Praxis II: Social Studies (5004)
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
House of Burgess
1st legislative assembly in American colonies

Magna Carta
1215; charter of political rights to rebellious English barons from King John
Mayflower Compact
1st written framework of government for United States created by English colonist aboard the Mayflower Ship
Great Awakening
1725-1770; religious revivals of Protestants in colonies
Proclamation of 1763
King George III; prohibited settlers from crossing West over the Appalachian Mountains; attempt to stop conflicts between settlers and Native Americans
Taxation Acts of 1764-1774
1) Sugar Act: increased duties on non-British goods;
2) Currency Act: American colonies were prohibited from issuing their own currency;
3) Quartering Act: required colonies to provide shelter and supplies to British troops;
4) Stamp Act: direct tax on paper products for the colonies to raise money for Britain;
5) Townshend Acts: taxes on glass, lead, paint, paper and tea;
6) Tea Act: reduced tax on imported British tea for unfair selling advantage in America;
7) Coercive Acts: punished Massachusetts after Boston Tea Party with restrictions
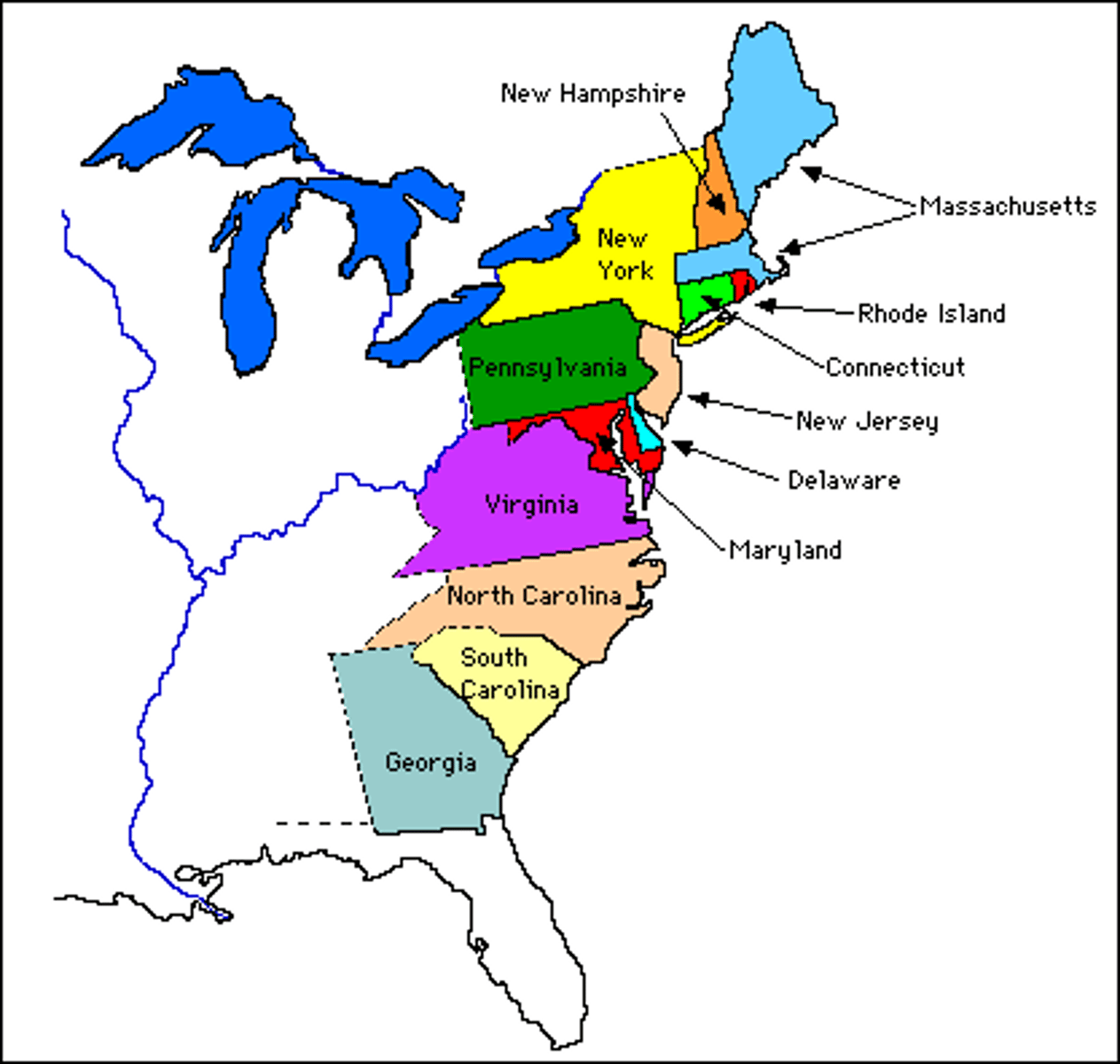
13 colonies
Connecticut, Delaware, Georgia, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Caroline and Virginia
Reasons for American Revolution
1) British control was overbearing and made American colonies feel inferior
2) Anglican Church potentially expanded their power over colonies limiting religious freedom
3) Taxation
4) Colonies had no official representation in English Parliament
5) British attempts to block Westward expansion
Events Leading up to American Revolution
1) Sons of Liberty: Samuel Adams led protest group
2) Boston Massacre: 1770; soldiers fired on a crowd
3) Committees of Correspondence: set up through colonies to spread revolutionary ideas
4) The Boston Tea Party: 1773; Sons of Liberty dumped tea into the Boston Harbor from a British ship to protest tax
5) First Continental Congress: 1774; colonies list grievances and develop a plan to boycott
6) The Shot Heard Round the World: 1775; fight ensued between English soldiers and colonial militia (Minutemen)
Turning Points of American Revolution
1) Actions of Second Continental Congress: established Continental Army led by George Washington
2) "Common Sense": written by Thomas Paine in 1776; called for independence
3) Alliance with France: 1778; Benjamin Franklin negotiated an agreement with France to fight with the Americans
4) Treaty of Paris: 1782; signaled the end of the war; granted colonies independence and gave them territorial rights
Declaration of Independence
July 4th, 1776; the document that proclaimed independence of the colonies from Great Britain by the 2nd Continental Congress; written by Thomas Jefferson
