04.E BIO, HN Active Transport (PART E)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Active Transport (Definition)
The movement of materials from an area of low concentrations to high concentration LOW → HIGH; a carrier transport protein and energy (ATP) are required OR bulk transport where vesicles are formed; includes proton/ion pumps, endocytosis and exocytosis
Active Transport (Types)
Proton/Ion Pumps
Endocytosis
Exocytosis
Active Transport (Materials Transported)
Large polar molecules
Some Ions (H+, Na+, K+, Ca+2)
Hormones
Enzymes/Proteins
Food/Wastes
Carrier Protein
A type of transport protein that spans the membrane, contains 2 active sites, a recognition site and an ATP binding site
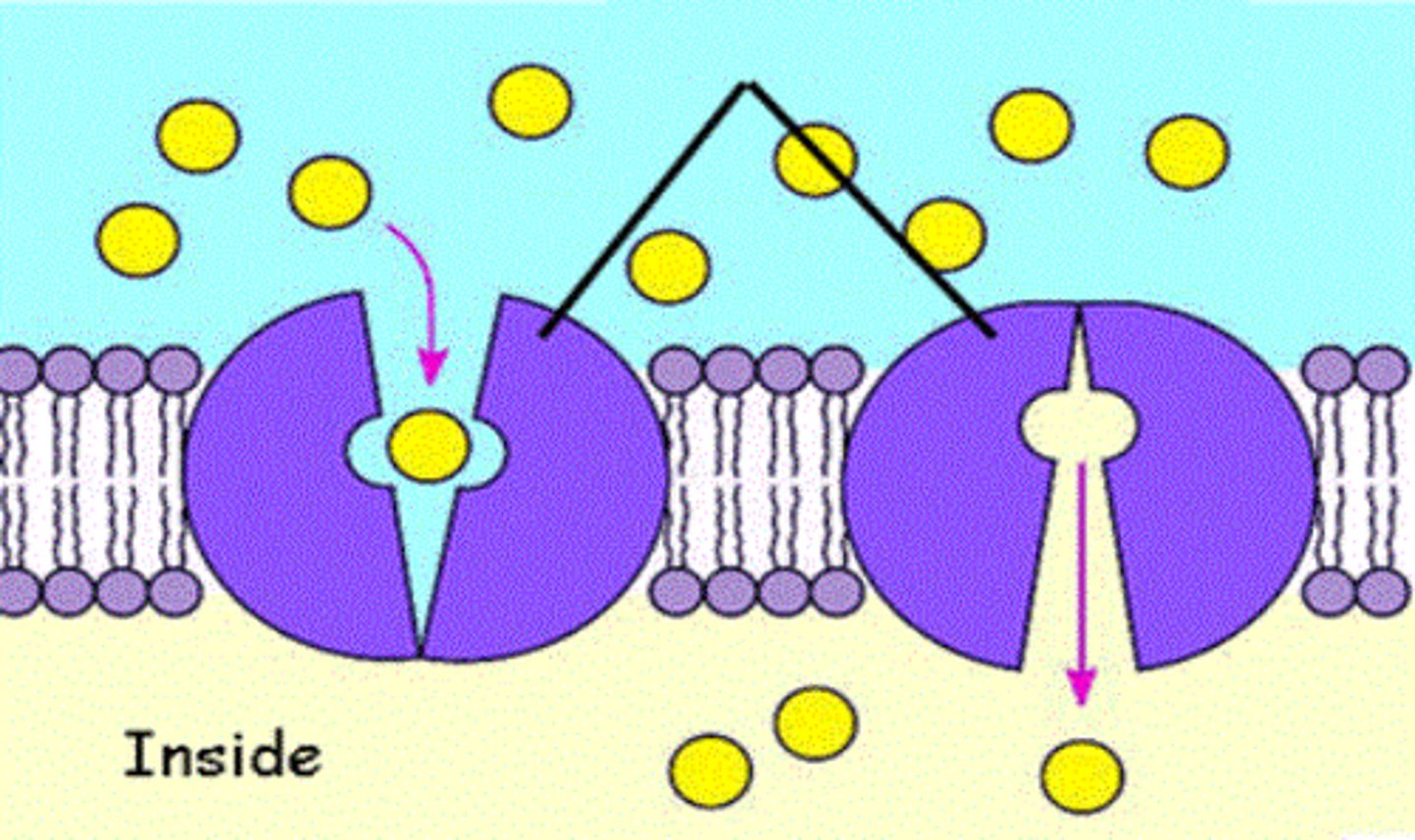
Ion pump
A carrier protein that uses cellular energy to "pump" ions such as H+, Na+, K+, Ca+2 across the membrane
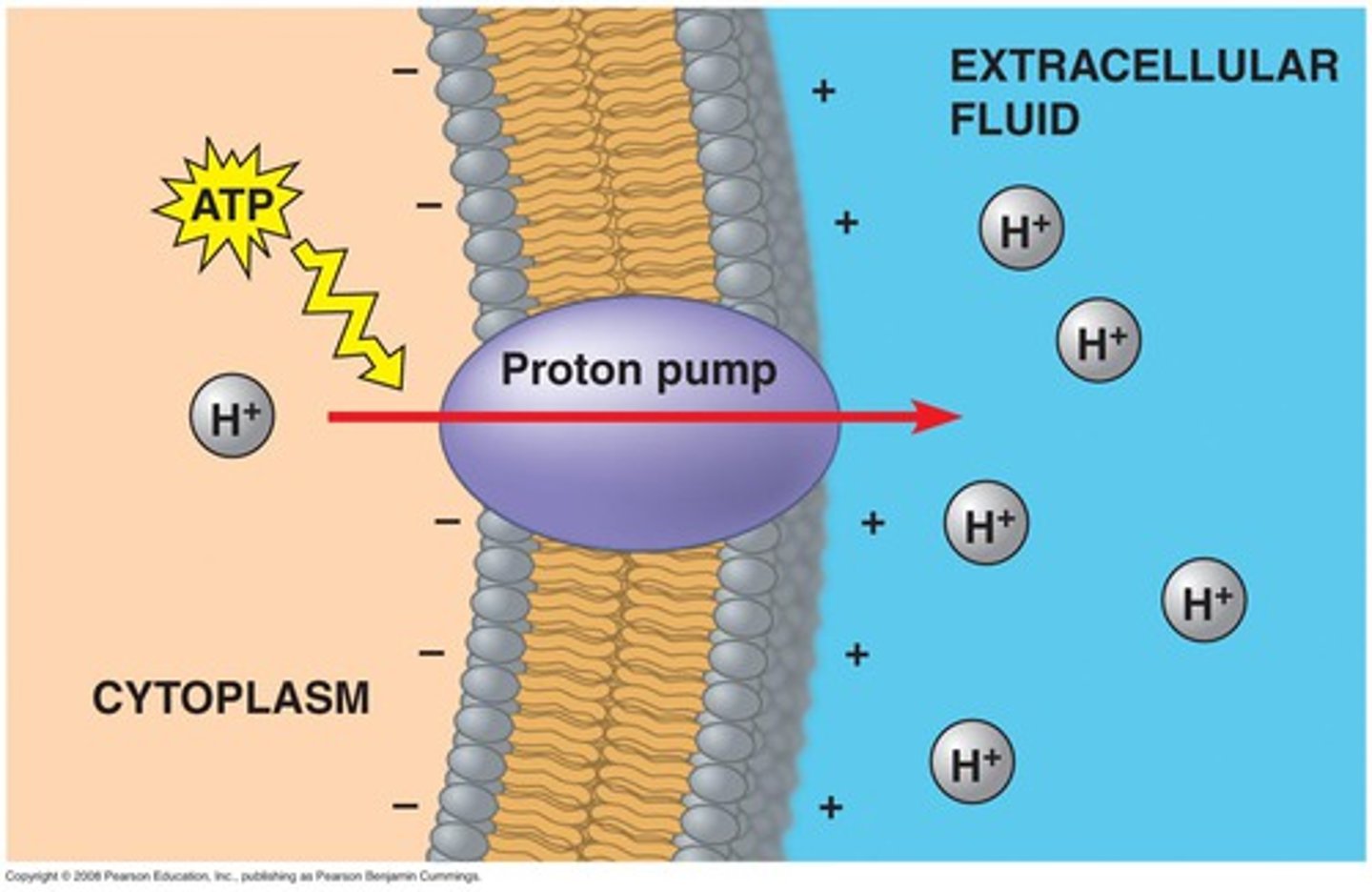
Proton Pump
A specific type of ion pump that uses cellular energy to "pump" hydrogen ions (H+) against concentration gradient (from low to high concentration)
