IB Biology Proteins
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What are proteins made of?
- amino acids form polypeptides
- polypeptides form ————
How many amino acids are there?
20 different amino acids
Structure of general amino acid
STUDY PICTURE
-amine NH2 and carboxylic group
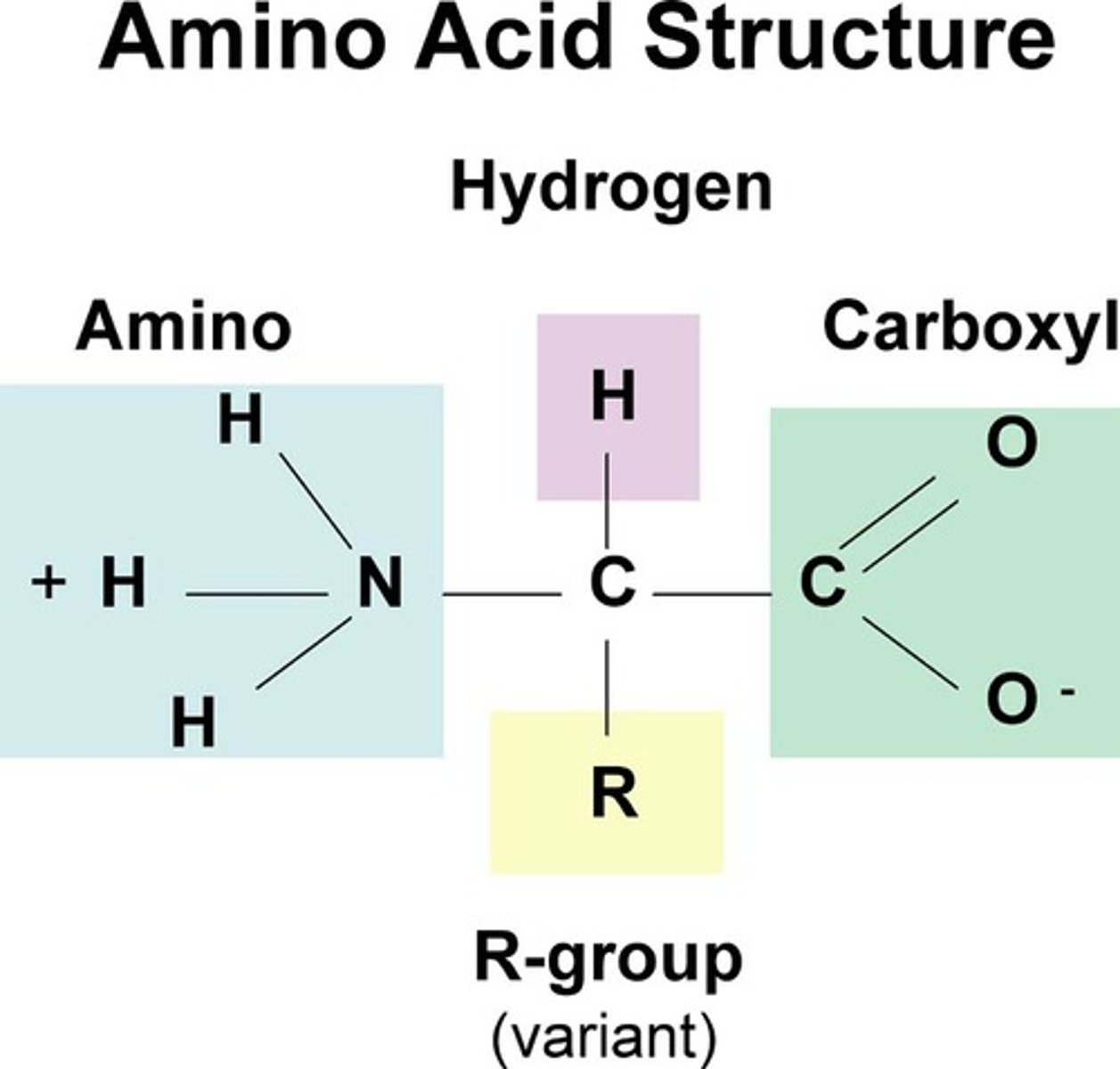
How do amino acids differ from each other?
The R-group or side group/chain makes each amino acid different
What makes proteins different from other compounds?
They will contain nitrogen
How many different R groups are there?
20 different R groups, simple H or CH3 to complex ring structures
The R group charge
- can have a positive/negative charge
- can be polar or nonpolar
***** polarity dictates shape
How many amino acids are essential and nonessential?
- 8 are essential: you MUST get them thru diet by eating protein
- 12 are nonessential: you can make them from the other 8
Amino acids are linked together
- one at a time by ribosomes
- start w dipeptides and on up to polypeptides
How many possible sequences are there for protein?