Articles of Confederation
1777; the nation's first constitution designed to protect the states' rights over the national government
US Constitution
1789; created the 3 branches with checks and balances and a bicameral legislature for equal representation; Federalists v. Anti-Federalists
Federalist Papers
1787-88; Written by James Madison, John Jay and Alexander Hamilton
Basic Principles of the Constitution
1) Popular Sovereignty: people establish government and give power to it; government functions only with consent of the people
2) Limited Government: specifies limits on government authority
3) Separation of Powers: power is divided among 3 government branches
4) Checks and Balances: ensures each branch has the authority and ability to restrain the powers of the other 2 branches to prevent tyranny
5) Judicial Review: established by Marbury v. Madison; the judiciary may evaluate actions/powers of legislature and executive to ensure they are abiding by the Constitution; if unconstitutional the judicial branch can nullify
6) Federalism: division of power between the central government and local governments to limit the power of the Federal government and allows states to deal with local problems
Delegated Powers in the Constitution
Powers granted by the Constitution
1) Expressed/Enumerated: specific
2) Inherent: powers the National governments have historically possessed
3) Implied: not expressly stated; reasonably suggested
4) Reserved: powers that belong to the states
5) Exclusive: reserved to the national government
6) Concurrent: powers that are shared by national and state governments
3 Branches of Government
Executive (President/VP, elected for 4-year terms, enforce laws); Judicial (Supreme Court, appointed by the President and approved by Congress, interpret laws); Legislative (Congress, House of Reps: 2 year terms, Senate: 6 year terms, make the laws)

Federal System
Power is divided between the National and State governments
Bill of Rights
Added to Constitution in 1791; 10 statements of the fundamental rights/freedoms of United States citizens; 27 amendments to the federal Constitution
1st Amendment
Freedoms of speech, religion, press, assembly and petition

2nd Amendment
Right to bear arms
3rd Amendment
Protection against quartering soldiers
4th Amendment
Protection against illegal search and seizure
5th Amendment
Right to due process; protection against self-incrimination and double jeopardy
6th Amendment
Rights to a speedy trial by jury, to hear accusations and confront the accuser, to witness and to counsel
7th Amendment
Right to trial by jury in civil cases
8th Amendment
Protection against cruel and unusual punishment
9th Amendment
Protects rights not enumerated in the constitution
10th Amendment
Limits the powers of the federal government to those designated in the constitution
