AP Psychology sensation and perception
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Sensation
Detecting physical energy from the environment and encoding it as neural signals
Bottom-Up Processing
Analysis that begins with the sensory receptors and works up to the brain's integration of sensory information.
Externally Driven.
Perception
Selecting, organizing, and interpreting what comes in your window as meaningful objects and events.
Top-Down Processing
Guided by higher level mental processes, such as experience, motivation, and expectations
Perceptual Adaptation
Ability to adjust to an artificially displaced field
Psychophysics
The study of how physical energy relates to our psychological experience
Transduction
Conversion of one form of energy into another
Absolute Threshold
The minimum stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time
Difference Threshold
(JND)
The minimum difference a person can detect between any 2 stimuli 50% of the time
Weber's Law
Difference thresholds differ by a constant percentage rather than a constant amount.
Signal Detection Theory
Predicts when we will detect weak stimuli amid background noise
Depends on experience, expectations, motivation, and fatigue level
Subliminal Messages
Stimuli below one's absolute threshold
Unconsciously sensed
Works to an extent
Sensory Adaptation
Diminished sensitivity as a consequence of constant stimulation
Wavelength
Determines Hue
Amplitude
Determines Brightness
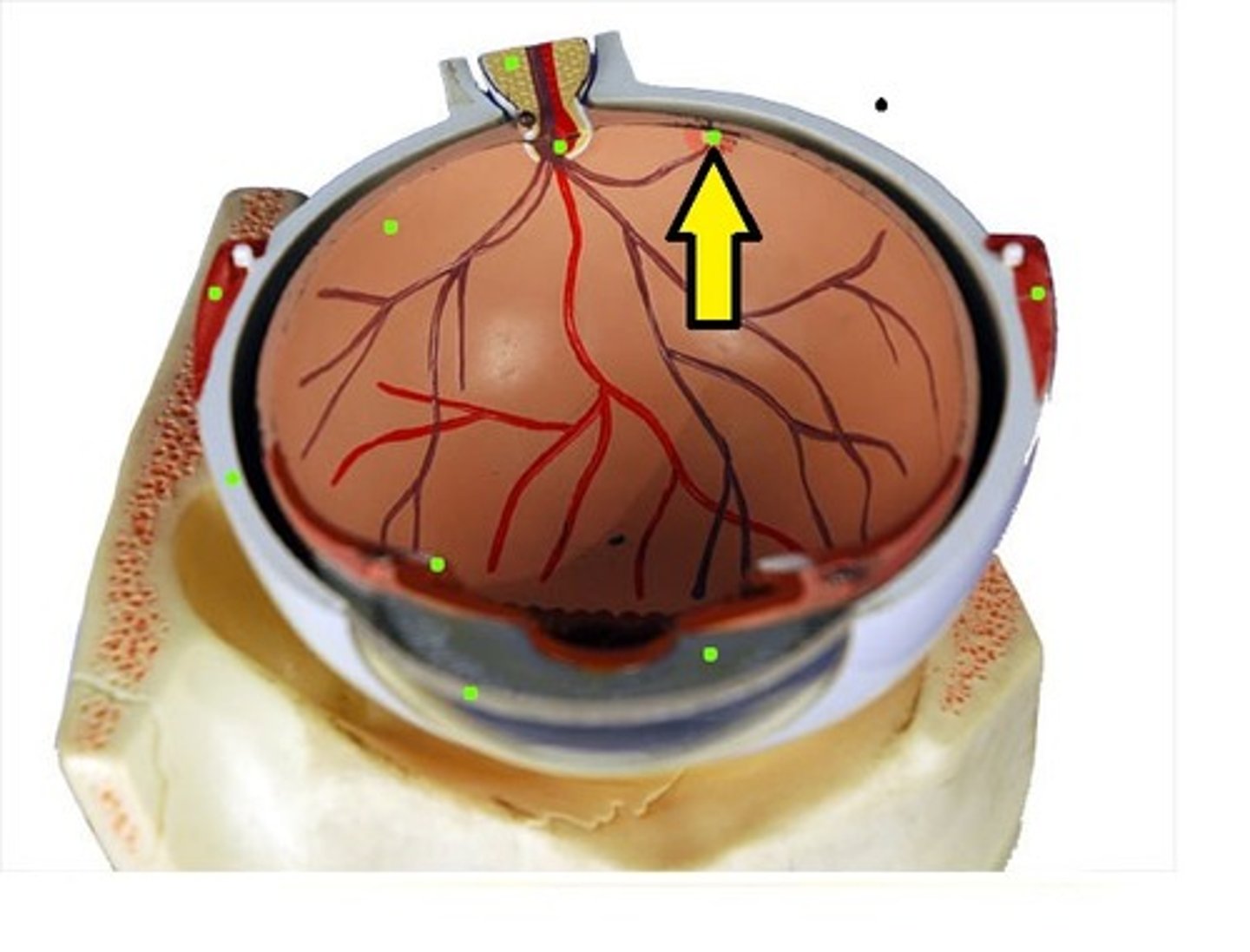
Pupil
A small adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enters
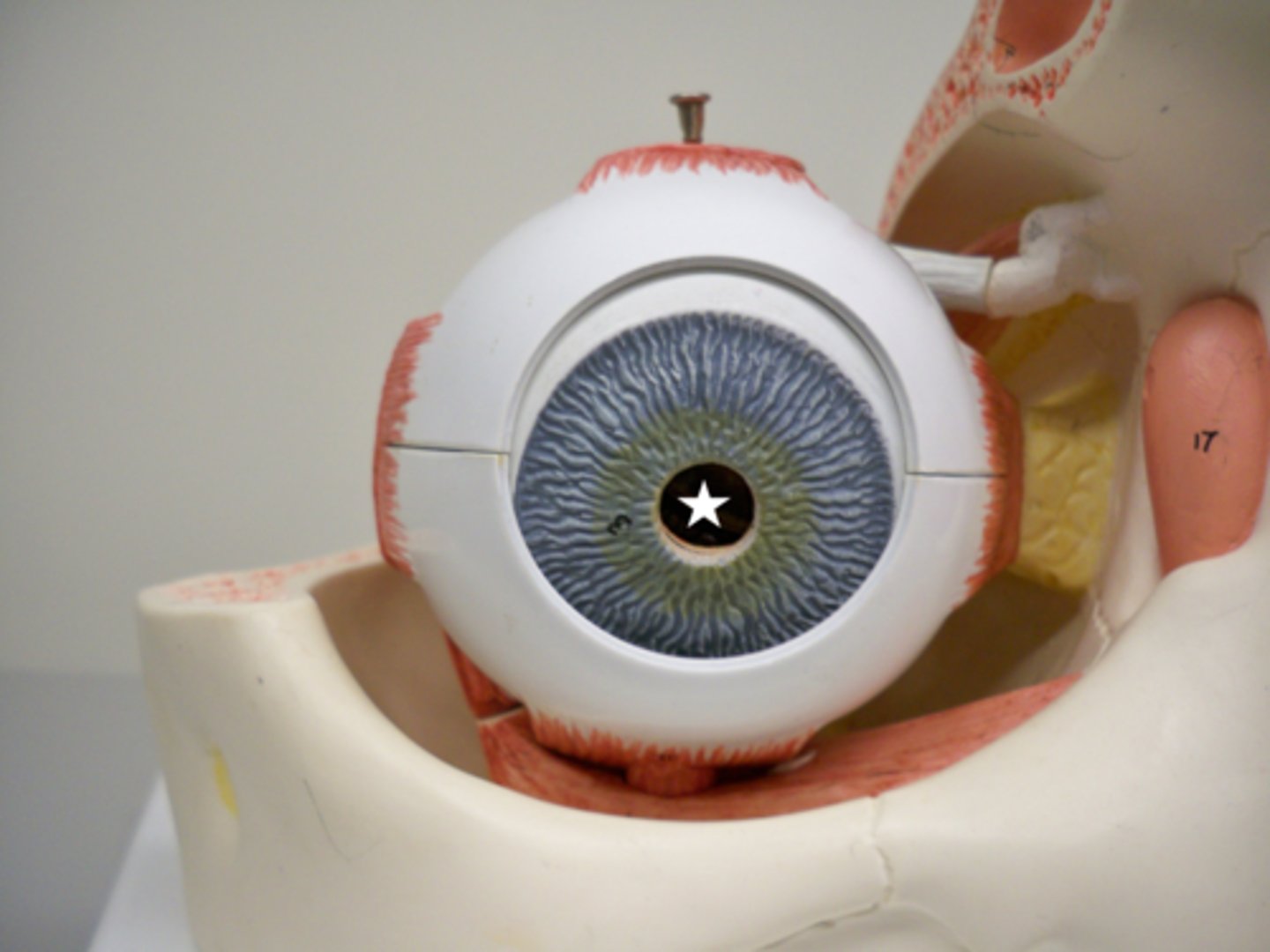
Iris
A ring of muscle tissue that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil's opening
Cornea
Protects the eye and bends light to provide focus

Lens
The transparent structure behind the pupil that changes shape to help focus objects on the retina

Accomodation
Lens changes shape to focus near or far images on the retina
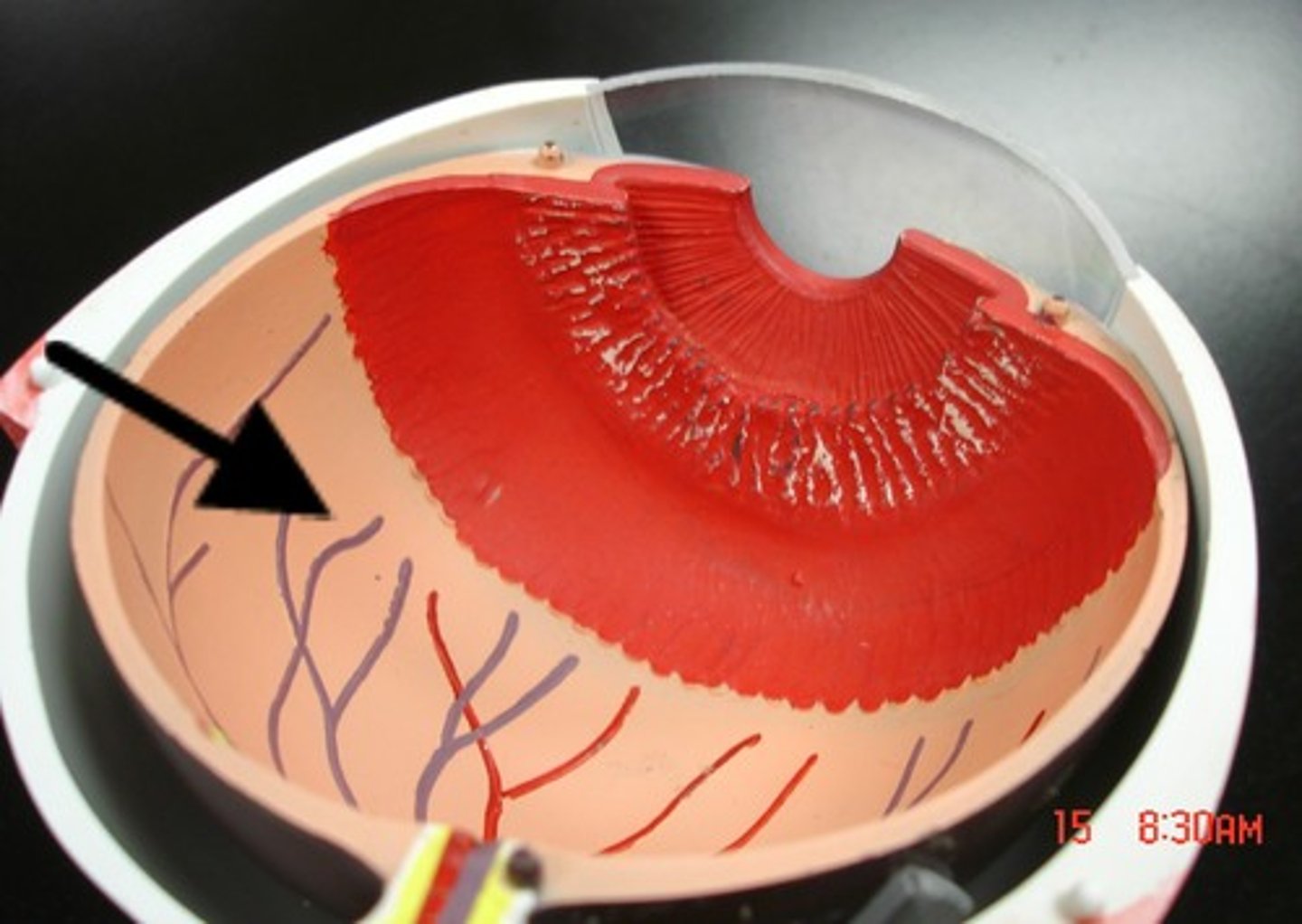
Retina
Light sensitive inner surface of the eye containing the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information
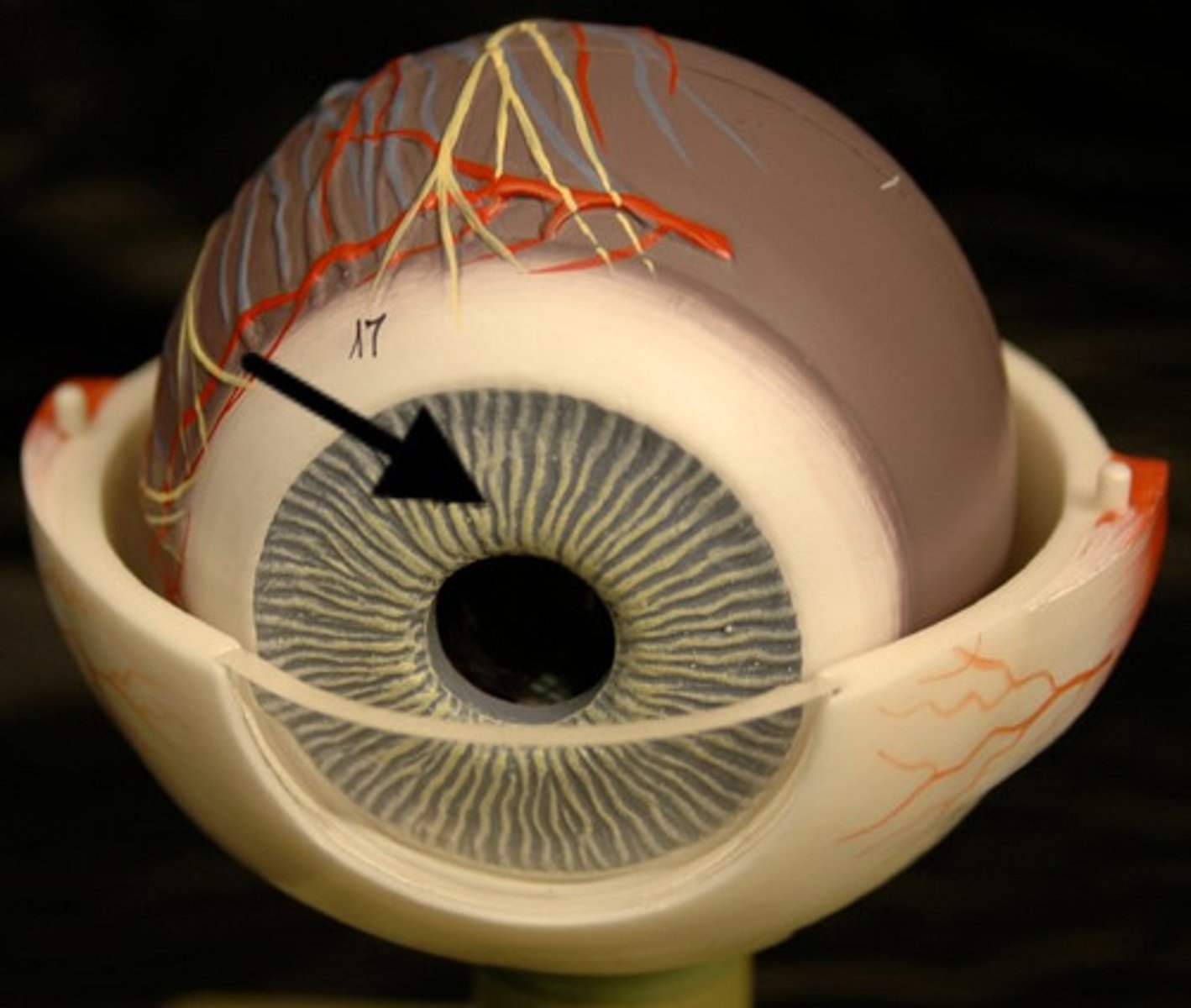
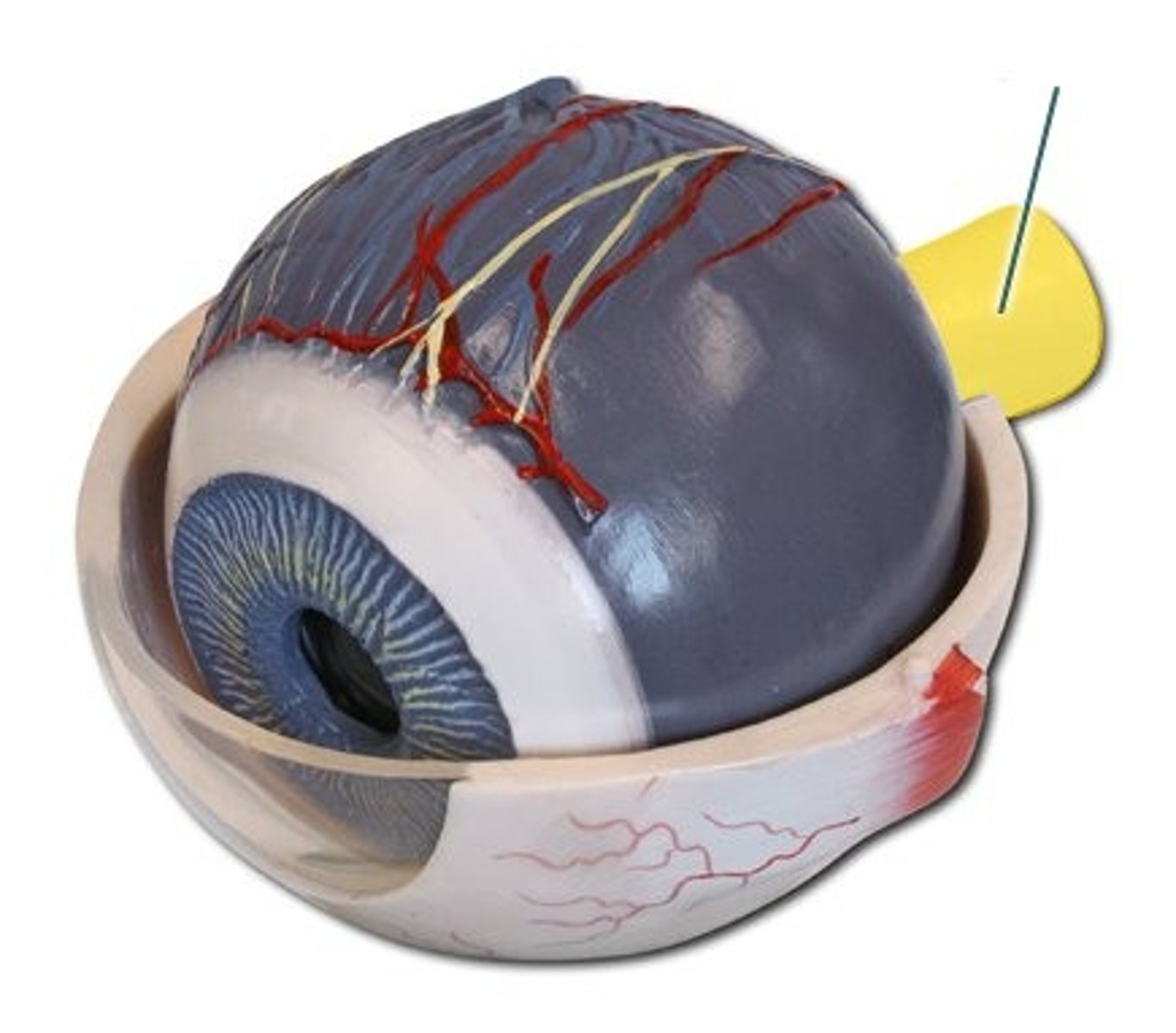
Optic Nerve
The nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
Blind Spot
The point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye
