Entropy
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are the implications of reactions being able to occur at room temperature?
enthalpy changes alone do not control whether reactions occur
What is entropy?
A measure of the amount of disorder in a substance.
The natural direction of change is increasing total entropy.
When is there an increase in entropy?
An increase in disorder will lead to a positive entropy change.
there is a change of state from solid to liquid or gas
There is a significant increase in number of moles between products and reactants

How can you calculate the entropy change of the system?
Remember to respect balancing!!!

How can you calculate the total entropy change?

What infers that a reaction is thermodynamically feasible / spontaneous at a specific temperature?
the total entropy change must be a positive value
However, the reaction might not happen if kinetic factors prevent it from occurring e.g. if the reaction has a very high activation energy then the rate of reaction will be very slow and so the reaction might not happen
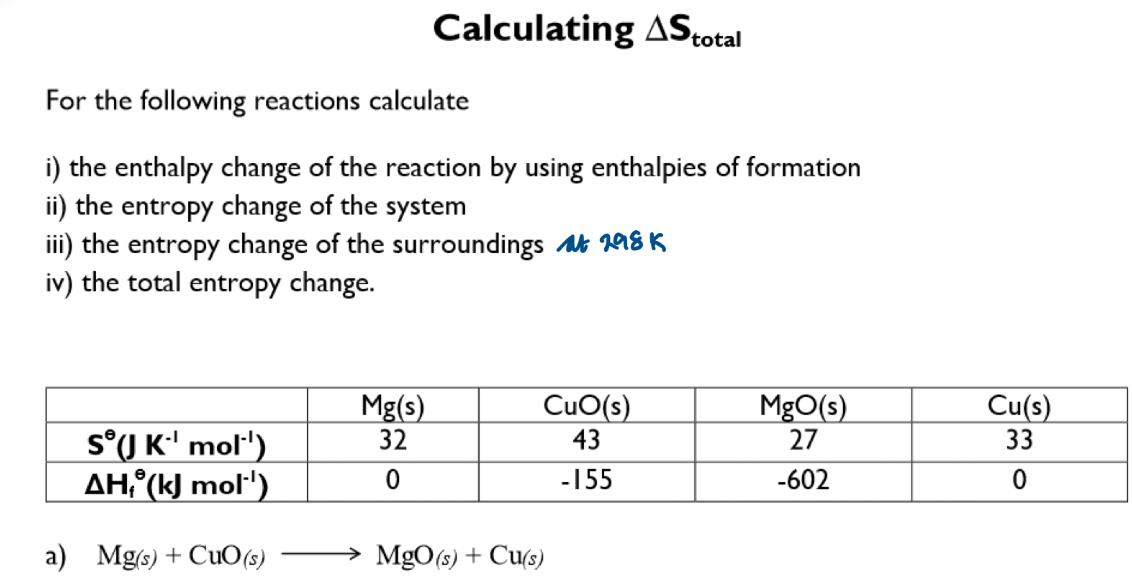


Discuss in terms of entropy change:
→ dissolving ammonium nitrate crystals in water
entropy of the system is positive as the disorder increases
One mole of a giant ionic lattice breaks up into two moles of aqueous ions
The temp decreases therefore reaction is endothermic
Therefore the entropy of the surroundings is negative using -\Delta H/T
Therefore total entropy must be positive as the reaction does happen, so the magnitude of the entropy of the system must be greater than the magnitude of the entropy of the surroundings
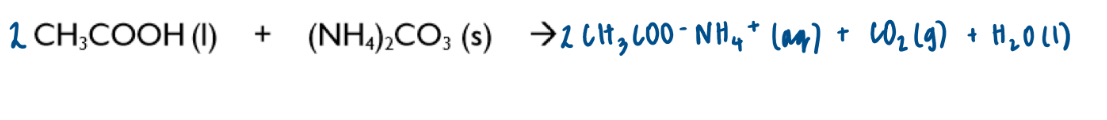
Discuss in terms of entropy change:
→ reacting ethanoic acid with ammonium carbonate
Increase in disorder, therefore the entropy of the system is positive
Reaction is endothermic (delta H is positive) therefore the entropy of the surroundings is negative


Discuss in terms of entropy change:
→ burning magnesium ribbon in air
decrease in disorder therefore entropy of the system is negative
Reaction is exothermic therefore entropy of the surroundings is positive

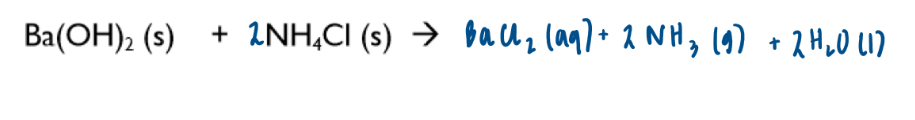
Discuss in terms of entropy change:
→ mixing solid barium hydroxide with solid ammonium chloride
disorder increases therefore entropy of the system is positive
Reaction is endothermic therefore entropy of the surroundings is negative
Water freezes when placed underneath reaction vessel on a wooden bench
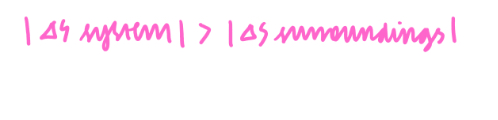
What is Gibbs Free Energy?