Forms of Government
1) Feudalism: rule of local lords who are loyal to the king and control the lives and production of those who work on their land
2) Republic: representative democracy; elected leaders
3) Absolute Monarchy: King or Queen
4) Authoritarianism: individual or group has unlimited authority
5) Dictatorship: those in power are not held responsible to the people
6) Autocracy: rule by 1 person who uses power tyrannically
7) Oligarchy: self-appointed elite rulers
8) Liberal Democracy: government based on consent of the people that protects individual rights and freedoms
9) Totalitarianism: citizens' lives controlled by the government
Powers of Government
1) National: coin money, regulate trade, raise forces, declare war, conduct foreign relations
2) Concurrent: levy and collect taxes, borrow money, establish courts, set punishments
3) State: regulate trade and business in a state, establish public schools, pass license requirements for professionals, establish local governments
Primaries
How a candidate for a political party is selected
1) Open: anyone can vote
2) Closed: only party members can vote for their own candidates
3) Blanket: voters can vote in primaries of both parties; ruled against in 2000
Louisiana Purchase
1803; under the presidency of Thomas Jefferson; Reasons for Purchase: to gain port in New Orleans, remove French threat with trade along Mississippi River and double territory belonging to the United States; brought into question the use of Federal power/constitutionality; Jefferson sent Meriwether Lewis and William Clark to explore the lands
War of 1812
France v British; blockades hurt American trade; Jefferson imposed an embargo against France and Britain; British captured Washington, D.C. and burned down the White House; war ended in 1815 with the Treaty of Ghent which negotiated peace with United States; war made America more self-sufficient with fewer ports
Mexican Revolution
1812-1823; fought for independence from Spain and for social justice
National Bank
Alexander Hamilton to Congress; private stockholders and the national government to provide financial stability to US (e.g. loans, funds, credit)
The American Civil War
1861-1865; war fought between the North (the Union) and the South (the Confederacy); fought on the grounds of slavery and states' rights; Gettysburg Address made by Lincoln united the nation
The Reconstruction Era
1865-1877; South was under strict control of the U.S. government; terminated state governments of the former confederacy; amendments were made to rectify the problems caused by slavery
1) 13th Amendment: slavery is illegal
2) 14th Amendment: made all persons born/naturalized in the country US citizens and states couldn't interfere with civil rights
3) 15th Amendment: made it illegal to deny individuals the right to vote on grounds of race
