Epidemiology and Etiology of Schizophrenia
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Prevalence
Approximately 1% of the population affected.
Gender Differences
Men and women affected equally in prevalence.
Women's Prognosis
Women have better outcomes than men.
Age of Onset
Women develop schizophrenia at a later age.
Hospitalization Frequency
Women hospitalized less frequently than men.
Hospitalization Duration
Women hospitalized for shorter periods.
Negative Symptoms
Women exhibit milder negative symptoms.
Social Adjustment
Women show better social adjustment when not psychotic.
Cultural Influence
Delusions vary across cultures and upbringing.
Prognosis in Developing Countries
Better prognosis and lower prevalence observed.
Urbanicity
Urban living linked to increased schizophrenia risk.
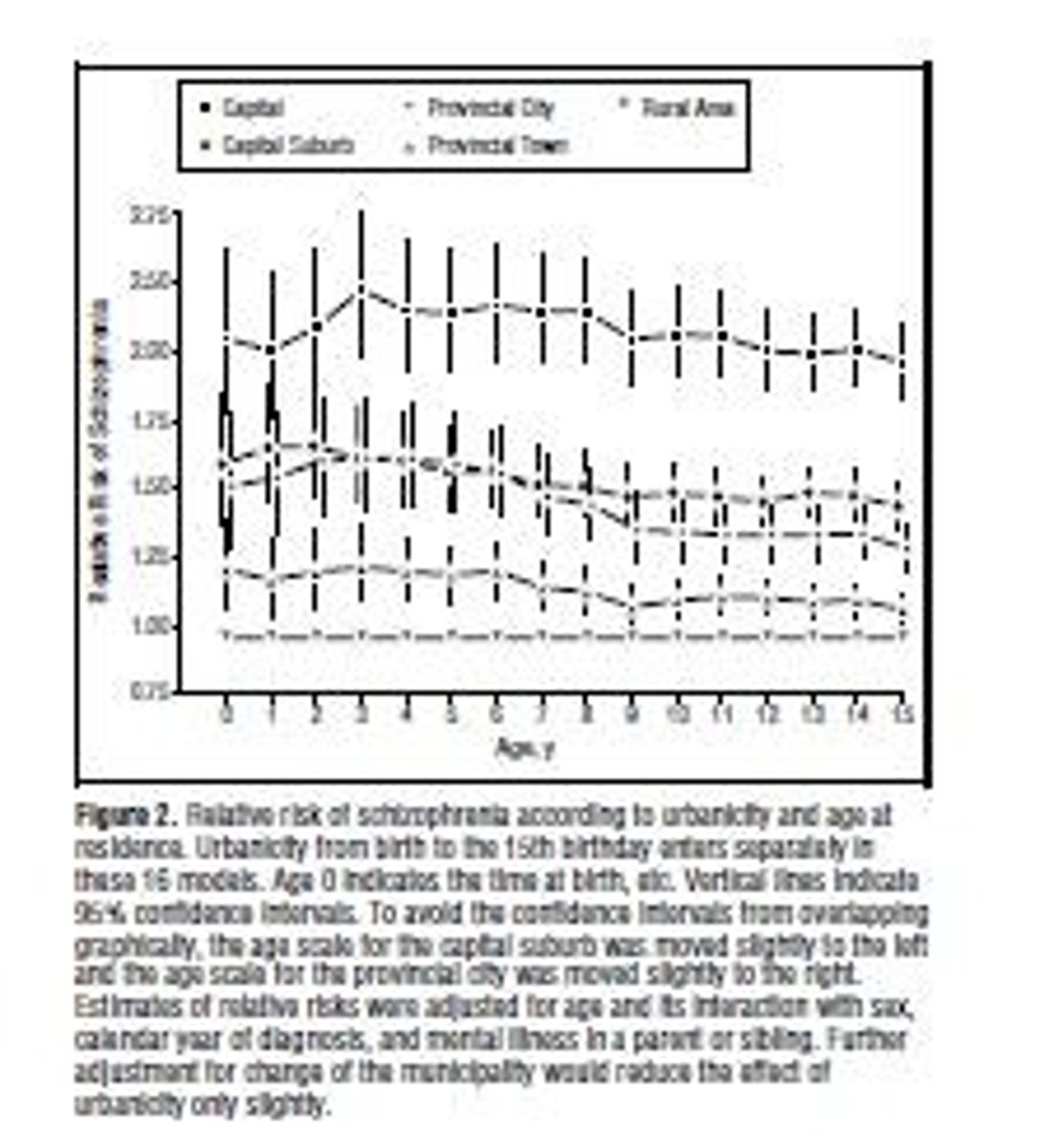
Sociogenic Hypothesis
Urban stressors contribute to schizophrenia development.
