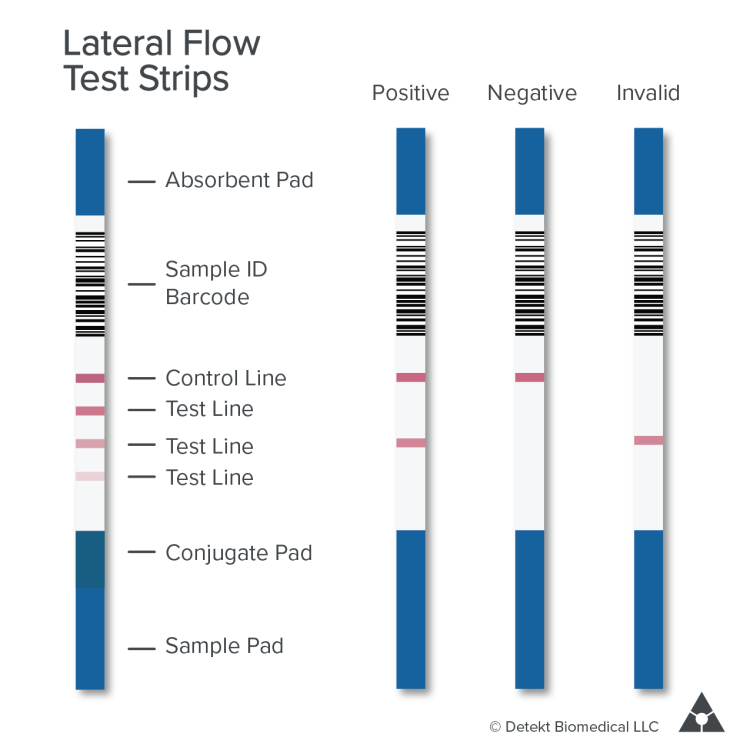
What are the common methods used in detecting antibodies or antigens via qualitative analysis?
Qualitative (Is it present?): These methods determine whether the target substance is present.
Lateral flow assays: Quick tests to check for the presence of a substance (e.g., pregnancy tests).
Western blot: Detects specific proteins in a sample.
Immunocytochemistry or immunohistochemistry: Identifies proteins in cells or tissues using antibodies.
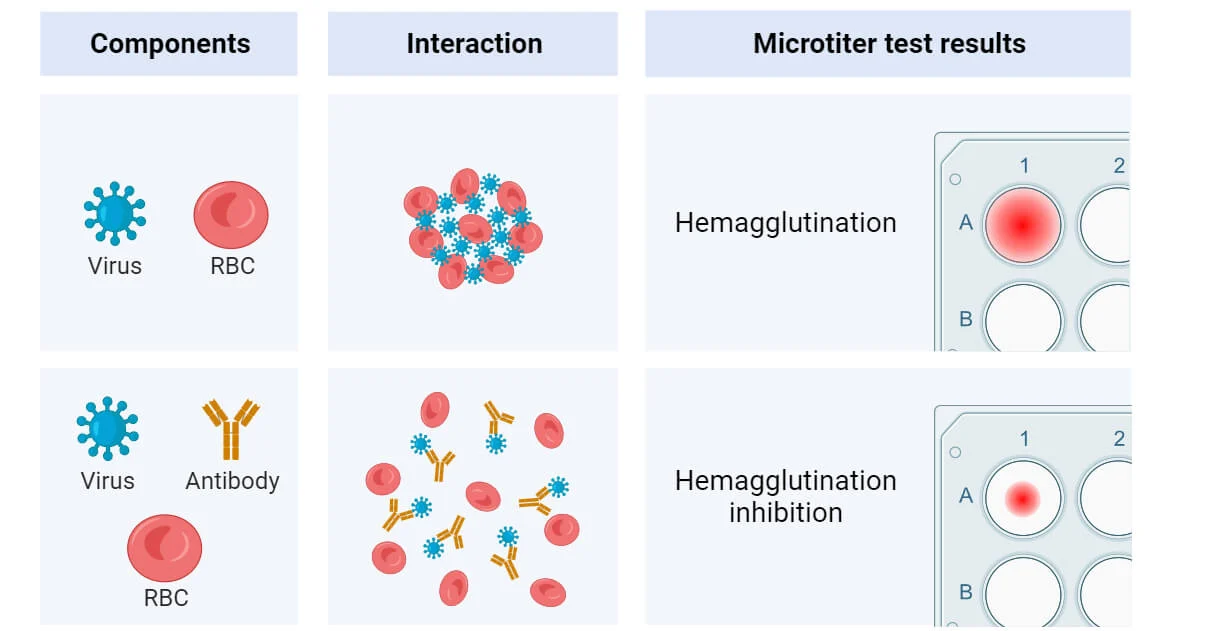
What are the common methods used in detecting antibodies or antigens via semi-quantitative analysis?
Semi-quantitative (How much, roughly?): These methods estimate the concentration of a substance but not exact amounts.
Agglutination: Detects antigen-antibody reactions by clumping particles.
Immunodiffusion: Measures antibody or antigen levels based on how they spread through a gel.
What are the common methods used in detecting antibodies or antigens via quantitative analysis?
Quantitative (Exact amount): These methods provide precise measurements of substances.
Enzyme immunoassay and Enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA): Measure specific antibodies or antigens with high sensitivity.
Immunofluorescent assay: Uses fluorescent labels to quantify proteins or antibodies in a sample.
Differences:
Detection method: ELISA uses enzymes and color changes; immunofluorescence uses fluorescent dyes and light.
