Potable water
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Potable water
drinking water
water resources in the UK
rivers
lakes
aquifers
reservoirs
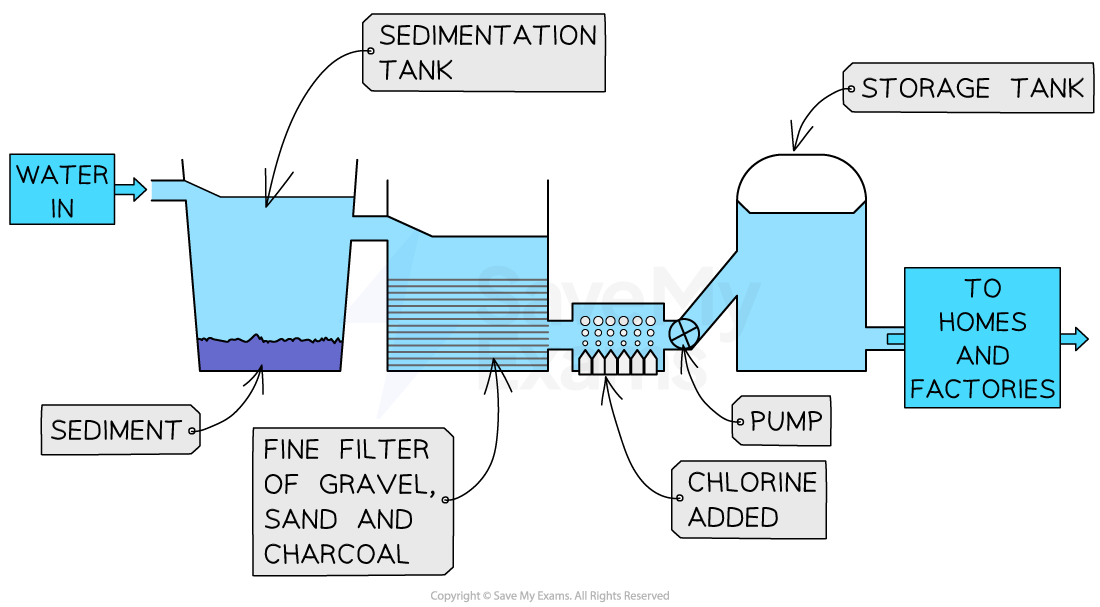
treating ground water
water is in then screened and pumped through to a coarse filter
insoluble solids like leaves and soil are removed
then put in a sedimentation tank which causes tiny particles to clump together into larger particles by adding aluminium sulphate
fine filter removes fine particles
chlorine is added
stored in storage tank then transported to homes and factories
desalination
removal of salt from water
method one for desalination
distillation
method two for desalination
pre treatment filtration
membrane filtration → reverse osmosis
disinfecting (e.g adding chlorine)
chlorinisation
the process of adding chlorine to water or other liquids to disinfect them
Why is chlorine added to water?
to make it safe for drinking
Advantages of chlorination
kills harmful microorganisms
reduces risk of waterborne illness
removes unpleasant smells
disadvantages of chlorination
can form harmful byproducts
toxic gas
how is chlorine gas produced & potential long time effects?
electrolysis
its energy intensive → global warming
electrolysis
electricity applied sodium chloride in water which splits sodium and chloride
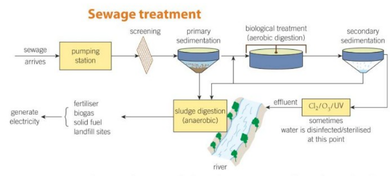
treating waste water
metal grid moves large objects
solid sediment sinks to the bottom → large puddle pushes sludge which is pumped into the storage tank
bacteria feed on organic matter through aerobic respiration → air bubbled for oxygen
bacteria settles to bottom and moves into sludge → water is now safe to go in rivers
sometimes water is sterilised with chlorine and filtered through a bed of sand
sludge can be fried and buried for electricity
Testing if water is pure
evaporate water → if nothing left behind its pure
test if it conducts electricity → shouldn’t as its simple covalent
boil water sample → i8f boils at 100 degrees its pure