Jim Crow Laws
Laws that separated whites and blacks in public areas so African Americans had unequal opportunities in housing, education and government
American Abolition Movement
Radical efforts under the direction of William Lloyd Garrison (The Liberator - leading anti-slavery newspaper) that worked to get rid of slavery; created sectional differences as most abolitionists were from the North
Missouri Compromise
1820, there were an equal amount of slave states to free states and there was an imminent power imbalance when Missouri petitioned to become a slave state;
The Solution: Maine was brought in as a free state and the southern border of Missouri was set as the Northernmost line of any slave territory; Western states could come in as free states
Monroe Doctrine
President James Monroe in 1823; foreign policy that warned European powers to cease colonization of Central and South America or face military intervention by United States; United States would not meddle in political affairs or standing colonies of Europe
Indian Removal Act
1830; took natives out of territories that whites wanted to settle; Trail of Tears removed Cherokees from Georgia and relocated them to Oklahoma
Nullification
The right of states to nullify any Federal laws they thought were unconstitutional; tariffs
Whig Party
1833-1856; started in opposition to Jackson's authoritarian policies; concerned with depending the supremacy of Congress over the executive branch, states' rights, economic protectionism and modernization; 4 presidents: William Henry Harrison, Zachary Taylor, John Tyler and Millard Fillmore; split over slavery caused the party to dissolve
Manifest Destiny
1840s; popular belief that it was the right and duty of the United States to expand Westward to the Pacific

Uncle Tom's Cabin
A book written by Harriet Beecher Stowe that contributed to the Civil War; showed Northerners and the rest of the world the horrors of slavery while the South saw it as an exaggeration
Compromise of 1850
Allowed those who lived in the Mexican cession to decide for themselves whether to be a free or slave territory
Fugitive Slave Law of 1850
Allowed slave owners to go into free states to retrieve their escaped slaves
Kansas-Nebraska Act
1854; repealed the Missouri Compromise to allow the lands from the Louisiana Purchase to settle the slavery issue by popular sovereignty; enraged Northerners began the Republican party
"Bleeding Kansas"
The name applied to the state when a civil war broke out between pro- and anti- slavery advocates while Kansas was trying to formalize its statutes before being admitted as a state
Dred Scott Decision
1857 Supreme Court Case that ruled Congress had no authority to exclude slavery from the territories; upheld property rights over human rights
Industrialization