Quantification vs. localization: ELISA is better for quantifying the amount of antigen/antibody; immunofluorescence is better for visualizing the location of antigens in cells or tissues.
Type of sample: ELISA often uses liquid samples (like blood), while immunofluorescence is commonly applied to tissue sections or cell samples.
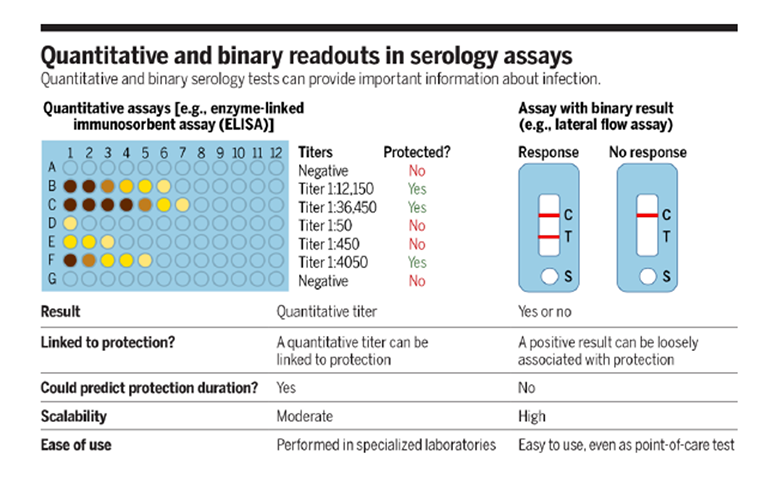
What is used as the gold standard for detecting anti-nuclear antibodies?
Immunofluorescent assay as it allows for the precise visualization of antibodies binding to the nucleus of cells using fluorescent markers.
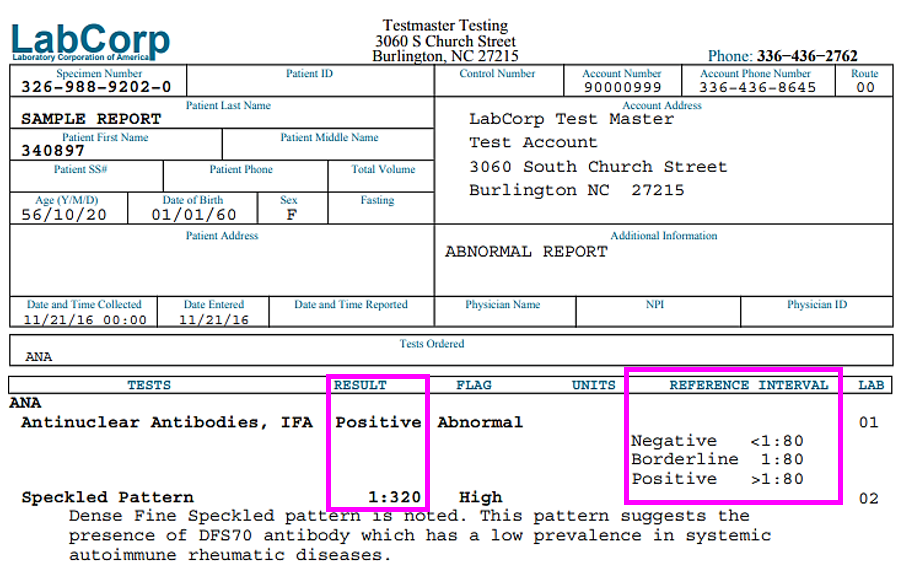
What is buoyant density?
Refers to the density of a substance when it is in equilibrium with a fluid of a different density. It's often used in centrifugation techniques, where particles or cells are separated based on their buoyant densities.
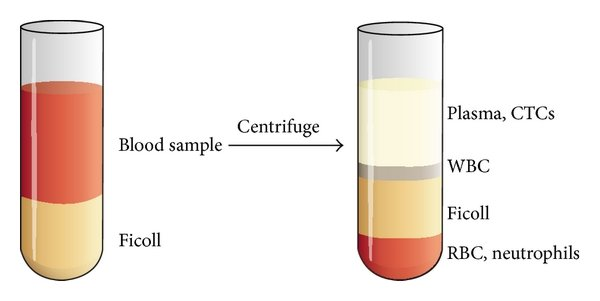
What does “humanizing an antibody” refer to?
Monoclonal antibodies are used for treating diseases, diagnostics, research, and prevention. Humanizing an antibody involves modifying a mouse-derived monoclonal antibody to closely resemble human antibodies, reducing the risk of immune reactions in patients. This process includes replacing mouse sequences with human ones while maintaining the antibody's target specificity. The humanized antibody is then tested for effectiveness and safety.
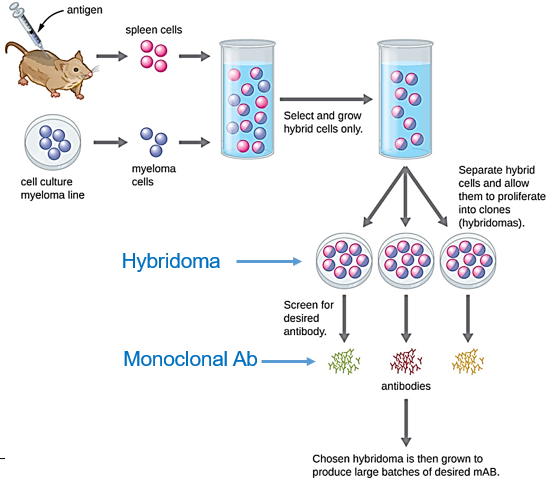
Describe the immunologic technique of immunofluorescence and provide examples.
