Nutrition Final
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
180 Terms
1
New cards
Nutrients
\
* Substances essential for health that the body cannot make or makes in quantities too small to support life
* Primarily provide energy
* Important for growth and development
* Keep body functions running smoothly
* Substances essential for health that the body cannot make or makes in quantities too small to support life
* Primarily provide energy
* Important for growth and development
* Keep body functions running smoothly
2
New cards
Essential Nutrient
\
* specific biological function
* Absence from the diet leads to decline in biological function
* Adding missing substance back to the diet before permanent damage occurs restores normal biological function
* specific biological function
* Absence from the diet leads to decline in biological function
* Adding missing substance back to the diet before permanent damage occurs restores normal biological function
3
New cards
Macronutrients
carbs, proteins, lipids, water
4
New cards
micronutrients
vitamins, minerals
5
New cards
Carbs
4kcal/g
6
New cards
Complex Carbs
Starch, Fiber
7
New cards
Simple Carbs
Sugar, readily usable
8
New cards
Lipids
9kcal/g
insoluble in water
insoluble in water
9
New cards
Fats
lipids solid at room temp
10
New cards
Oils
lipids liquid at room temp
11
New cards
Triglycerides
3 fatty acids attached to glycerol backbone
12
New cards
Saturated Fats
solid at room temp
animal sources
raise blood cholesterol lead cardiovascular disease
animal sources
raise blood cholesterol lead cardiovascular disease
13
New cards
unsaturated fats
liquid at room temp
plant sources
healthier than saturated
plant sources
healthier than saturated
14
New cards
Essential Fatty Acids, Unsaturated fatty acids
Linoleic Acid
Alpha-linolenic acid
* structural cell wall
* blood pressure
* nerve transmissin
* found vegetable oils and fish
Alpha-linolenic acid
* structural cell wall
* blood pressure
* nerve transmissin
* found vegetable oils and fish
15
New cards
Trans Fatty acids
unsatured fats processed from cis form to trans form
deep-fried food, snacks
pose health risk
deep-fried food, snacks
pose health risk
16
New cards
Proteins
4kcal/g
17
New cards
Vitamins
main functional component to enable chemical reactions to occur
helps release energy but does not provide energy
helps release energy but does not provide energy
18
New cards
Water soluble vitamins
vitamin C and B-vitamins
excreted more readily
\
excreted more readily
\
19
New cards
Fat soluble vitamins
vitamins A, D, E, K
more likely accumulate and cause toxicity
more likely accumulate and cause toxicity
20
New cards
Minerals
inorganic substances (no carbon bound to hydrogen)
not destroyed by cooking
yield no energy
not destroyed by cooking
yield no energy
21
New cards
Major minerals
need in gram amounts daily
22
New cards
Trace minerals
needed
23
New cards
Phytochemicals
physiologically active compounds found in plants that may provide health benefits
24
New cards
Zoochemicals
physiologically active compounds found in foods of animal origin that may provide health benefits
25
New cards
Claims about health
must be approved by FDA
* Claims about nutrient “great source of”
* Claims about nutrient “great source of”
26
New cards
Claim about structure or function
does NOT have to be approved by FDA, but need to have evidence its true
27
New cards
%DV
based on standard 2000-calorie diet and allows for comparison of products, percentage of nutrient provided by standard serving of food in relation to approximate requirement for nutrient
28
New cards
Calorie
amount heat energy needed to raise the temp of 1 gram of water 1 degree celsius
29
New cards
Alchohol
7kcal/g
30
New cards
North American Diet
16% protein
50% carbs
33% fats
50% carbs
33% fats
31
New cards
hunger vs appetite
physical need for food vs psychological desire to eat
32
New cards
undernutrition
nutrient intake does not meet needs
nutrient stores depleted
nutrient stores depleted
33
New cards
overnutrition
consumption of more nutrients than body needs
34
New cards
Assessing Nutritional Status
\
* **Family history and self history**
* **Anthropometric assessment**
* **Biochemical assessment**
* **Clinical assessment**
* **Dietary assessment**
* **Environmental assessment**
* **Family history and self history**
* **Anthropometric assessment**
* **Biochemical assessment**
* **Clinical assessment**
* **Dietary assessment**
* **Environmental assessment**
35
New cards
EAR
meet need of 50% people
36
New cards
DRI graph
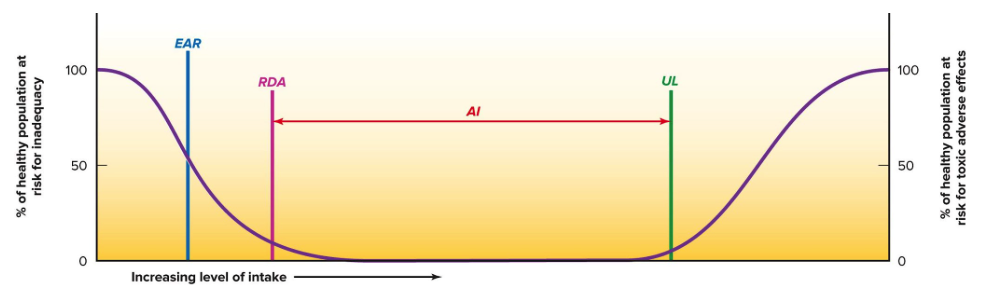
37
New cards
AMDR (acceptable macronutrient distribution ranges)