No receptor cells
Brain fills the "hole" without permission
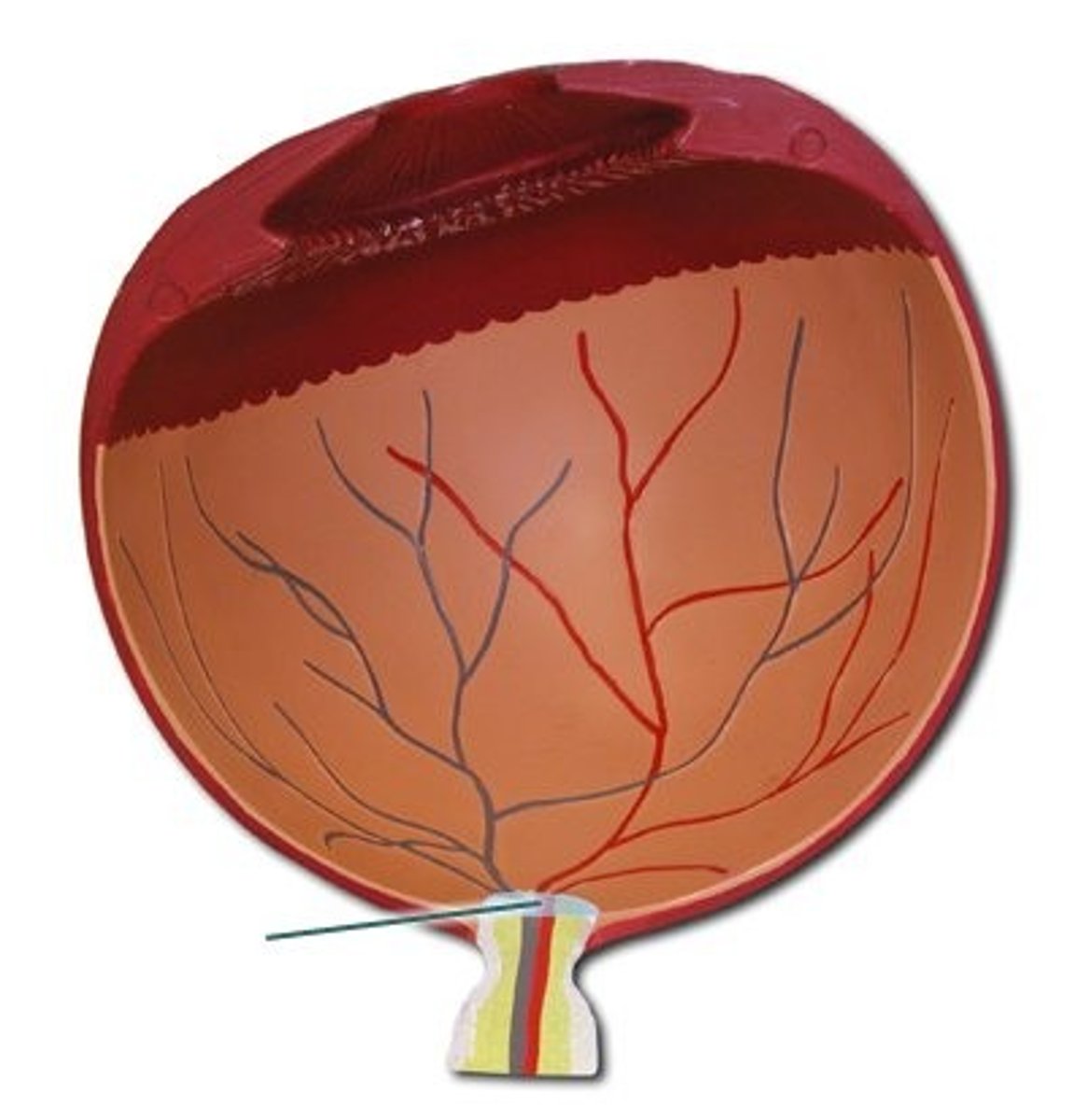
Fovea
The central focal point in the retina
Acuity
Resolution
Nearsightedness
Too much curvature of the cornea/lens
Near objects are more clear
Farsightedness
Not enough curvature of the cornea/lens
Far objects are more clear
Rods
Retinal receptors that detect black, white, and grey
Necessary for peripheral vision
Cones
Retinal receptors that are concentrated near the center of the retina
Detect fine detail and give rise to color sensations
Feature Detectors
Nerve cells in the brain the respond to specific features of the stimulus, such as shape, angles, or movement
Parallel Processing
The processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously
Trichromatic Theory of Color Vision
The eye has 3 types of color receptors (red, green, and blue)
Cones work in 3's
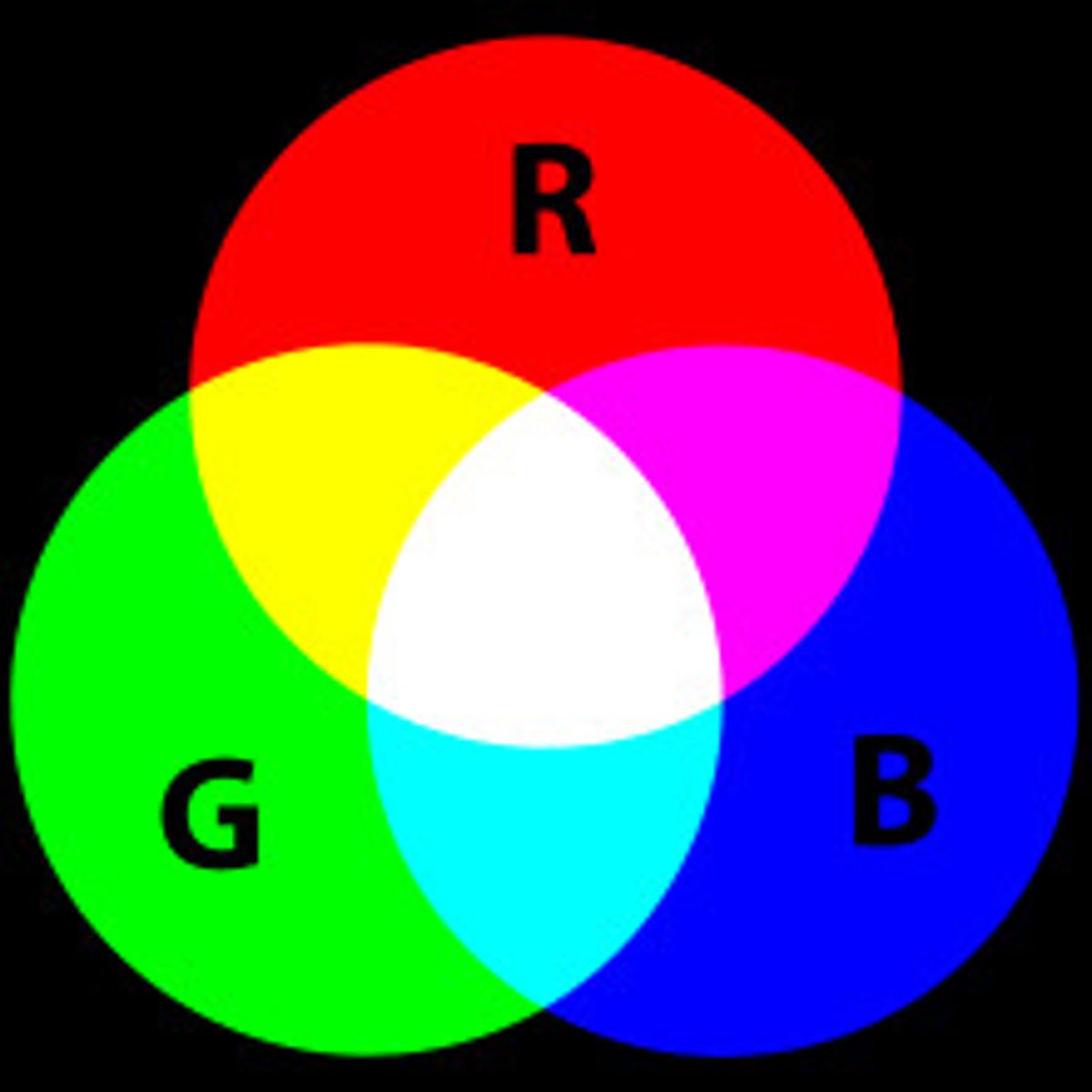
Color Blind
People who lack a chemical produced by one or more types of cones
Opponent Process Theory of Color Vision
Certain neurons can be either excited or inhibited depending on the wavelength of light
Complementary wavelengths have opposite effects.