A time of enormous business growth and exploitation of natural resources for new inventions during the mid-1800s
1) Railroad Expansion: Transcontinental Railroad stretched over 35,000 miles
2) Gold and Silver Mining: Prospectors came to the West
3) Cattle Ranching: established the "Bread Basket" in the High Plains
Began in England with new inventions and factories; steel industry grew rapidly; steam engine revolutionized transportation and work power; factory-based/technologic era resulted; society went from agrarian to urban with poor working conditions and overcrowded/polluted cities
Gilded Age
1870s-1890; enormous wealth enjoyed by powerful families; control of major industries was held by robber barons (e.g. Carnegie- steel, Rockefeller- oil, Morgan- banking and Vanderbilt- steamboat)
Knights of Labor
Formed in 1878 that called for social and economic reform; replaced by American Federation of Labor led by Samuel Gompers
American Progressive Era
1890s-1920s; social movement to reform American society/order and increase trade with foreign markets
1) Hepburn Act: 1906; ICC
2) Pure Food and Drug Act: 1906; protect consumers from fraudulent labeling
3) Forest Service: 1898-1910; conservation methods and efficient use of resources
4) Federal Reserve System: 1913; supervise banking/commerce
5) Fair Trade Commission: 1914; established to ensure fair competition
19th Century Immigration Trends
Population of the US was doubled between 1860-1890; immigrants lived in the North in cities and slums; 1880s: Immigrants came from Italy, Poland, Hungary, Greece, Jewish groups from central and Eastern Europe; Roman Catholicism was on the rise
Woodrow Wilson
28th President of the US; known for: World War I leadership, created Federal Reserve, Federal Trade Commission, Clayton Antitrust Act, progressive income tax, lower tariffs, women's suffrage, Treaty of Versailles and League of Nations
Theodore Roosevelt
26th President of the US; known for: creating Progressive party, Conservationism, Trust-Busting, Hepburn Act, Safe Food Regulations, "Square Deal" and Panama Canal
Calvin Coolidge
30th President of the US after taking over for Harding; nickname "Silent Cal" for being so soft-spoken; true Republican and Industrialist; believed in government supporting Big Business and a rigid economy
Franklin D. Roosevelt
32nd President of the US; only president that served more than 2 terms in office; central figure in economic crisis and World War II; New Deal
Sherman Anti-Trust Act
An act under Theodore Roosevelt that banned formations that would restrict trade and not distinguish between bad and good trusts. The act was a hamper on worker unions, but it showed that the government was slowly moving away from laissez faire ideals.
Causes for World War I
Militarism
Alliances
Nationalism
Imperialism
Assassination

World War I