Purpose: Detection and localization of antigens in tissues or cells using fluorescent-labeled antibodies.
Example: Viral antigens in a biopsy (e.g., rabies, herpes simplex virus).
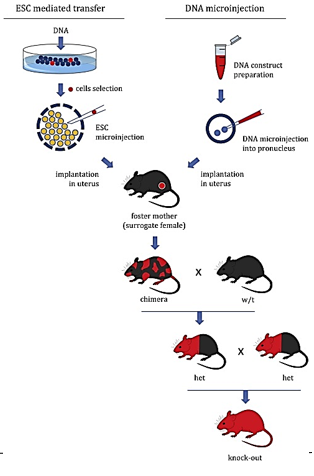
What are the mice that are genetically modified and used for research?
Transgenic mice. The process involves either adding (knock-in) or deleting (knock-out) specific genes:
How are transgenic mice created?
Gene Insertion/Deletion: A cloned gene is inserted into the genome of fertilized mouse eggs, or a gene is inactivated by deleting or inserting a sequence to prevent its expression.
Implantation and Birth: The modified eggs are implanted into a female mouse, resulting in the birth of Tg pups.
Inheritance: The altered genetic sequences are passed to offspring following Mendelian inheritance patterns.
Breeding: Mice are cross-bred to achieve homozygosity for the genetic modification, ensuring that all offspring carry the altered gene.
What is a lymphocyte proliferation assay?
Measures how well lymphocytes can multiply in response to a stimulus.
The procedure involves isolating lymphocytes, culturing them with a stimulant (like a mitogen), and then adding a reporter (radioactive thymidine or a dye) to track cell division. The uptake of the reporter or the amount of cytokine produced is measured to assess the proliferation rate.
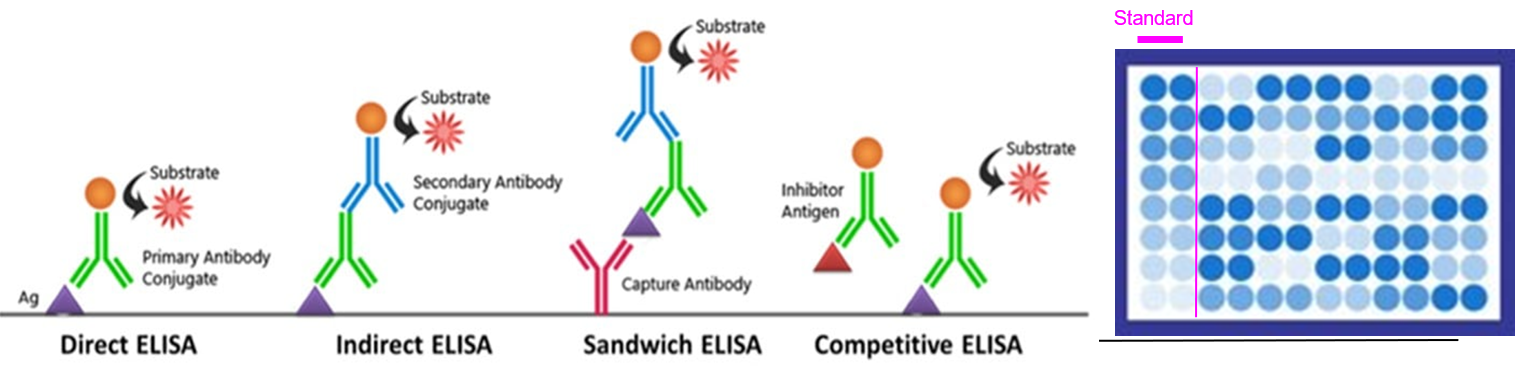
Describe the immunologic technique of ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) and provide examples.
Purpose: Detect and quantify specific antigens or antibodies in a sample. It involves attaching an antigen or antibody to a surface (usually a plate), then adding a specific antibody or antigen linked to an enzyme. A substrate is added, which reacts with the enzyme to produce a measurable color change, indicating the presence and amount of the target substance. Video
Example: Viral antigens in a biopsy (e.g., rotavirus in stool samples, rabies, herpes simplex virus).
Describe the immunologic technique of Immunofluorescence Flow Cytometry and provide examples.
Purpose: Analysis of cell populations for antigen-positive cells; useful for immunophenotyping (identifying cell types based on surface markers).
Example: Identifying immune cell types in blood samples (e.g., CD4+ cells in HIV).
Describe the immunologic technique of Hemagglutination Inhibition and provide examples.
Purpose: Quantitation of antigens or antibodies in a sample.
Example: Detecting viral antigens (e.g., rotavirus) or antibodies (e.g., anti-HIV).