Wavelength
Pitch
Measured in Hz (Hertz)
Amplitude
Loudness
Decibels
Unit of measurement for sound
(dB)
Transduction in the Ear
Vibration/mechanical energy -> neural impulses
Hair Cells
Bent by the vibrations and transduce mechanical energy to neural impulses
In the cochlea
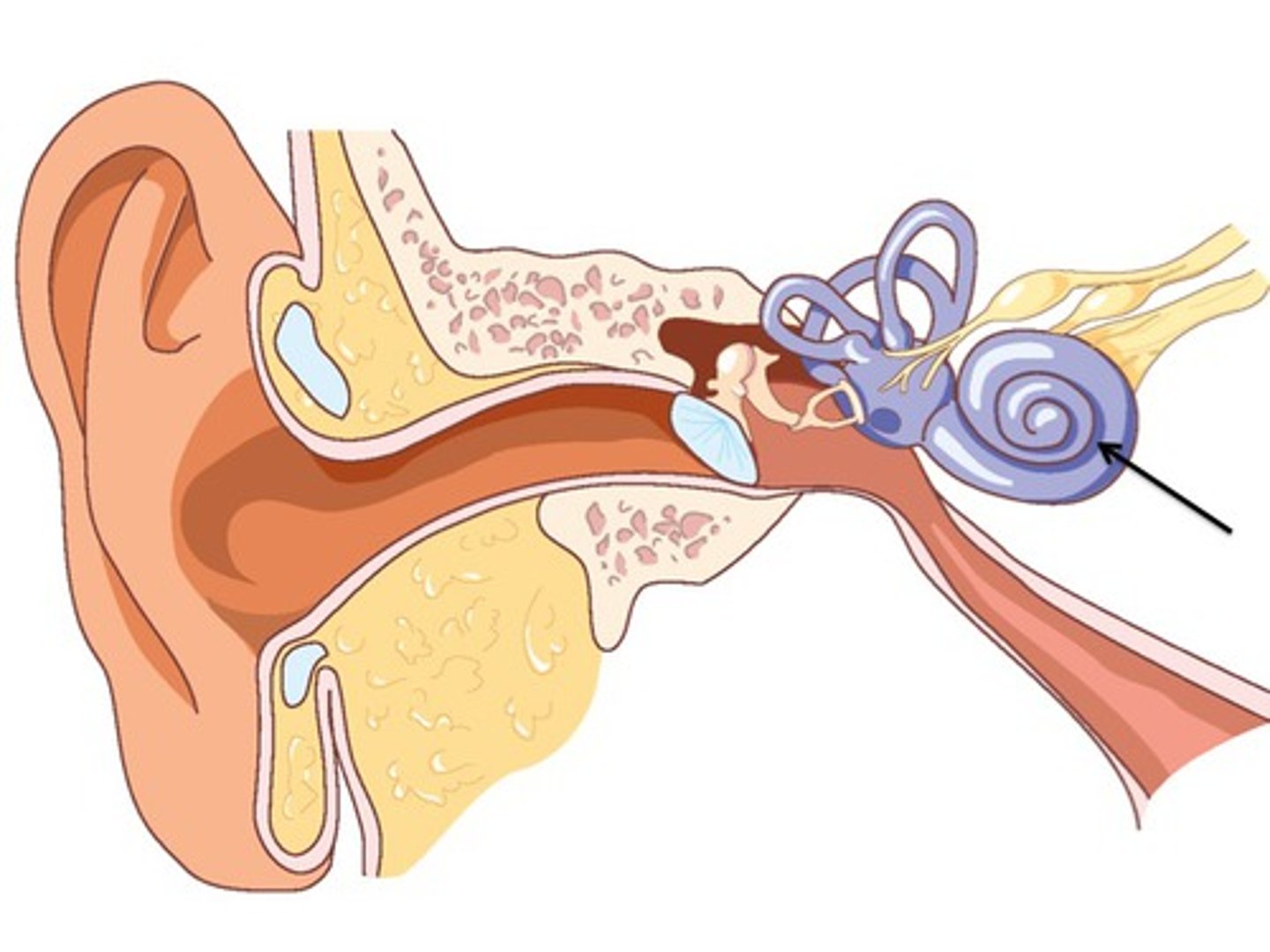
Frequency Theory
The theory that the rate of nerve impulses travelling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of a sound
(Explains low-pitch)
Place Theory
The theory that links pitch with the place where the cochlea's membrane is stimulated.
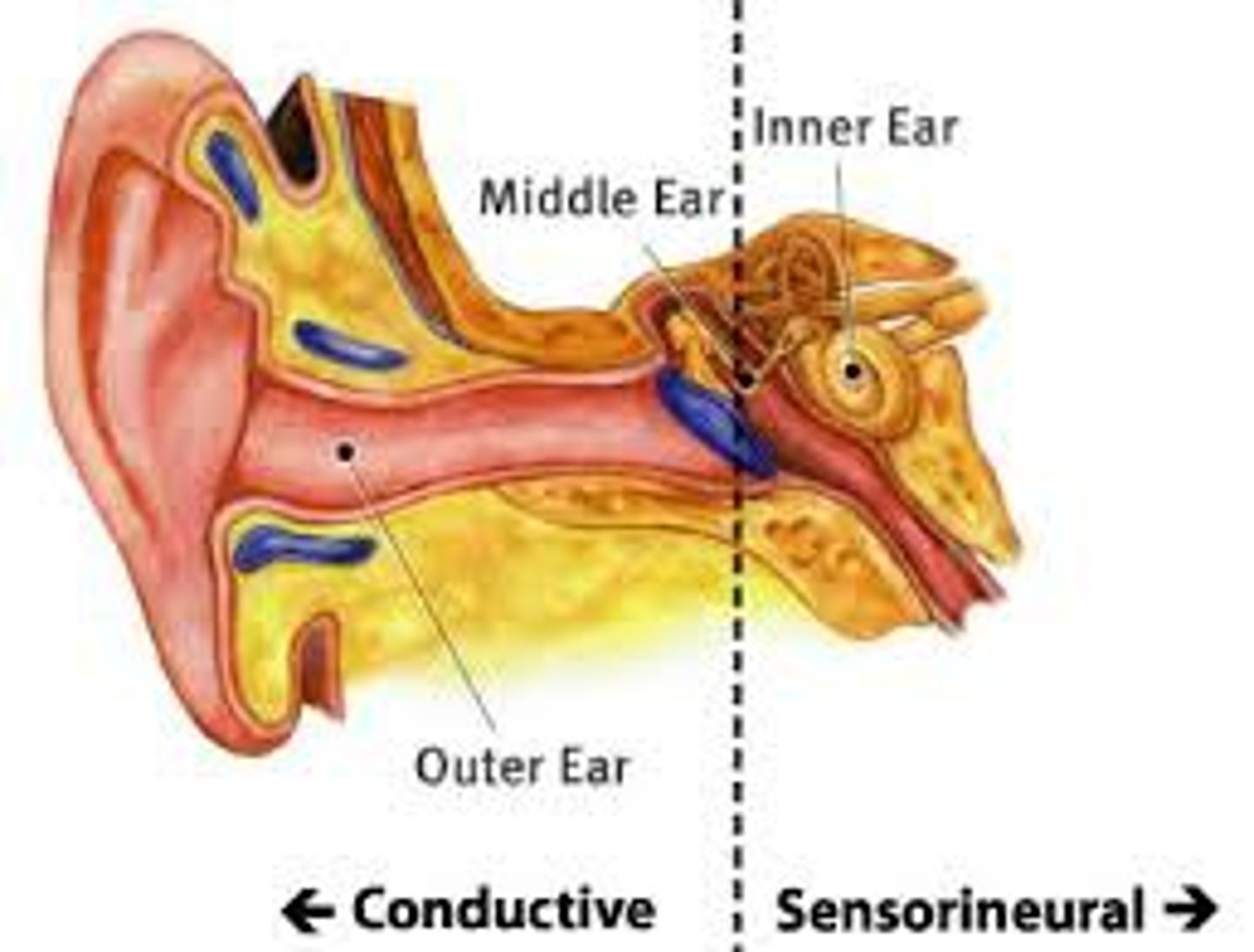
Conduction Deafness
Caused by damage to the mechanical system that conducts sound waves to the cochlea
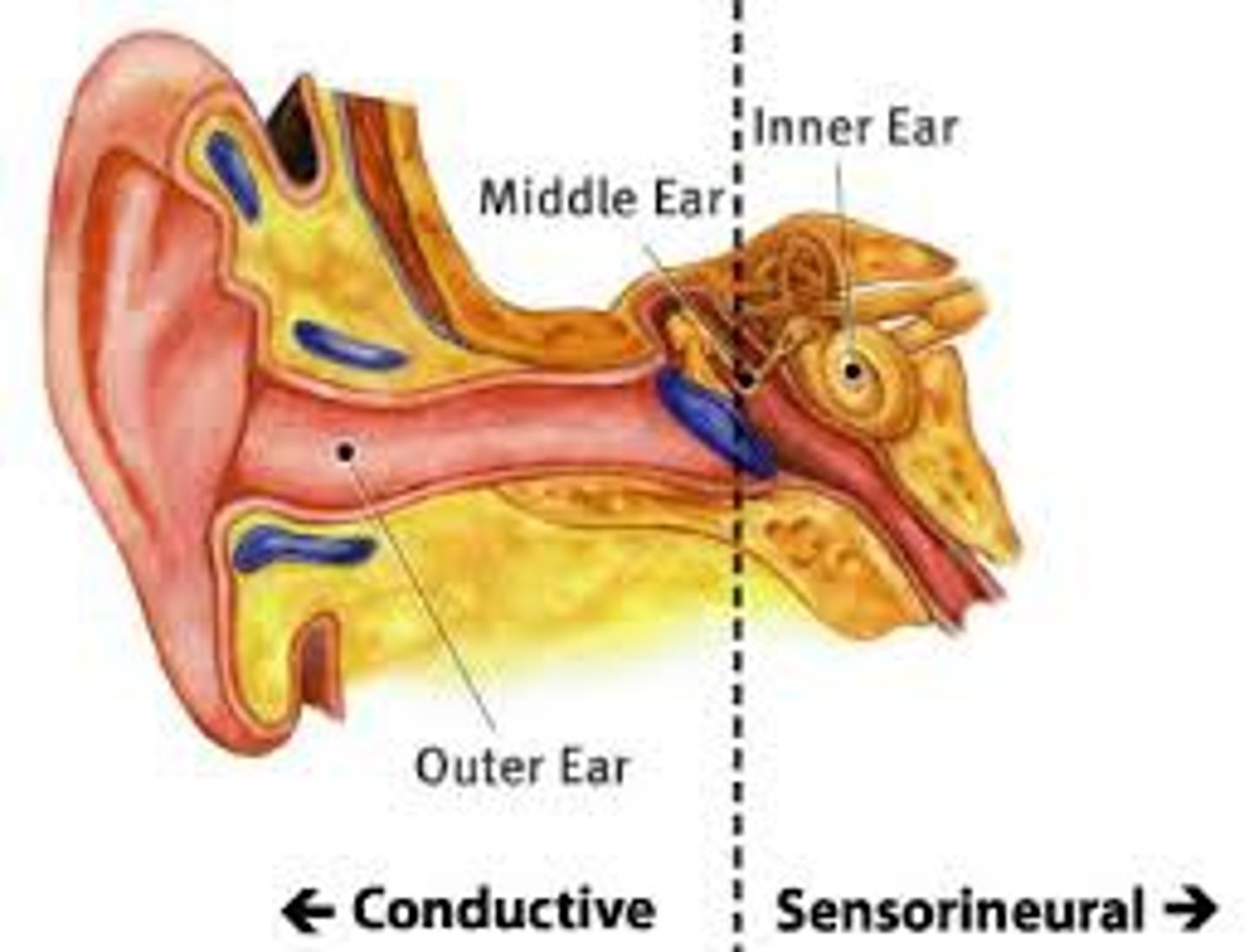
Sensorineural Deafness
Caused by damage to the cochlea's receptor cells or to the auditory nerves
Four Skin Senses
Pressure, Warmth, Cold, and Pain
Gate Control Theory of Pain