- infinite
- amino acids can be linked together in any sequence, it gives a huge range of possible polypeptides
The amino acid sequence is ———— for by ————
Coded, DNA
- genes store info in the sequence of nucleotide bases
Since there are 20 dif amino acids, it is possible to have an ————
Incredible diversity of primary structures
- diversity of polypeptides within cells of dif types of organism is relatively low
Proteins can be
Single polypeptides or many polypeptides long
changing one amino acid
May completely alter protein
Ex. Substitution of one amino acid for another in hemoglobin causes sickle cell disease
Examples of proteins
Lysozyme, integrin, collagen, hemoglobin
Lysozyme
1 polypeptide
Enzyme in nasal mucous and tears
Kills bacteria by digesting peptidoglycan in cell walls
Integrin
2 polypeptides
membrane protein used to make connections inside and outside a cell
Collagen
3 polypeptides
Structural protein in tendons, ligaments, skin and blood vessel walls
Provides high tensile strength with limited stretching
Hemoglobin
4 polypeptides
Transport protein in red blood cells
Binds O2 in lungs and releases it in tissues that need it
How are proteins made? : Formation of a dipeptide and a polypeptide
- condensation reaction/ dehydration synthesis
- peptide bond forms between the carboxyl group of the 1st amino acid and the amine group of the second amino acid
- amine group (N terminal) at one end and a carboxylic group at the other end
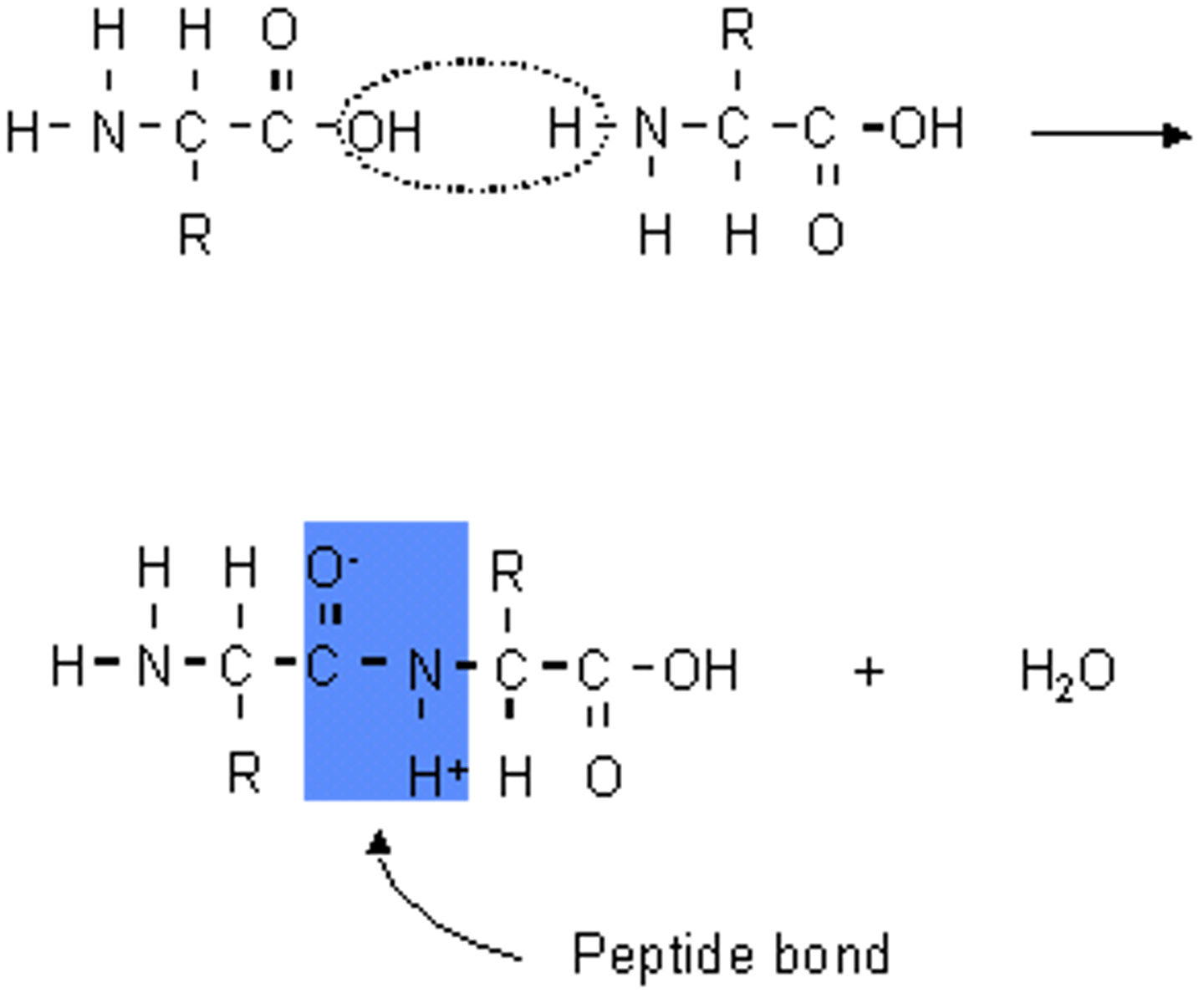
polypeptides can be --------- in the same way as ----------- (----------)
hydrolysed, polysaccharides, (need to incubate w acids)
amino acid sequence determines
3-D conformation of protein as well as polypeptides that make up protein
Levels of protein structure or conformation
primary, secondary, tertiatery, quaternary
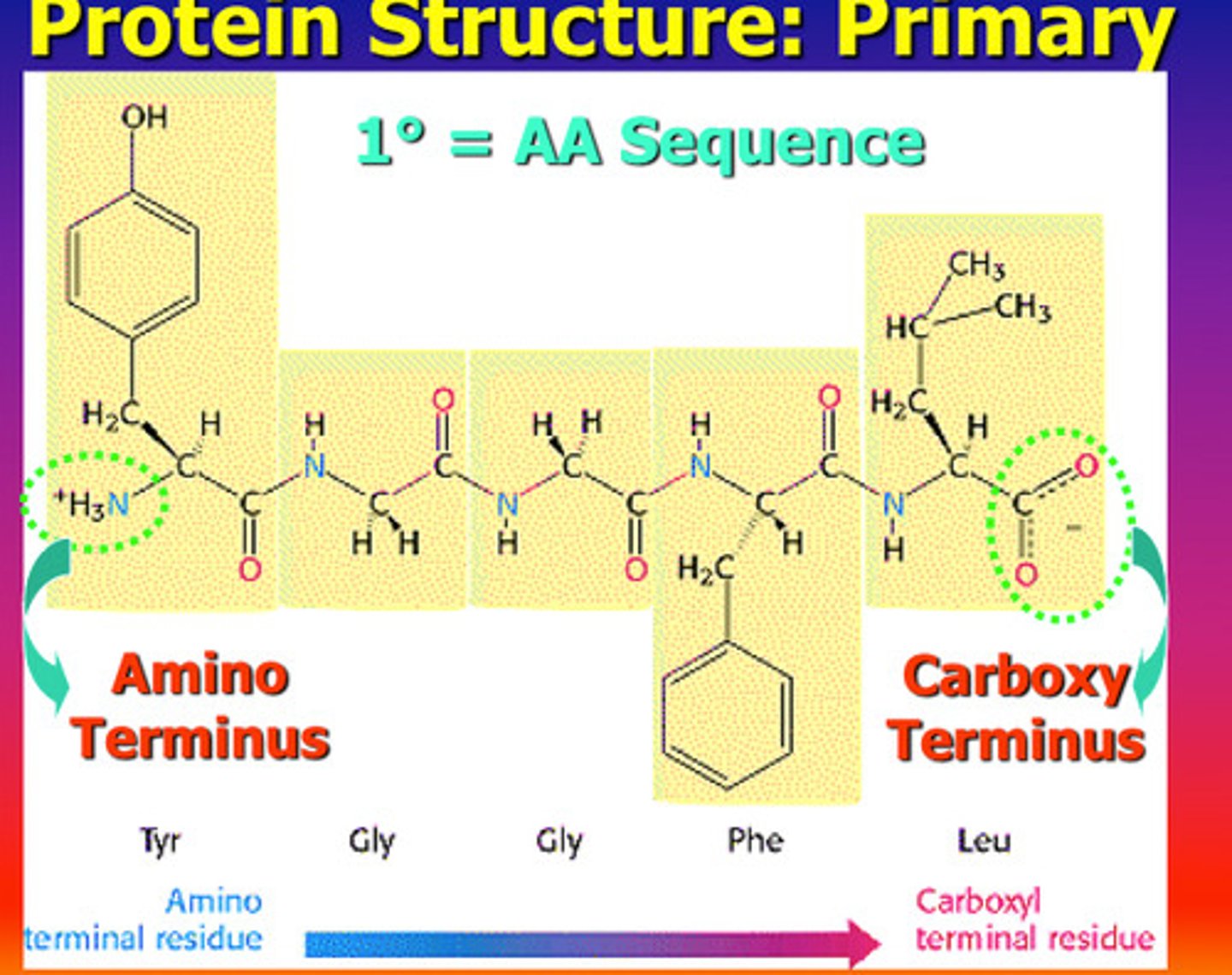
Levels of protein structure or conformation: Primary Structure
