Ketones and DKA:
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
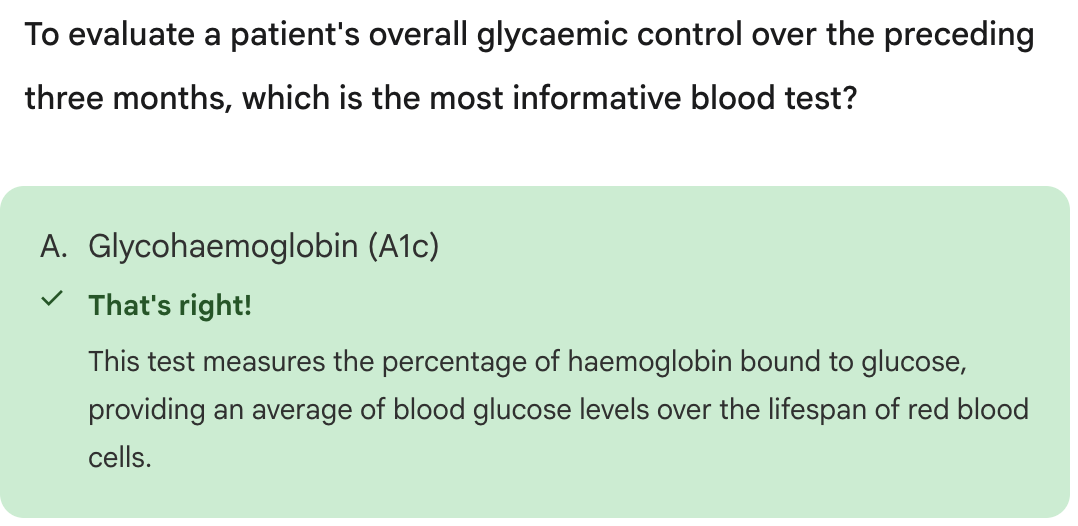
How do we monitor for ketones?
Ketones are measured in urine on a urine ketone strip
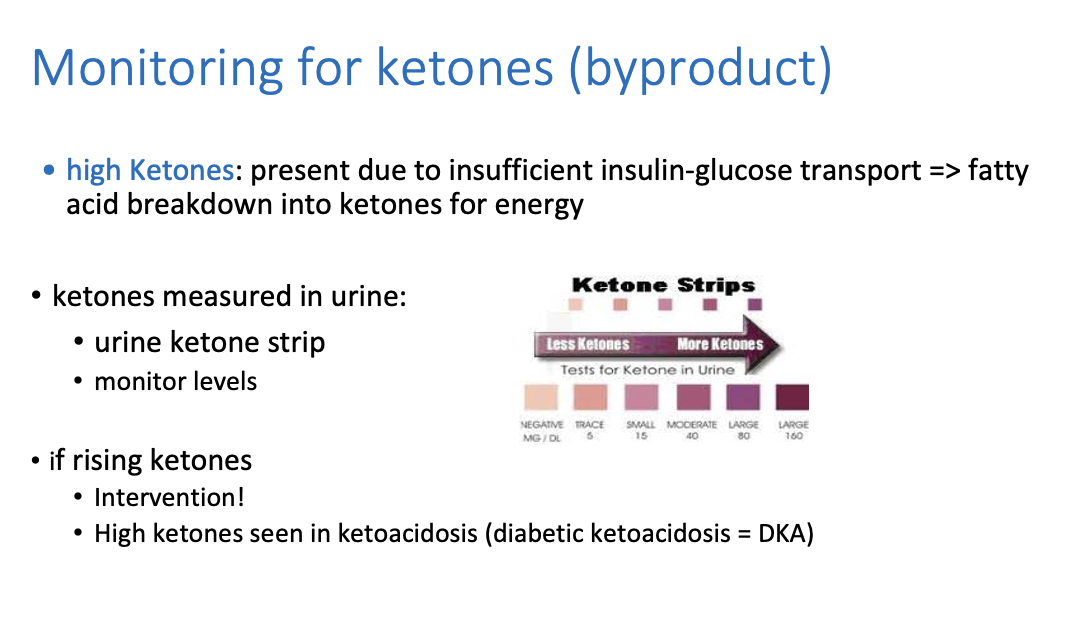
What causes high ketones?