The spinal cord contains a neurological "gate" that blocks pain signals or allows them to pass onto the brain
Five Taste Sensations
Sweet. Salty, Bitter, Sour, Umami
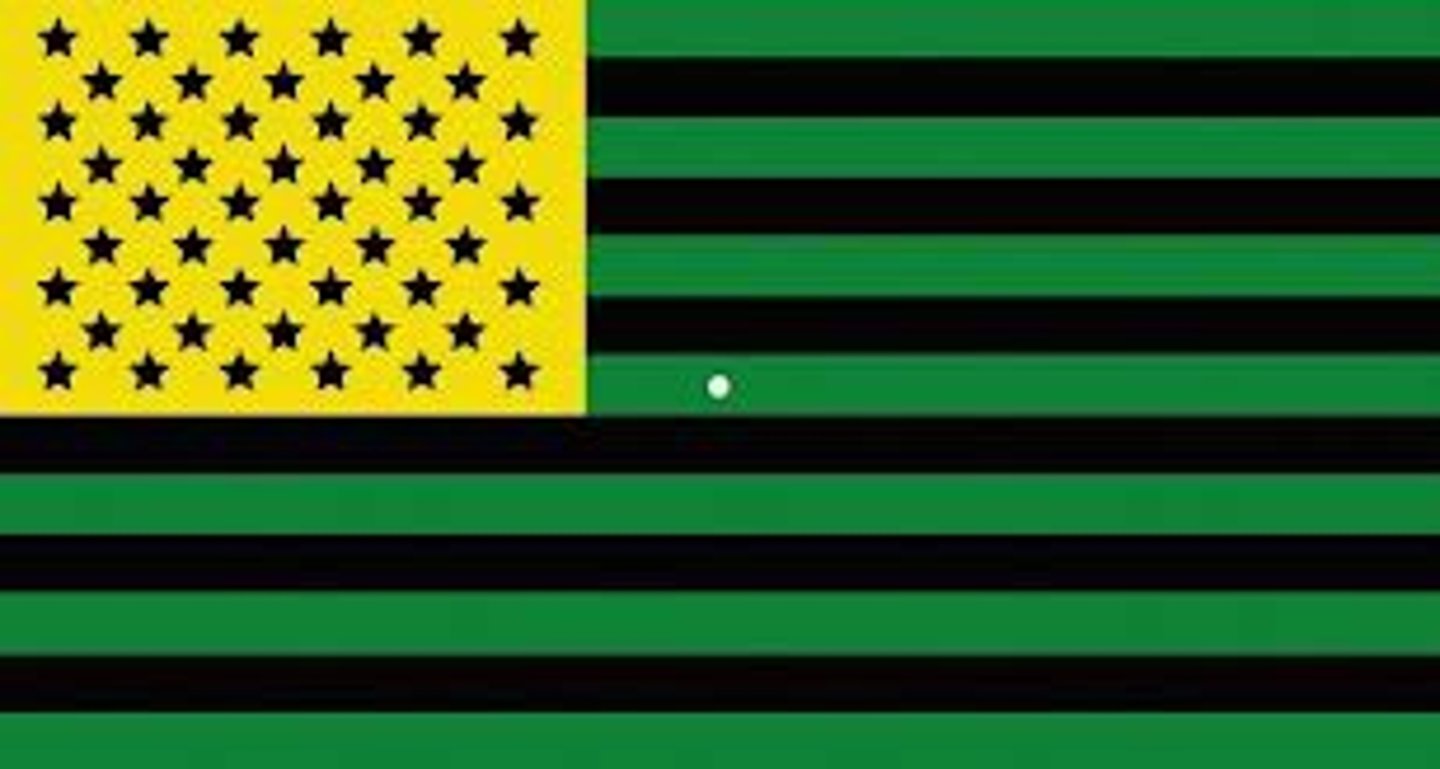
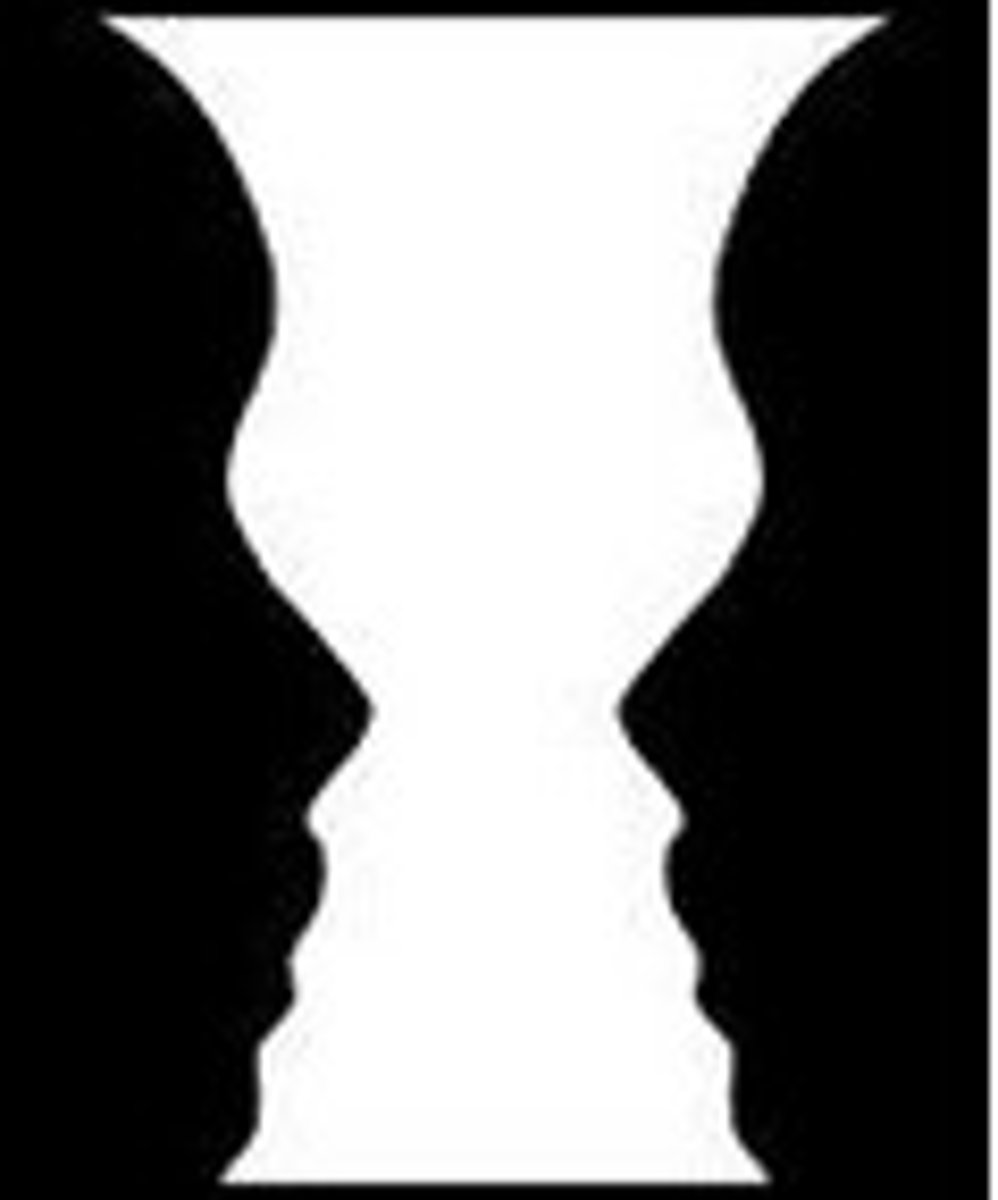
Gestalt Psychology
Emphasize the tendency to integrate pieces of information into meaningful wholes
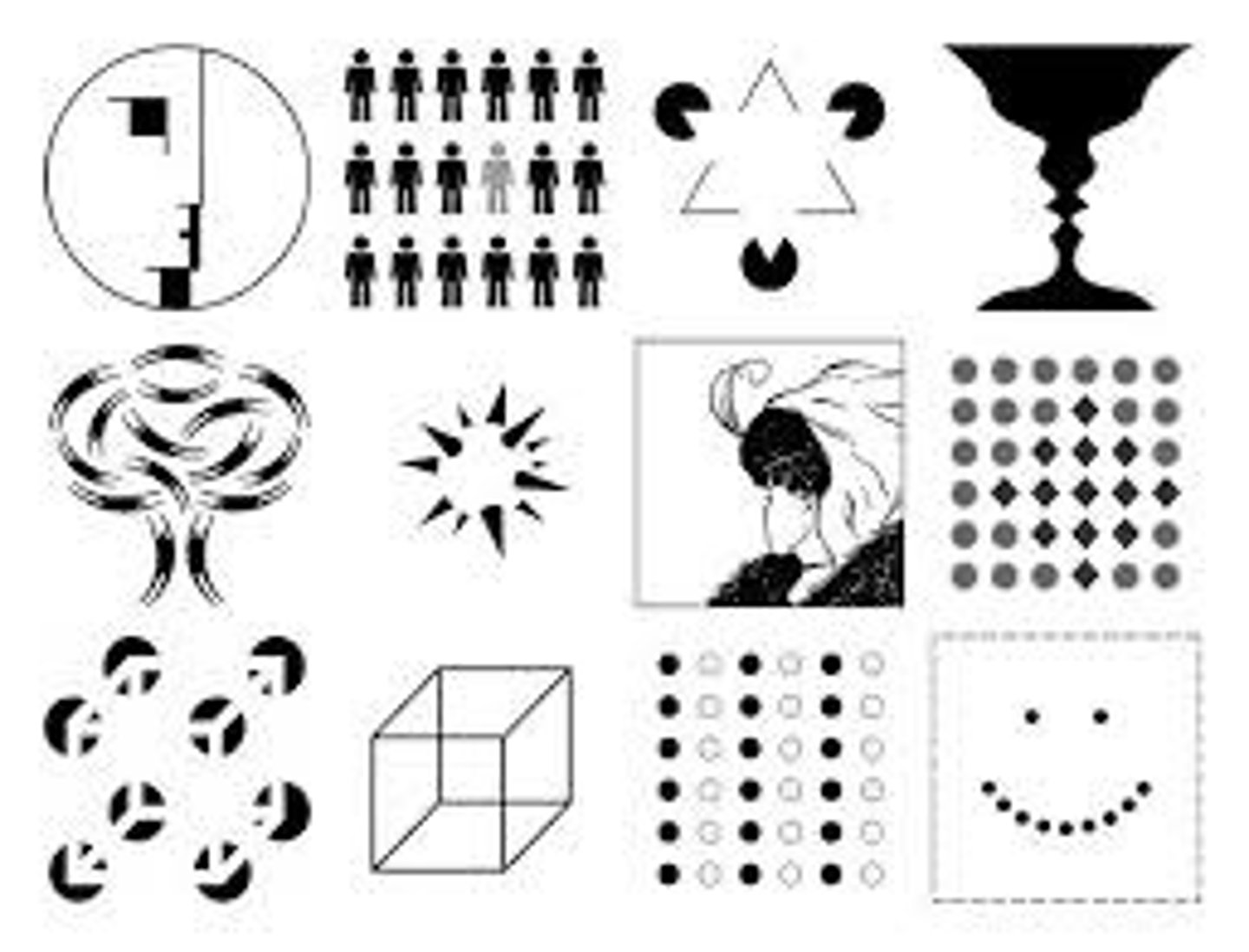
Figure Ground Relationship
The organization of the visual field into objects that stand out from their surroundings

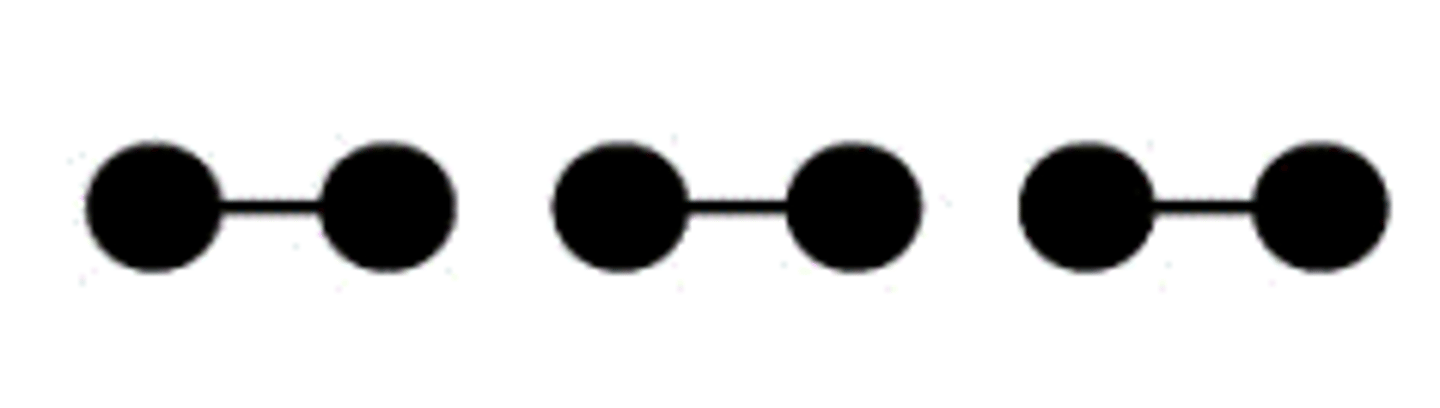
Proximity
We group nearby objects together
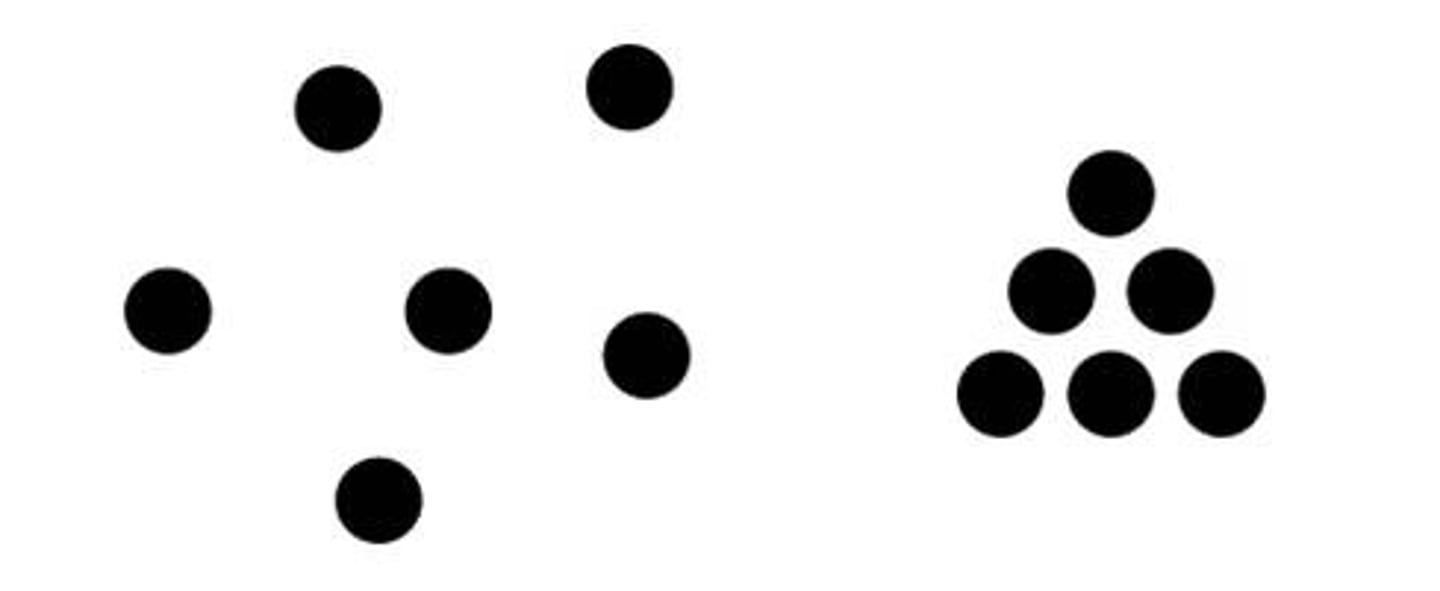
Similarity
We group similar objects together

Continuity
We perceive smooth continuous patterns rather than disconnected ones
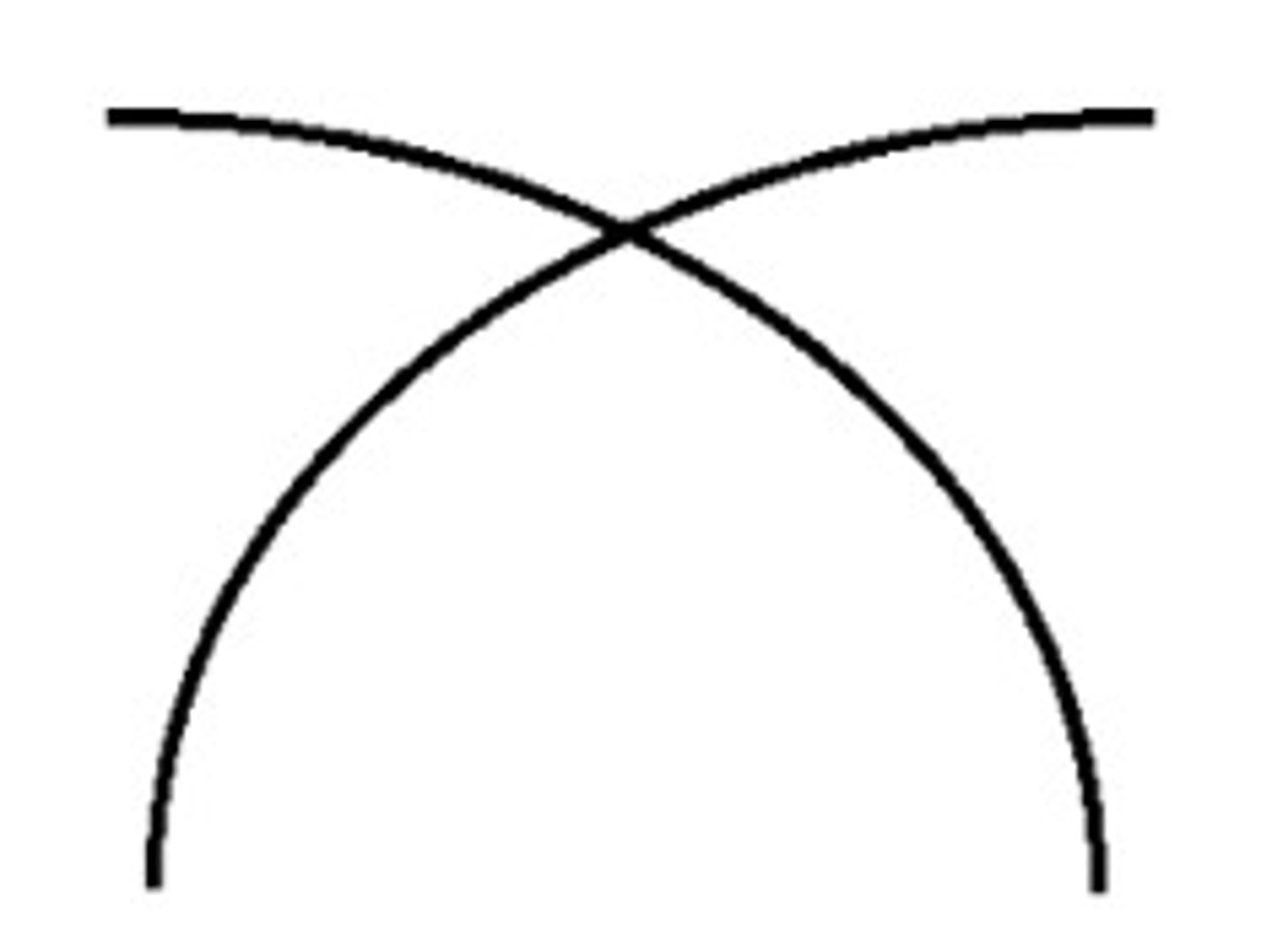
Connectedness
Uniform and Linked
Depth Perception
The ability to see objects in 3D although the images that strike the retina are 2D
Allows us to judge distance