Carb (45-65%)
Protein (10-35%)
Fat (20-35%)
Protein (10-35%)
Fat (20-35%)
38
New cards
Daily Values
compares amount nutrient in food with set of standards
39
New cards
Food security
access by all people at all times to enough food for an active, healthy lift
40
New cards
food insecurity
fewer servings of nutrient dense foods and consume poorer quality diets, linked with obesity
41
New cards
Household manage any level food security by:
skipping meals, reducing the size of meals, not eating when hungry
42
New cards
____ __US below poverty guiltiness of__ _____for family of 4
12%, $25,750
43
New cards
Food desert
geographic areas where fresh, affordable, healthy food cannot be purchase easily
44
New cards
Government programs
\
* Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)
* Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC)
* National School Lunch Program
* School Breakfast Program
* Child and Adult Care Food Program
* Programs for seniors: Meals on Wheels, Senior Farmers’ Market Nutrition Programs, congregate meal programs
* Food distribution programs: food banks and pantries
* Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)
* Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC)
* National School Lunch Program
* School Breakfast Program
* Child and Adult Care Food Program
* Programs for seniors: Meals on Wheels, Senior Farmers’ Market Nutrition Programs, congregate meal programs
* Food distribution programs: food banks and pantries
45
New cards
Food waste
1/3 all food product lost
46
New cards
Food sustainability
ability to produce enough food to maintain the human population
47
New cards
Agrobiodiversity
diversifying species to increase variety in food supply leading to higher quality diet
48
New cards
GMO Pros
1. improve quality food
2. easier to grow
3. increase food yields
4. shipped to remote areas
5. herbicide use is less
6. GMO foods meet same requirements as all other foods
49
New cards
GMO cons
1. increase food related allergies
2. trigger allergies from alternative foods
3. antibiotic resistance
4. GMOs connected cancer
5. monopolies
6. herbicide resistance happens naturally w/o genetic engineering
7. independent research not allowed
50
New cards
Food irradiation
use radiation to extend shelf life food and control growth insects or pathogens
51
New cards
Danger zone bacteria in food
41 F - 135 F
52
New cards
Food safety procedures
Clean, separate, chill, cook
53
New cards
gastrointestinal tract organs
* Mouth
* Esophagus
* Stomach
* Smallintestine
* Large intestine
– Rectum
– Anus
* Esophagus
* Stomach
* Smallintestine
* Large intestine
– Rectum
– Anus
54
New cards
Mechanical Digestion
* Begins in the mouth
– Teeth masticate
– Food bolus
* Esophagus
– Peristalsis
* Stomach
– Smooth muscle contractions
– Storage
– Chyme
* Smallintestine
– Segmentation
– Teeth masticate
– Food bolus
* Esophagus
– Peristalsis
* Stomach
– Smooth muscle contractions
– Storage
– Chyme
* Smallintestine
– Segmentation
55
New cards
Chemical Digestion
* Enzymes
* Hormones
* Mouth
– Salivary glands
\-- Saliva
\-- Amylase
\-- Lipase
* Stomach
– Gastric juices
\-- Acid
\-- Proteases
\-- Lipase
* Liver
– Bile is synthesized
* Small Intestine
\- CCK
* Gallbladder
– Bile is released
* Pancreas
– Pancreatic juices
\-- Bicarbonate
\-- Amylase
\-- Proteases
\-- Lipase
* Hormones
* Mouth
– Salivary glands
\-- Saliva
\-- Amylase
\-- Lipase
* Stomach
– Gastric juices
\-- Acid
\-- Proteases
\-- Lipase
* Liver
– Bile is synthesized
* Small Intestine
\- CCK
* Gallbladder
– Bile is released
* Pancreas
– Pancreatic juices
\-- Bicarbonate
\-- Amylase
\-- Proteases
\-- Lipase
56
New cards
Small Intestine
Three regions
– Duodenum
• Proximal
– Jejunum
• Middle
– Ileum
• Distal• Longest
– Duodenum
• Proximal
– Jejunum
• Middle
– Ileum
• Distal• Longest
57
New cards
Brush border
– Villi
– Microvilli
• Surface area for absorption
– Microvilli
• Surface area for absorption
58
New cards
Large Intestine
Three regions
* Cecum
* Colon
• Bacterial flora
* Rectum
• No villi
• Mucus
* Cecum
* Colon
• Bacterial flora
* Rectum
• No villi
• Mucus
59
New cards
Probiotic
beneficial bacteria
60
New cards
Prebiotics
* Food for the beneficial bacteria
* Chicory, whole-grain rye, oats, wheat , barley, leeks, onions, and garlic
* Chicory, whole-grain rye, oats, wheat , barley, leeks, onions, and garlic
61
New cards
Diverticulitis
pouches form in wall of digestive tract
62
New cards
Gastritis
roup of conditions that cause inflammation of the stomach lining. It can be caused due to alcoholic abuse, infection or underlying conditions
63
New cards
Ulcer