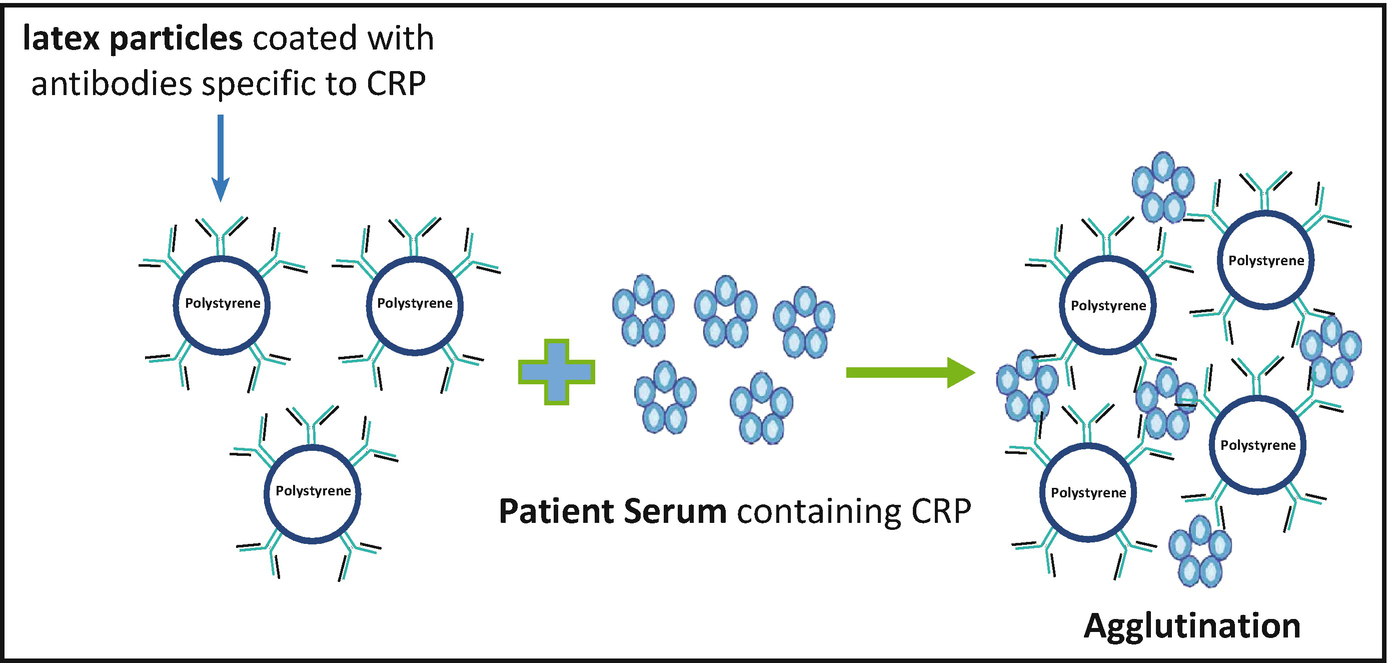
Describe the immunologic technique of Latex Agglutination and provide examples.
Purpose: Quantitation and detection of antigens or antibodies through visible clumping.
Example: Detection of rheumatoid factor; fungal antigens; streptococcal antigens (e.g., group A strep).
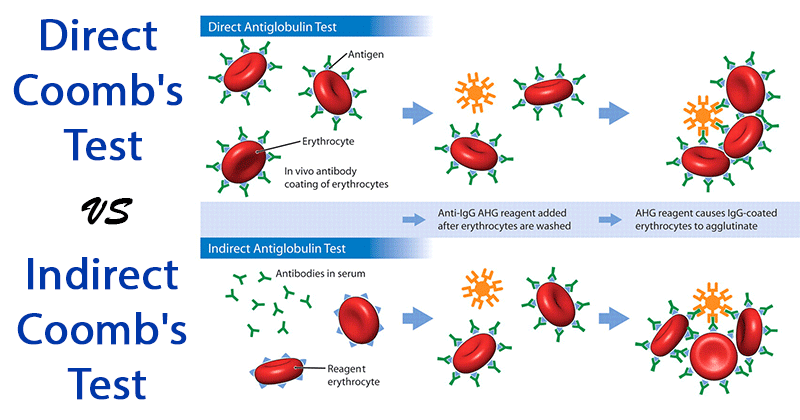
What are the two agglutination tests used to detect antibodies against viruses or red blood cells?
Direct Coombs test: Checks for antibodies already bound to RBCs, indicating autoimmunity affecting the RBCs.
Indirect Coombs test: Detects antibodies not yet bound to RBCs, used to find circulating autoantibodies in the blood.
What are monoclonal antibodies?
Laboratory-made molecules designed to bind to specific targets, such as proteins or cells. They are produced by creating identical copies (clones) of a single type of immune cell, which produces a specific antibody.
They can be used for various purposes, including diagnosing diseases, treating conditions like cancer or autoimmune disorders, and targeting specific cells or proteins in research.
Video
What is flow cytometry?
A technique used to analyze and sort cells or particles as they flow in a stream through a laser or other detection system. It measures various characteristics, such as size, shape, and fluorescence, allowing researchers to identify and quantify different types of cells or particles in a sample.
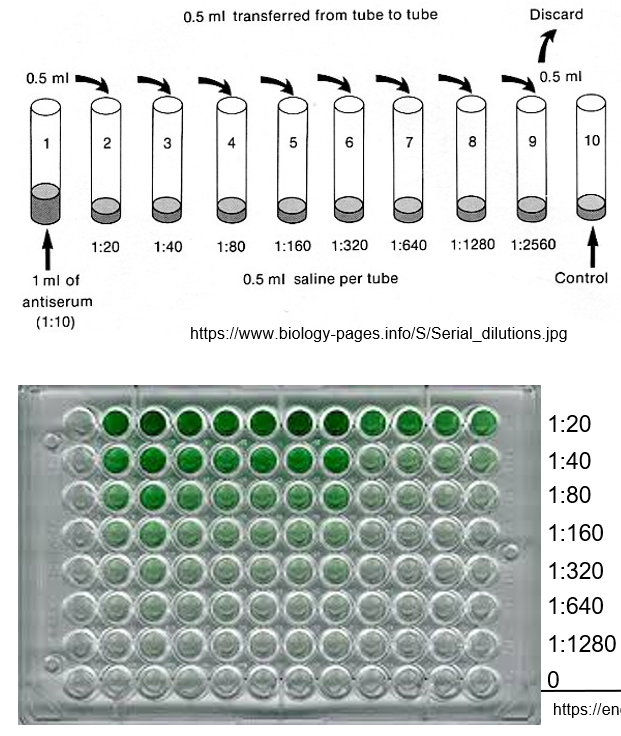
How does ELISA determine the concentration of antibodies in a patient's serum using dilution?
