4 - 5: Meristems and Fundamental Tissues
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Promeristem
The initiating cells (initials) and their most recent derivatives in an apical meristem; the least differentiated, or determined, part of an apical meristem
Primary Meristem
- Produces tissues of the primary plant body
partly differentiated tissues such as protoderm (epidermis), procambium (vascular cambium), ground meristem (ground tissue)
meristem
actively dividing cells
1. dense cytoplasm (bc metabolically active)
2. lack large vacuoles (nucleus still in the middle)
meristem characteristics
Apical Meristem
Shoot and Root Tips; function is to produce the primary plant body for primary growth
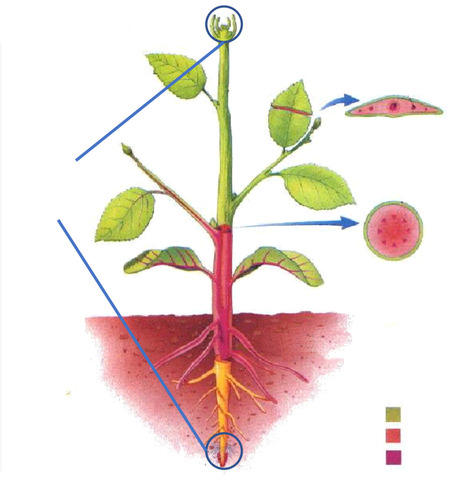
Vascular Cambium (eudicots, gymnosperms)
Cork Cambium
Lateral Meristems for 2ndary growth - thickness
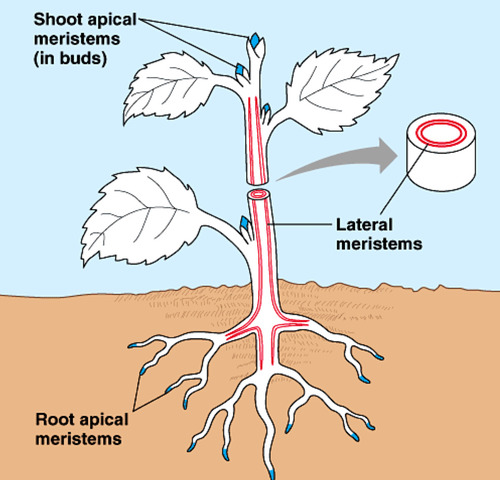
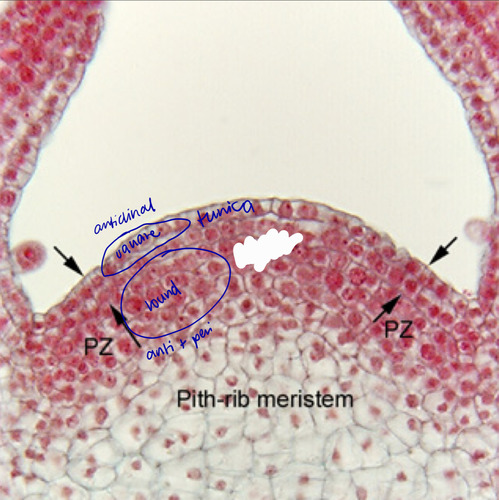
Tunica - outer layer; anticlinal plan perpendicular to surface - SQUARE CELLS
Corpus - inner layer; both anticlinal and periclinal (parallel to plane) surface - ROUND CELLS
Tunica corpus theory of the shoot apex