when inflammation becomes bad enough, the acid in your stomach brakes through the stomach lining and creates a hole or a sore. Related to diet, but also related to high levels of stress and anxiety
64
New cards
Celiac Disease
* Completely treatable by avoiding **gluten**
– Protein found in wheat, rye, and barley
* Can lead to damage of microvilli
– Can led to malabsorption and malnutrition
– Protein found in wheat, rye, and barley
* Can lead to damage of microvilli
– Can led to malabsorption and malnutrition
65
New cards
Monosaccharides
Glucose, fructose, galactose
66
New cards
disaccharides
maltose: 2 glucose
sucrose: glucose, fructose,
lactose: glucose, galactose
sucrose: glucose, fructose,
lactose: glucose, galactose
67
New cards
Complex carbs
starch, fiber, glycogen
68
New cards
Glycogen
Stored glucose in the body
– Liver• Broken down to provide glucose in the blood
– Muscle• Broken down to provide energy to do work
– Liver• Broken down to provide glucose in the blood
– Muscle• Broken down to provide energy to do work
69
New cards
Whole grains
Contain the endosperm, germ, and bran in original proportions
70
New cards
Refined Grains
Stripped of the germ and bran, leaving only the endosperm
71
New cards
Enriched grains
Some nutrients lost in processing are added back
72
New cards
Amylase
* Mouth
– Breaks starch into smaller links of glucose
* Small intestine
– Continue digestion of starch into maltose and glucose
– Breaks starch into smaller links of glucose
* Small intestine
– Continue digestion of starch into maltose and glucose
73
New cards
Small intestinal cells
* Maltase
– Hydrolyzes maltose to produce two glucose monosaccharides
* Sucrase
– Hydrolyzes sucrose to produce one glucose and one fructose monosaccharide
* Lactase
– Hydrolyzes lactose to produce one glucose and one galactose monosaccharide
– Hydrolyzes maltose to produce two glucose monosaccharides
* Sucrase
– Hydrolyzes sucrose to produce one glucose and one fructose monosaccharide
* Lactase
– Hydrolyzes lactose to produce one glucose and one galactose monosaccharide
74
New cards
Monosaccharides
______ are absorbed by small intestine, and then transported to the blood
75
New cards
lactose intolerance
* Low lactase activity
* Lactose maldigestion
– Diarrhea, Gas, cramps, abdominal pain
* Treatment
– Decrease dairy intake, Lactase pills, Calcium-rich foods
* Lactose maldigestion
– Diarrhea, Gas, cramps, abdominal pain
* Treatment
– Decrease dairy intake, Lactase pills, Calcium-rich foods
76
New cards
Normal fasting blood glucose levels:
* 70-100 mg/dl
77
New cards
Hyperglycemia, Hypoglycemia
* Above 126 mg/dl is classified as diabetes _____
• Hunger• Thirst• Frequent urination • Weight loss
* Below 50 mg/dl is classified as _____
• Hunger • Shakiness • Irritability• Weakness • Headache
• Hunger• Thirst• Frequent urination • Weight loss
* Below 50 mg/dl is classified as _____
• Hunger • Shakiness • Irritability• Weakness • Headache
78
New cards
liver
\
* ____ determines amount of glucose that is needed to enter the bloodstream after a meal
– Stored as glycogen for later use
* ____ determines amount of glucose that is needed to enter the bloodstream after a meal
– Stored as glycogen for later use
79
New cards
Pancreas secretes:
insulin, glucagon
80
New cards
insulin
Released after eating, when blood glucose levels are high,
* Promotes: Glucose uptake by cells, Use of glucose as energy, Storage of excess glucose as glycogen
* Promotes: Glucose uptake by cells, Use of glucose as energy, Storage of excess glucose as glycogen
81
New cards
Glucagon
Released if no dietary carbohydrates are present, blood glucose levels have fallen
Promotes: Breakdown of glycogen, Gluconeogenesis
Promotes: Breakdown of glycogen, Gluconeogenesis
82
New cards
Refined sugars are added to:
– Add flavor
– Increase energy density
– Decrease nutrient density
– Contribute to obesity
– Increase energy density
– Decrease nutrient density
– Contribute to obesity
83
New cards
nutritive sweeteners
– Provide calories, but fewer than sugars – Have reduced absorption– Include sugar alcohols (polyols)
84
New cards
non-nutritive sweeteners
calorie free
85
New cards
Soluble fibers
– Softens stool and decreases constipation
– Decreases hemorrhoids and diverticular disease
– Decreases hemorrhoids and diverticular disease
86
New cards
Soluble fiber
– Slows stomach emptying
– Slows digestion and absorption
– Reduces the risk of coronary artery disease
– Slows digestion and absorption
– Reduces the risk of coronary artery disease
87
New cards
Dietary fibers
• Nondigestible carbohydrates
• These fibers pass through the small intestine into the large intestine, where they may be partially or completely fermented by gut bacteria.