- the number and order of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
- N-C-C-N-C-C-N-C-C "backbone" to the chain
- --------- is always read from the N terminus to the COOH terminal
Levels of protein structure or conformation: Secondary Structure
- has atoms projecting from the N-C-C backbone
- O2 from carboxyl C=O and the H from the Amino N-H can form hydrogen bonds
- does NOT involve R-groups
3 forms of --------- : alpha helix, beta-pleated sheet, open loops
- only N, H, and O
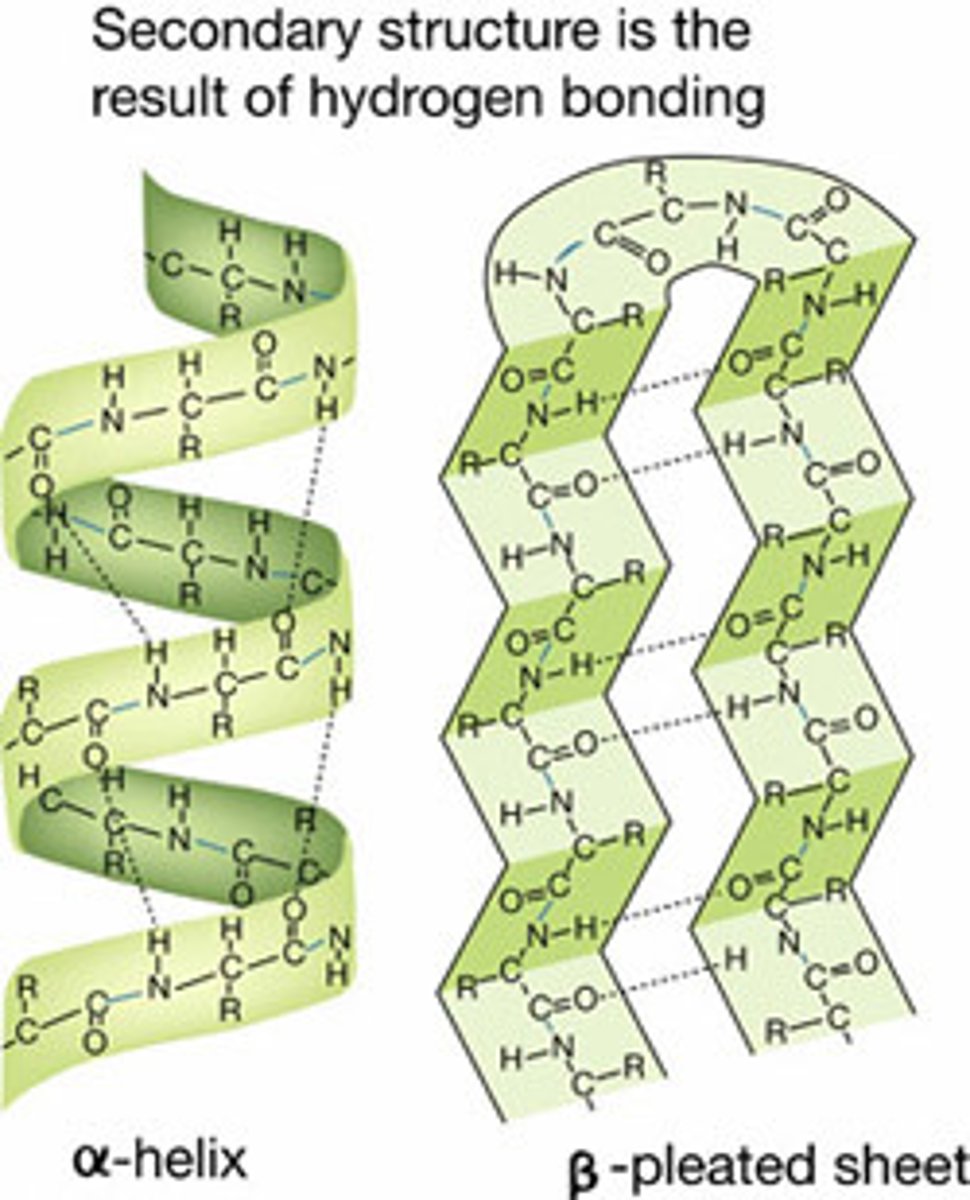
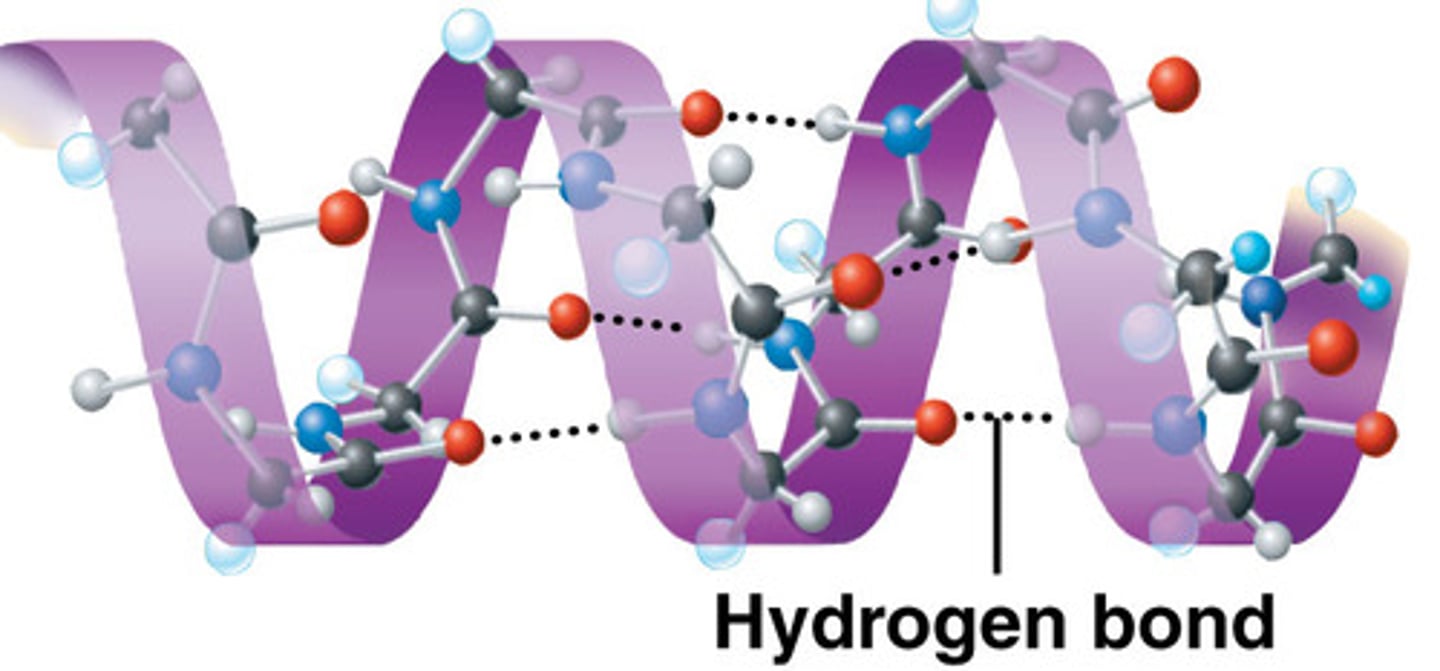
Secondary Structure: Alpha helix
-3.6 amino acid per turn of helix
- basis of fibrous polymers
- discovered by Linus Pauling
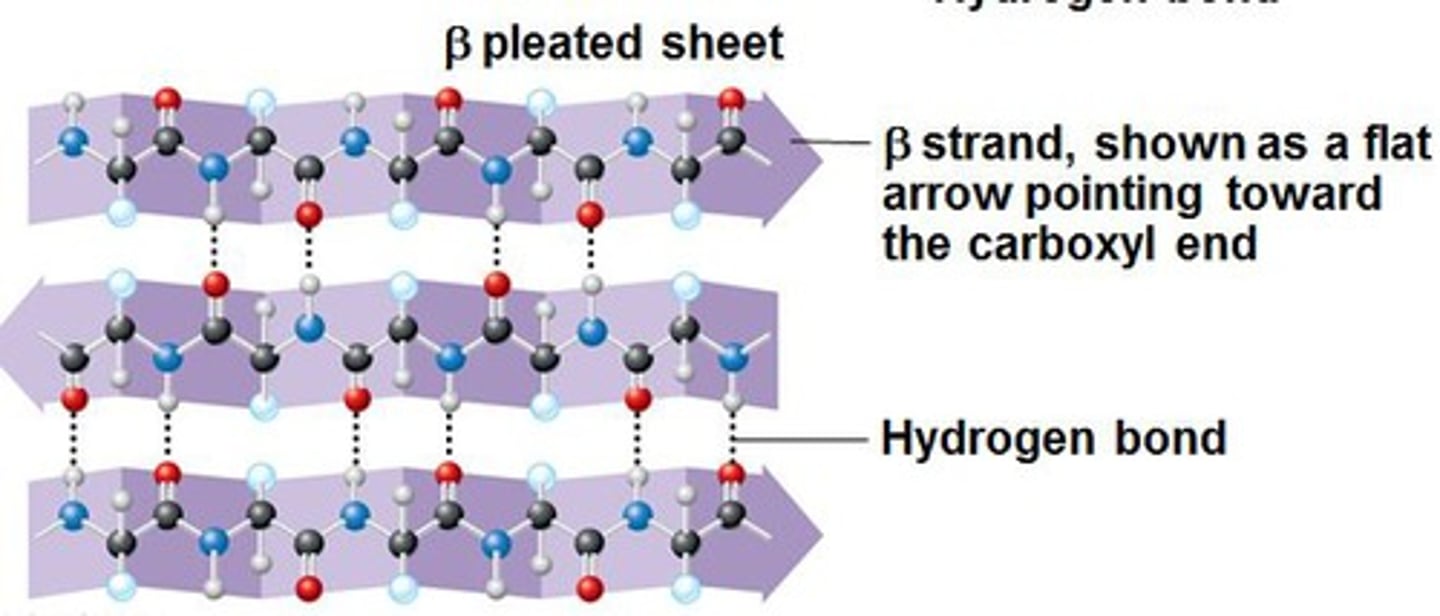
Secondary Structure: Beta- pleated sheet
- stretched out in comparison to the alpha helix
- has twists that increase the strength and rigidity of the structure
Secondary Structure: Open loops