Ketones are present due to insufficient insulin-glucose transport ==> so it causes fatty acid breakdown into ketones for energy
==> More ketones produced and accumulates = very very high which is the cause of metabolic acidosis
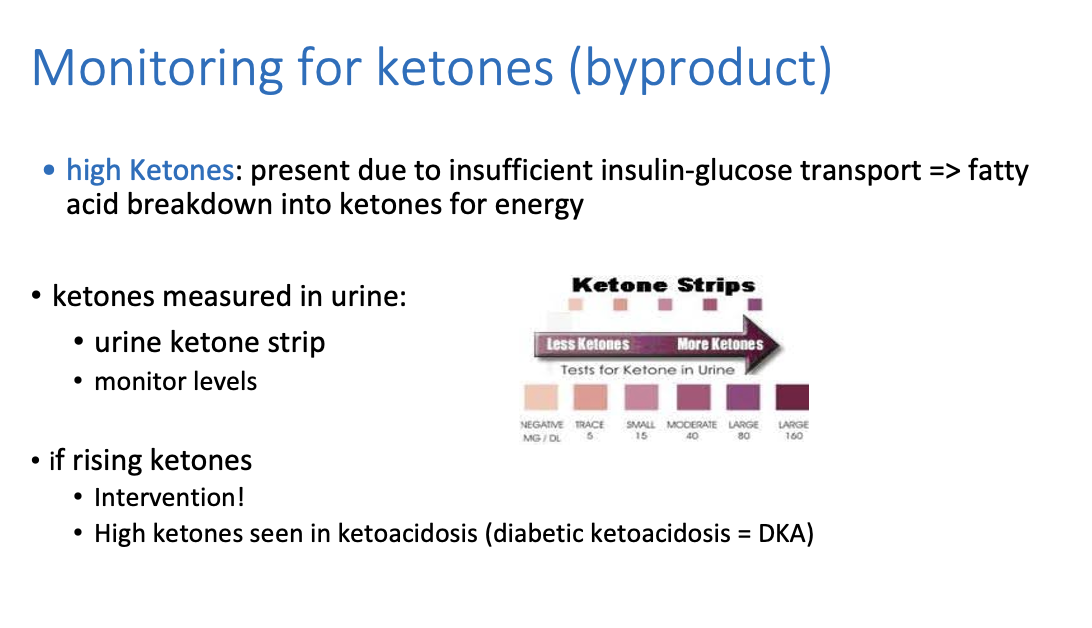
High ketones are seen in __________
ketoacidosis (diabetic ketoacidosis = DKA)
symptoms of Hypoglycaemia ==> low glucose in blood:
shaking/tremors
sweating
hunger
fast heartbeat (tachycardia)
anxiety
confusion
dizziness
headache
seizures
blurred vision
fatigue
Hypoglycemia:
Low blood sugar IN BLOODSTREAM
Hypo vs. Hyperglycemia symptoms
Hypo: ==> dizzy, shaking, sweating, hunger, headache, pale, clumsy
Hyper: polyuria, thirsty, tired, weak, blurry vision

What are the main symptoms of hyperglycemia
Thirst & Fatigue, high BG, high urine ketones + glucose in urine, high serum lactate (metabolic acidosis)
it takes a while for the S&S to show, dangerous longterm
Diabetic ketoacidosis can be dependant on pt’s, some get it at 14 BG and some at 40 BG
What are the main symptoms of hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia has rapid onset S&S
==> loss of focus, nervous, shaking
What causes hyperglycemia?
high blood glucose
S&S: cellular dehydration and polyuria ==> always peeing due to high solute content in circulation so water follows excretion
shift of potassium out of cells => ECF => excreted
low cellular function and ketone accumulation
Hyperglycemia leads to ===>
DKA (diabetic ketoacidosis)
What is kussmaul respirations?