Monocular Cues
Available to either eye alone
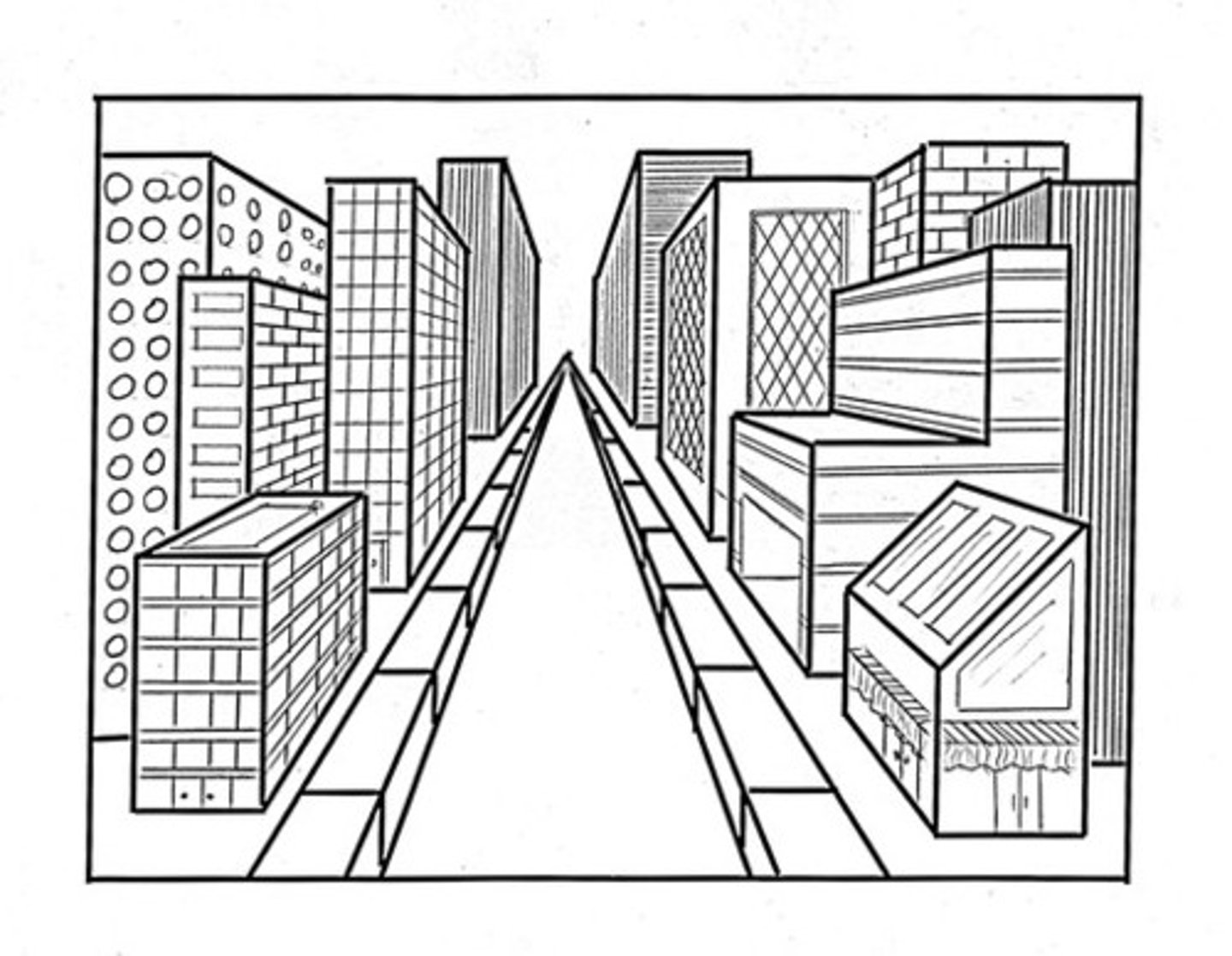
Linear Perspective
Parallel lines appear to converge with distance
The more they converge, the greater their perceived distance
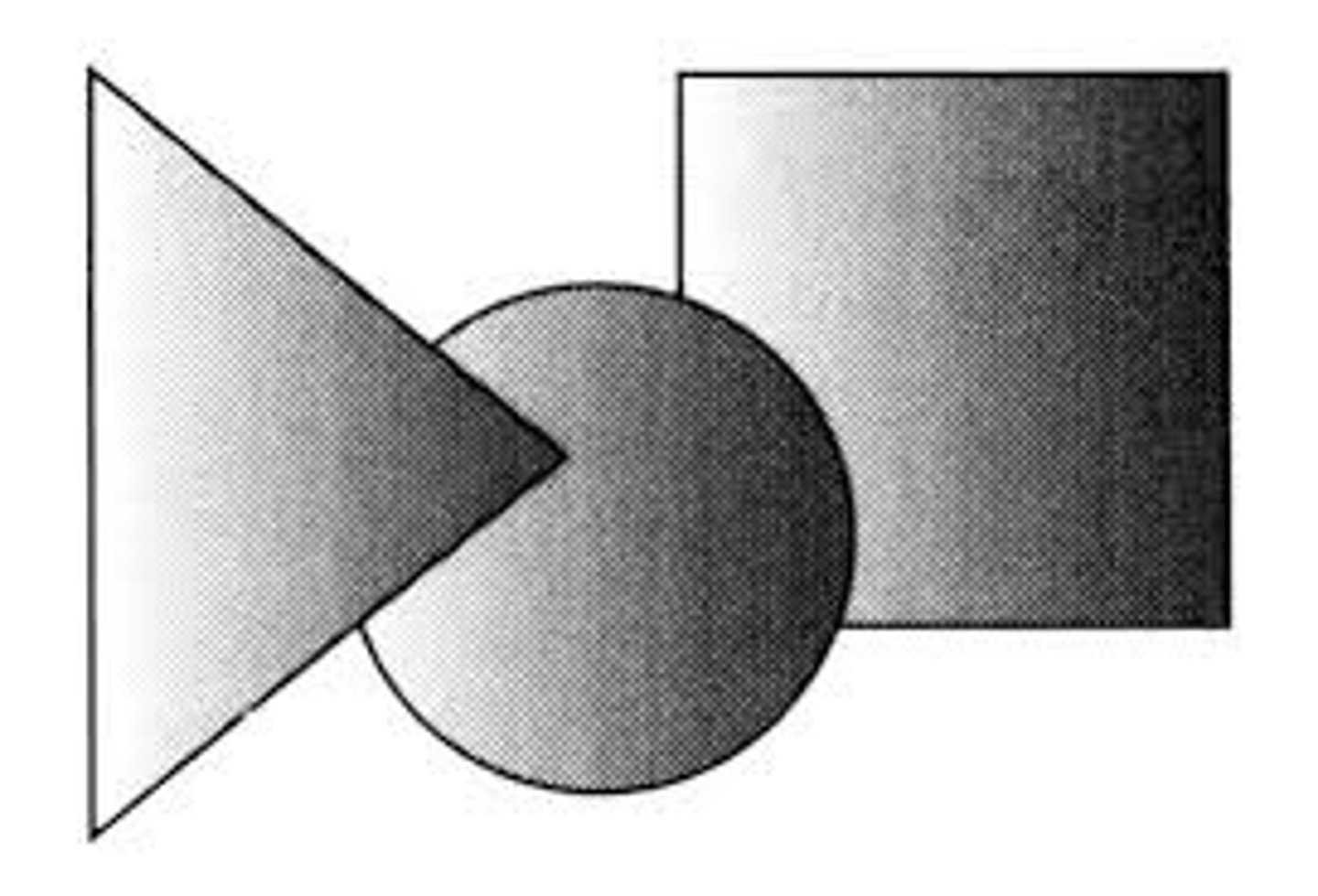
Interposition
If one object partially blocks our view of another, we perceive it as closer
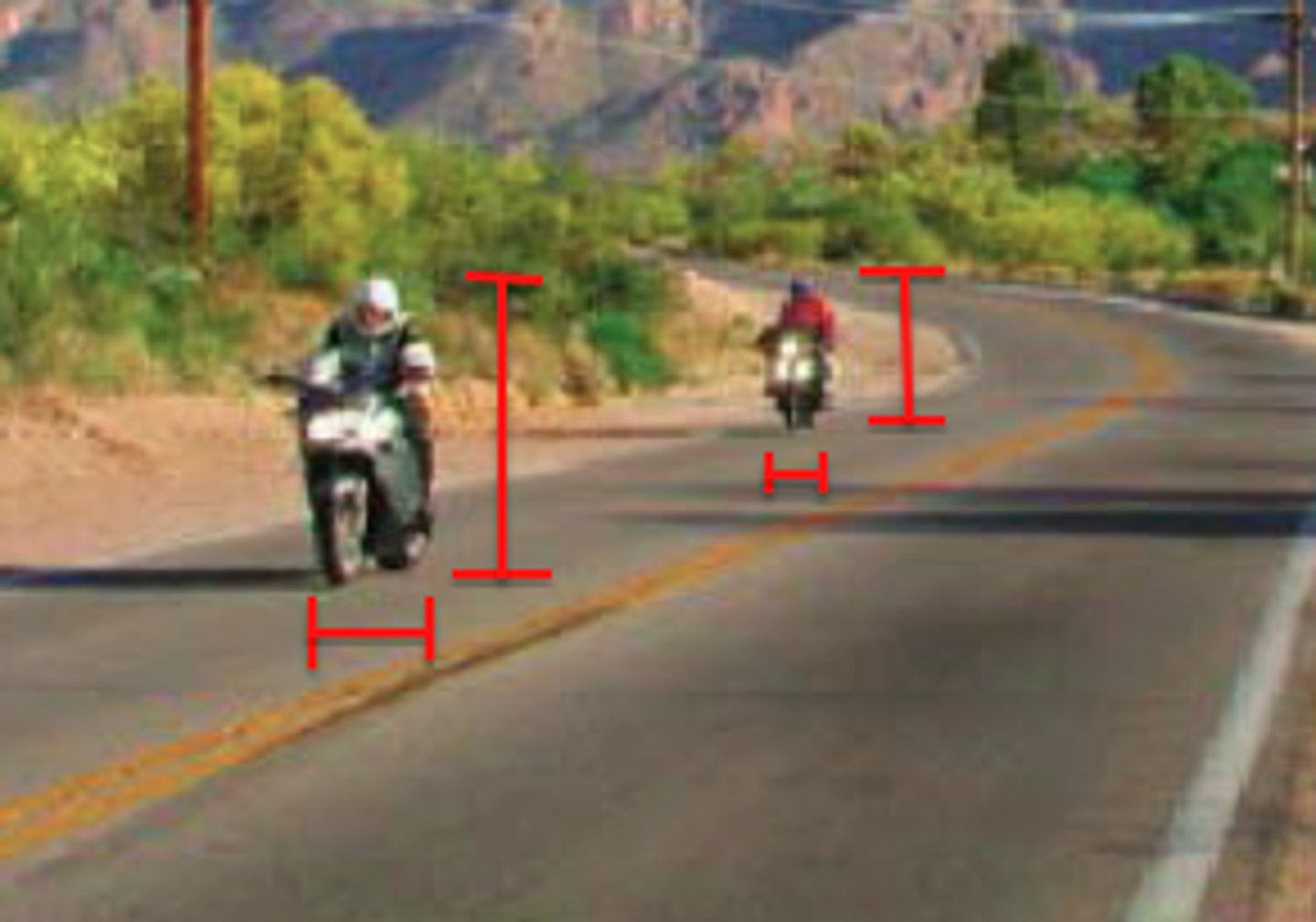
Relative Size
If we assume 2 objects are similar in size, most people perceive the one that casts the smaller retinal image as farther away

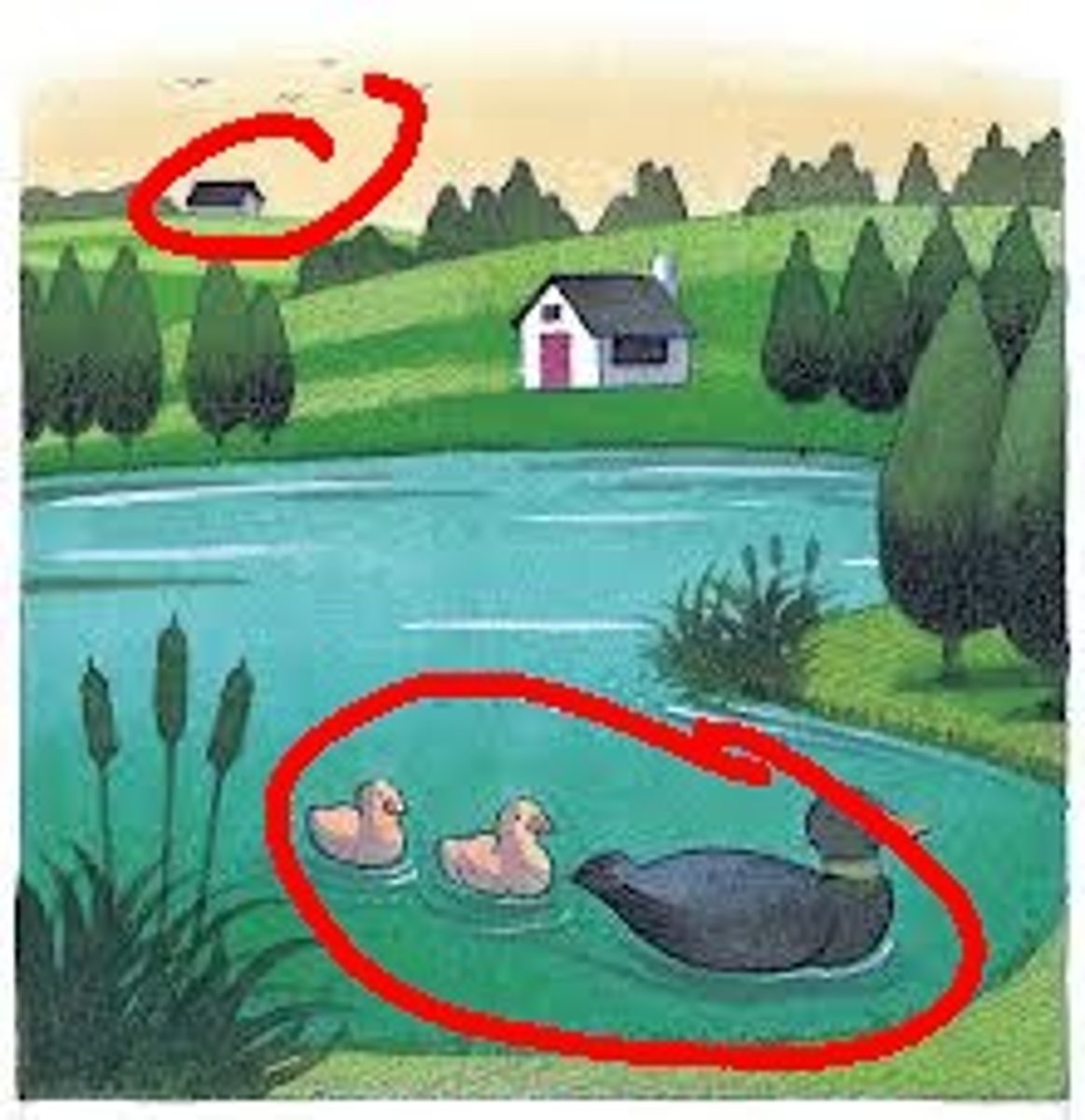
Relative Height
We perceive objects higher in our field of vision as farther away

Light and Shadow
Nearby objects reflect more light to our eyes
Dimmer seems farther away

Binocular Cues
Depends on both eyes
Retinal Disparity
By comparing the images from the retinas in the 2 eyes, the brain computes distance
Greater the difference/disparity the closer the object