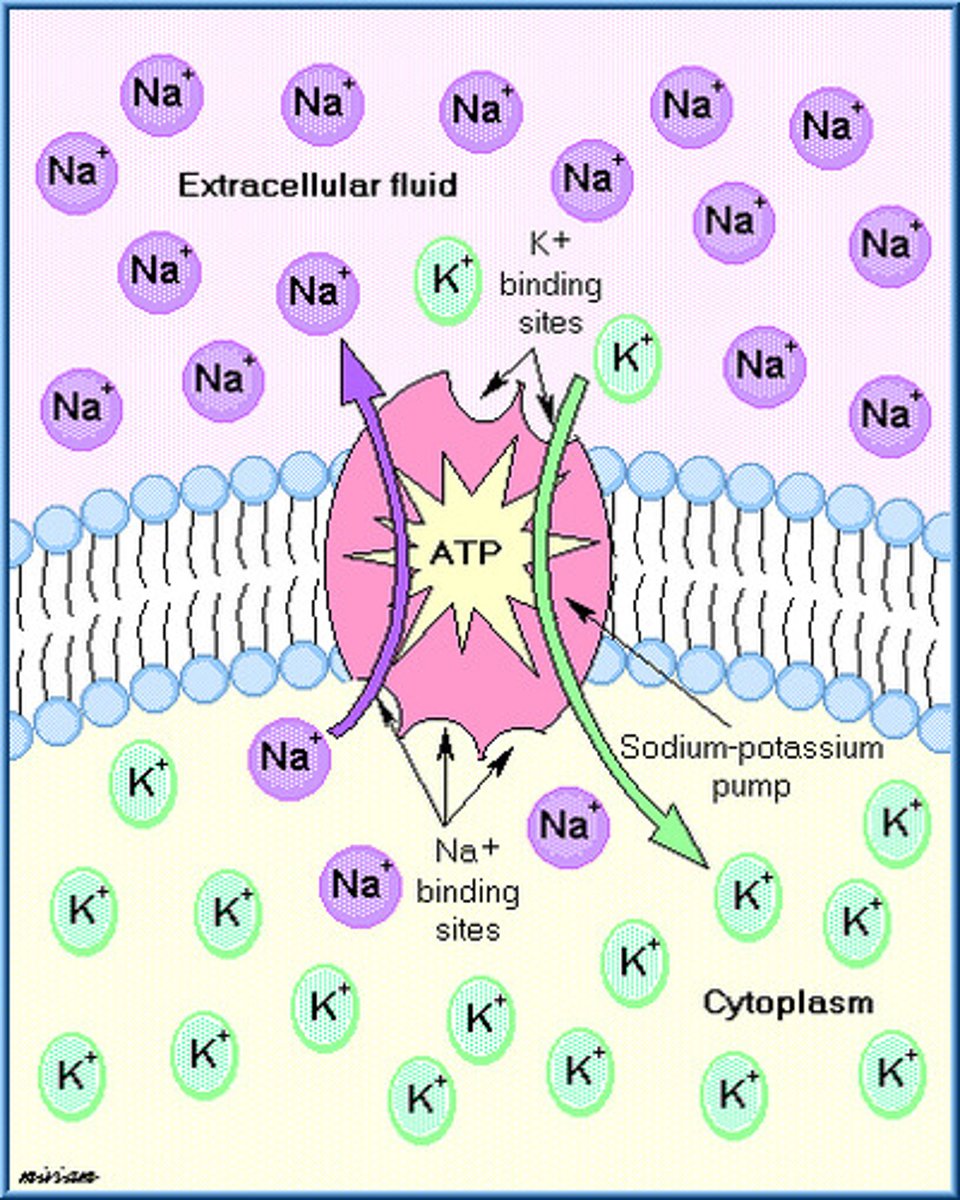
Sodium-Potassium Pump
A carrier protein that actively transports sodium ions (Na+) and potassium ions (K+) against their concentration gradients; ATP is required to change the shape of the carrier protein; three Na+ are pumped out of the cell and two K+ are pumped into the cell
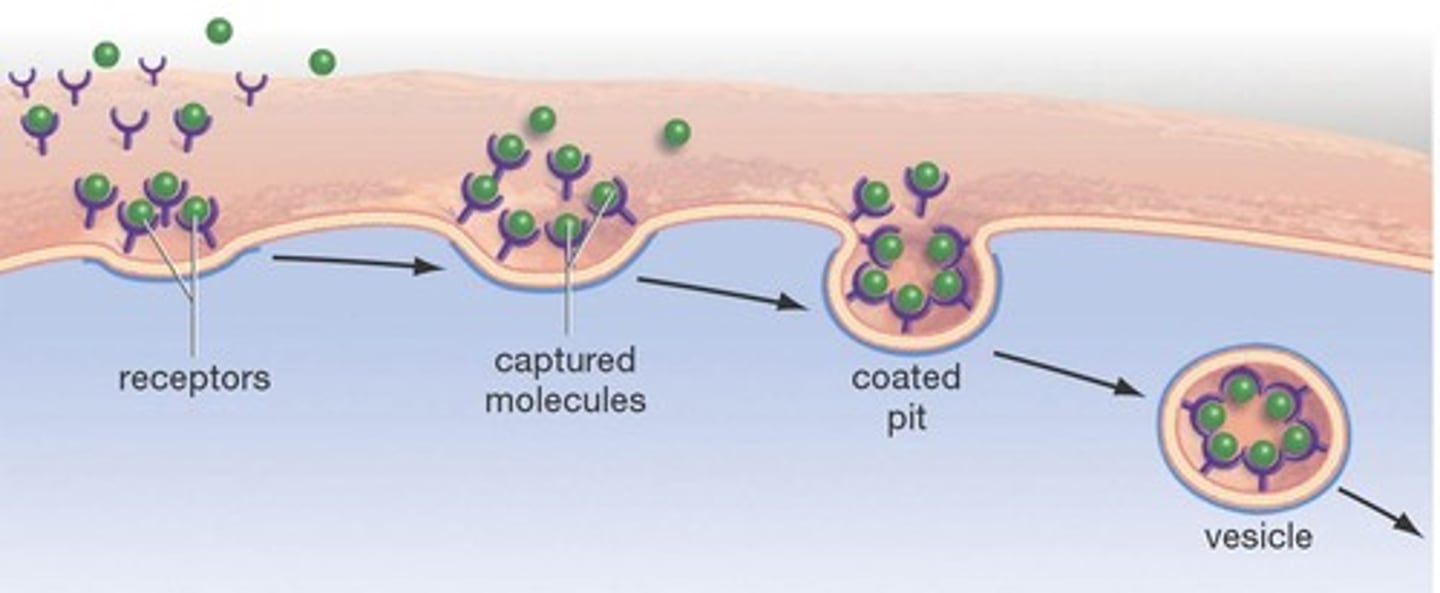