Seen in hyperglycemia, it’s deep, rapid, and labored breathing pattern often described as "air hunger"
What is the tx for hyperglycemia?
Regular insulin IV (short-term insulin)
IV fluids
KCl
Close monitoring
When a patient has hyperglycemia, what do we use to neutralize DKA?
sodium bicarbonate
What do we always do first to treat DKA?
FLUIDS FIRST!!!
Because if cells are dehydrated, they won’t respond to or take in any insulin!!!
Why do we have hypokalemia with DKA and hyperglycemia?
because potassium is excreted
Look at potassium levels (sodium influx and potassium efflux) when pumps fail (very telling),
potassium won’t be able to go back into cell and goes into serum so high serum potassium
==> K+ leaking into bloodstream and continuously excreted
What are early signs of mild DKA?
non-specific
fruity acetone smell
weakness
vomiting (most common for DKA)
abdominal pain
Significant electrolyte imbalances è hyperkalemia, renal failure
What fluids/tx do we use for DKA?
whatever crystalloid is most accessible
If someone is severely dehydrated d/t to DKA, what fluids do we give for hypovolemic shock bcs of severely low blood volume?
0.9% NaCl or plasma expander
—> Push fluid back into cells so hypotonic fluids
What is the protocol for hypoglycemia?
15-15 rule
can give any source of carbs such as glucose tablets, honey, apple juice
Glucose PO 15g —> reassess every 15 minutes
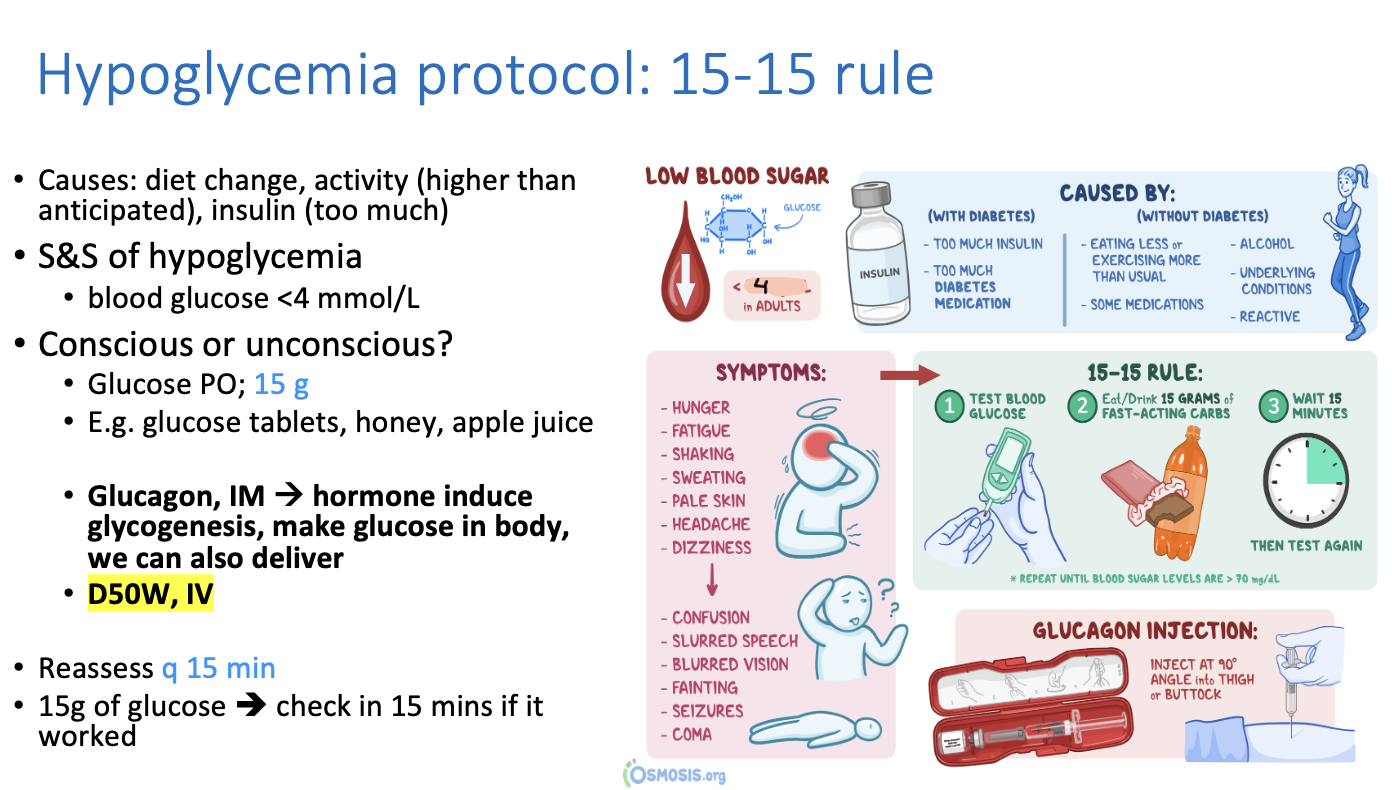
What causes hypoglycemia?