What is the connection to Gibbs Free Energy and thermodynamic feasibility?
in order for a reaction to be thermodynamically feasible, Gibbs free energy must be negative
This means the reaction can happen
The term spontaneous is taken to mean the same thing as thermodynamically feasible
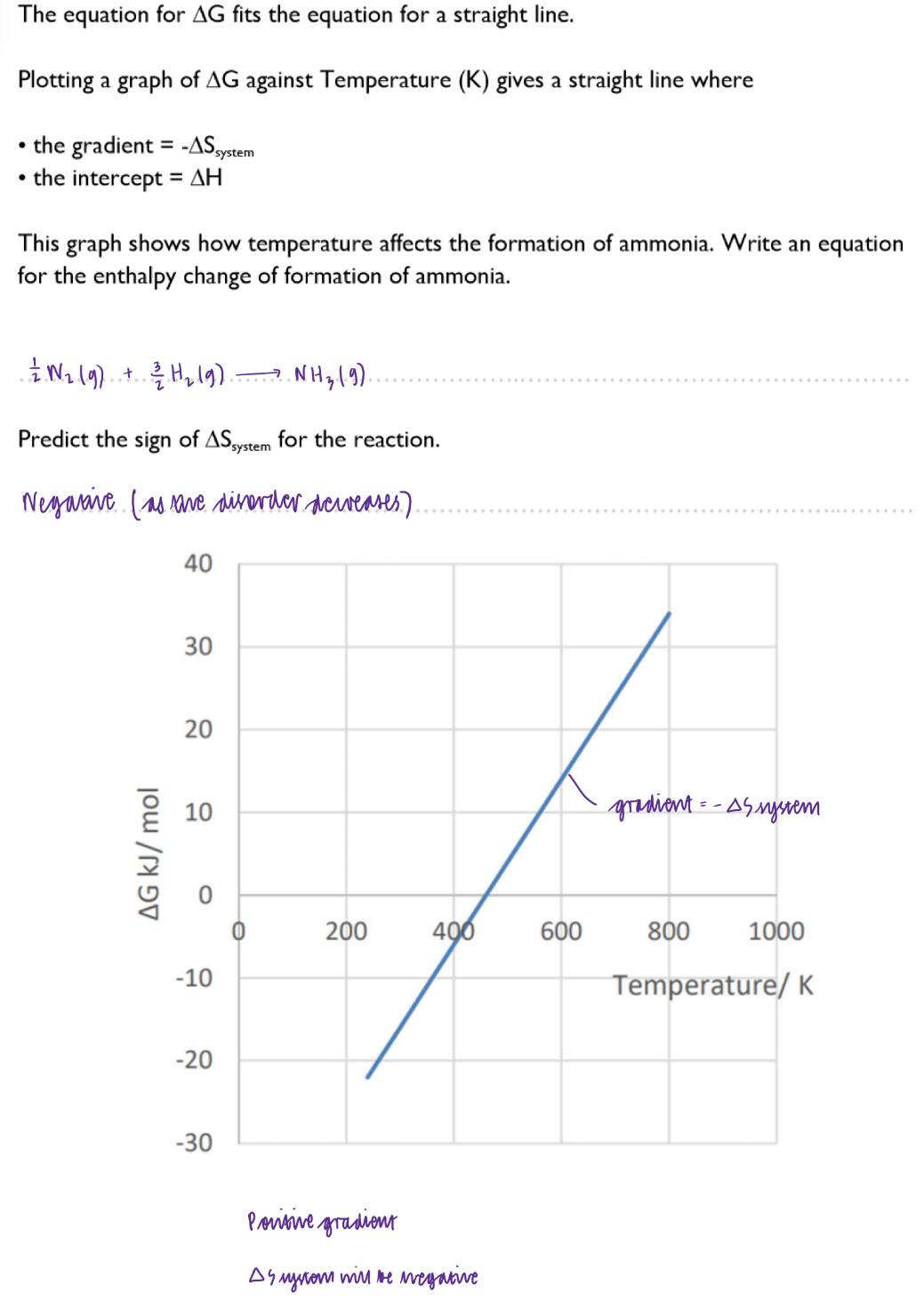
Use the Gibbs free energy equation to predict whether a reaction is feasible and determine the temperature at which a reaction is feasible:

What would infer that a reaction is more feasible?
A more negative value of delta G
How does temperature affect feasibility?

How else can the effect of temperature on thermodynamic feasibility be shown?
On a graph:
How does delta G relate to changes of state?
Melting:
a substance cannot melt below its melting point as delta G is positive below the melting point
At the melting point, delta G = 0 and so melting is feasible and the substance melts
Boiling:
a substance cannot boil below its boiling point as delta G is positive below the boiling point
At the boiling point, delta G = 0 and so boiling is feasible and the substance boils.

What might thermodynamically feasible reactions be inhibited by?
kinetic factors
Use the magnitude and signs of the entropy changes to explain the effect of a temperature increase on the equilibrium constant of this endothermic reaction
as reaction is endothermic, and delta H is positive
Entropy of surroundings must be negative (using equation)
If the temperature is increased, the magnitude of the entropy of the surroundings decreases (still according to equation)
The total entropy becomes more positive (as total entropy = entropy of the system + entropy of the surroundings)