Endocytosis (Definition)
Bulk transport of materials INTO the cell through the formation of a vesicle; energy is required (ATP); includes phagocytosis and pinocytosis
Endocytosis (Types)
Types include:
- Pinocytosis - "drinking"
- Phagocytosis - "eating"
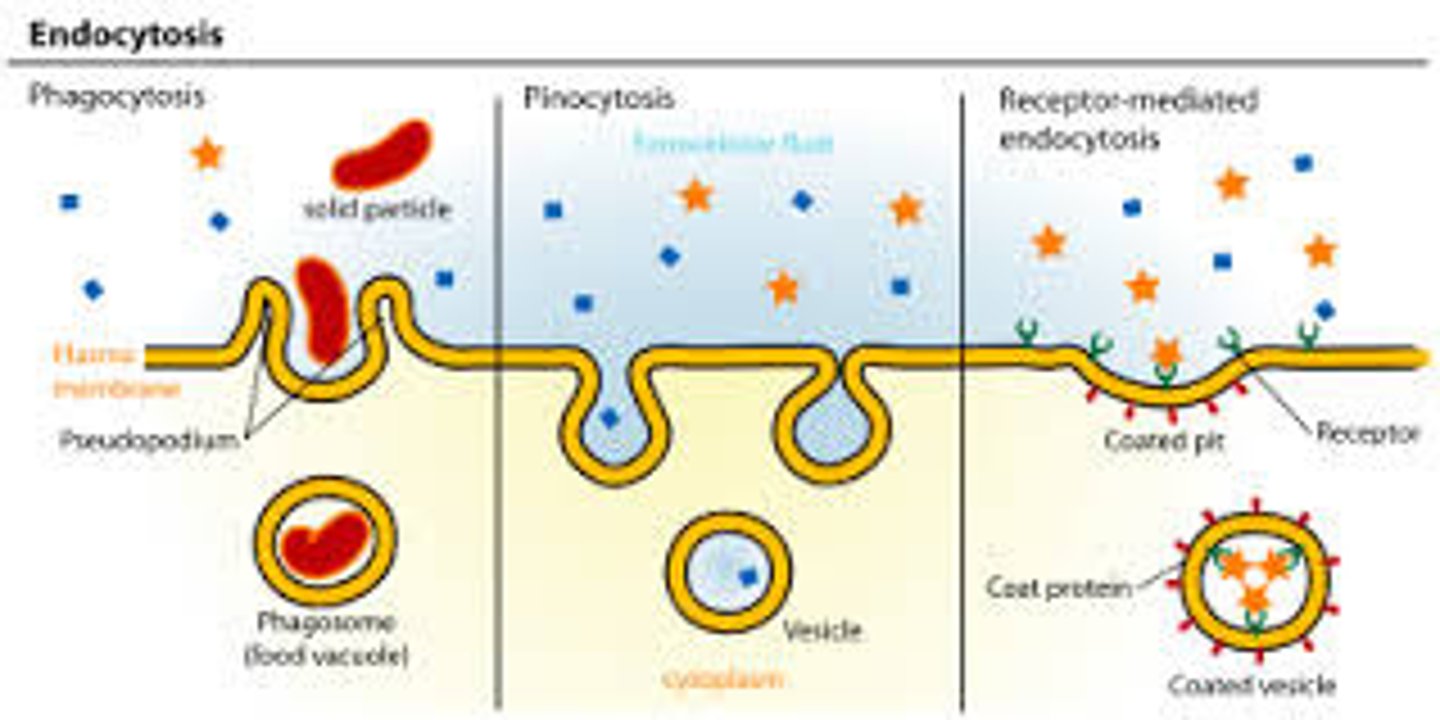
Endocytosis (Materials Transported)