diet change
too much activity depleting glucose/energy
too much insulin
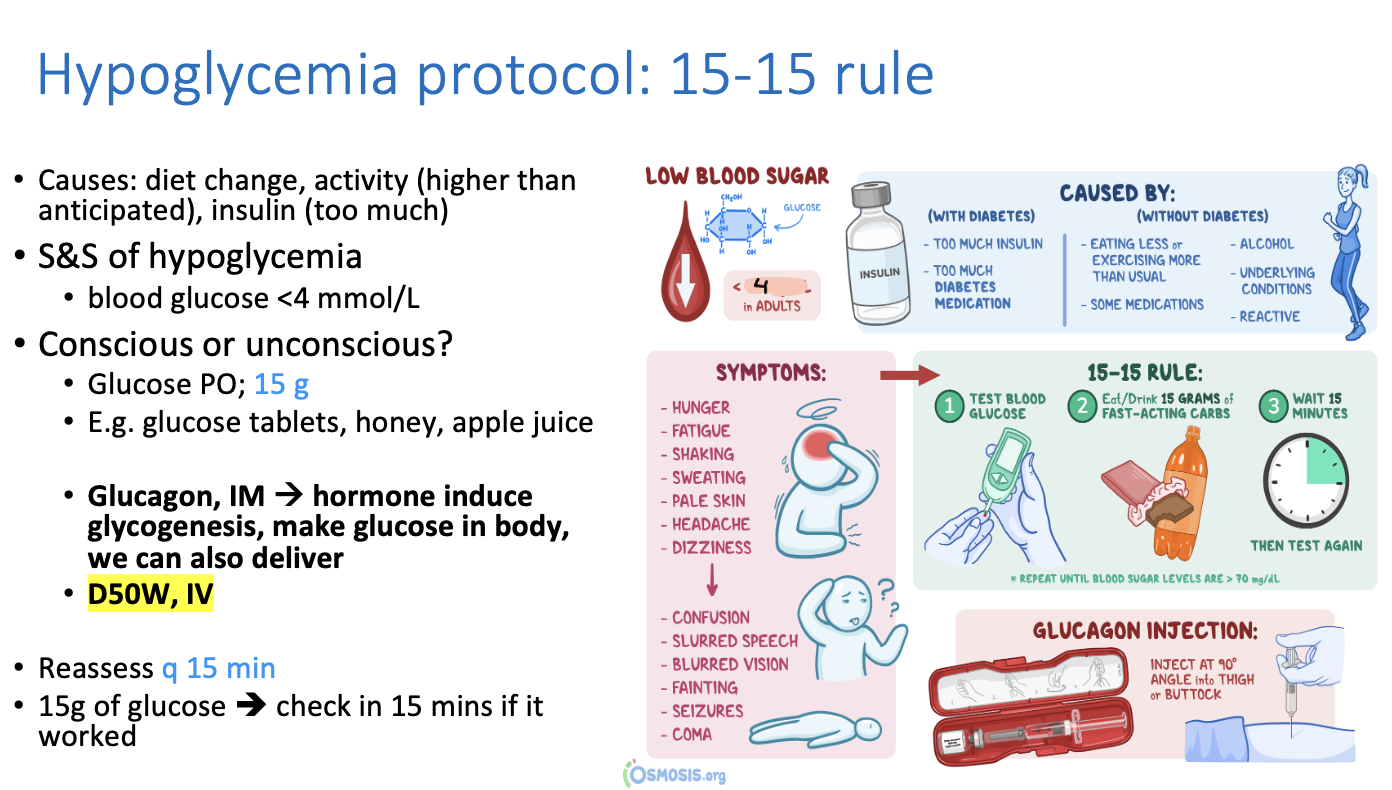
What is another tx for hypoglycaemia other than glucose stuff?
