Anatomy 2 Unit 2 ch 21 cardiovascular system: blood vessels and hemodynamics
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What are the 3 types of blood vessels in the body?
Tunica interna, tunica media, and tunica externa
Describe tunica interna
Aka tunica intima: innermost layer, DEEP, adjacent to lumen
Describe tunica media?
Middle layer, smooth muscle and elastic fibers
Describe tunica externa
Aka tunica adventitia: outermost layer, adjacent to surrounding tissue
Do veins, arteries, and or capillaries have valves?
Only veins have valves.
What do arteries do, whats their function?
They carry blood away from the heart to tissues
What is special about the walls of arteries?
They’re elastic, allows them to absorb the pressure created by ventricles of the heart as they pump blood into the arteries
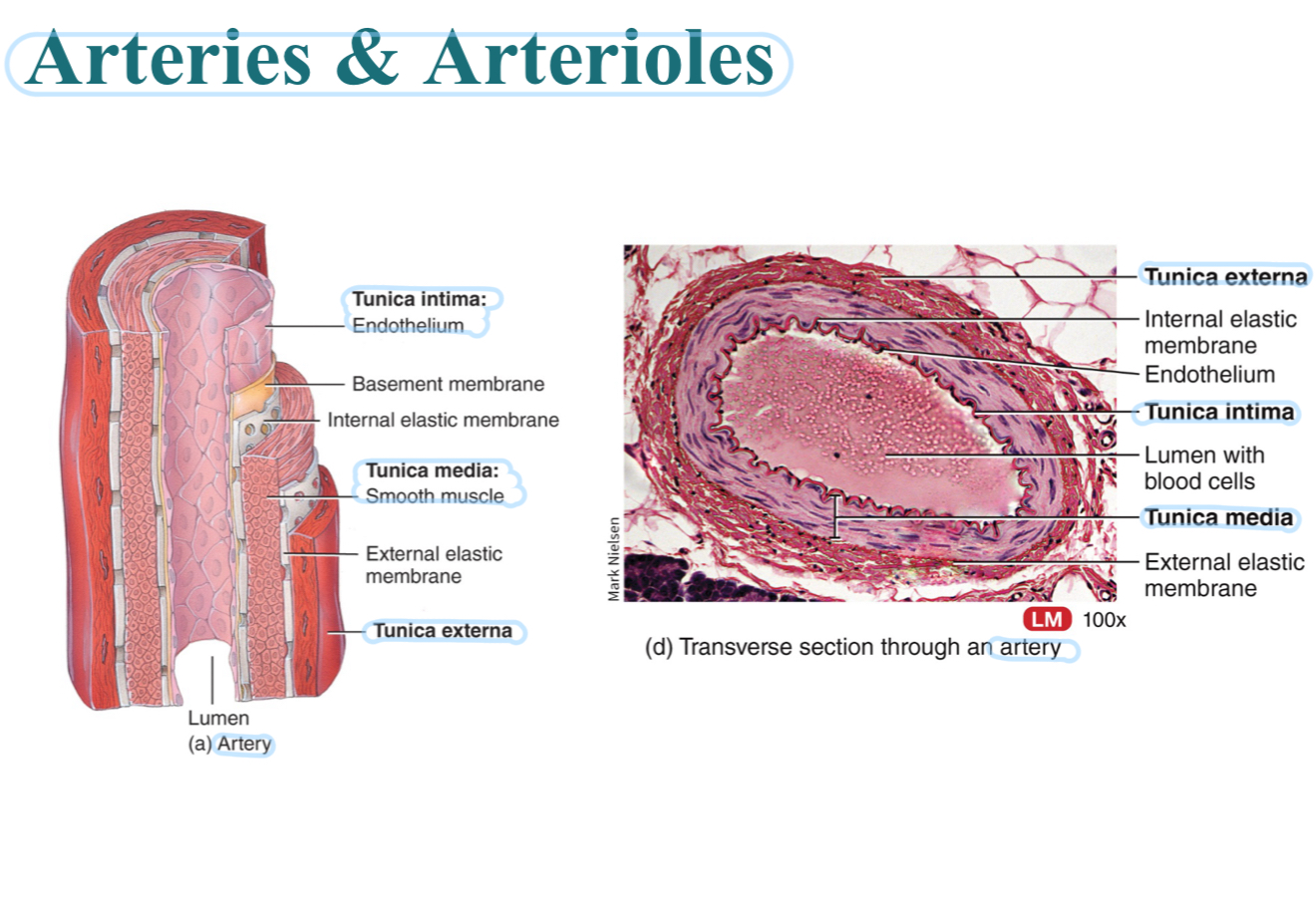
Which tunica or which layer of the artery has smooth muscle?
In tunica media. Allows arteries to regulate their diameter
Arteries act as…
Pressure reservoirs
What are the types of arteries?