Phi Phenomenon
An illusion of movement created when two or more adjacent lights blink on and off in quick succession
Perceptual Constancy
Perceiving objects as unchanging even as illumination and retinal images change
Consistent shape, size, lightness, and color
Perceptual Set
A mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another
Extrasensory Perception (ESP)
Claim that perception can occur apart from sensory input
Telepathy
One person sending thoughts to another or perceiving another's thoughts

Clairvoyance
Perceiving remote events

Precognition
Perceiving future events
Psychokinesis
"Mind over matter"

Visual Capture
The tendency for vision to dominate the other senses
Papillae
Tiny bumps on the surface of the tongue covered in taste buds

5 Taste Sensations
Sweet, salty, bitter, sour, umami
Olfactory Bulb
Brain structure responsible for our sense of smell
Processes info about odors after receiving sensory input form the nose

Kinesthetic Sense
The system for sensing the position and movement of individual body parts
Vestibular Sense
The sense of body movement and position, including the sense of balance
Selective Attention
The focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus
Cocktail Party Effect
Being able to focus one's attention on a particular stimulus while filtering out a range of other stimuli
Inattentional Blindness
Failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere
Change Blindness
Failing to notice change in the environment
Visual Cliff Experiment
Tested depth perception in infants
Human Factors Psychology
A branch of psychology the explore how people and machines interact and how machines and physical environments can be made safe and easy to use
Parapsychology
The study of paranormal phenomena
Including ESP and Psychokinesis
Decibels
Unit of measurement for sound
(dB)
Transduction in the Ear