Anesthesia
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Responsibilities of anesthesiologist
Induction
Amnesia
Analgesia
Secure airway/monitoring
Safe emergence/reversal of NMBA
Treatment of any anesthesia emergencies during induction, procedure, emergence
Most important risk factor for anesthesia complications
cardiac
Revised cardiac risk index
High-risk surgery (e.g., vascular, intraperitoneal, intrathoracic)
History of ischemic heart disease (e.g., angina, MI)
History of congestive heart failure (CHF)
History of cerebrovascular disease (e.g., stroke, TIA)
Pre-op insulin use
Creatinine >2.0 mg/dL
Should beta blockers and statins be discontinued perioperatively for cardiac patients?
no. continue meds
renal considerations for anesthesia
fluid balance
electrolytes
renal dosing
Signs of liver disease
Ascites
Hypoalbuminemia
Coagulation disorders
→ affects Anesthetic metabolism
which DM has higher risk of hypo/hyperglycemia
Type 1- higher risk for hyper and hypogylcemia
when should metformin be held before anesthesia for DM2
24 hrs prior to anesthesia
why should you check for thyroid labs and symptoms before surgery
concern for thyroid storm w the stress surgery has on body
What neurologic conditions are important to assess preoperatively for anesthesia, and why?
Intracranial mass, midline shift, or ↑ intracranial pressure (ICP)
bc → Risk of brain herniation with anesthesia induction
thyroid meds during surgery?
CONTINUE MEDS!
perioperative NSAIDs?
HOLD 72 hours bc bleeding risk
GLP-1 risk w anesthesia
delays gastric emptying → inc risk of aspiration
hold or continue ACE/ARBs for BP during surrgery
HOLD! (but dont d/c BB)
upper airway examination
Cervical spine ROM
Thyroid cartilage to mentum distance
Mouth opening
Dentition
Jaw alignment
Facial hair (interfere w mask seal)
Mallampati classification score
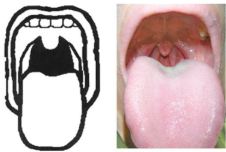
classify
Mallampati Class 1
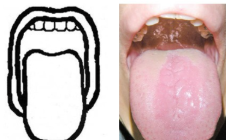
Classify
mallampati class 4
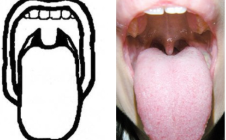
classify
mallampati class 2
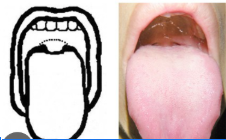
classify
mallampati class 3
Risk factors for difficult airway
Prior difficult airway
Increased neck circumference
Secretions or blood in airway
Short neck
Large tongue
What ASA classification: normal and healthy without acute or chronic disease
ASA 1
What ASA classification: Mild systemic disease without substantive functional limits
ASA 2
What ASA classification: severe systemic disease with substantive functional limitations
ASA 3
What ASA classification: severe systemic disease w a constant threat to life
ASA 4
What ASA classification: moribund and not expected to survive without surgery
ASA 5
What ASA classification: brain dead; organs removed for donation
ASA 6
components of anesthesia informed consent
Role of anesthesia provider
Review of medical history
Review of NPO time
Plan for pre-medication, induction, plan for airway management, plan for recovery/pain management
Discussion of increased risks based on particular comorbidities (cardiac, neurologic, respiratory)
PONV
Aspiration
Injury to teeth/dental work
Damage to vocal cords
Rare complication of needing higher level of care- ICU admission, intervention, procedure, surgery
Answer questions/concerns
Written or verbal
minimum fasting after having clear liquids by mouth
2 hours
minimum fasting after having non-clear liquids or LIGHT meal
6 hours
minimum fasting after fried, fatty foods or meat
8 hours or more
general anesthesia vs sedation
general anesthesia → fully unconscious
sedation → decreased level of consciousness but not fully
order of general anesthesia
pre-oxygenate
mask/IV induction
patient unconscious
airway management
maintain anesthesia
emergence/ reversal of anesthesia agent
which general anesthetic causes cardiovascular stimulation rather than depression
ketamine (protective airway but cause delirium and hallucinations)
Etomidate uses
RSI, induction of anesthesia
Fluorinated ethers vs nitrous oxide
Fluorinated ethers has less risk of post-op nausea and vomitting
which general anesthetic helps w post-op cognitive and behavioral dysfunction
Dexmedetomidine
Neuromuscular Blocking Agents (NMBAs) purpose
paralyze voluntary muscles and decrease muscle tone
*NO sedation or analgesic effects
depolariizing NMBA
succinylcholine
non-depolarizaing NMBA
Rocuronium
vecuronium
NMBA reversal agents
neostigmine
sugammadex
Possible analgesics
Opioids→ Analgesia, supplement sedation, post-op pain management
NSAIDS
Ketamine
Tylenol
Antiemetic options
Ondansetron
Metoclopramide
Dexamethasone
Meclizine/promethazine
Scopalomine
what is monitored anesthesia care (MAC)
anesthesia where pt is sedated but can breath on own (natural airway) →
IV sedation + local anesthetic and then monitor throughout to readily adjust or convert to general anesthesia if needed
Pros and cons of MAC over general anesthesia
less side effects
less airway injury risk
faster cognitive recovery
cons:
more frequent hypoexmic episodes than general anesthesia
can over sedate → apnea
challenging emergency airway management
whats procedural sedation
done by physician performing procedure, not anesthesiologist
administer sedatives/analgesics during procedure
difference between spinal and epidural anesthesia
epidural leaves catheter in epidural space while spinal is just a shot
4 things monitored for anesthesia
Oxygenation →pulse ox
Ventilation →Capnography
Circulation → EKG, arterial blood pressure monitor, HR
Temp → oral, skin, nasal, or bladder temp probes
complications of anesthesia
Malignant hyperthermia
Pseudocholinesterase deficiency
Anesthesia Awareness
Hypothermia
PONV
Peripheral Nerve Injury
Respiratory, cardiac and neurologic complications
how to recognize malignant hyperthermia early
check core temp
how to treat malignant hyperthermia
stop triggering agent
intubate
dantrolene
malignant hyperthermia
rare genetic reaction to certain anesthetics causing abnormal calcium release which leads to rapid muscle contraction, high fever, and a life-threatening metabolic crisis.
Pseudocholinesterase Deficiency
deficiency in Pseudocholinesterase enzyme that breaks down NMBA like succinylcholine → prolonged paralysis
just need to be sedated and ventilated til muscle strength returns
anesthesia awareness is associated with
NMBA (pt cant move to to signal awareness)
Total Intravenous Anesthesia (TIVA)
risk factors for post op nausea and vomiting
Female sex
History of PONV or motion sickness
Non-smoker
Postoperative opioid use
Use of volatile anesthetics and nitrous oxide