Responsible for the transport of large proteins or microorganisms; i.e. amoeba engulfing paramecium, WBC destroying bacteria
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which SOLID materials are engulfed and brought into the cell
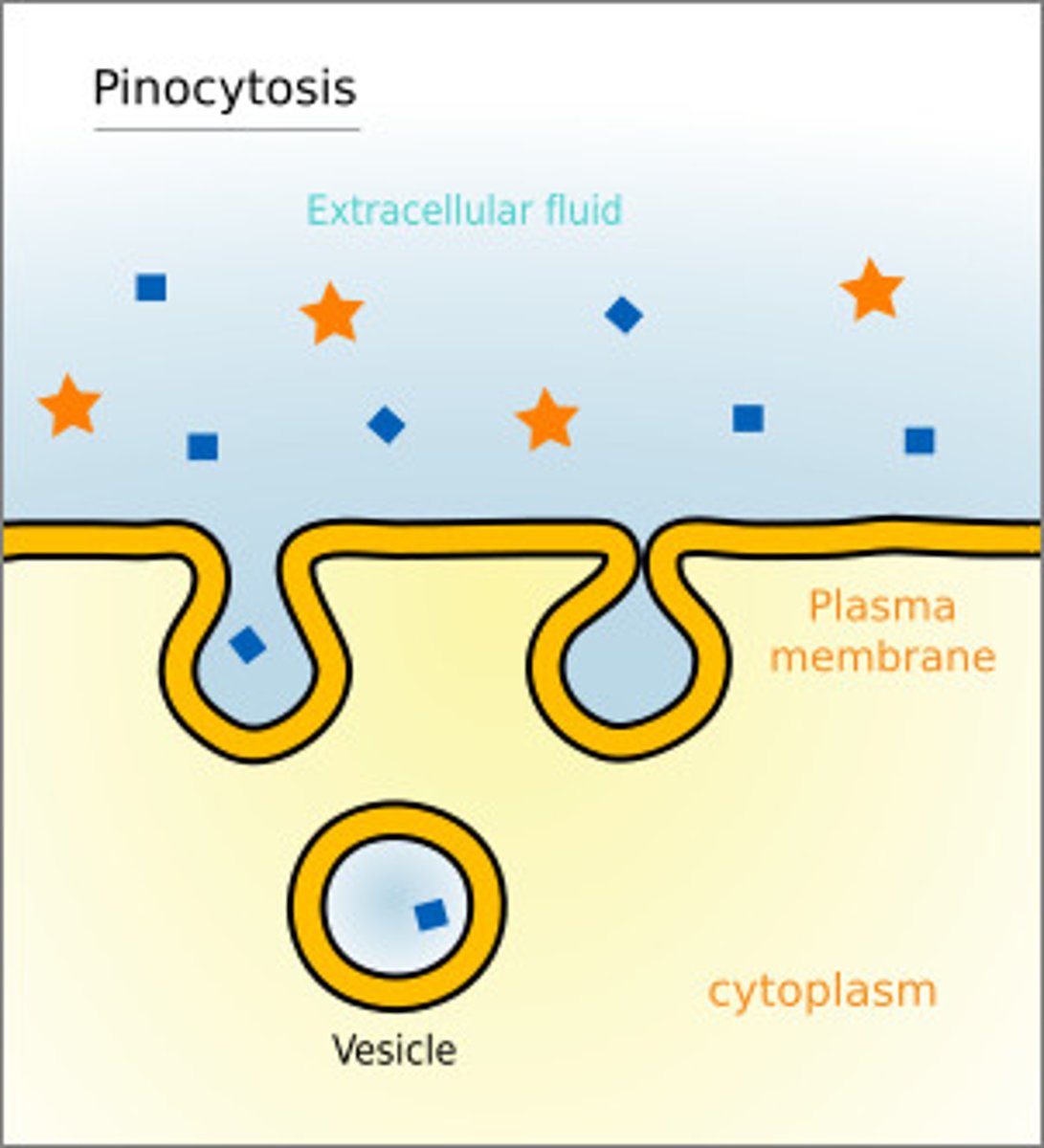
Pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which LIQUID materials are engulfed and brought into the cell