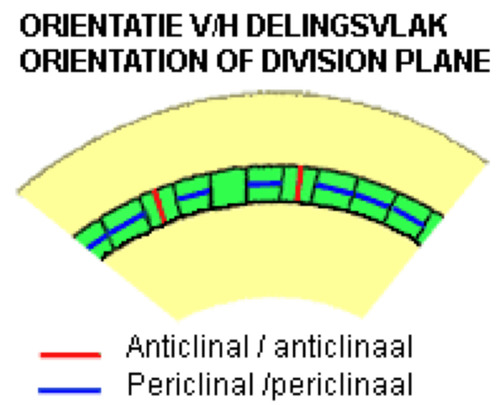
periclinal plane
division plane for addition of cells
anticlinal plane
division plane for increase in circumference
tunica
gives rise to leaves and buds, epidermis and most of the cortex
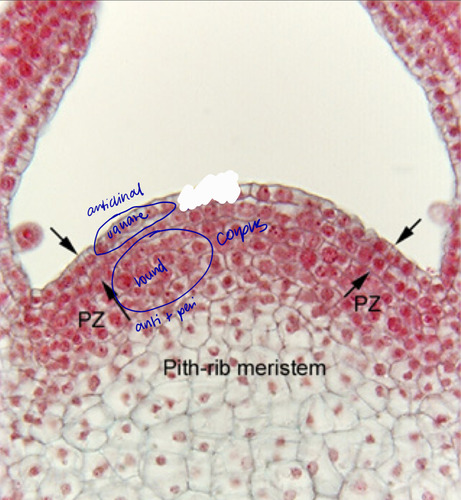
corpus
gives rise to vascular system; central ground system
procambial strand
gives rise to first xylem and primary phloem in the apex
root apex
where there is no tunica-corpus
calyptrogen
meristem that produces the root cap
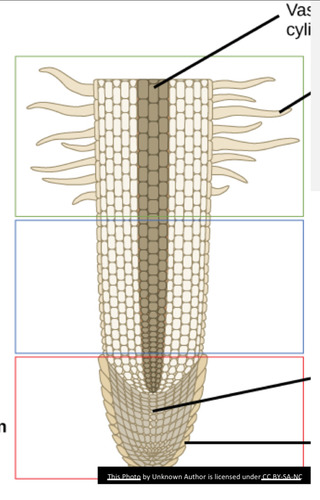
root cap
serves as protection of the soft apical meristem from soil particles
root apex
source of regulating substances involved in positive geotropic response
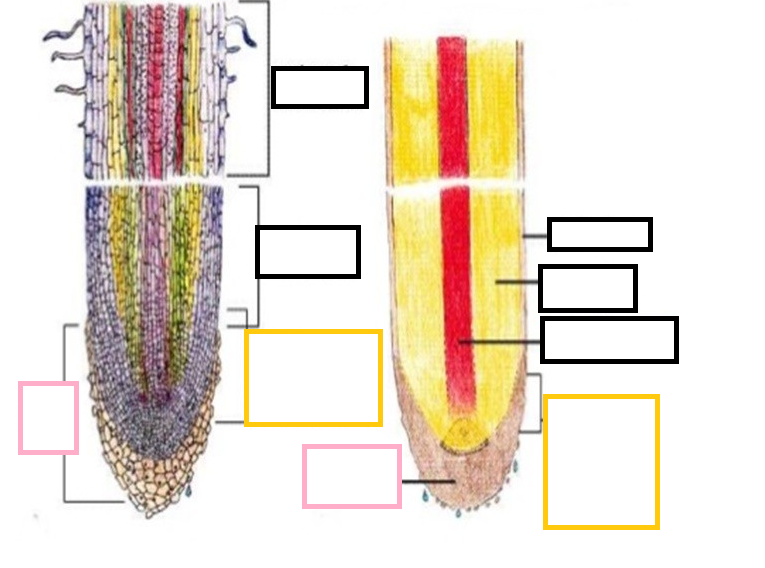
root hair
tiny hair-like extensions that increase the surface of the root allowing it to absorb more water and nutrients
region of maturation/differentiation
region where root cells become more specialized (green)
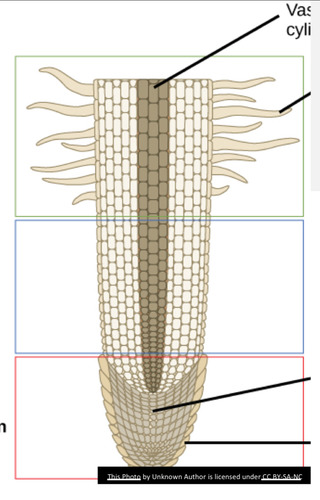
region of elongation
where root cell vacuoles begin to increase in size (blue)
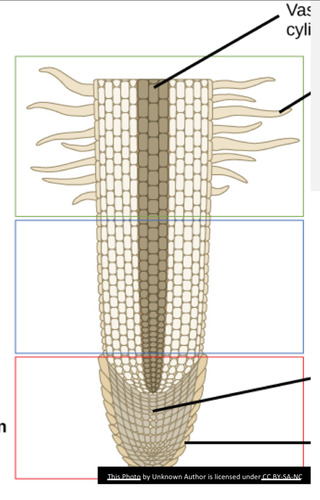
region of cell division
composed of apical meristem in the center of root tip (red)