Elastic arteries(conducting arteries), and muscular arteries (distributing arteries)
Describe Elastic arteries …
Have large diameter, more elastic fibers, less smooth muscle, function as pressure reservoirs
Describe muscular arteries…
Are medium diameter, more smooth muscle, fewer elastic fibers, distribute blood to various parts of the body
What is anastomoses?
The union of the branches of 2 or more arteries supplying the same region of the body. Some arteries are like this not all
What do anastomoses help with?
Provide an alternate route for blood flow
What are end arteries?
arteries that do not form an anastomosis are called
What happens if an end artery is blocked!?
Blood cannot get to that particular region of the body and necrosis can occur
What are capillaries?
Microscopic vessels
What do capillaries do?
Usually connect arterioles and venules
What are capillary walls composed of?
Single layer of cells, very thin, which helps with nutrient exchange
Capillaries branch to form…
An extensive capillary network throughout the tissues and are found near almost every cell in the body
Types of capillaries?
Continuous capillaries, fenestrated capillaries, sinusoid capillaries
Describe continuous capillaries.
Formed by endothelial cells
Describe fenestrated capillaries
for filtration, smaller pores, mostly found in kidneys
Describe sinusoid capillaries.
Biggerrr pores, red blood cells can slip out
What are venules?
Small vessels that are formed by the union of several capillaries
What do venules do? What’s their function
Drain blood from capillaries into veins
What are the valves in veins for?
No backflow
Compared to arteries, veins have a…
Thinner tunica interna and thinner tunica media, and a thicker tunica externa
Veins have… less or more? elastic tissue and less or more? smooth muscle than arteries?
Veins have less elastic tissue and less smooth muscle than arteries.
How are various veins formed?
When venous valves become weak or damaged
Varicose veins appear…
Twisted bc they’re dilated
Spider veins are…
Dilated venules close to the skin, especially in the lower limb/face
At rest where is the largest portion of blood in?
In systemic veins and venules which are considered “blood reservoirs”
CAPILLARY EXCHANGE: substances cross capillary walls by… *hint 3 ways
Diffusion, transcytosis, and bulk flow
Describe diffusion (involved in capillary exchange of substances across capillary walls)
Substances such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, glucose, amino acids, some hormones cross capillary walls via simple diffusion
Describe transcytosis (involved in capillary exchange of substances across capillary walls)
Large, lipid insoluble molecules (like insulin) cross capillary walls in vesicles via transcytosis
Describe bulk flow (involved in capillary exchange of substances across capillary walls)
a process in which large #s of ions, molecules, or particles in a fluid move together in the same direction
Bulk flow occurs from an area of…
Higher pressure to an area of lower pressure, and it continuos as long as a pressure difference exists
Bulk flow is more important for….
Regulation of the relative volumes of blood and interstitial fluid
What is filtration?
A pressure driven movement of fluid and solutes from blood capillaries into interstitial fluid
What is reabsorption?
Pressure driven movement of fluid and solutes from interstitial fluid into blood capillaries
Describe the process of capillary exchange?
lymphatic vessels draw fluid left over to the lymphatic system to filter and bring back to cardiovascular system
What is blood flow?
It’s the volume of blood that flows through any tissue in a given time period (in mL/min)
What is cardiac output?
Total blood flow, basically the volume of blood that circulates thru systemic blood vessels each minute
The higher the BP blood pressure, the___ the blood flow
Greater the blood flow
If blood is pushing faster then…
The higher the BP also means greater the blood flow
What generates the BP (blood pressure)?
Contraction of the ventricles generate BP
BP is determined by what 3 ?
CO, blood volume, and vascular resistance
Vascular R resistance is what?
The opposition to blood flow due to friction between blood and the walls of blood vessels
If the vascular resistance R is higher what does that mean?
The higher the R, the smaller the blood flow
R depends on what 3 factors? (R= vascular resistance)
Size of the blood vessel lumen, blood viscosity, and total blood vessel length
VENOUS RETURN: ___ are one way?
Valves are one way!
What is Venous return?
The volume of blood flowing back to the heart through the systemic veins
Why does venous return occur?
Due to the pressure generated by contractions of the hearts left ventricle.
Venous return is assisted by:
Valves, respiratory pump, and skeletal muscle pump
What in the brain regulates heart rate, contractility, and blood vessels each diameter?
The medulla oblongata contains a cardiovascular center, which is a group of neurons that regulate…
What are baroreceptors?
They’re important pressure sensitive sensory neurons that monitor stretching of the walls of blood vessels and the atria.
What is cardiac output?
Increased heart rate and contractility,
Hormones are norepinephrine and norepinephrine.
Blood pressure increases.
Describe blood volume
There r 2 types: increase and decrease.
Increased BP produces hormones: aldosterone, and anitdiuretic hormone
Decreased BP produces hormone: atrial natriuretic peptide