Chemistry Master
1/152
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
What is an element?
An element is a substance made up of a single type of atom. These substances cannot be broken down into any simpler substance.
What is a compound?
A substance made from two or more elements that are chemically joined. They have completely different properties from their constituent elements.
How are elements and simple molecules represented using chemical formulae?
Use chemical symbols to state the number and type of each atom present.
E.g. O₂ represents the element oxygen made up of 2 atoms of oxygen.
E.g. H₂O represents a molecule with 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen.
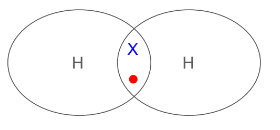
How can you represent simple molecules using a diagram and key?
Create a dot and cross diagram to model the bonding in simple molecules. E.g. A hydrogen molecule forms when a hydrogen atom shares its outer electron with another hydrogen atom.
Key:
● Outer shell of each atom is drawn as a circle.
● Circles overlap where there is a covalent bond.
● Electrons from one atom are drawn as dots, and electrons from another atom as crosses.
How can you determine the formulae of ionic compounds given the number of the ions they contain?
The overall charge of a compound is zero, so the number of positively and negatively charged ions must be balanced so there is no net charge.
E.g. Magnesium forms a 2+ ion and chlorine forms a 1- ion. So for every magnesium ion, there must be two chlorine ions to give the ionic compound an overall charge of zero. This gives the chemical formula MgCl₂.
What is relative atomic mass?
The average mass value, which takes the mass and abundance of isotopes of an element into account, on a scale where the mass of ¹²C is 12.
What is relative formula mass?
The addition of all the relative atomic mass values for all the atoms in the formula. The relative formula mass of a substance is called one mole of that substance.
What is the percentage composition of a compound?
Divide the relative atomic mass of each element by the total relative formula mass of the whole compound, then multiply by 100.
What are the methods by which mixtures can be separated (there are 4)? Do these involve chemical reactions?
Filtration, evaporation, chromatography, distillation. They do not involve chemical reactions as the atoms/molecules in mixtures are not chemically joined.
What is chromatographic data analysis?
An analytical technique separating compounds by their relative speeds in a solvent as it spreads through the paper. The more soluble a substance is, the further up the paper it travels. Compounds in a mixture separate into different spots, but a pure substance will produce a single spot in all solvents.
What are Rf values?
Rf value = distance moved by substance ÷ distance moved by solvent.
What is a chemical reaction?
A process by which atoms in the reactants are rearranged to form products. The number and type of each atom present in the reactants will also be present in the products—this is why chemical equations must be balanced.
What are the observations that show a reaction has taken place?
● Colour changes
● Effervescence - occurs when a gas is released and fizzing is seen
● Temperature changes - exothermic reactions give off heat to the surroundings (causing an increase in temperature), whereas endothermic reactions take in heat from the surroundings (causing a decrease in temperature).
How can you represent chemical reactions using word equations?
Word equations use the chemical names instead of formulas to show the reaction.
E.g. methane + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water.
How can you represent chemical reactions using chemical equations?
Chemical equations use the chemical formulas and show the ratio of molecules reacting—total relative mass of reactants and products is equal.
E.g. CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O (shows combustion of methane).
What is the percentage yield of a chemical reaction?
Percentage yield = (mass of product produced ÷ theoretical maximum mass of product possible) × 100.
How can you calculate the empirical formula from reacting mass data?
Calculate the number of moles = mass (in grams) ÷ relative atomic mass. The ratio is calculated by dividing each number of moles by the lowest number of moles present. Multiply the ratio so there are no decimals. This gives the empirical formula.
How can you calculate the masses of reactants or products from a balanced chemical equation?
Calculate the number of moles = mass (in grams) ÷ relative atomic mass.
Multiply the moles by the ratios given by the balanced chemical equation. Now calculate the mass of a reactant or product using the equation:
mass (in grams) = relative atomic mass × moles.
What is the Avogadro constant?
The number of atoms/ions/molecules that make up 1 mole of a substance. This number is called the Avogadro constant and is 6.02 × 10²³.
How can you convert amount of substance (in grams) to moles?
Number of moles = mass of particle (in grams) ÷ relative atomic mass of particle.