exogenously
how are leaves and buds produced; coming from the outside
endogenoously (pericycle)
how lateral roots arise
derived from apical meristems
origin of primary meristems
protoderm
gives rise to epidermis
procambium
gives rise to vascular tissue
ground meristem
gives rise to the ground tissue
leaf primordia
leaf originating from shoot apex (coming from the outside)
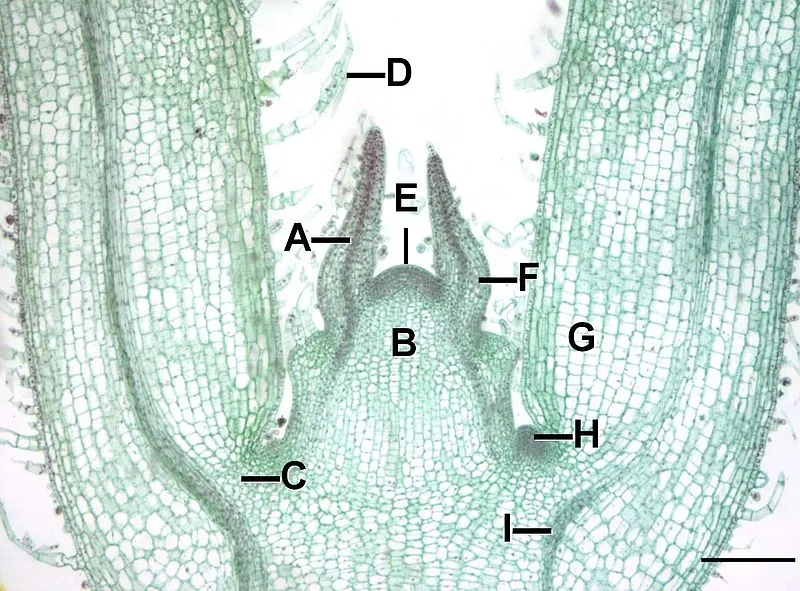
A - leaf primordia/ procambium
B - Corpus/ground meristem
C - ground meristem
D - trichomes
E - tunica
F - younger leaf primordium
G - ground meristem
H - axillary bud
vascular tissue
label the shoot apical meristem
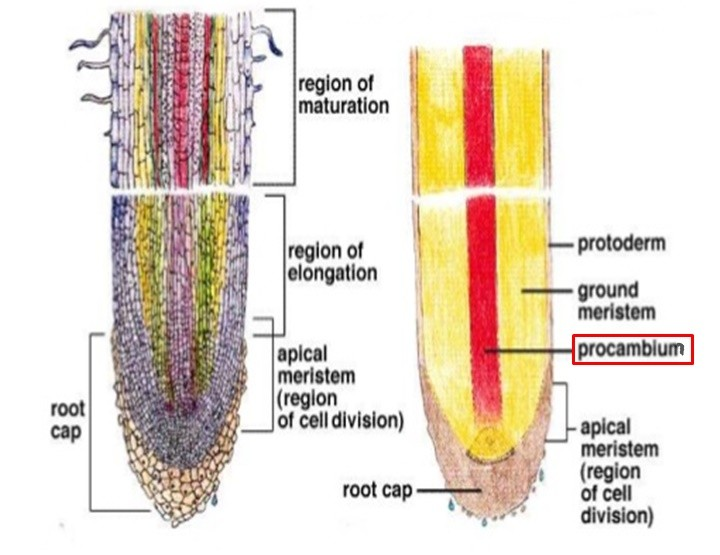
label the RAM
vascular cambium
cylinder of thin-walled cells that forms secondary vascular tissue
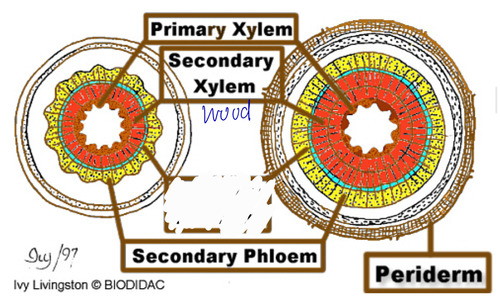
bark
tissues external to the vascular cambium; secondary phloem outward
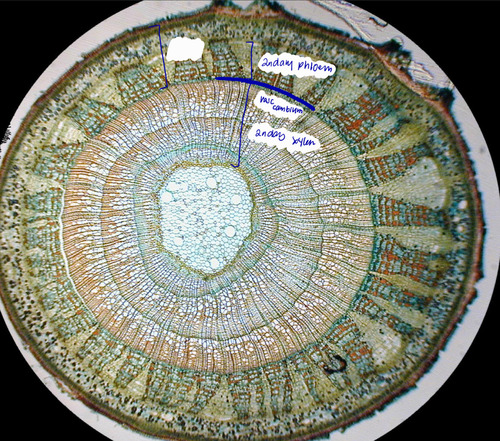
vascular cambium - 2ndary x and p
procambium - primary x and p
constituent cells of vascular cambium vs procambium
-ray cells
-fusiform initials
vascular cambium cells
ray initials; also known as xylem rays and phloem rays.
