Skull (cranium only) end of chapter questions
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
which cranial bone possesses the zygomatic process
temporal
what is the difference, in degrees, between the IOML and OML
7-8 degrees
A radiograph of a posteroanterior (PA) axial projection (Caldwell method) of the cranium reveals that the petrous ridges are located at the level of the lower one-third of the orbits. The technologist performed this projection with the CR angled 15° caudad to the orbitomeatal line (OML). How must positioning be altered if a repeat exposure is performed
none of the above; positioning was correct
A radiograph of an anteroposterior (AP) axial projection of the cranium reveals that the dorsum sellae is projected below the foramen magnum, but the posterior arch of C1 is visible within the foramen. Which of the following positioning errors led to this radiographic outcome
excessive central ray (CR) angulation
a radiograph of a lateral projection of the cranium reveals that the orbital roofs (plates) are not superimposed; one is slightly superior to the other. which of the following positioning errors led to this radiographic outcome
tilt
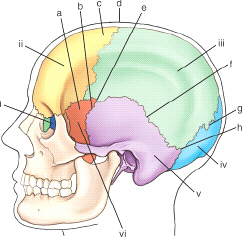
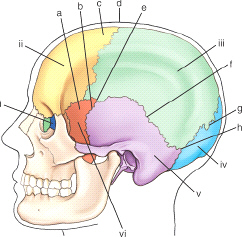
the sutural point or area labeled d is the: (anatomic structures are labeled i through vi and sutures a through h)
bregma
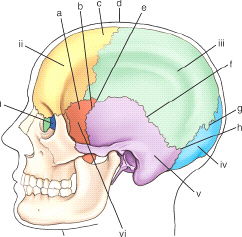
which bony structure is labeled v
mastoid process
which one of the cranial projections will best demonstrate a possible basilar fracture
horizontal beam lateral
which of the following cranial bones does not articulate with the parietal bone
all of the above articulate with the parietal bone
occipital
sphenoid
frontal
which one of the following technical consideration is most critical for demonstrating air and/or fluid levels within the cranium
erect or horizontal x-ray beam positioning
a radiograph of a submentovertical projection reveals that the mandible is superimposed over the ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses. which of the following modifications will eliminate this problem
increase the extension of the head and neck
the proper name for the parieto-orbital oblique projection is the schuller method
false
the pa axial projection (haas method) for the cranium requires a cr angle of 25 degrees caudad
false
which of the following landmarks corresponds with the level of the petrous ridge
top of ear attachment (TEA)
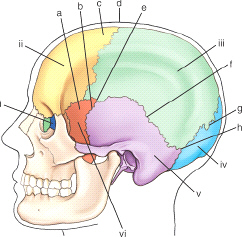
the cranial bone labeled i is the
ethmoid
which cranial suture is labeled g
lambdoidal
which of the following sutures separates the parietal from the occipital bone
lambdoidal
where is the cr centered for a lateral projections of the cranium
two inches (5 cm) superior to EAM
both CT and MRI can provide reconstructed images in three planes: axial, sagittal, and coronal
true
the slight depression above each eyebrow is termed the
supraorbital groove
which of the following terms describes the junction of the two nasal bones
nasion
where is the CR centered for a lateral projection of the cranium
two inches superior to EAM
A patient comes in with a clinical history of a possible pituitary adenoma. Because this is a rural hospital, CT and MRI are not available. Which radiographic projection or position would best demonstrate signs of bony erosion of the sella turcica because of the tumor
lateral position
which on of the following cranial projections will best demonstrate a possible basilar fracture
horizontal beam lateral
A patient enters the emergency department (ED) with a possible basilar skull fracture. Which of the following skull projections would best demonstrate any blood present in the sphenoid sinus
horizontal beam lateral
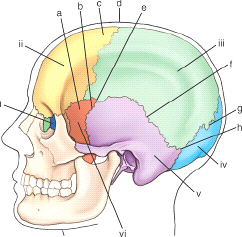
which cranial bone is labeled vi in this figure
greater wing of sphenoid
which cranial bone articulates with the other seven cranial bones
sphenoid
along with the use of erect positions, what other technical factor is important to demonstrate air/fluid levels in paranasal sinuses
horizontal x-ray beam
the cranial bone labeled i is the
ethmoid
which of the following sutures separates the parietal from the occipital bone
lambdoidal
the submentovertical projection requires that the IOML is placed parallel to the image receptor
true
A radiograph of a PA Caldwell (15° caudad) projection for cranium reveals that the petrous ridges are projected into the lower one-third of the orbits. Which of the following modifications should be made during the repeat exposure to produce a more diagnostic image
nothing; accept the initial radiograph
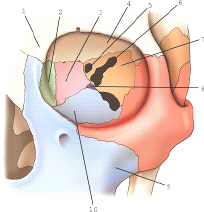
part 7 is part of which bone
sphenoid
the frontal bone articulates with ____ cranial bones
4
which cranial bone contains the cubiform plate
ethmoid
A patient comes to radiology with a possible bone cyst within the squamous portion of the frontal bone. Which of the following projections would best demonstrate this region with a minimal amount of distortion of the frontal bone
PA with no CR angulation to OML
an average-shaped skull with a 47 degree angle between the petrous pyramids and the midsagittal plane is classified as
mesocephalic