How can you convert moles to amount of substance in grams?
Mass of particle (in grams) = number of moles × relative atomic mass of particle.
What does an atom contain?
A positively charged nucleus with orbiting negatively charged electrons.
What is a proton?
A particle with a positive charge of +1 and a relative mass of 1.
What is a neutron?
A particle with no net charge and a relative mass of 1.
What is an electron?
A particle with a negative charge of -1 and a relative mass of 1/2000.
What does a nucleus contain?
Protons and neutrons make up the nucleus. The nucleus contains most of an atom’s mass.
What is an atom’s electrical charge?
Atoms have no overall charge because the number of protons and electrons are equal. Therefore, the positive and negative charges balance out to an overall charge of 0.
What is atomic number?
The number of protons in the nucleus—this dictates what element it is.
What is mass number?
The relative mass of the atom given by the total number of protons and neutrons.
What is an isotope?
Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. As a result, they have different masses. They are known as isotopes of the same element.
How do you calculate the relative atomic mass of elements with more than one isotope?
Relative atomic mass = ((isotope 1 mass × abundance) + (isotope 2 mass × abundance)) ÷ 100. Keep repeating for all isotope masses. Abundance is in %.
How are elements arranged in the periodic table?
In order of increasing atomic (proton) number, which places elements with similar properties in the same column (group).
What are the columns of the periodic table called?
Groups.
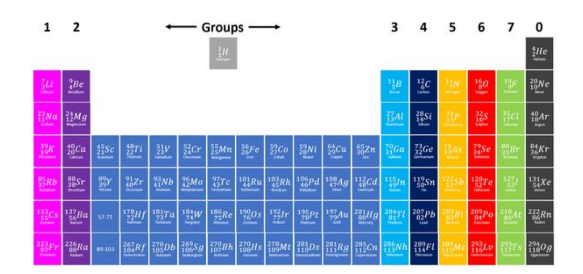
What are the rows of the periodic table called?
Periods.
Where are metals found in the periodic table?
The left side and centre of the periodic table.
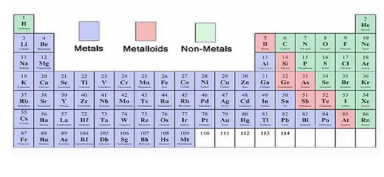
Where are non-metals found in the periodic table?
Right side.
What type of elements lie between the metals and non-metals in each period?
Elements with intermediate properties.
List the electronic configurations of the first 20 elements.
H - 1,
He - 2,
Li - 2.1,
Be - 2.2,
B - 2.3,
C - 2.4,
N - 2.5,
O - 2.6,
F - 2.7,
Ne - 2.8,
Na - 2.8.1,
Mg - 2.8.2,
Al - 2.8.3,
Si - 2.8.4,
P - 2.8.5,
S - 2.8.6,
Cl - 2.8.7,
Ar - 2.8.8,
K - 2.8.8.1,
Ca - 2.8.8.2.
What is the relationship between electronic structure and position in the periodic table?
The group number of an atom is equal to the number of electrons in its outer shell.
What similarities do elements in the same group have?
Similar chemical properties, as they have the same number of electrons in the outer shell.
What are the Group 1 elements known as?
The alkali metals.
What are Group 7 elements known as?
The halogens.
What physical trends do the alkali metals show?
Atomic radius increases down the group. Densities gradually increase down the group. Melting and boiling points gradually decrease down the group.
What is involved in the reactions between Group 1 and Group 7 elements?
The loss or gain of electrons, forming ions:
● Group 1 elements lose one electron to form a +1 ion.
● Group 7 elements gain one electron to form a -1 ion.
What is the reactivity trend of the alkali metals down the group?
Electrons are lost more easily down the group. Reactivity increases down the group as alkali metals react by losing an electron.
What is the reactivity trend of Group 7 elements down the group?
Electrons are attracted less down the group. Reactivity decreases down the group as there are more electron shells and so the ability to attract another electron decreases.
What does the reaction of an alkali metal with oxygen produce?
An oxide.
What does the reaction of an alkali metal and a halogen produce?
A white precipitate (crystalline halide salt). The reaction occurs very quickly.
What does the reaction of an alkali metal and water produce?