Cambium cells that produce radial files of parenchyma cells
fusiform initials
tapered, elongated cells that divide periclinally and give rise to 2X and 2P
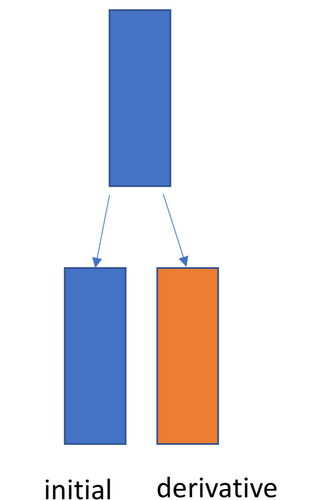
- initial - remains meristematic
- derivative - becomes matured cell
vascular cambium cells
multiplicative division
anticlinal; involved in increase of meristem circumference (perpendicular)
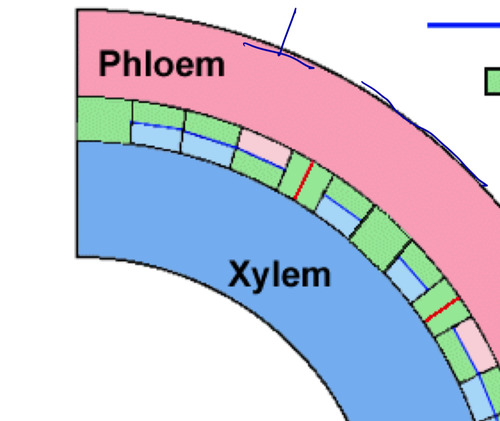
additive division
periclinal; more X and P in plant body (parallel)
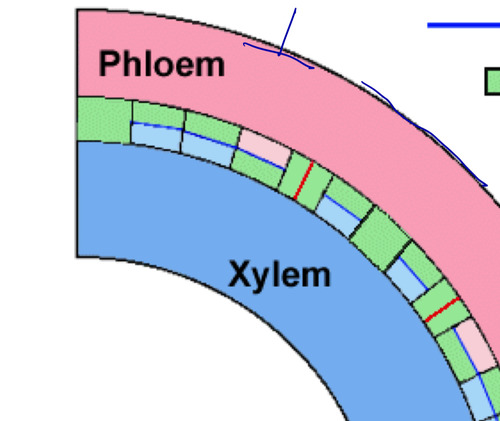
phellogen
other word for cork cambium
cork cambium
one type of initials (laging meristematic)
phellem or cork cells (outer side) and phelloderm (inner side)
cork cambium divides to form which cells?