Glucagon IM ==> induces glucose production via glycogenesis
D50W, IV ==> lots of dextrose
What else can influence Blood glucose imbalances other than just straight blood sugar?
Illness (increases BG)
SNS stimulation ==> increases BG
increased BMR (basal metabolic rate) ==> demand on resources due to fever, inflammation etc.
Excercise (decreases BG)

How does Illness increase Blood Glucose ?
Increase blood glucose is due to cortisol release ==> breaks down storage and makes more blood glucose
hyperglycemia simply d/t illness is possible
**SO being on steroids increases cortisol release which increases BG

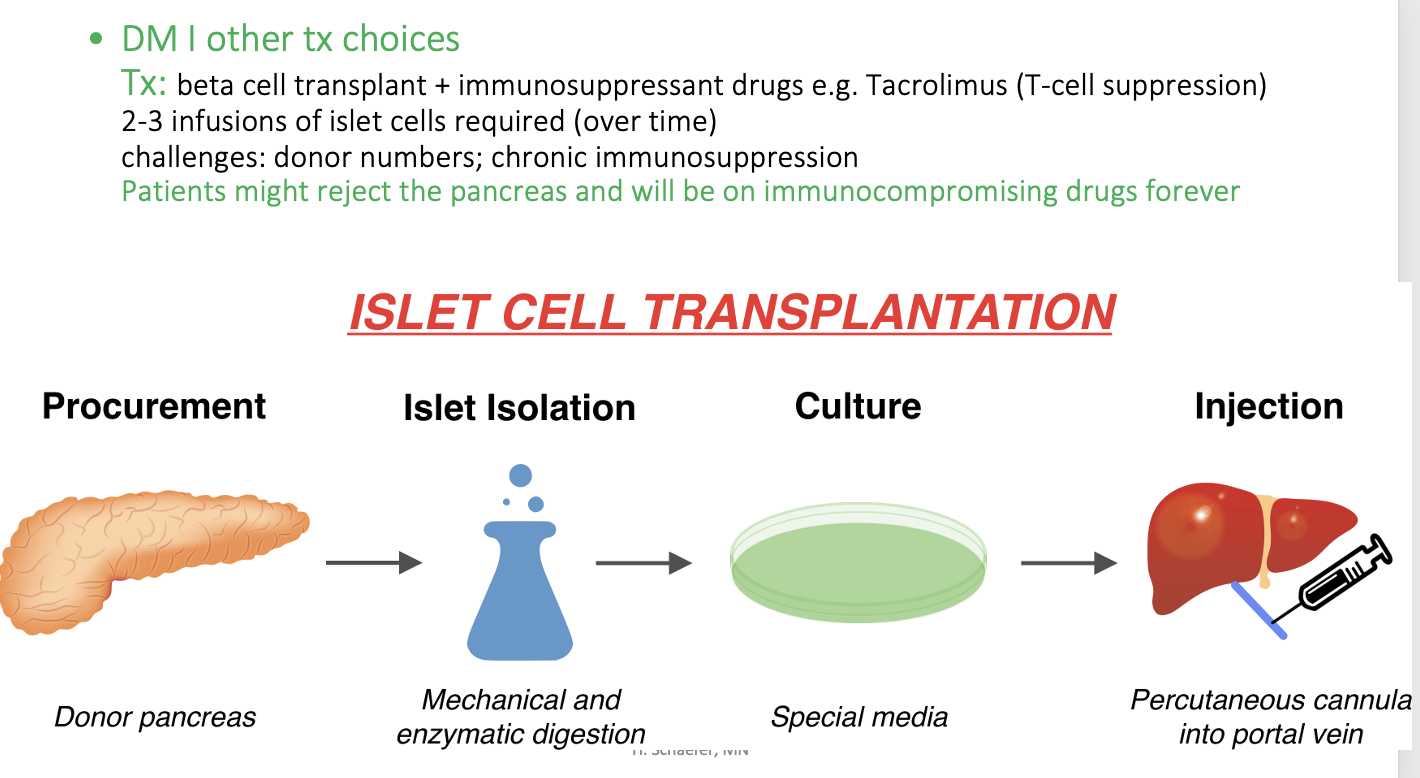
What are other choices for DM I other than insulin?