Exocytosis (Definition)
Bulk transport of materials OUT of cell through the formation of a vesicle; energy is required (ATP)
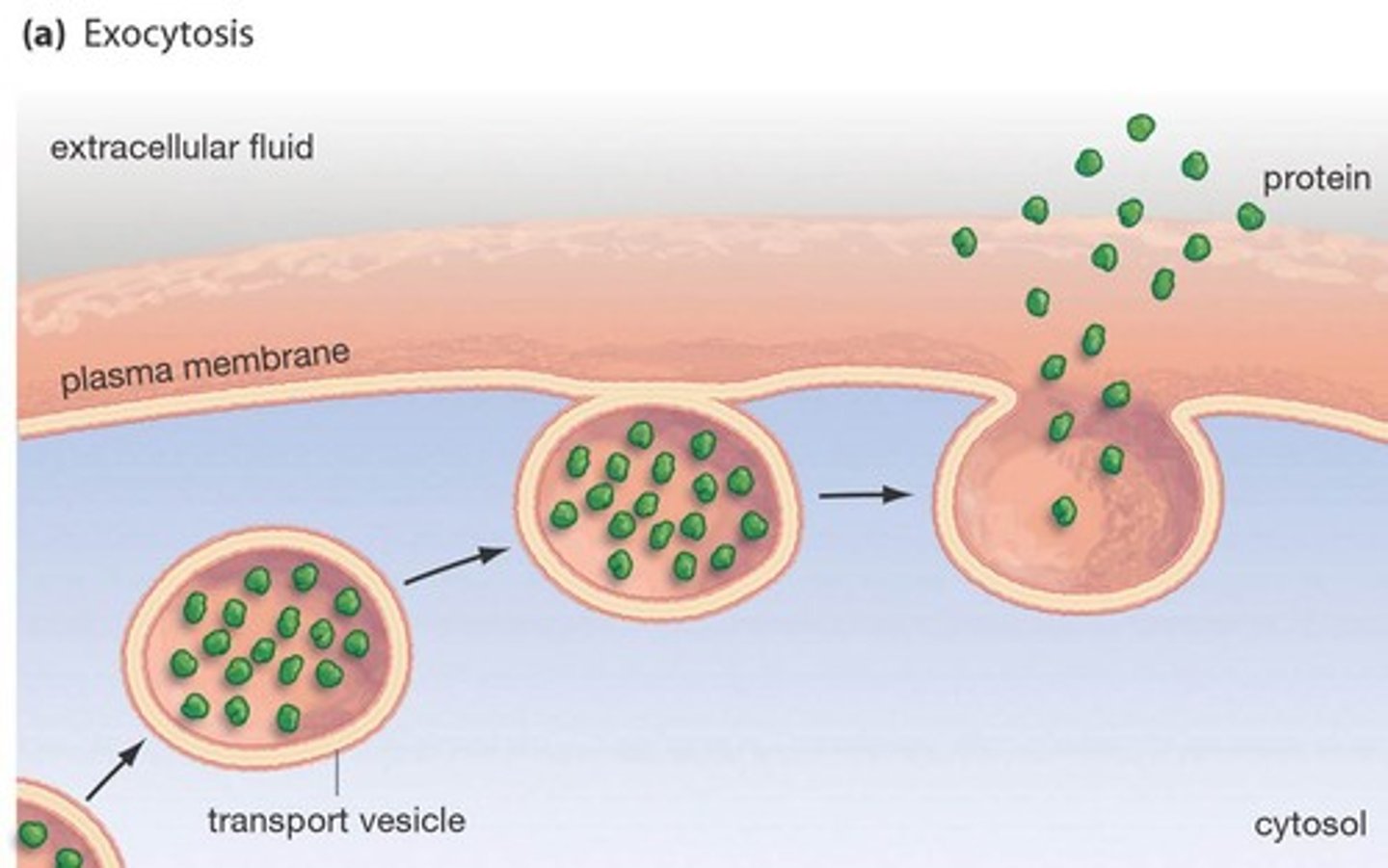
Exocytosis (Materials Transported)
Responsible for the transport of:
- Large molecules
- Enzymes/proteins
- Hormones (proteins or lipids)
- Wastes