By measuring how much the patient’s serum needs to be diluted to detect the antibodies.
Principle: The higher the concentration of antibodies, the less dilution is needed to reach a detectable level.
Titer Reporting: The dilution level that produces a positive result is reported as the patient’s titer, indicating the amount of antibodies present.

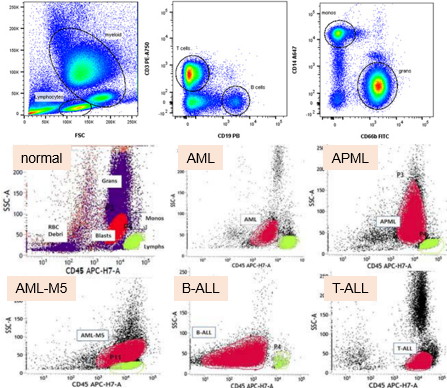
Describes methods for isolating and identifying specific types of white blood cells
Density Gradient Centrifugation: This method separates cells based on their size and density. A sample with mixed cells is layered onto a solution with varying densities. During centrifugation, cells move to the density layer that matches their own, allowing separation into different layers based on cell density.
Flow Cytometry (FACS) and Magnetic-Activated Cell Sorting (MACS): These methods use specific markers to identify and isolate cells. In FACS, cells are labeled with fluorescent antibodies and sorted based on fluorescence. In MACS, cells are tagged with magnetic beads and separated using a magnetic field. This allows for targeted isolation of cells based on specific antigens or markers.
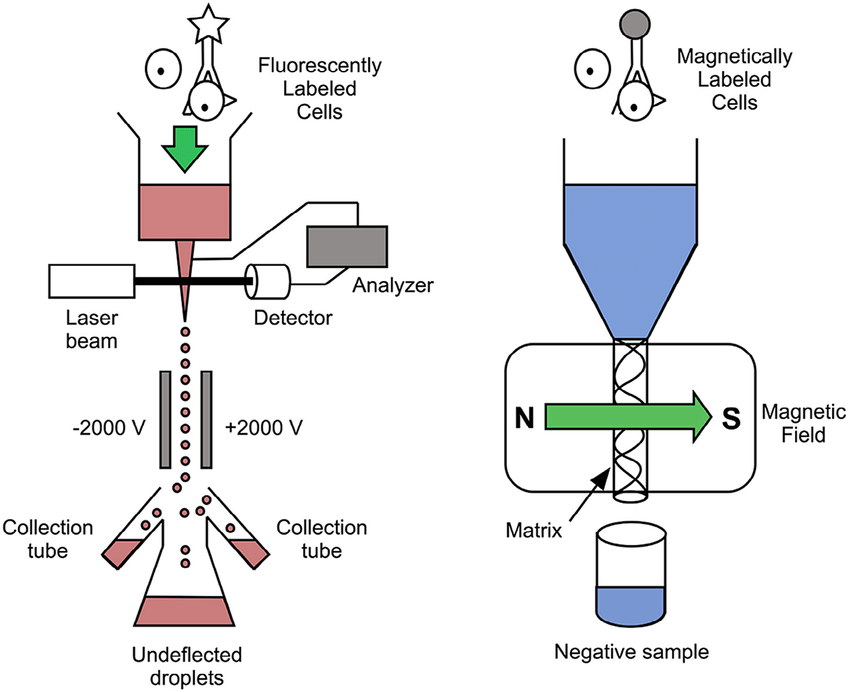
What is immunophenotyping?
Immunophenotyping is the process of identifying and classifying cells based on specific markers or proteins they express.
For example, we can identify and sort cells based on specific markers, such as CD3 or CD19.