Fizzing that produces an alkaline solution and hydrogen.
What is the test to identify hydrogen gas?
Collect some of the gas in an upturned test tube. Place a lighted splint into the test tube. A squeaky pop sound means hydrogen gas is present.
What does iron + fluorine produce?
Cold iron wool reacts almost instantly to form white iron (III) fluoride.
What does iron + chlorine produce?
Reacts vigorously to form an orange-brown precipitate of iron chloride.
What does iron + bromine produce?
Reacts quickly to form a red-brown precipitate of iron bromide—the reaction has to be warmed.
What does iron + iodine produce?
Reacts slowly in iodine vapour to form a grey iron iodide precipitate—the reaction has to be heated strongly.
What are the relative reactivities of the halogens as demonstrated by precipitation reactions?
A decrease in reactivity down the halogen group means that a more reactive halogen can displace a less reactive one:
● Chlorine will displace bromine and iodine.
● Bromine will displace iodine but not chlorine. ● Iodine will not displace chlorine or bromine.
What are the uses of chlorine?
Chlorine is a disinfectant and kills bacteria, so it is used to sterilise drinking water and clean swimming pools. Reacts with sodium hydroxide and water to form bleach. Used in manufacturing chemicals, including insecticides, PVC, and chlorofluorocarbons.
What is iodine used for?
Iodine is an antiseptic, so it can be used to prevent infection in hospital procedures.
What are the flame test colours for Li+, Na+, K+, Ca²⁺, and Ba²⁺ ions?
Li⁺ Crimson flame.
Na⁺ Orange-yellow flame.
K⁺ Lilac flame.
Ca²⁺ Orange-red flame.
Ba²⁺ Green flame.
What are the precipitates for Cl⁻, Br⁻, and I⁻ reaction with silver nitrate solution?
Cl⁻ precipitate is white. Br⁻ precipitate is cream. I⁻ precipitate is yellow.
What are the ionic equations for the reactions of Cl⁻, Br⁻, and I⁻ with silver nitrate solution?
Ag⁺(aq) + Cl⁻(aq) → AgCl(s).
Ag⁺(aq) + Br⁻(aq) → AgBr(s).
Ag⁺(aq) + I⁻(aq) → AgI(s).
Why are the Group 0 gases unreactive?
Group 0 gases (noble gases) are unreactive because they have full outer electron shells, making them stable and unlikely to gain or lose electrons.
What are four harmful substances found in ‘natural’ water supplies?
Microorganisms, ions, dissolved gases, and pollutants
Why are microorganisms in ‘natural’ water supplies treated? How are they treated?
Many of the bacteria and microorganisms cause disease, so they must be treated - most commonly chlorine is used to kill the microorganisms.
How do ions end up in ‘natural’ water supplies?
Water dissolves ions from rocks and other materials as it flows within rivers to reach lakes. Although a small amount of dissolved ions is important, too much is dangerous for your health.
What are the dissolved gases in ‘natural’ water supplies?
Oxygen and carbon dioxide, a byproduct of respiration from the microorganisms living in the water - essential for photosynthesis in aquatic plants. Other gases from the atmosphere can dissolve into natural water.
Which dangerous pollutants can dissolve into ‘natural’ water supplies?
Pesticides, herbicides, and chemical fertilisers - in high concentrations, these can affect health.
How do you maintain a sustainable water supply?
Reduce water consumption, reduce environmental impacts of abstracting water, distribute and treat water efficiently.
Give examples of how we can reduce water consumption
Take short showers instead of baths Turn off taps when they’re not being used Install a short flush button on toilets Use leftover bath water for things like watering the plants Eat less meat Put on full washing machine loads Use dishwashers instead of washing by hand Buy less cotton clothes - it takes 10,000 litres to make a single pair of cotton jeans!
Give examples of water abstraction
Desalination of seawater Building dams and reservoirs Collecting from surface sources such as rivers, lakes, and streams Collecting rainwater Accessing underground sources
What are the 3 main steps for treatment of water?
Sedimentation, Filtration, Chlorination
What is sedimentation?
Water is added to a large tank. This stops it from flowing, allowing large insoluble particles to sink to the bottom of the tank.
What is filtration?