Social Drift Hypothesis
Schizophrenia symptoms lead to downward social drift.
Population Density
Higher genetic risk individuals live in urban areas.
Structural Abnormalities
Enlarged ventricles linked to severe schizophrenia.
Prefrontal Cortex
Smaller and hypoactive in individuals with schizophrenia.
Hippocampus
Reduced volume associated with stress sensitivity.
Synaptic Pruning
Abnormal pruning reduces synapses in schizophrenia.
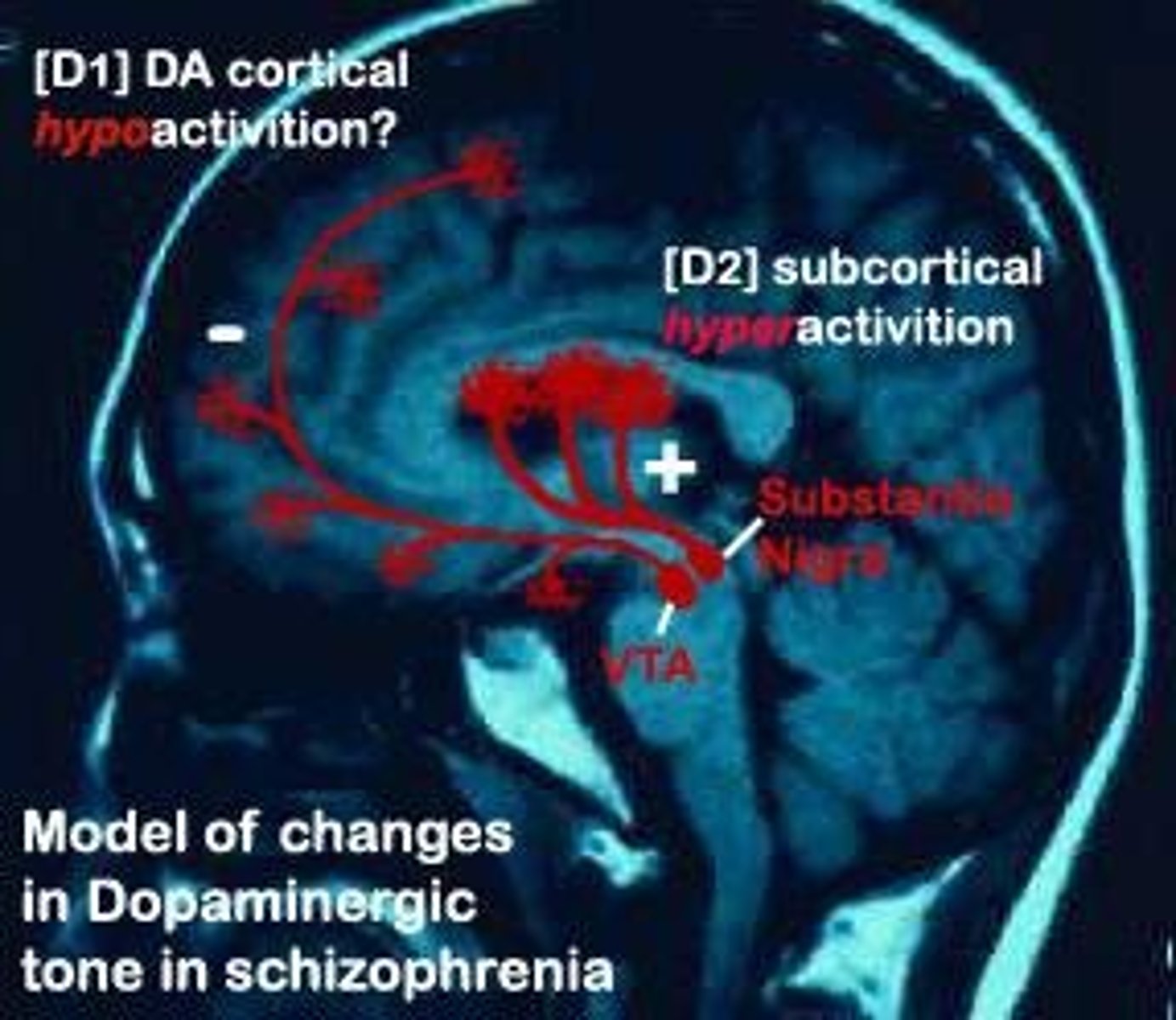
Dopamine Activity
High dopamine linked to positive schizophrenia symptoms.
Perinatal Hypoxia
30% of schizophrenia patients had oxygen deprivation.
Prenatal Infection
Influenza exposure increases schizophrenia risk in offspring.
Expressed Emotion
High EE environments lead to poor prognosis.
Relapse Rates
58% relapse in high EE homes vs. 10% low.