1914-1918; fought by the Allies: Britain, France, Russia, Greece, Italy, Romania and Serbia against the Central Powers: Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria and Turkey; United States joined the Allies in 1917 after years of neutrality; sinking of the Lusitania caused the US to join
Fourteen Points Speech
1918; Woodrow Wilson; outlined plans for peace and the League of Nations
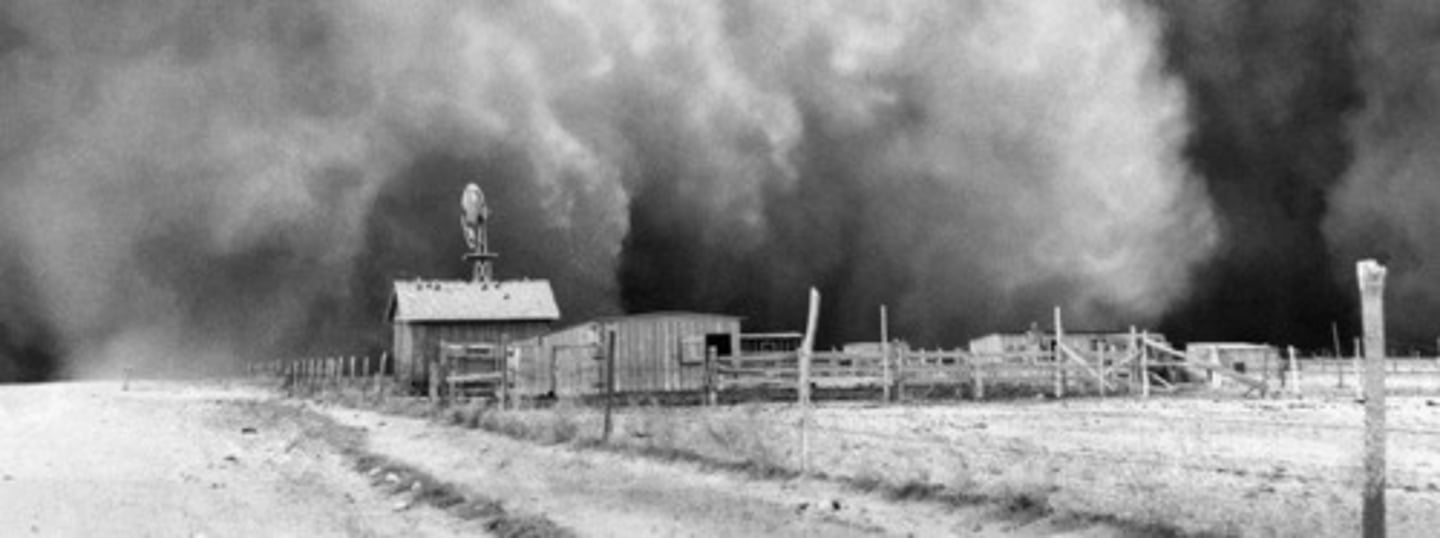
Dust Bowl
1930s; Inadequate conservation techniques caused topsoil to be blown away in great dust storms; deaths from blackened skies that led to lung disease and failed crops

Great Depression
Farmers went into a Depression when foreign markets started growing their own crops again; increased credit buying, bank war debts and gaps between the rich and the poor allowed the stock market to crash in October 1929; The Result: the economy spiraled downward, banks failed, people became unemployed, industrial production fell and national income level dropped
World War II
1939-1945; Allies v Axis powers; fought on every continent; Pearl Harbor attacks in 1941 by Japan caused the US to join war efforts on the Allies side "a day that would live in infamy"; women worked in the factories while men entered the military so great manufacturer of goods/munitions for the war effort; rationing and war bonds; production brought an end to the economic depression
Cold War
Soviet Union kept control of Eastern Europe spreading Communism around the world, led to:
1) The Truman Doctrine: 1947; policy designed to protect free peoples everywhere against oppression
2) Marshall Plan: 1948; $12 billion went to rebuilding Western Europe and strengthening its defenses
3) Organization of American States: 1948; bolstered democratic relations in the Americas
4) Berlin Blockade: 1948-49; Soviets tried to starve out West Berlin so US air dropped supplies
5) North Atlantic Treaty Organization: 1949; Formed to militarily link the US and Western Europe so an attack on one was an attack on both
6) Korean War: 1950-1953; This divided the country into the communist North and democratic South
7) The McCarthy Era: 1950-54; Senator McCarthy of Wisconsin held hearings on supposed Communist conspiracies that ruined innocent reputations and led to the blacklisting of suspected sympathizers in the government/media

Brown v Board of Education
1954; segregation was a violation of the Equal Protection Clause; "separate but equal" practice was unconstitutional in education; overturned the 1896 Plessy v Ferguson ruling that permitted segregation if facilities were equal

Miranda v Arizona
1966; made the reading of the Miranda rights to those arrested for crimes the law; ensured confessions could not be illegally obtained and that citizens rights to fair trials and protection under the law would be upheld

1960s