beta cell transplant + immunosuppressant drugs so that immune system doesn’t attach the islet cells
What’s an example of a drug that causes T-cell suppression?
Tacrolimus
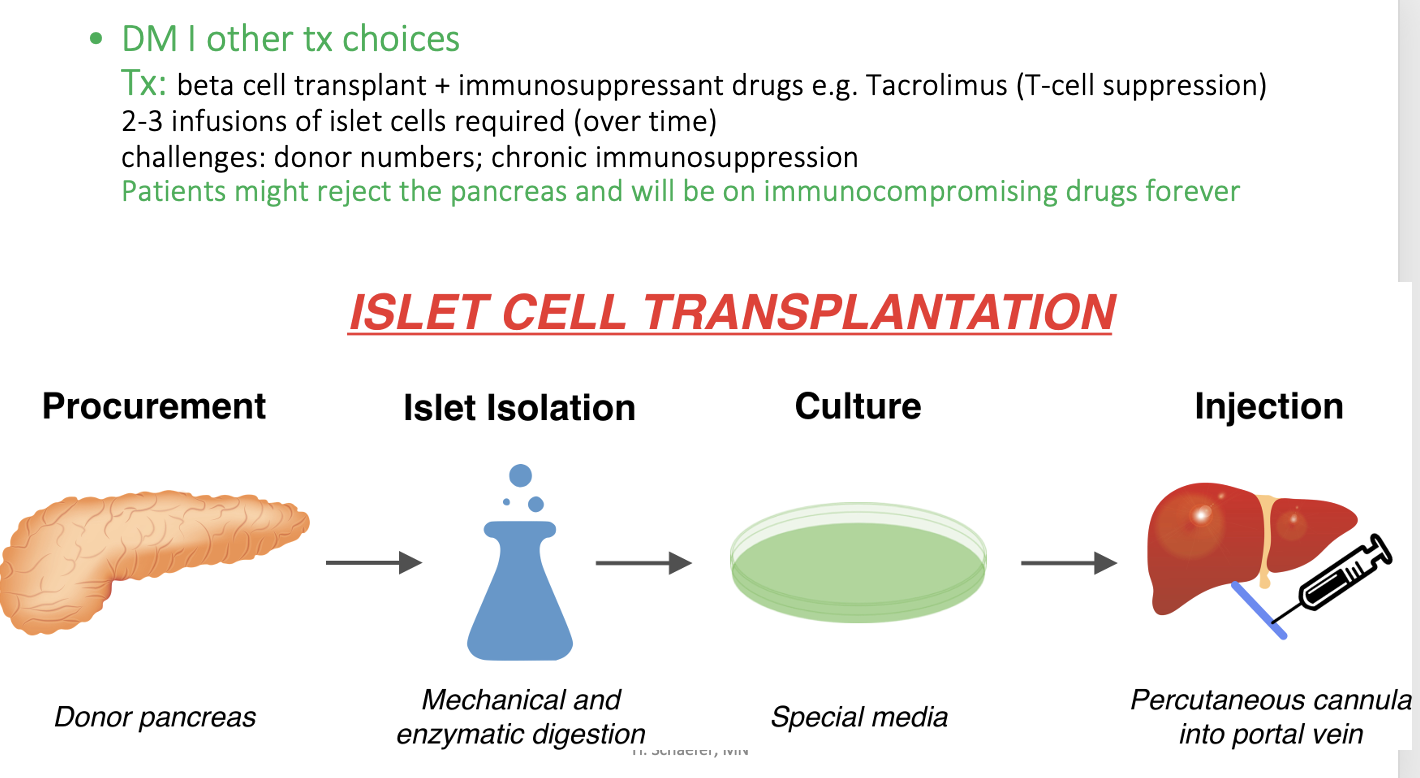
Islet cell transplantation:
Patients might reject the pancreas and will be on immunocompromising drugs forever
What CBC thing other than blood glucose reflects pre-diabetic/diabetic conditions?