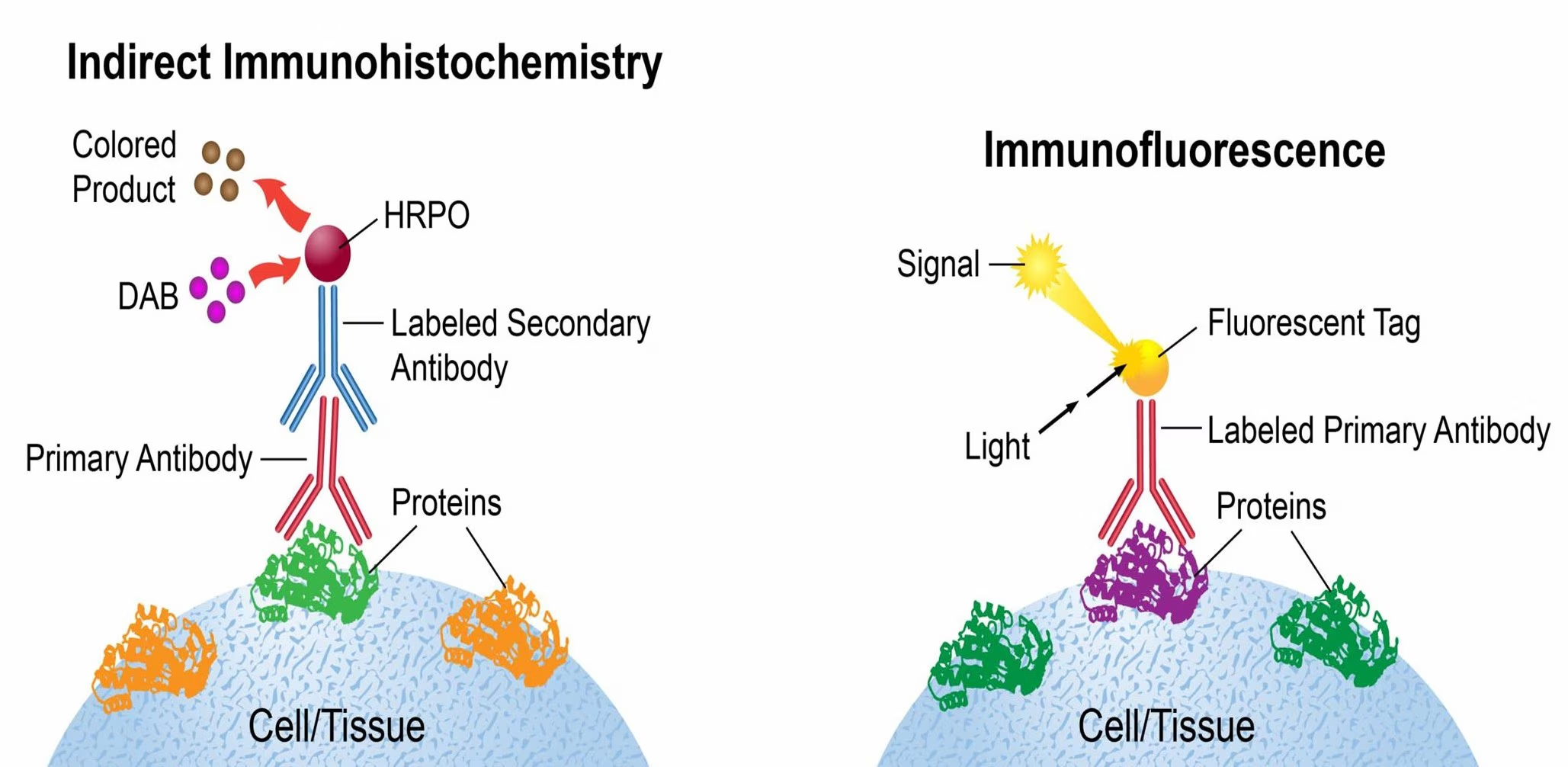
What is the difference between immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry?
Immunohistochemistry: Uses antibodies to label and visualize specific cells or proteins within tissue sections.
Immunocytochemistry: Uses antibodies to label and visualize specific parts of individual cells that are isolated or grown in culture.
Both techniques can use colorimetric or fluorescent labels to detect the antibodies.
How can the activity of phagocytic cells be measured?
Using fluorescent beads:
Phagocytic cells are (consumed) exposed to small beads labeled with a fluorescent molecule.
After incubation, the number of beads taken up by the cells is measured.
The cells can be analyzed using flow cytometry or fluorescent microscopy to count and visualize the beads within the cells.
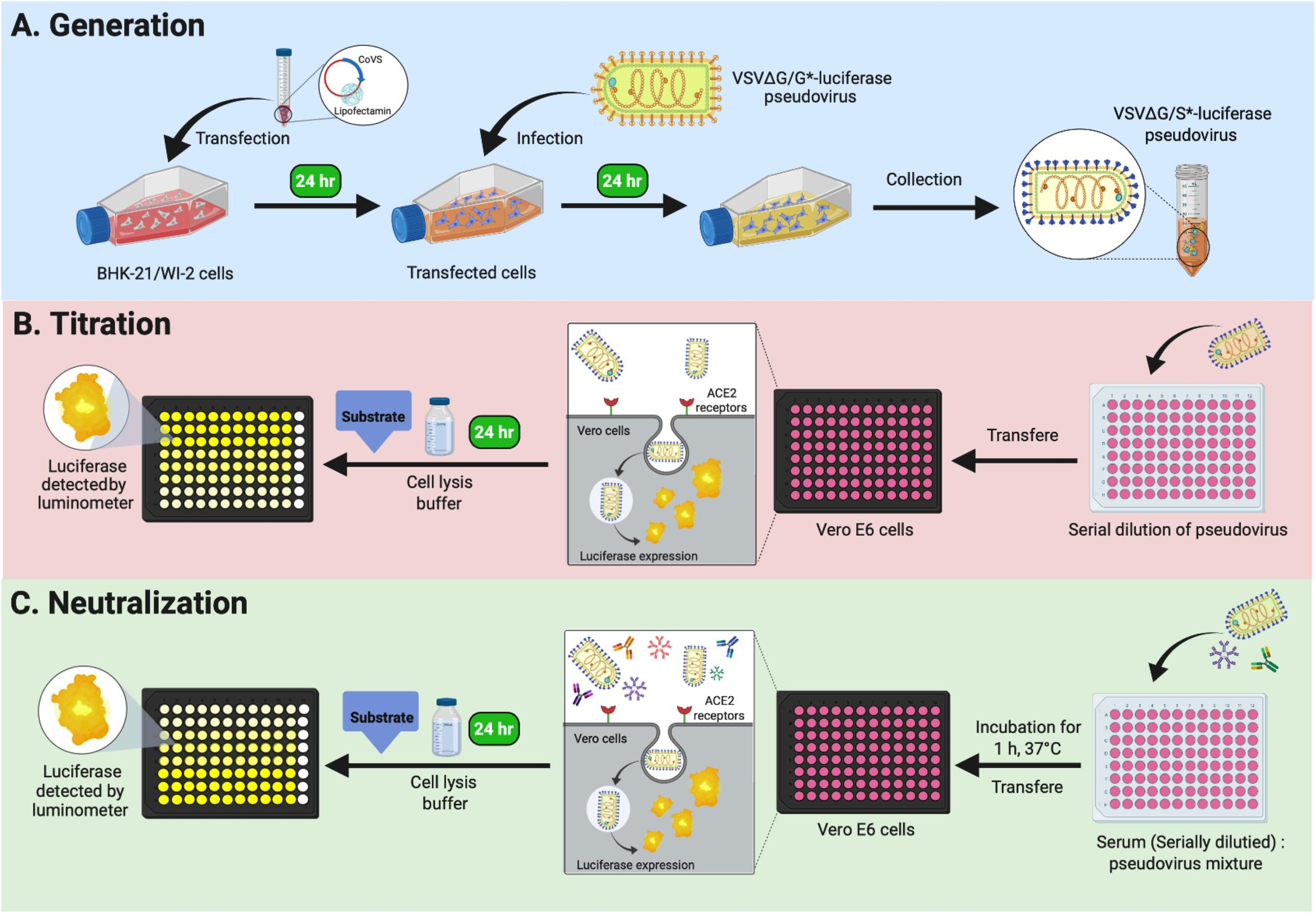
What is a neutralization assay?