1) Cuban Missile Crisis: 1961; stand-off between the United States and the Soviet Union over a build-up of missiles in Cuba; nuclear war was averted when Soviets stopped shipments
2) Assassinations of President Kennedy (1963) and MLK Jr (1968)
3) Civil Rights Movement: 1960s; social movements to end racial segregation and discrimination that drew attention to the plight of African Americans
4) Vietnam War: 1964-1973; resulted in the military draft; heavy involvement of American personnel and money
5) Major Legislation: Civil Rights Act, the Clean Air Act, Water Quality Act, Medicare, War on Poverty
Time Zones
1 hour = 15 degrees longitude (4 minutes = 1 degree turn)
27 nations agreed at the 1884 International Meridian Conference to create the time zone system which consists of 24 time zones (to equal 24 hours in a day)
The 1884 Conference established the meridian passing through Greenwich, England (zero point AKA prime meridian)
180th meridian = International Date Line (the place where a day begins and ends)
Cartography
The art and science of mapmaking; maps of local areas were drawn by Egyptians as early as 1300BC and Greeks made maps of the known world in 6th century BC
Steps: 1) Survey: selecting key sites for benchmarks for measurements; 2) Compile Info and Computer Draft a Map Based on Collected Data; 3) Reproduce/Print
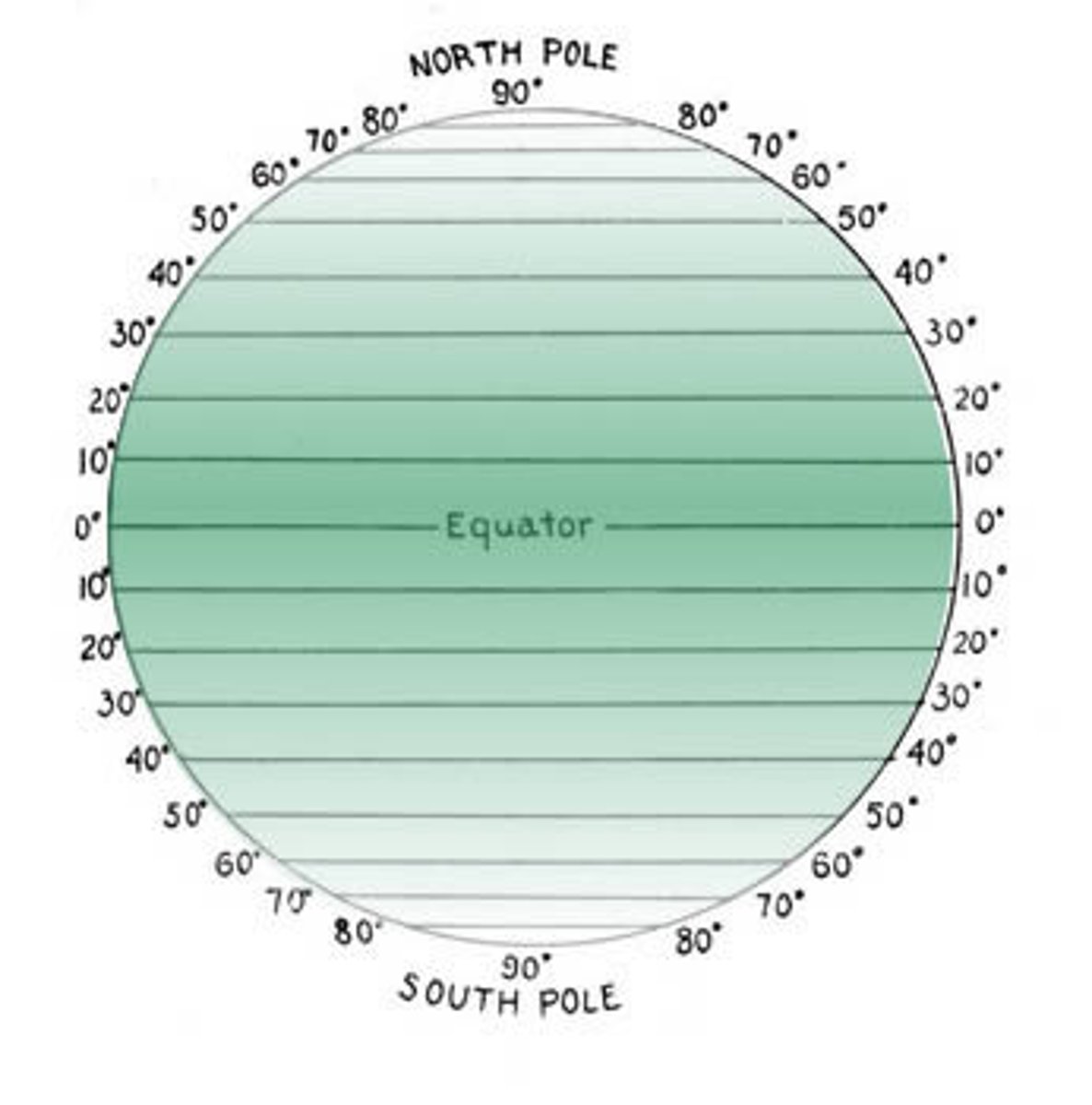
Latitude
Imaginary Horizontal line that divides the globe into a grid (360 degrees); Parallels=lines of Latitude
Longitude
Imaginary Vertical line that divides the globe into a grid (360 degrees); Meridians=lines of Longitude; circle the Earth and connect at the Poles
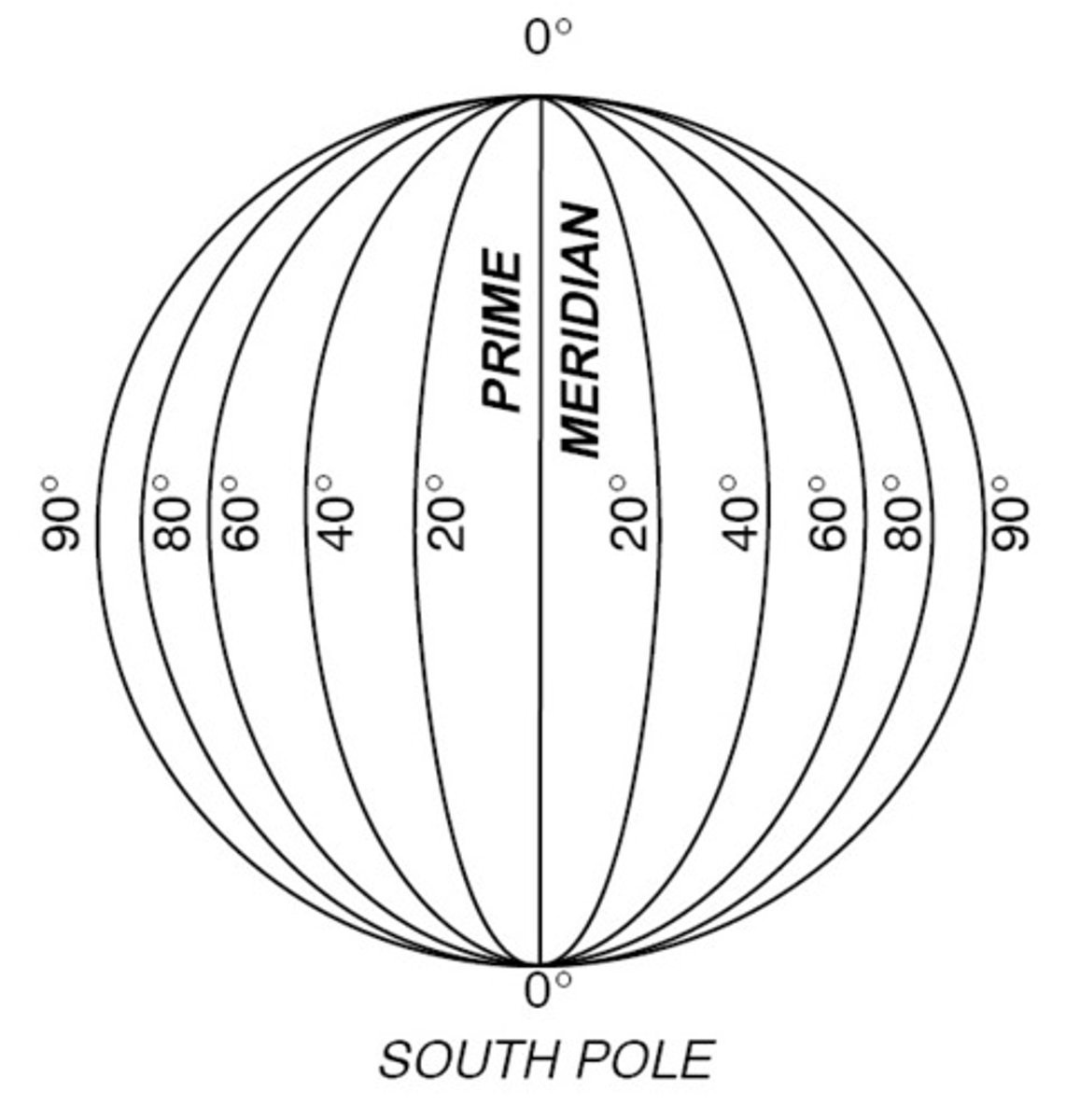
Absolute Location
Exact spot where coordinates meet
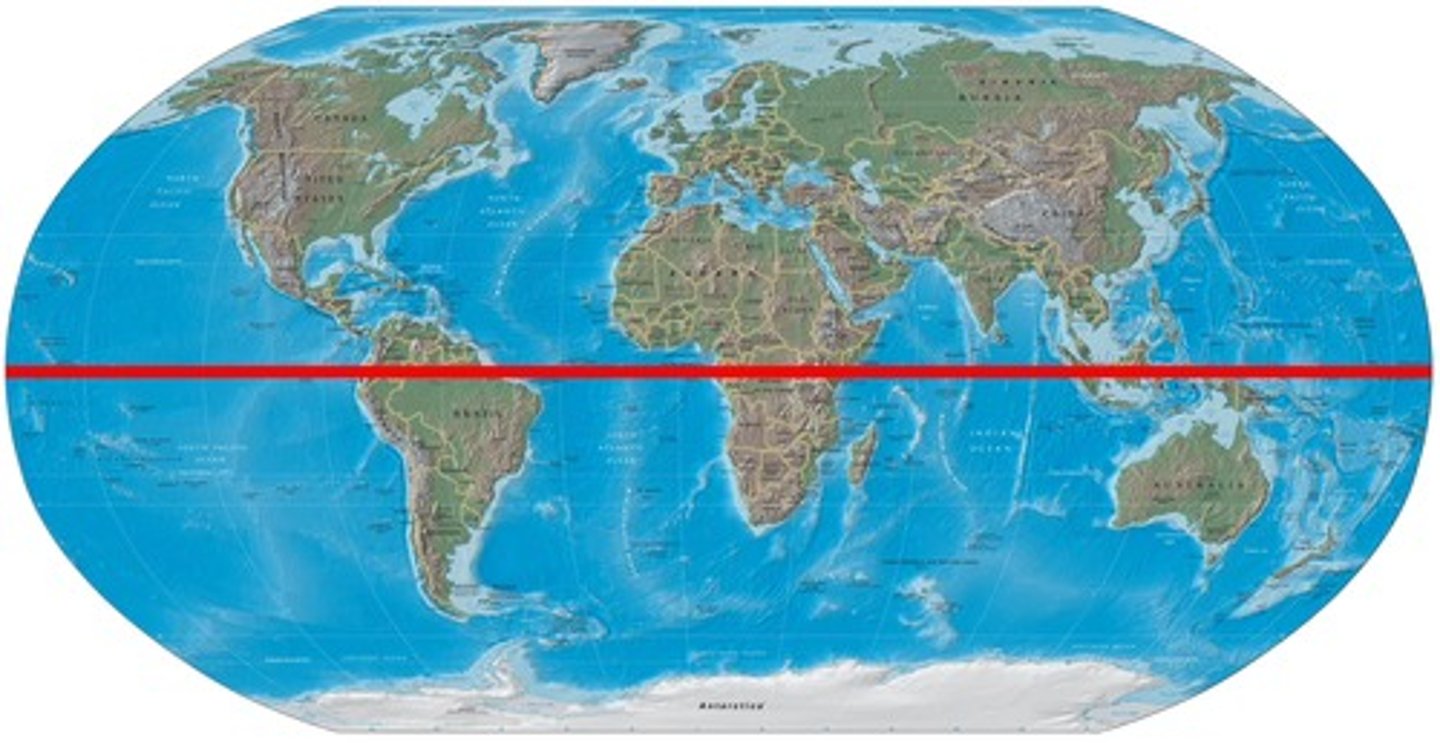
Equator
0 degrees Latitude (2 equal halves - Northern/Southern hemispheres with areas on the sides Western and Eastern)
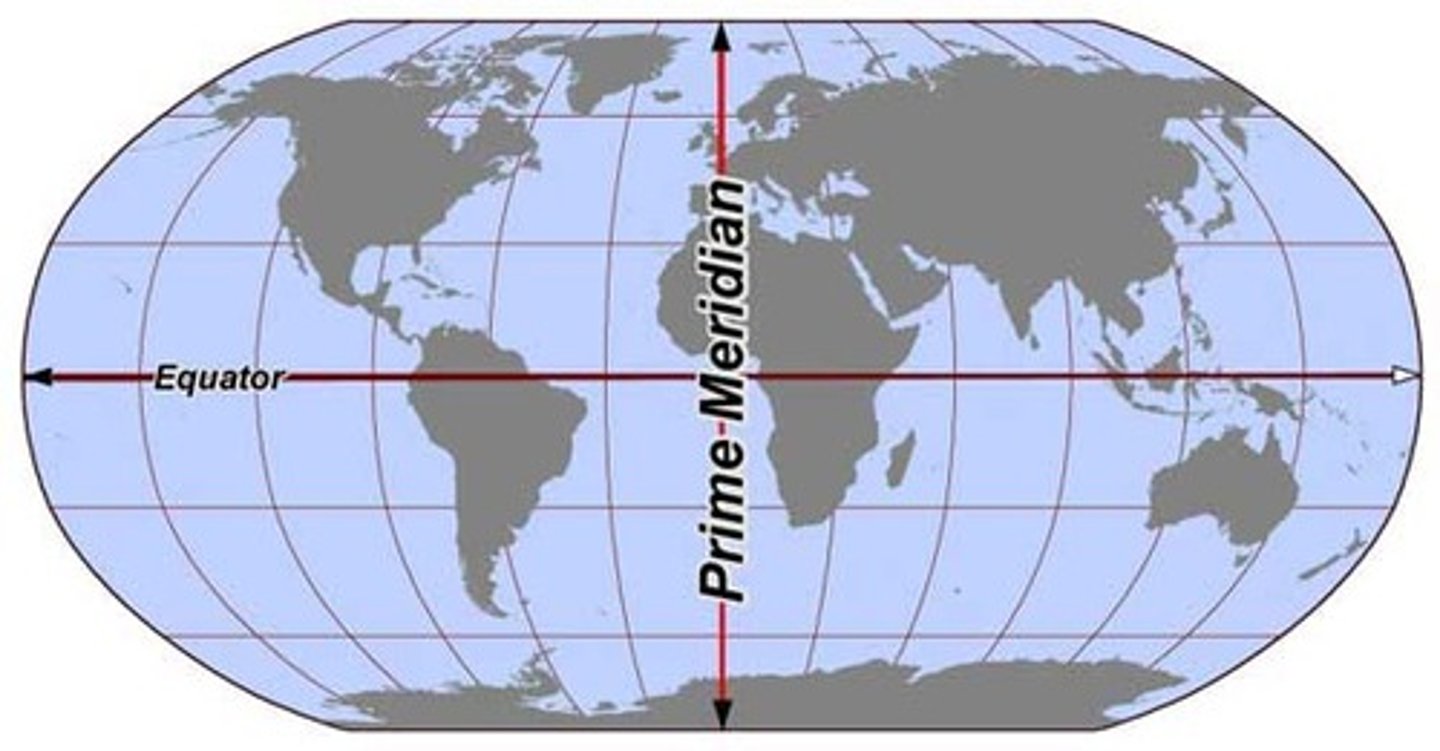
Prime Meridian
0 degrees Longitude; starting point for measuring distance
Poles
North: 90 degrees North latitude
South: 90 degrees South latitude
Tropic of Cancer
23.5 degrees North of the equator
Tropic of Capricorn
23.5 degrees South of the equator
Arctic Circle
66.5 degrees North of the equator
Antarctic Circle
66.5 degrees South of the equator
Physical Features of Geographic Locations
Vegetation Zones/Biomes - forests, grasslands, deserts and tundra
Climate (the long-term average weather conditions of a place) Zones - tropical, dry, temperate, continental and polar
Cultural Features of Geographic Locations
Population Density: the number of people living in each square mile/kilometer of a place (divide population by area)
Religion: dominant religions of a place (Christianity, Hinduism, Judaism, Buddhism, Islam, Shinto, Taoism, Confucianism)
Languages: official language of a place; 12 major language families; Indo-European family is spoken over the widest geographic area