• These fibers pass through the small intestine into the large intestine, where they may be partially or completely fermented by gut bacteria.
88
New cards
Functional Fibers
• Isolated or purified carbohydrates that are nondigestible
• Absorbed in the small intestine, and have beneficial physiological effects in humans
• Absorbed in the small intestine, and have beneficial physiological effects in humans
89
New cards
Categories of lipids
fatty acids, triglycerides, sterols, phospholipids
90
New cards
Saturated fatty acids
fully hydrogenated, solid room temp
91
New cards
monounsaturated fatty acids
one double bond or point of unsaturation in carbon chain
92
New cards
polyunsaturated fatty acids
more than one point of unsaturation or more than one double bond
93
New cards
Triglycerides
3 carbon glycerol molecule with 3 fatty acids attached, storage form of fat
94
New cards
Phospholipids
3 carbon glycerol molecule with 2 fatty acids and a phosphate group on 3rd carbon
95
New cards
Sterols
complex lipid 4 carbon rings and hydrocarbon side chain
cholesterol most common sterol
cholesterol most common sterol
96
New cards
Lipid digestion
\
* salivary Glands
* stomach
* liver
* produces bile
* gallbladder
* stores bile
* pancreas
* release enzymes
* small intestine
* adds bile, enzymes and emulsifies lipids
* salivary Glands
* stomach
* liver
* produces bile
* gallbladder
* stores bile
* pancreas
* release enzymes
* small intestine
* adds bile, enzymes and emulsifies lipids
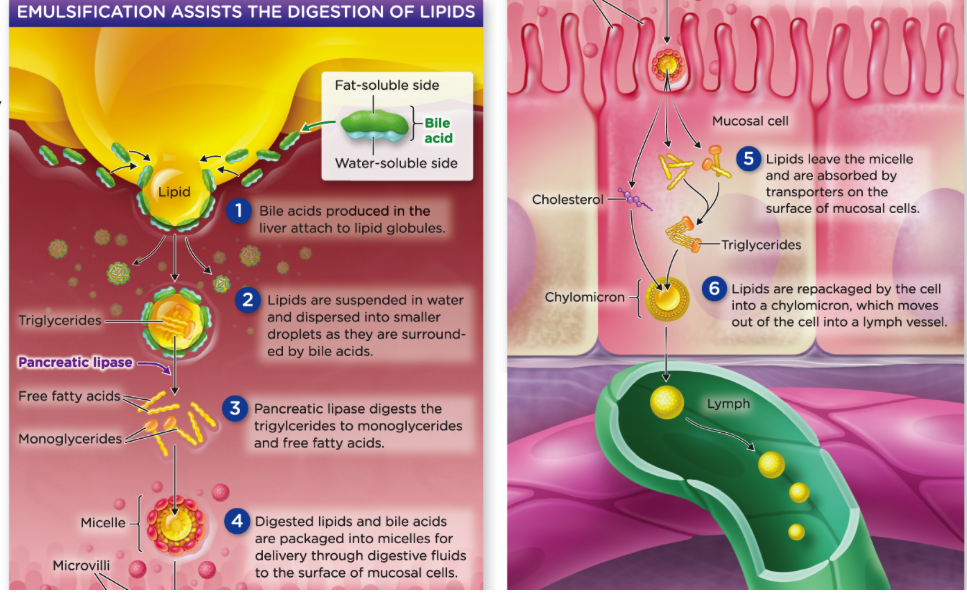
97
New cards
Chylomicrons
lipoproteins made in intestinal cells or enterocytes
transport fat from intestine to body
transport fat from intestine to body
98
New cards
very low density lipoprotein (VLDL)
made in liver
transports fat from liver to body
transports fat from liver to body
99
New cards
low density lipoprotein (LDL)
made in liver
transports cholesterol from liver to cells of body
“bad cholesterol”
transports cholesterol from liver to cells of body
“bad cholesterol”
100
New cards
high density lipoprotein (HDL)
collects fat and cholesterol from body to transport back to liver
“good cholesterol”
“good cholesterol”