Hemogloblin A1C
serum test of glucose bound hgb
assessment of longterm glucose control (e.g. over 3 months)
a tool to monitor DM patients & dx patients at risk for DM
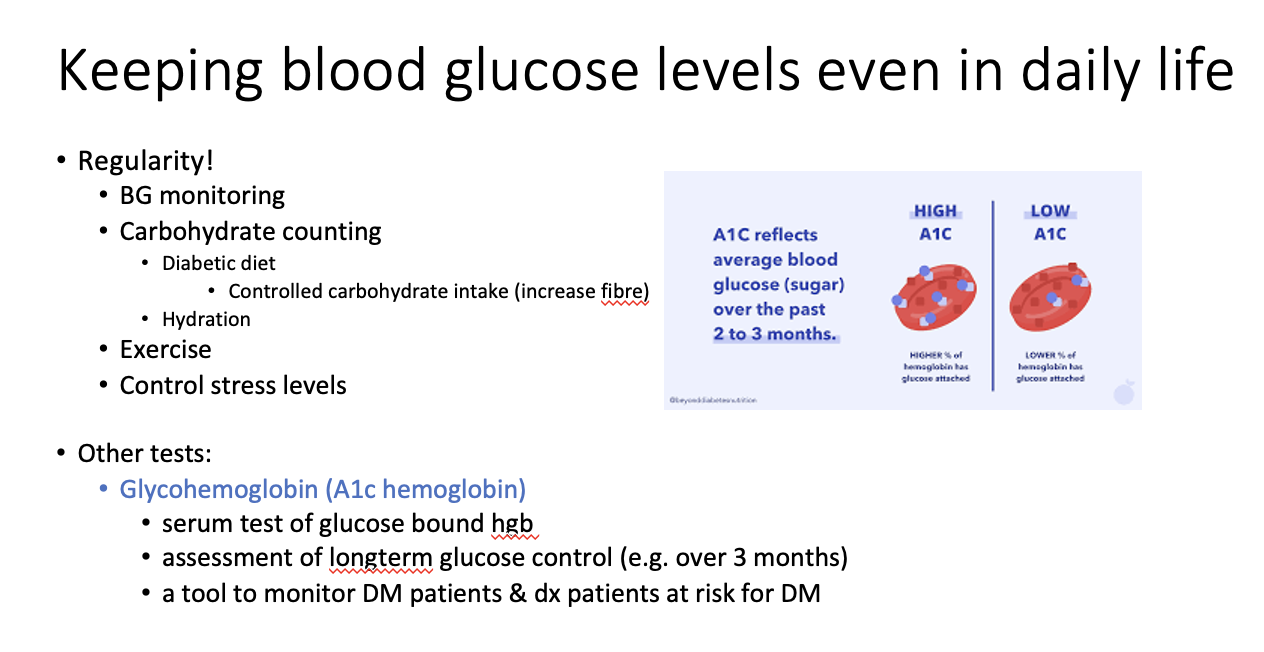
Hemogloblin A1C is good to assess long-term BG control because?
It shows long-term glucose molecules attached to hemogloblin