Measures how effectively antigen-specific antibodies inhibit the target, such as a virus. If the antibodies are neutralizing, the assay will show reduced activity, indicated by lower virus titers or decreased toxic effects.
What measures the oxidative burst of phagocytes? (the rapid production of reactive oxygen species by phagocytes)
DCF-DA Assay: The gold standard for measuring this activity.
DCF-DA (2',7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate) is a substrate that enters cells and is converted to a fluorescent form by ROS.
Process: The substrate diffuses into the cell and is cleaved by hydroxyl, peroxyl, or other ROS.
Measurement: The fluorescence produced is proportional to the amount of ROS generated by the phagocytes.
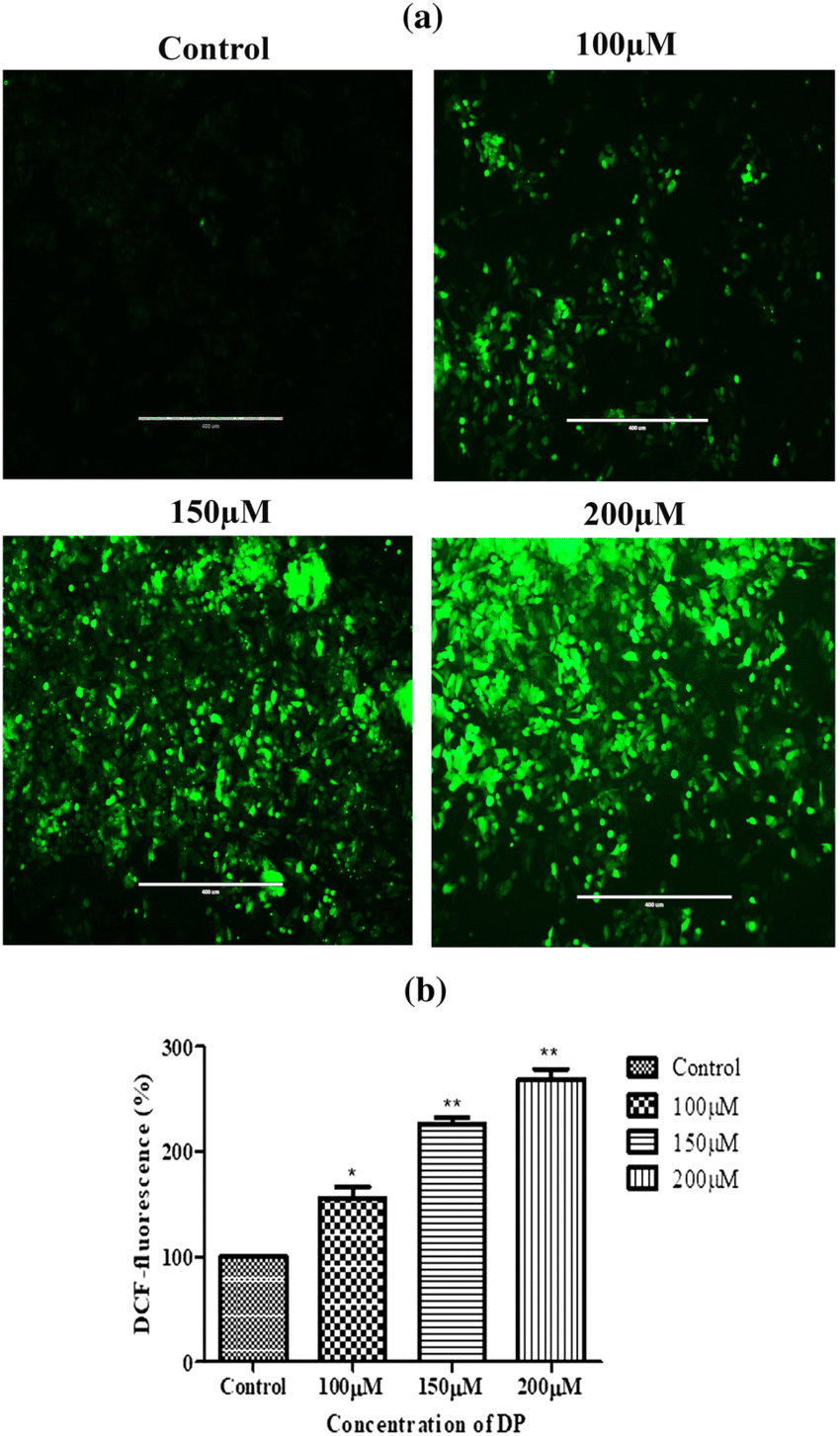
A patient’s serum electrophoresis results show a pronounced increase in the peak representing IgG. Which of the following is the most likely implication of this finding?