Water is flowed through beds of sand and gravel of different sizes, which removes small insoluble particles.
What is chlorination?
Chlorine gas is bubbled through the water to kill the bacteria and other microorganisms.
What is water fluoridation?
The process where fluoride is added to water.
What are the advantages of fluoridation?
Strengthens the enamel of teeth which prevents tooth decay and cavities Protects teeth by demineralisation
What are the disadvantages of water fluoridation?
It is a form of mass medication as people do not have a say in how much fluoride is in their water If children are exposed to too much fluoride they can develop fluorosis People can make a choice themselves about fluoride by using a toothpaste that contains it Links have been made between fluoride and thyroid problems, neurological disorders, and some cancers - although evidence is not concrete
What is desalination and what are the two main methods?
Desalination is the removal of salt from seawater. Distillation and reverse osmosis
What are the advantages of desalination?
Useful water to supply to countries with low rainfall and lots of coastlines Water produced is of a higher quality than the required standards of potable water Using water from the ocean can help protect habitats for animals in natural sources such as rivers or lakes
What are the disadvantages of desalination?
Requires a lot more energy than typical water treatment processes More expensive so harder for poorer countries to afford Increases GHG emissions as more fuel is required in desalination Desalination plants are often far from where the water is needed, so lots of piping must be installed Building of desalination plants is an expensive and high-energy process
What is the process of distillation?
The seawater is heated, causing pure water to evaporate The water vapour is collected and cooled, causing it to condense back into a liquid, giving distilled water The leftover salt may be used for various purposes
What is a miscible liquid and how is it distilled?
A miscible liquid is where one liquid completely dissolves into another liquid solution. You must heat liquids to various temperatures to individually evaporate and condense them.
What is solubility?
A substance (called the solute) is described as soluble if it will dissolve in another substance, known as a solvent.
How is solubility measured?
In terms of the maximum mass of solute (in grams) that will dissolve in a given volume of solvent.
What is the method of determining solubility?
Gradually add the solute to a known volume of solvent so it dissolves Add solute until no more solute dissolves Filter the undissolved solute and discard it Heat the leftover solution to evaporate the solvent, leaving the solute that had dissolved Weigh the remaining solute and calculate the mass of solute that was dissolved
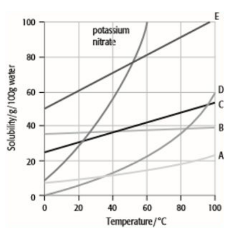
What is a solubility curve?
A solubility curve shows the variation of how solubility changes with temperature - generally, solubility increases as temperature increases.
What causes hardness in water?
Hardness in water is caused by dissolved calcium and, to a lesser extent, magnesium.
What do hard water and soap form?
They form scum, as it is difficult to form a lather with hard water.
What do soft water and soap form?
They readily form a lather.
What is temporary hardness in water?
Caused by dissolved calcium hydrogencarbonate The hardness can be removed by boiling the water and thermal decomposition occurs
What is permanent hardness in water?
Caused by dissolved calcium sulphate This hardness cannot be removed by boiling the water
What are the processes to soften water?
There are three: Distillation Adding sodium carbonate Using an ion exchange column
What are the advantages of using distillation to soften water?
Removes both temporary and permanent hardness.
What are the disadvantages of using distillation to soften water?
High energy process and therefore high cost.
What are the advantages of using sodium carbonate to soften water?
Cheap and easy. Removes both temporary and permanent hardness.
What are the disadvantages of using sodium carbonate to soften water?
The calcium carbonate (limescale) builds up and can block pipes.
What are the advantages of using an ion exchange column to soften water?
Removes both temporary and permanent hardness.
What are the disadvantages of using an ion exchange column?
The column is expensive. The column becomes saturated and less efficient.
How does using distillation to soften water work?
The hard water is heated so the water evaporates. The water then condenses and is collected, leaving behind the ions that made it hard.
How does an ion exchange column work?
A column is packed with resin which contains sodium ions. As hard water flows through the column, Mg2+ and Ca2+ are exchanged for Na+ ions, removing the magnesium and calcium ions, leaving the water soft.
How does adding sodium carbonate make water soft?
The carbonate ions in Na2CO3 react with the calcium ions in the water to form solid calcium carbonate.