A radiograph of an anteroposterior (AP) axial projection of the cranium reveals that the dorsum sellae is projected below the foramen magnum, but the posterior arch of C1 is visible within the foramen. Which of the following positioning errors led to this radiographic outcome
excessive CR angulation
which three cranial bones articulate directly with the zygomatic bone
frontal, sphenoid, temporal
the ethmoid notch is part of which cranial bone
frontal
which positioning line should be perpendicular to the plane of the IR for the AP axial (towne) projection with a 37 degree caudad CR angle
IOML
the slight depression above each eyebrow is termed the
supraorbital groove
A radiograph of a parietoacanthial (Waters method) projection reveals that the petrous ridges are superimposed over the lower 30% of the maxillary sinuses. What specific positioning error (if any) led to this radiographic finding
insufficient extension of skull and neck
A patient comes to radiology with a possible bone cyst within the squamous portion of the frontal bone. Which of the following projections would best demonstrate this region with a minimal amount of distortion of the frontal bone
PA with no CR angulation to OML
the PA axial projection (haas method) for the cranium requires a CR angle of 25 degrees caudad
false
A patient enters the ED with a possible nasal bone fracture. The physician is concerned about a possible bony nasal septum deviation and fractured nasal bones. Which of the following routines would best diagnose these injuries
modified parietoacanthial and lateral nasal bone projections
A radiograph of a submentovertical projection reveals that the mandible is superimposed over the ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses. Which of the following modifications will eliminate this problem
increase the extension of the head and neck
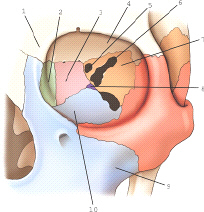
part 3 is part of which bone
ethmoid
which of the fontanels is the last to close at about 18 months of age
anterior
which cranial bone possesses the sella turcica
sphenoid
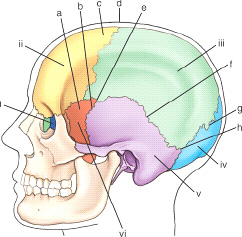
the sutural point or area labeled d is the
bregma
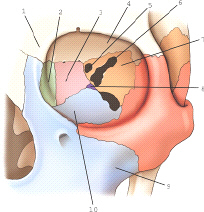
the part labeled 8 is part of which bone
palatine
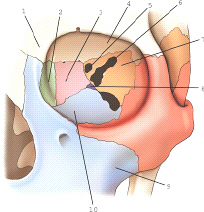
part 6 is which of the following
superior orbital fissure
there are a total of ____ fontanels in an infant
six
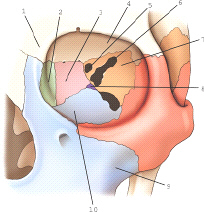
the bone labeled 2 is the
lacrimal
A patient comes to radiology for a routine study of the cranium. He is unable to flex his head and neck sufficiently to place the OML perpendicular to the IR for the AP axial projection. What should the technologist do to compensate for this problem without creating excessive magnification of the occipital bone
use the IOML and increase the CR angulation by 7 degrees
A radiograph of a posteroanterior (PA) axial projection (Caldwell method) of the cranium reveals that the petrous ridges are located at the level of the lower one-third of the orbits. The technologist performed this projection with the CR angled 15° caudad to the orbitomeatal line (OML). How must positioning be altered if a repeat exposure is performed
none of the above; positioning was correct
which cranial bone possesses the zygomatic process
temporal
the modified parietoacanthial (modified waters) projection requires more extension of the head and neck as compared with the parietoacanthial (waters) projection
false a
A pediatric patient enters radiology for a paranasal sinus series. Because of her age, the child is unable to hold still for the projections even with the use of immobilization devices. The decision is to hold the child during each exposure. Which of the following individuals should be asked to hold the child
guardian
the pituitary gland (hypophysis cerebri) is associated with and protected by the ____ bone
sphenoid
A radiograph of a lateral cranium reveals that the mentum of the mandible was cut off from the bottom of the radiograph. A 24 × 30-cm (10 × 12-inch) IR was used, and it was placed landscape. What must be altered if a repeat exposure is performed
none of the above; all of the critical structures were demonstrated
A radiograph of a lateral cranium reveals that the mentum of the mandible was cut off from the bottom of the radiograph. A 24 × 30-cm (10 × 12-inch) IR was used, and it was placed landscape. What must be altered if a repeat exposure is performed
increase the extension of the skull
the sensory apparatus of both equilibrium and hearing are contained in the internal ear
true
which one of the following positioning errors most often results in repeat exposure of a cranial position
incorrect rotation and tilt
A PA axial projection with a 25 degree caudad angle of the cranium reveals that the petrous ridges are at the level of the superior orbital margins. Which of the following modifications are required to correct this error
increase extension of cranium
which division of the temporal bone contains the organs of hearing and equilibrium
petrous
which of the following landmarks corresponds with the level of the petrous ridge
Top of ear attachment (TEA)
which of the following bones is part of the floor of the cranium
temporal
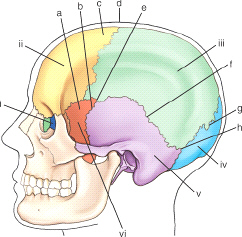
which bony structure is labeled v
mastoid process
which cranial bone contains the foramen ovale
sphenoid