A. Acute inflammatory response with elevated albumin.
B. Chronic or established humoral immune response.
C. Recent infection with increased IgM levels.
D. Presence of positive acute phase proteins.
Chronic or established humoral immune response.
An increase in the IgG peak often indicates a chronic or established immune response, as IgG is typically produced in response to ongoing or past infections.
A patient’s serologic titers are reported as 1:512. What does this high titer suggest about the patient's immune response?
A. Low level of antibody response.
B. Recent exposure to an antigen.
C. Strong and sustained antibody response.
D. Acute phase of infection with initial antibody response.
Strong and sustained antibody response.
A high titer such as 1:512 indicates a robust and sustained immune response, often reflecting either a strong response to a persistent infection or previous exposure to an antigen.
Which type of assay is used to evaluate the ability of antibodies to neutralize a pathogen?
A. Complement-fixing assay.
B. Neutralization assay.
C. Isotype determination assay.
D. Immunoprecipitation assay.
Neutralization assay.
Neutralization assays test the ability of antibodies to inhibit the biological activity of pathogens, such as viruses or toxins, effectively neutralizing their harmful effects.
Which process involves creating antibodies that are specific to a single epitope and produced by a single clone of cells?
A. Polyclonal antibody production.
B. Monoclonal antibody production.
C. Phage display technology.
D. Serum electrophoresis.
Monoclonal antibody production.
Monoclonal antibodies are derived from a single clone of cells, making them specific to a single epitope, unlike polyclonal antibodies which are produced by different clones and recognize multiple epitopes.
Why is the process of “humanizing” monoclonal antibodies important in clinical applications?
A. To increase the immunogenicity of the antibody.
B. To improve the affinity of the antibody for the antigen.
C. To reduce the risk of immune rejection in human patients.
D. To enhance the antibody’s ability to cross the blood-brain barrier.
To reduce the risk of immune rejection in human patients.
Humanizing monoclonal antibodies reduces the risk of immune responses against the therapeutic antibody by making it more similar to human antibodies, thus improving safety and efficacy.
Which assay is commonly used for the qualitative detection of proteins in complex samples and provides visual results on a strip?
A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
B. Immunofluorescence assay (IFA).
C. Lateral flow assay.
D. Western blot.
Lateral flow assay.
Lateral flow assays provide a quick, qualitative result through visual detection on a strip, commonly used for rapid diagnostic tests like pregnancy tests.
A patient with suspected leukemia undergoes immunophenotyping. What does this technique help identify?
A. The specific genetic mutations in cancer cells.
B. The functional activity of immune cells.
C. The surface markers and cell types within a sample.
D. The presence of neutralizing antibodies.
The surface markers and cell types within a sample.
Immunophenotyping analyzes cell surface markers to identify and classify different cell types, crucial for diagnosing and monitoring hematologic malignancies like leukemia.
Which method uses a gradient of different densities to isolate cell subsets based on their buoyant density?
A. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS).
B. Magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS).
C. Buoyant density gradient centrifugation.
D. Immunoprecipitation.
Buoyant density gradient centrifugation.
Buoyant density gradient centrifugation separates cells based on their density, with different cell types reaching different layers in the gradient.
Which assay measures the engulfment of labeled beads to assess the phagocytic activity of immune cells?
A. Flow cytometry.
B. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
C. Phagocytosis assay.
D. Western blotting.
Phagocytosis assay.
Phagocytosis assays measure the ability of immune cells to engulf and internalize labeled beads, providing a quantitative assessment of their phagocytic activity.
A researcher wants to measure the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by immune cells. Which assay should they use?
A. DCF-DA assay.
B. ELISA.
C. Lateral flow assay.
D. Immunohistochemistry.
DCF-DA assay
The DCF-DA assay measures ROS production by using a fluorescent reporter molecule that reacts with ROS, allowing quantification of oxidative burst activity.
In which assay are isolated lymphocytes exposed to a stimulus and proliferation measured by the uptake of a reporter label?
A. Phagocytosis assay.
B. Lymphocyte proliferation assay.
C. Western blotting.
D. Immunoprecipitation.
Lymphocyte proliferation assay.
Lymphocyte proliferation assays measure cell division and proliferation in response to a stimulus by tracking the incorporation of a reporter label or other proliferation markers.
Which key step is involved in creating a transgenic mouse model for studying immunologic responses?
A. Altering the genetic sequence of a fertilized egg through recombination.
B. Administering monoclonal antibodies to pregnant mice.
C. Inactivating the gene of interest in adult mice.
D. Transferring the genetic material into differentiated somatic cells.
Altering the genetic sequence of a fertilized egg through recombination.
Transgenic mice are created by altering the genetic sequence of a fertilized egg, introducing or modifying specific genes to study their effects on immunologic responses and disease.
In an agglutination test, what is observed when antigens are detected?
A. Formation of a visible precipitate in a liquid sample.
B. Macroscopic clumping of antigen-antibody immune complexes.
C. Fluorescence emission from bound antibodies.
D. Absence of any visual reaction.
Macroscopic clumping of antigen-antibody immune complexes.
Agglutination tests detect antigens by observing the clumping of antigen-antibody complexes, which indicates a positive reaction.