Spatial Organization
How things or people are grouped in a given space anywhere on Earth
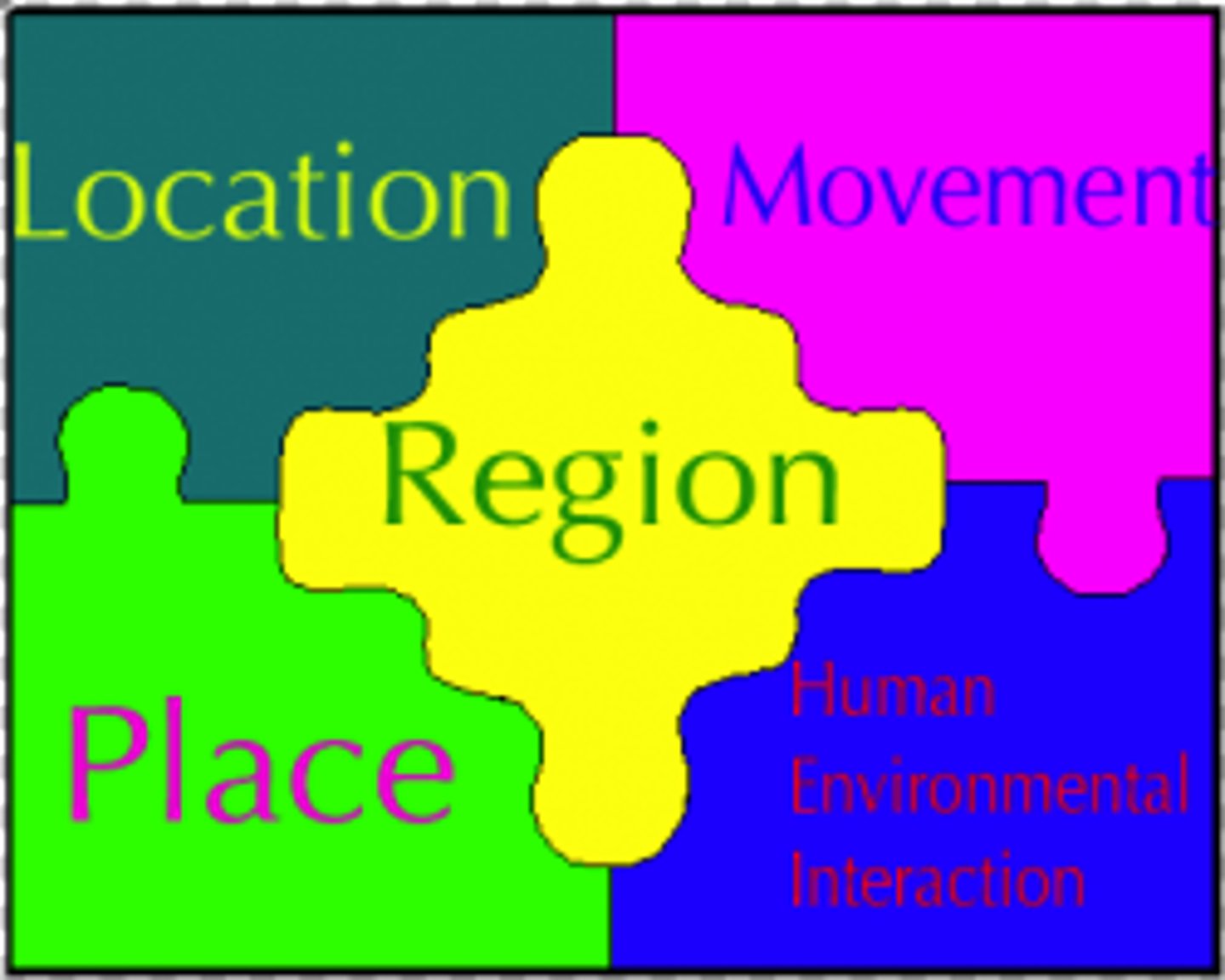
Themes of Geography
1) Location: relative and absolute
2) Place: physical characteristics and human characteristics
3) Human-Environmental Interaction: human adaptation/modification/dependence to the environment
4) Movement: interaction through trade, migration, communications, political boundaries, ideas and fashions
5) Regions: formal (e.g. cities, states, countries), functional (e.g. common connection) and vernacular (e.g. divisions based on perceptions/mental images)
Geomorphology/Physiography
The study of landforms; a science that considers the relationships between geological structures and surface landscape features; studies the processes that change these features (e.g. erosion, deposition, plate tectonics) and biological factors
Landform
Landscape feature or geomorphological unit (e.g. hills, plateaus, mountains, deserts, canyons, deltas, valleys) categorized according to elevation, slope, orientation and stratification
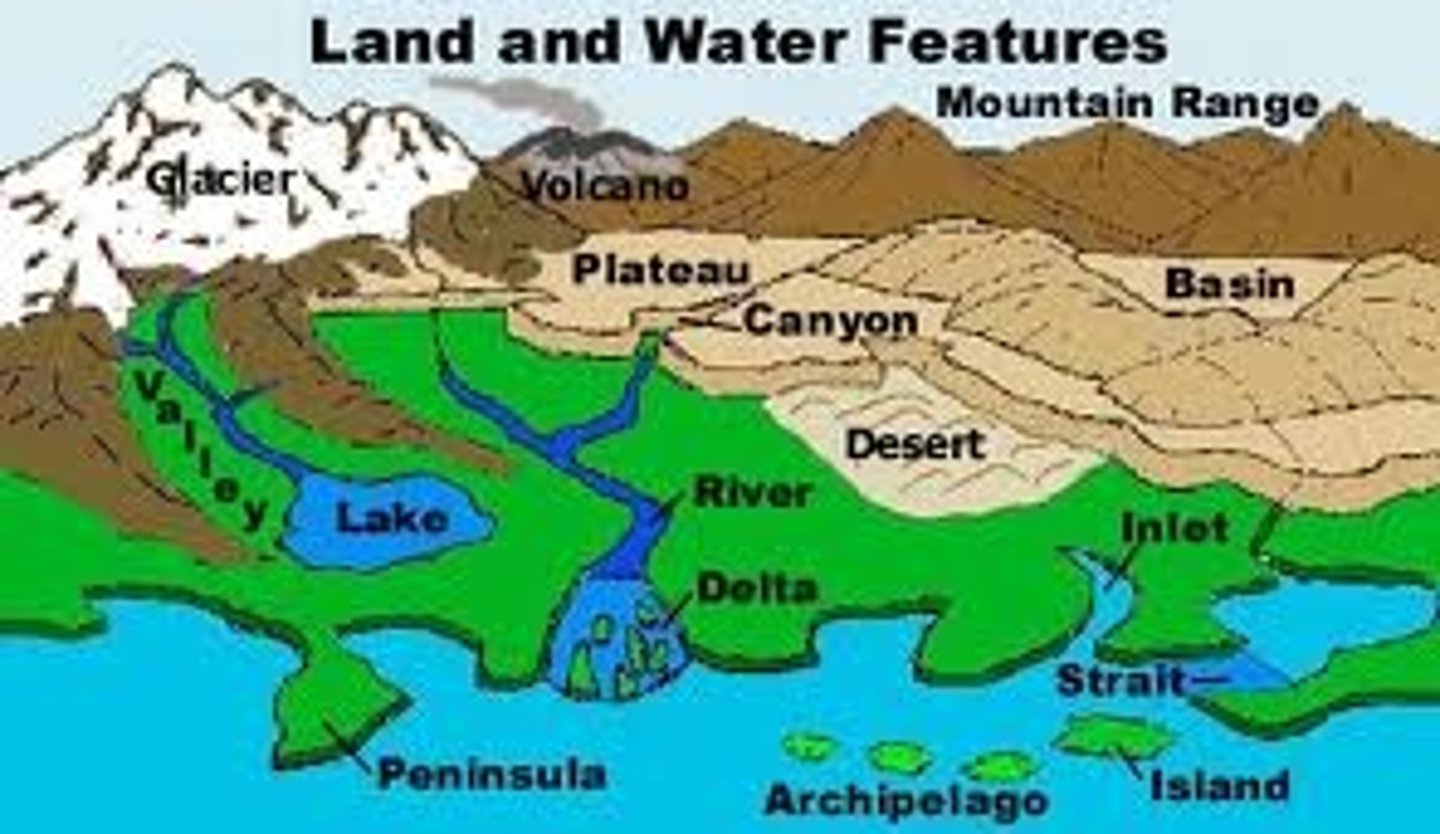
Oceans
Largest bodies of water on Earth (cover 71% of Earth's surface); 5 major oceans: Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, Southern
Seas
Smaller than Oceans and somewhat surrounded by land; Examples: Mediterranean, Baltic, Caspian, Coral and Caribbean
Lakes
Bodies of water in a depression; Examples: Great Lakes and Lake Victoria
Rivers
Channeled flow of water that start out as a spring/stream formed by runoff from rain or snow; flow from higher to lower ground and empty into a sea or ocean; Examples: Amazon, Nile, Mississippi, Ganges, Yangtze
Canals
Artificial waterways constructed by humans to connect two larger bodies of water; Examples: Panama and Suez
Climates
1) Humid Continental: four seasons; cold winter, hot summer; sufficient rainfalls
2) Prairie Climates: in steppe regions; dry flatlands
3) Subtropical Climates: humidity in the tropical areas; moisture produces long summers and mild winters
4) Marine Climate: near or surrounded by water; warm oceans bring moisture, mild temperatures and plentiful rain
Physical Geography
The study of climate, water and land and their relationships with each other and humans; locates and identifies the Earth's surface features and explores how humans thrive
Cultural Geography
The study of the influence of the environment on human behaviors and the effect of human activities
Sumer
Ancient civilization; used the 1st known writing system, advanced the development of the wheel and irrigation, urbanized their culture
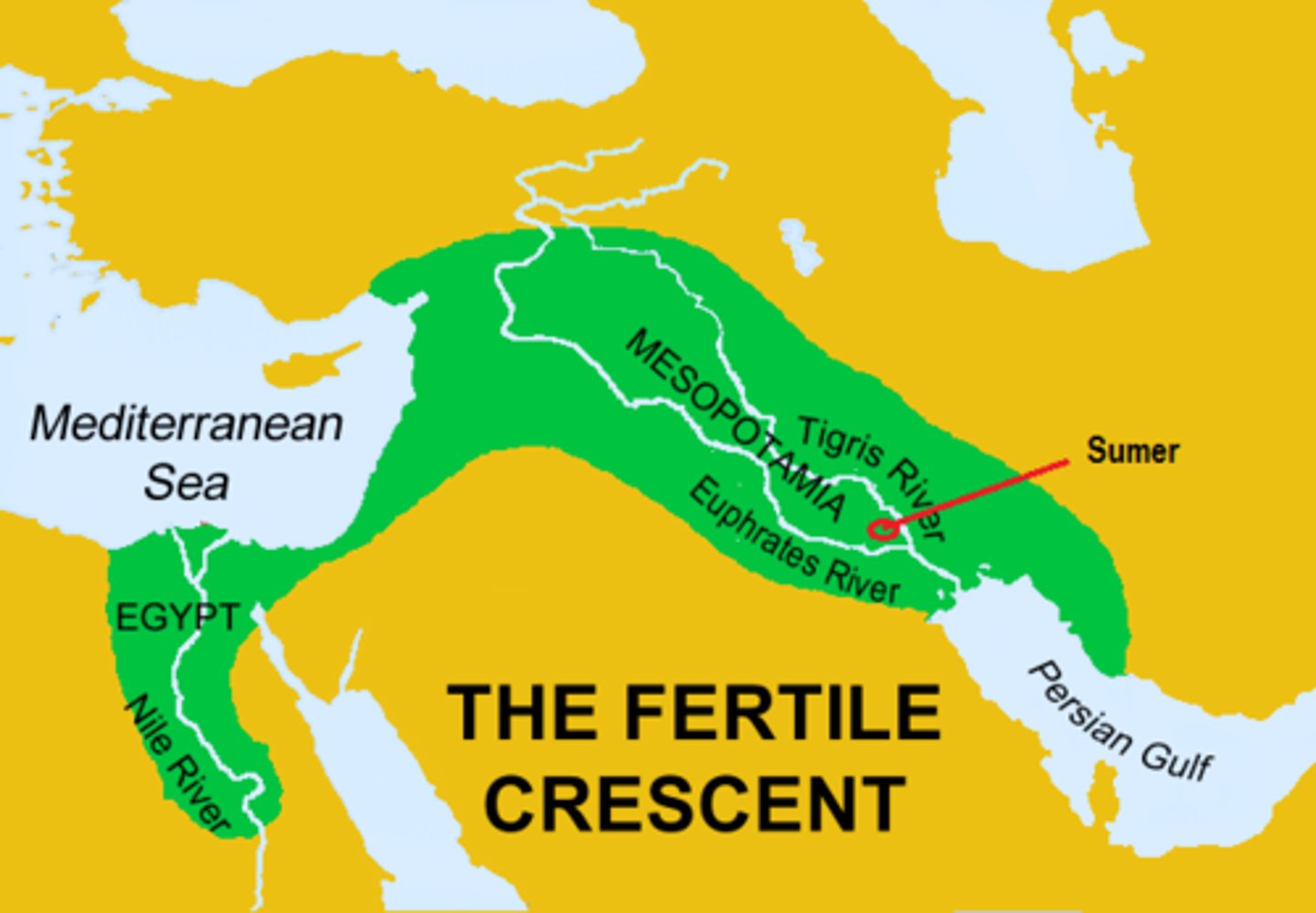
Egypt
Ancient civilization; united by the Nile River, settled in villages, pharaohs served as Gods, central government controlled civil and artistic affairs