auto sympathomimetics: beta and alpha agonists (part 2 and 3)
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
2 examples of non-selective beta 2 agonists
isoproterenol (prototype), dobutamine
effects of isoproterenol on TPR, SBP, and DBP
- lowered TPR (via beta vasodilation and no effect on alpha)
this causes decrease in DBP
unchanged or raised (via beta 1) SBP
effects of isoproterenol on MAP and CO
MAP decreased
CO increased (via HR, contraction, and lowered TPR)
t/f: isoproterenol relaxes almost all smooth muscle
true
how is isoproterenol metabolized
in liver by COMT
(not by MAO or reuptake)
isoproterenol adverse effects
tachycardia, palpitations, arrhythmias, headache, flushing, afib, vtach
therapeutic use of isoproterenol
bradycardia and heart block
dobutamine
+ vs - isomer
+ isomer: beta AGonist and alpha ANTagonist
- isomer: beta AGonist (more potent) and alpha AGonist
(alpha activity cancels out, making it a non-selective beta agonist)
dobutamine therapeutic uses
cardiac decompensation after surgery, congestive heart failure, cardiogenic shock, acute MI
* note short half life (about 2 mins)
tx aim of selective beta 2 agonists
asthma or COPD (via bronchial smooth muscle relaxation)
metaproterenol
beta-2 selective agonist
- less selective than others; greater potential for cardiac stimulation
- resistant to COMT
albuterol
beta-2 selective agonist
- inhaled for COPD and asthma
terbutaline
beta-2 selective agonist
- given orally (1-2hrs)
- NOT metabolized by COMT
for COPD and bronchospasms
(higher chance for cardiac adverse effects)
levalbuterol
r-enantiomer of albuterol
selective beta- 2 agonist
pirbuterol
beta 2 selective agonist
inhaled q4-6hrs
salmeterol
LABA
long duration: >12hrs
slow onset
- for COPD, NOT acute asthma attacks
formoterol
LABA
quick onset and long acting (up to 12hrs)
arformoterol
r- enantiomer of formoterol; 2x more potent
indaceterol
quick onset, long acting; doesnt antagonize SABAs
ritodrine
beta 2 agonist; developed for uterine relaxation
- removed from US market
adverse effects of beta 2 agonists
-potential risk for cardiovasc disease
- risk to pts on MAO inhibitors
- may lead to hyperglycemia
- tremor
mirabegron
selective beta-3 agonist
- relaxes detrusor muscle, helps bladder filling
- approved for overactive bladder
therapeutic uses of dopamine, NE, and EPI
raise bp under hypotensive conditions (ex: shock)
alpha-1 selective agonists
cardiovasc effects?
uses?
vasoconstriction via alpha 1 on vascular smooth muscle
causes increased TPR and increased MAP
used for hypotensive states, nasal decongestants, and mydriasis
phenylephrine
alpha-1 selective
- venous and arterial vasoconstriction
uses: nasal decongestant; mydriasis
does phenylephrine cross bbb
no. polar (like EPI)
oxymetazoline
alpha-1 agonist
(alpha 2 partial agonist; less selective for 1)
vasoconstrictor, decongestant, eye drops to reduce redness
mephentermine
- both direct AND indirect
- alpha-1 selective= vasoconstriction
- NE release= increased cardiac contractility (for acute hypotensive states)
crosses BBB!= CNS excitation, hypertension, arrhythmias (unlike metaraminol)
can mephentermine cross bbb
yes-> can cause CNS excitation
mephentermine contraindications
MAO inhibitors (bc mephentermine stimulates NE release)
caution: TCAs
t/f: mephentermine is an alpha agonist that can also cause NE release and stimulate beta receptors
