15.5 Describe the hormonal control of the ovarian and menstrual cycles
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Name the female reproductive system organs
- Ovaries
- Duct System
( - Uterine tubes
(fallopian tubes)
- Uterus
- Vagina)
- External genitalia
Describe the ovaries
-Development, maturation and release of oocytes
- Controlled by hormones (FSH & LH)
- All phases of oocyte development in this diagram
What are the 3 ovarian follicle stages
- primary follicle
- graafian (vesicular) follicle
- ovulation
Describe the primary follicle stage
- contains an immature oocyte
Describe the graafian (vesicular) follicle
- growing follicle with a maturing oocyte
Describe ovulation
- when the egg is
mature the follicle ruptures.
The egg is released and
follicular cells remain part of
ovary as corpus luteum (CL)
- occurs about every 28 days
Female reproductive system
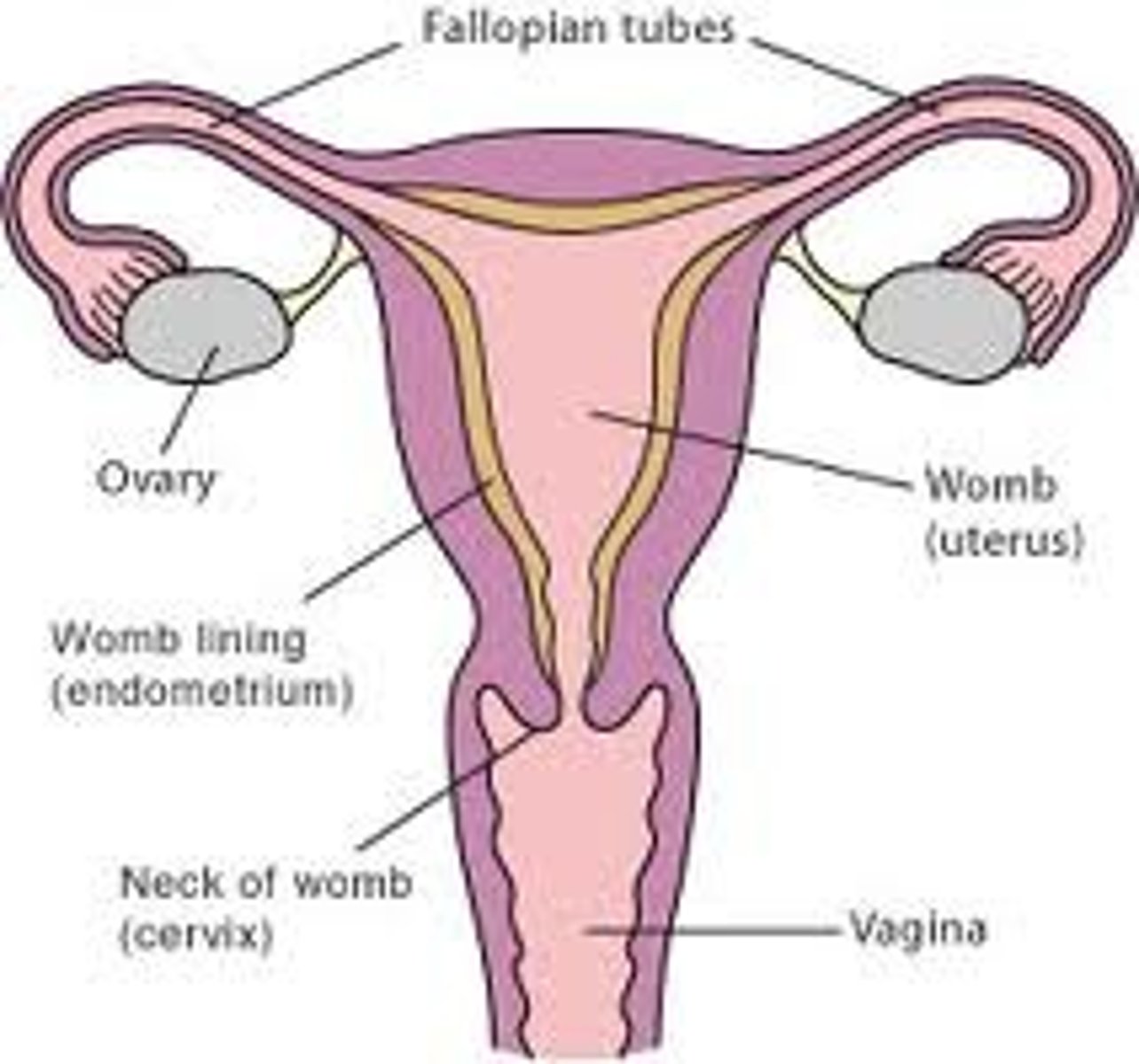
Describe the menstural (uterine) cycle
- cyclic changes of the endometrium (inside lining of the uterus)
- regulated by cyclic production of estrogens (E) and progesterone (P) produced by the ovaries
- preparation for implantation of fertilised egg
What are the stages of the menstrual cycle
menses
proliferative stage
secretory stage
Describe the menses stage
functional layer
of the endometrium is
sloughed = period (low E &
P)
Describe the proliferative stage
regeneration of functional
layer - rising E
Describe the secretory stage
endometrium increases in size and readies for implantation, rich in nutrients - E& P
Hormonal Control of the Ovarian and Uterine Cycles
1. Follicles stimulated to grow by follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) from anterior
pituitary
2. Growing follicles produce E. Uterine wall
proliferative phase.
3. High levels E promote release of luteinizing hormone (LH) resulting in
ovulation
4. Corpus luteum left on ovary produces E & P.
Uterine wall secretory phase.
5. E & P inhibit release of FSH & LH (no more eggs
develop)
6. Waiting to see if fertilisaton occurs
7. Corpus luteum dies if not pregnant and E & P drop
= period