cork cells/phellem
suberized; protection (form periderm)
periderm
cork + cork cambium + phelloderm; replaces epidermis
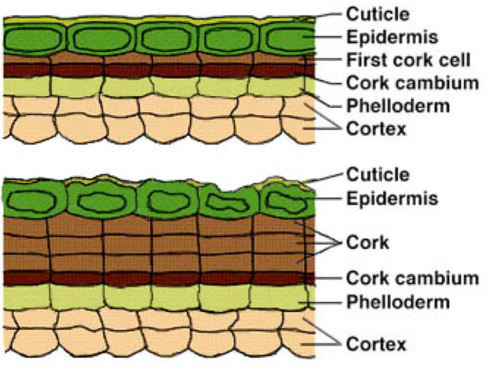
2ndary meristems
Another name for some of the lateral meristems
primary meristems are derived from meristems
secondary from mature cells
primary vs 2ndary meristem origin
from being permanent, can reverse back to being meristematic —> dedifferentiation
what can be considered a true secondary meristem
cork cambium
true secondary meristem
parenchyma/collenchyma near the epidermis or deeper into the cortex
origin of cork cambium
vascular cambium
not a true secondary meristem
- procambium (meristem)
- interfasicular parenchyma (mature tissue)
origin of the vascular cambium
simple
one type of cell E.g. parenchyma
complex
more than one type of cell E.g. xylem
parenchyma
• Most common type
• Alive at maturity
• Least specialized
• Thin-walled
• Isodiametric
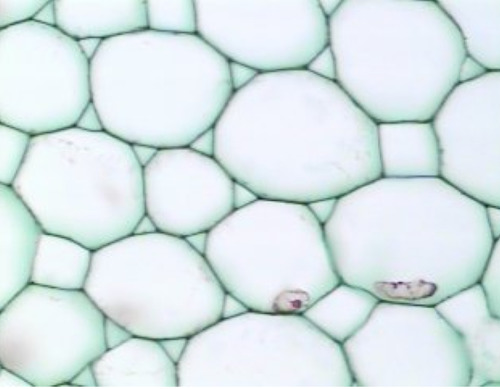
1. Space fillers
2. Basic metabolism
3. Storage
functions of parenchyma
collenchyma
• Usu. elongated
• Alive at maturity
• Uneven thickening of primary walls
• Large amount of pectins and hemicelluloses
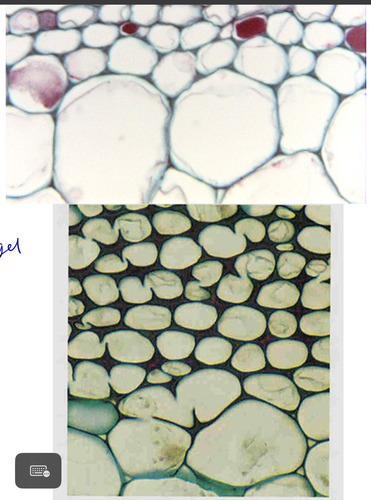
Provide flexible (plastic) support in growing organs and mature herbaceous organs
function of collenchyma
usually in cortex, just beneath epidermis
location of collenchyma
sclerenchyma
• Have secondary walls (+lignin)
• Dead at maturity; loses protoplast, forms lumen
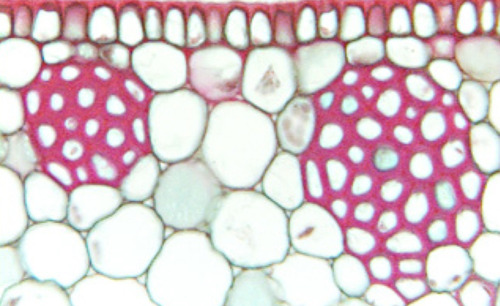
1. Elastic support for regions that have stopped growing in length
2. Water conducting tissues
functions of sclerenchyma
sclerenchyma fibers
• Long cells and tapered at both ends
• Less pittings
• Arise from meristematic cells
• Usually occur in groups
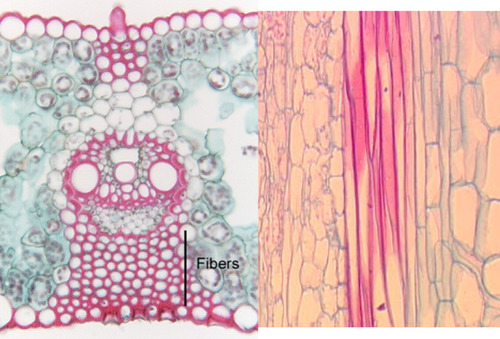
sclerenchyma sclereids
• Usu. cubical or spherical
• More conspicuous pittings
• Sclerosis of parenchyma cells
• Isolated or scattered