true
metaraminol
- both direct AND indirect
- alpha-1 selective= vasoconstriction
- NE release= increased cardiac contractility (for acute hypotensive states and atrial tachycardia)
does NOT cross BBB! unlike mephentermine
midodrine
- given orally, onset about an hour, duration 4-6hrs
PRODRUG converted to desglymidodrine= selective alpha 1 agonist
does NOT cross BBB
use: for orthostatic hypotension, autonomic insufficiency
midodrine uses
for orthostatic hypotension, autonomic insufficiency
t/f: midodrine crosses the BBB
false
midodrine counseling point
pts on midodrine can have supine hypertension (bp rises when they lay down)
- do not give 4hrs before bed, and give to pt while upright during the day
- elevate the head of the bed
alpha 2 selective agents are often _______philic meaning they ______ cross the BBB
lipophilic; do cross
what are alpha 2 selective agents most often used to treat
hypertension; ocular therapy
alpha 2 selective agonist prototype
clonidine
which receptors does clonidine target
alpha-2 selective but concentration dependant (will target alpha 1 at high doses)
IV vs oral clonidine
IV: biphasic
- acute increase in bp (via vasoconstriction)
followed by prolonged decrease in bp and hr (via CNS)
oral: lowers bp and hr (no increase in bp at all)
where are alpha 2 receptors found
brain stem vasomotor centers (CNS)
post ganglionic presynaptic receptors (PNS)
describe clonidine's moa and effect
alpha-2 selective agonist (low dose alpha 2 predominates, high dose targets alpha 1)
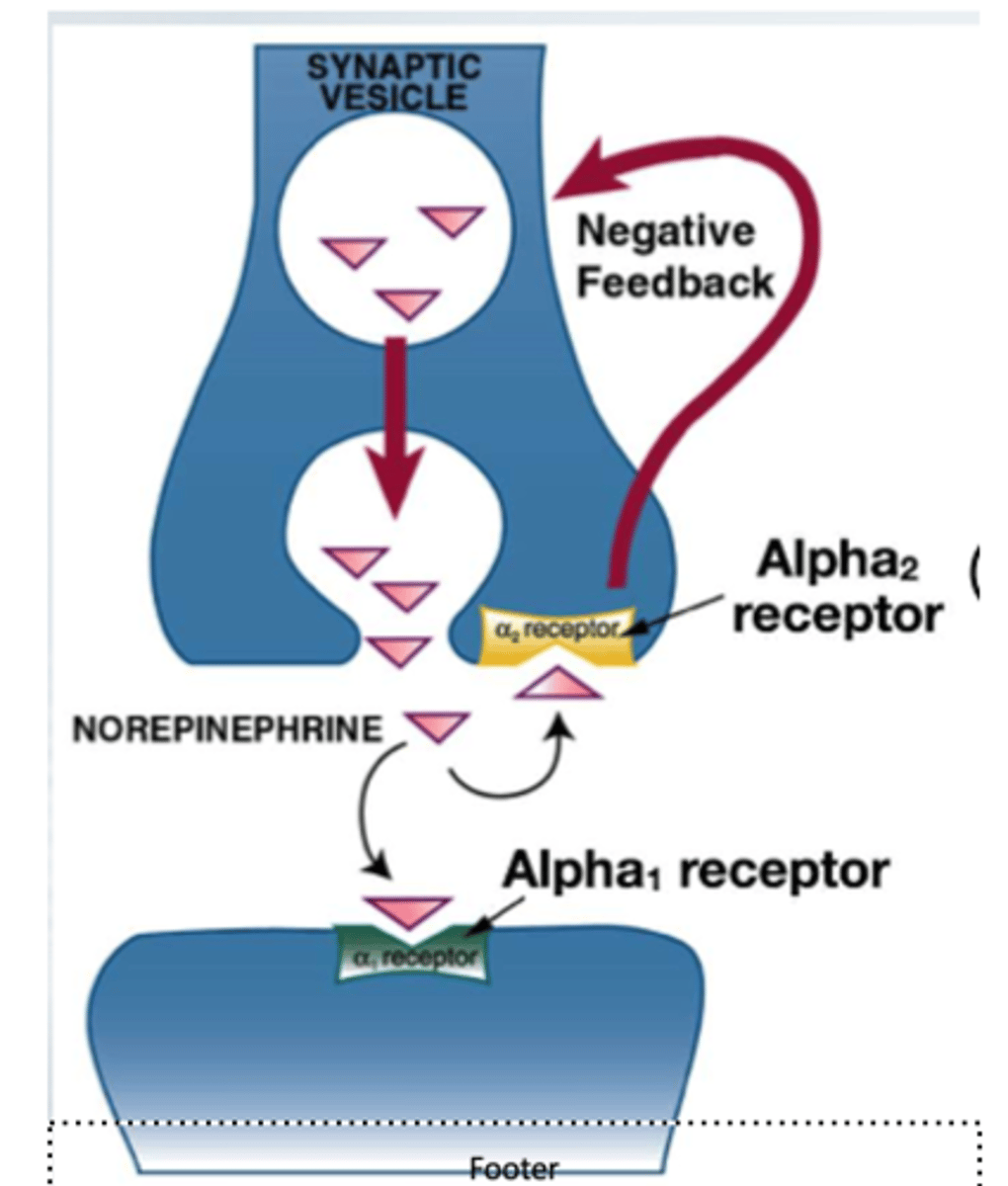
1. targets alpha 2 receptors on post gang presynaptic neurons= lowers NE release
2. targets alpha 2 receptors in brainstem vasomotor center= increases parasymp tone
=this causes lower bp and hr
(note IV will cause temporary increase in BP)
clonidine administered _______ has a biphasic effect meaning ________
IV;
1. acute increase in BP due to vasoconstriction
2. followed by prolonged decrease in BP and HR due to CNS
t/f: clonidine acts on both the PNS and CNS
true
PNS: activation of pre-synaptic receptors on post gang neurons which decreases NE release (auto)
CNS: stimulates alpha 2 receptors in CNS= decreases symp tone and increases para tone
why is there no increase in BP in oral clonidine but there is in IV clonidine
IV clonidine goes straight to blood and targets alpha 2 receptors on vascular smooth muscle causing vasoconstriction before it reaches CNS to lower symp tone
oral clonidine must first be absorbed and metabolized and has time to reach CNS and avoid instant vasoconstriction
cardiovasc response to IV clonidine (slides 8/9)
what happens to mean BP, symp nerve activity (SNA), HR
BP: initial rise (only for IV) that then lowers as baroreceptor reflex kicks in
SNA: large drop due to rise in BP (baroreceptor reflex), once bp restored, SNA goes back up BUT still lower than baseline (bc clonidine is being distributed to brain)
HR: drop bc SNA drops (baroreceptor), but still says lower than initially due to lower SNA
given an IV clonidine vs BP/SNA/HR graph, how do you know when the baroreceptor reflex is activated vs when the response is a result of clonidine's central action
if BP is elevated, then the drop in symp NA would most likely be due to the baroreceptor reflex. but if the bp is normal/ below normal and SNA is still low, thats probably clonidine and not the reflex
clonidine ADE