- loops that often connect the more alpha helices and pleated sheets
- are often important regions of proteins including the active sites of enzymes
Levels of protein structure or conformation: Tertiary Structure
- three dimensional conformation of a polypeptide, where it starts to take shape
- folds in polypeptide chain
- shape is maintained by intramolecular bonds
- hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges
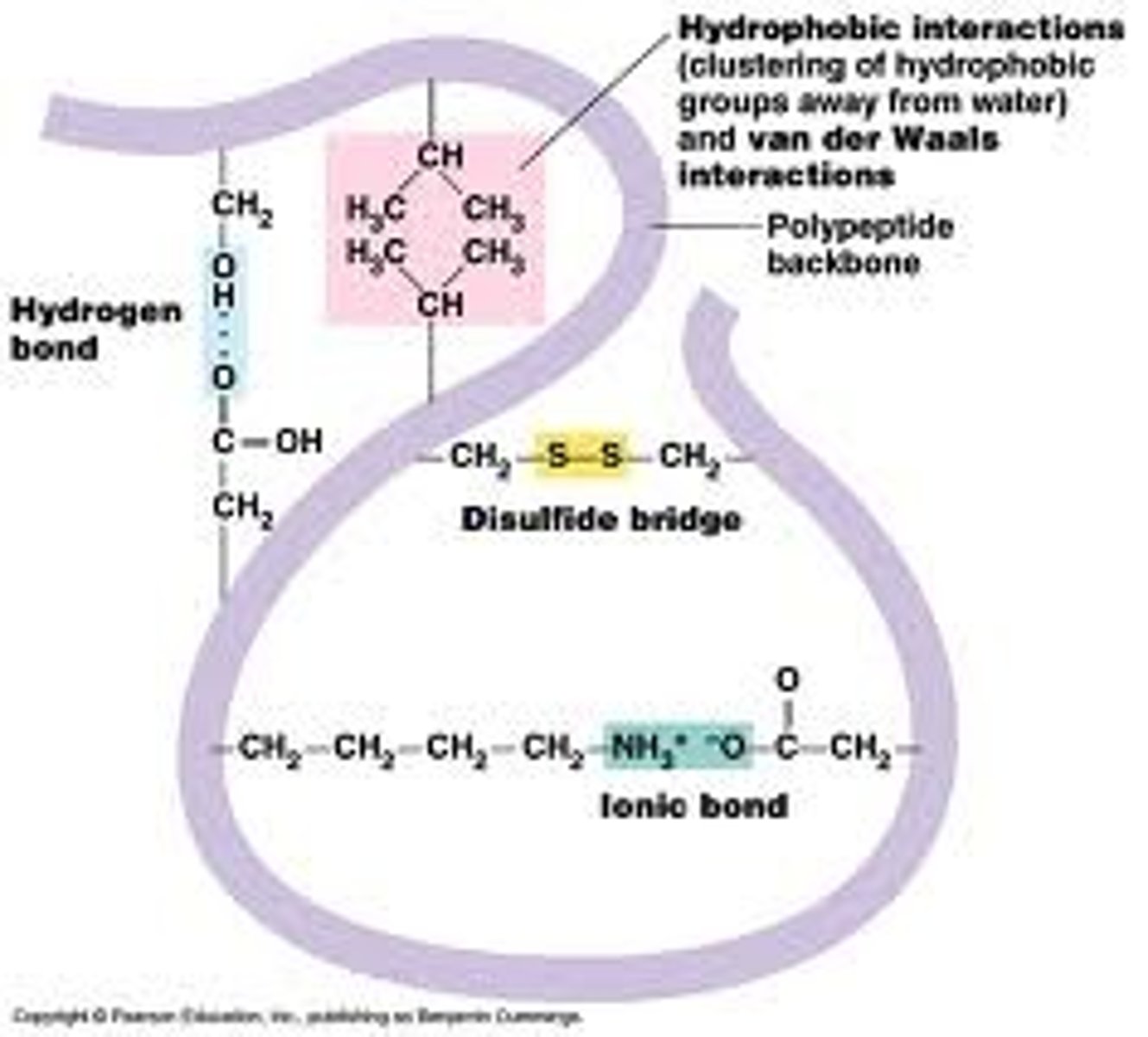
R side chains have the ability to
form hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds
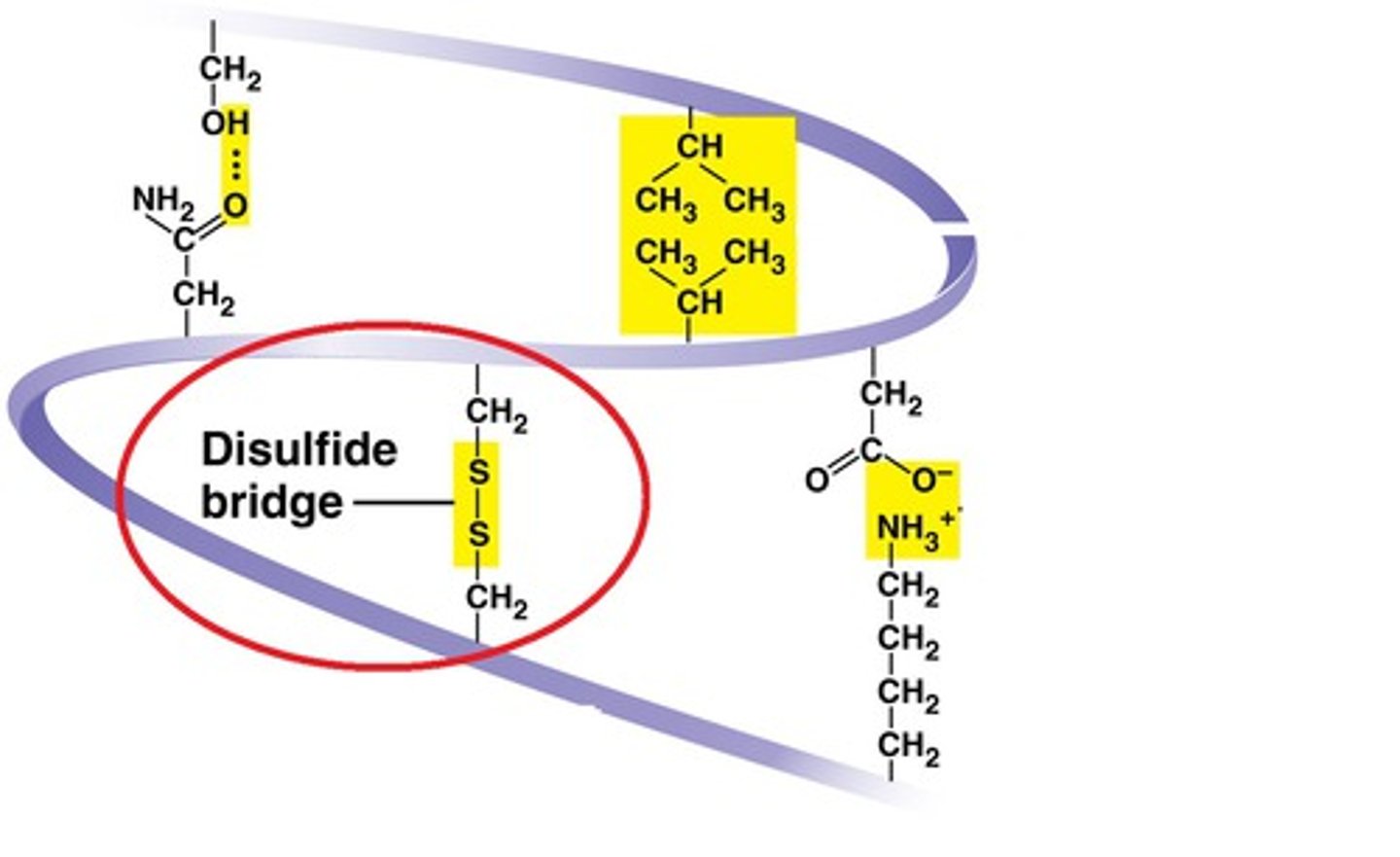
Disulfide bridges
- covalent bonds formed between 2 adjacent cysteine amino acids
- stabilizes the tertiary shape of a protein
Levels of protein structure or conformation: Quaternary Structure
- number of tertiary polypeptides joined together
ex hemoglobin
example of quaternary structure
hemoglobin
- composed of 4 dif polypeptide chains