- xerostomia (dry mouth)
- sedation
- sexual dysfunction
- excessive bradycardia, hypotension
- withdrawal rxn (rebound increase in symp activity and bp)
withdrawal reaction present in clonidine
rebound increase in symp activity and bp when clonidine is removed.
clonidine lowers setpoint when you take the drug away, you may get hypertensive crisis->> titrate down!
therapeutic uses of clonidine
HTN, diarrhea in diabetes, addiction tx (narcotics, alcohol, tobacco), preoperative med to lower anesthetic need, ADHD, Tourette's
apraclonidine
moa?
use?
BBB?
selective alpha 2 agonist
topically into eye to lower IOP via aqueous humor reduction (open angle glaucoma)
does NOT cross BBB (unlike clonidine/brimonidine)
brimonidine
moa?
use?
BBB?
selective alpha- 2 agonist
topically into eye to lower IOP via aqueous humor reduction (open angle glaucoma)
CAN cross BBB and produce hypotension/sedation
t/f: unlike apraclonidine, brimonidine does not cross the BBB and is the primary choice in glaucoma pts to prevent hypotension/sedation
false.
apraclonidine= does NOT cross BBB
brimonidine= DOES cross BBB and might cause hypotension
is guanfacine or clonidine more selective for alpha-2
guanfacine
guanfacine
moa?
use?
BBB?
selective alpha 2 agonist (MORE selective than clonidine)
lipophilic so DOES cross BBB
use/ADEs same as clonidine BUTT withdrawal symptoms are better bc longer half life
main difference between guanfacine and clonidine
both are selective alpha 2 agonists with similar uses
- guanfacine is more selective
- guanfacine has longer half life so more mild withdrawal rxn
guanabenz
moa
use
BBB
selective alpha 2 agonist
lipophilic-> crosses BBB
- use/ADEs same as clonidine/ guanfacine
BUTT extensively metabolized in liver (watchout for liver disease pts)
alpha methyldopa
moa?
what is it converted to and what happens?
BBB?
selective alpha 2 agonist
analog of DOPA
crosses BBB
-converted to alpha-methylnorepinephrine which is stored in adrenergic vesicles.->> released as a false transmitter instead of NE
- this stimulates central alpha-2 receptors and lowers BP/HR (like clonidine)
which selective alpha-2 agonist must be converted into another form before it can exert its effect and into what?
alpha-methyldopa
converted into alpha- methylnorepinephrine
released as false transmitter to stimulate central alpha-2 receptors
(uses catecholamine synthesis pathway)
tizanidine
moa
use
selective alpha-2 agonist
similar to clonidine. also used as muscle relaxer (so both central and motor neuron activity)
alpha 1 receptor subtypes
1A:
- only one in prostate!
- vasoconstriction
- responds to IV non-selective alpha-1 agonists
1B:
- MOST abundant subtype in heart; cardiac growth
- LESSER role in pressor response in IV
1D:
- vasoconstriction in aorta/ coronary arteries
-all present in brain
-A and B in lungs and vasculature, D is not
which alpha 1 subtype is present in the prostate
alpha 1A
which alpha 1 subtype is the most abundant in the heart
alpha 1B
alpha 2 receptor subtypes
where?
what do they do?
2a:
- brain, spinal cord, post gang symp neurons
- knockout: decreased prejunctional adrenergic neuron modulation
- can decrease SNA through CNS and decrease NE release through nerve terminal
2b:
- kidney, liver, vasc
- knockout: peripheral pressor response
- vasoconstriction
2c:
- brain, adrenal medulla
- inhibits epi release from adrenal medulla