- each chain forms a tertiary structure called a
heme group each w/ Fe 2+
- prosthetic groups
- proteins are often bound to inorganic
compounds/ elements
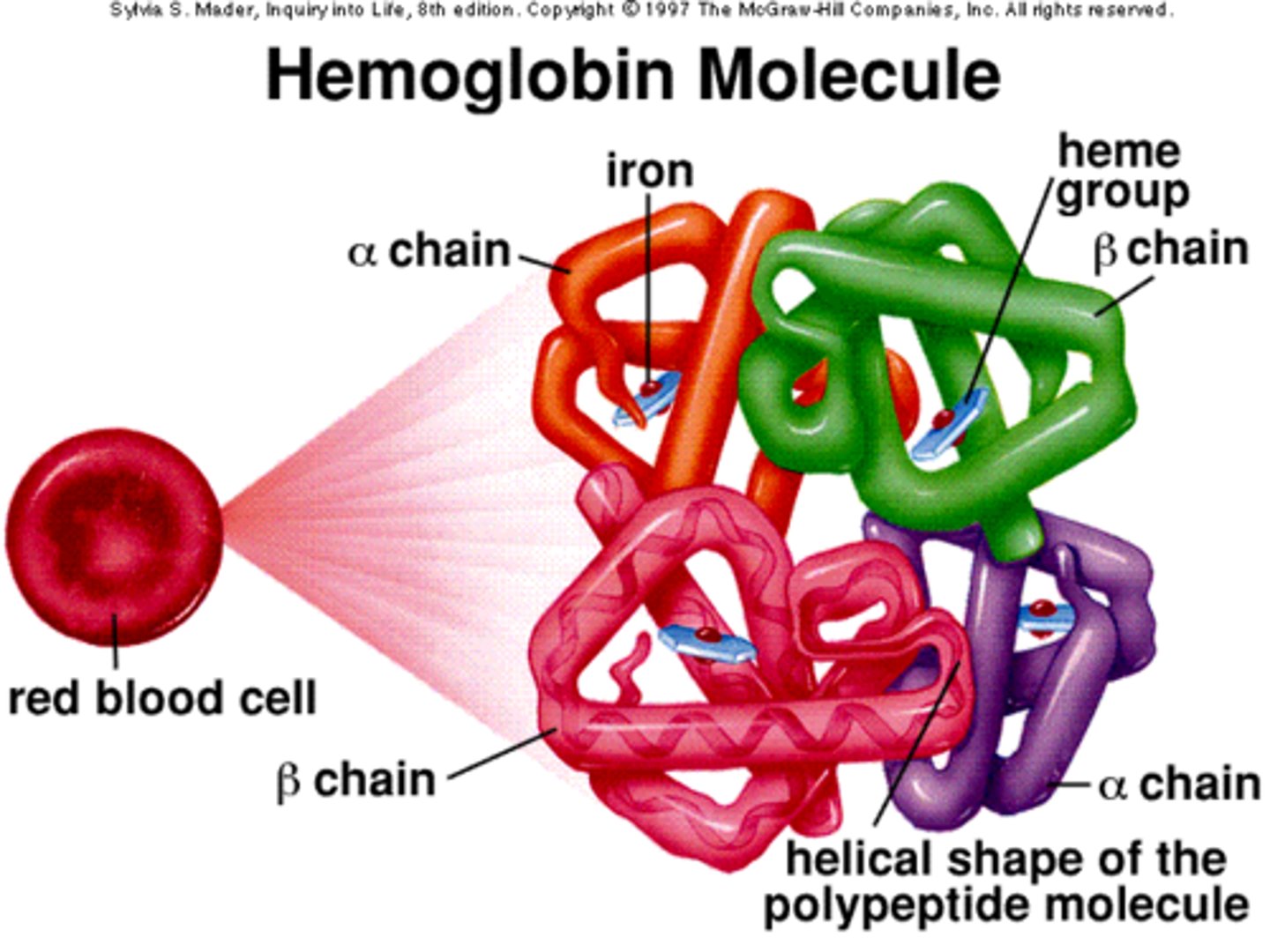
shape of protein determines
function
Two Classifications of proteins
fibrous and globular
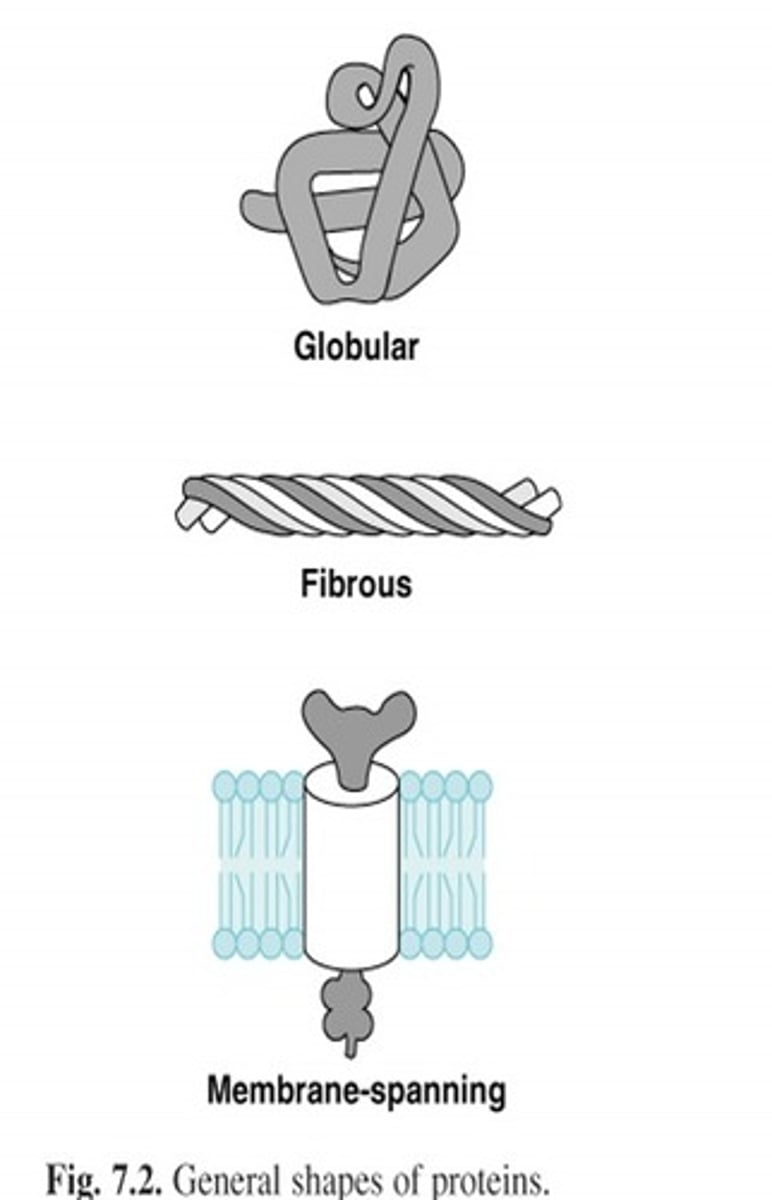
Two Classifications of proteins: fibrous proteins
- water insoluble, long, narrow proteins
- structural- provide strength and support to tissues
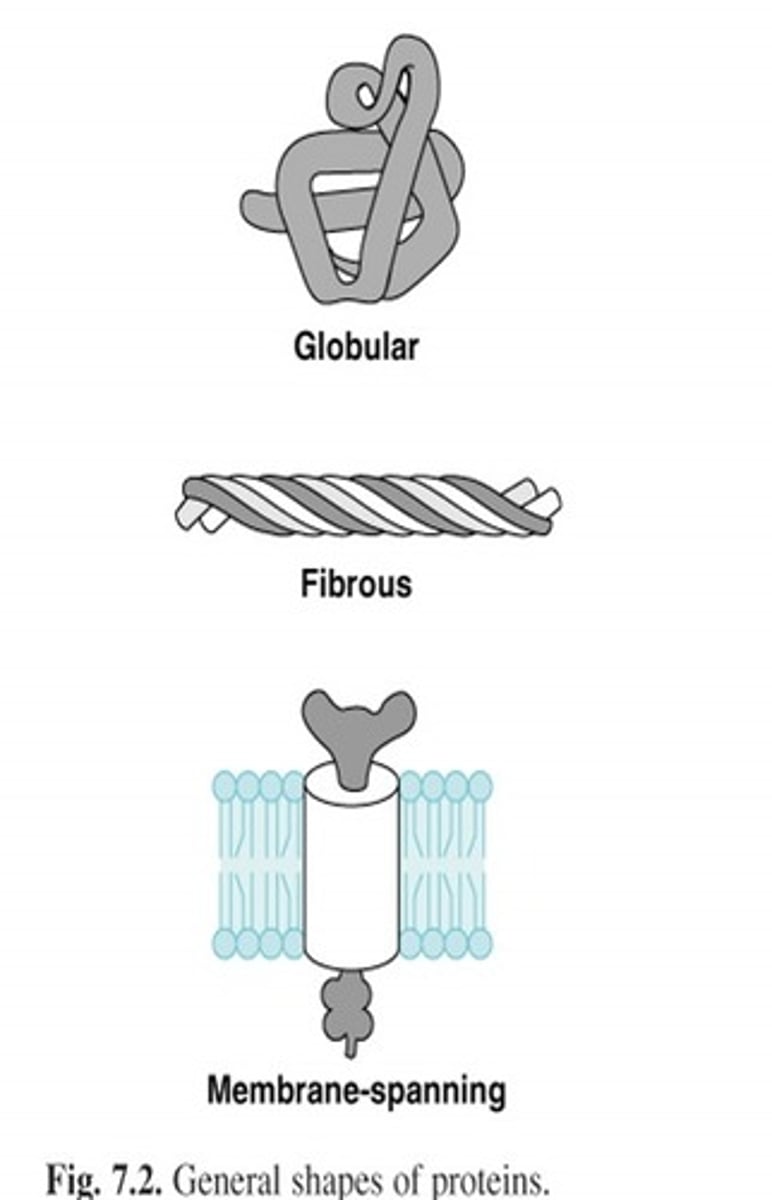
examples of fibrous proteins
collagen:
- basis of the connective
- composed of 3 left handed helices
- most common protein in animals
keratin:
- common fibrous protein
- composed of 7 helices
- major protein in hair and nails structure
Two Classifications of proteins: globular proteins
- near soluble (colloids)
- more compact and rounded shape
- functional- pigments (myoglobin), transport (hemoglobin and lipoproteins), antibodies (immunoglobulins)
The Importance of polar and nonpolar amino acids
- in cell membrane proteins:
- nonpolar amino acids allow protein to pass thru cell membrane
- polar amino acids are in contact w water inside and outside the cell; allows polar molecules to pass thru cell membrane
Examples of Proteins
Hormones, Immunoglobulin, Rubisco, Collagen, Spider Silk, Rhodopsin, Hemoglobin, Amylase, Actin and Myosin and Enzymes
Hormones
Insulin
-51 amino acid polypeptide
-it is in all cells, especially muscle and liver
Hormones help
glucose enter cells
-helps the storage of glucose as the insoluble polymer glycogen
Immunoglobulin
-Antibodies
-Produced in an immune response to an infectious antigen
-Great variation in the heavy chains (allows a response to virtually any possible antigen surface)
Rubisco
Ribulose Biphosphate Carboxylase
- the most abundant protein on the planet
-most important enzyme in the world
- catalyzes the reaction that fixes CO2
Rubisco catalyze the reaction that ...
fixes carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
Collagen takes the form of
-Many forms of rope-like proteins
- forms a mesh of fibers in skin and blood vessels that resists tearing
Purpose of Collagen
-provides immense strength to ligaments and blood vessel walls
-prevents cracks and fractures in bones and teeth,
Purpose of Collagen
-provides immense strength to ligaments and blood vessel walls
-prevents cracks and fractures in bones and teeth
Rhodopsin
"Visual Purple" strongly absorbs green/blue light
-pigment in rod of retina sensitive to light
Hemoglobin
Transports O2 and CO2
Amylase
Helps digest Starches
Actin and Myosin
Proteins in muscle cells that interact to cause contractions
Enzymes
-large globular proteins often with prosthetic groups
-speed up chemical reactions
Denaturation
Changing proteins native conformation
Change shape= change in activity
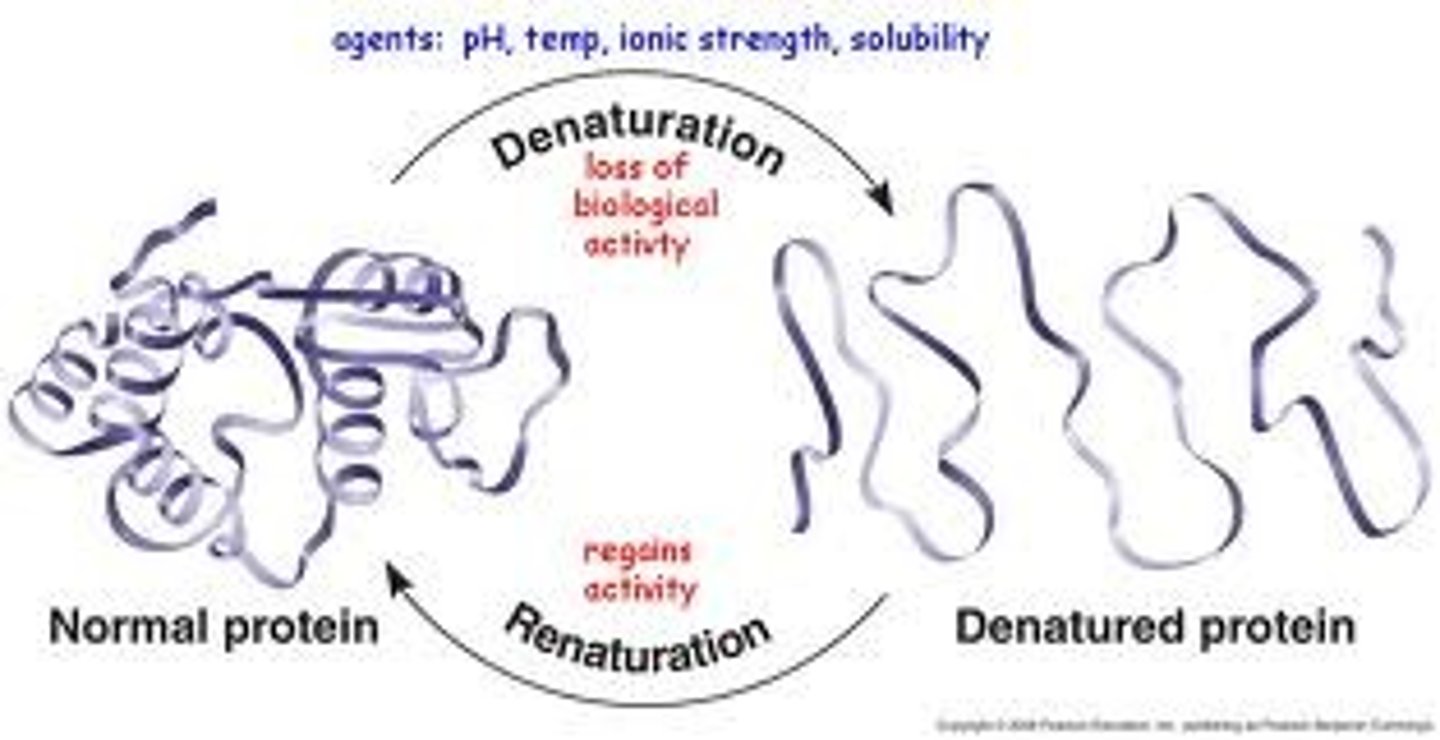
How does denaturation happen?
1. High Temperature
2. Chemical agent (acid or base) change in pH
3. Organic Solvent
What is the end result of denaturation?
Proteins have complex shapes
-Can have areas that are polar or Nonpolar, therefore have varied functions in living things
Denaturation can be used for
Energy, but is not the first choice
Functions of Proteins
Catalysis, Muscle Contraction, Cytoskeletons, Tensile Strengthening, Blood Clotting, Transport of Nutrients and Gases, Cell Adhesion, Membrane Transport, Hormones, Receptors, Packing of DNA, Immunity
What kind of bonds form in the formation of proteins?
Peptide bonds
Proteins are made of how many amino acids
Thousands