NCLEX: Mark Klimek - Lecture 12 (Prioritization, Delegation, Staff Management, Organ and Pulse Locations, & Guessing Strategies)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
If the question states that there was a disaster in town and you are making room for the wounded, who would you discharge - highest or lowest priority?
The lowest priority patient
If the question states that you receive handoff end-of-shift reports on 4 pts. Which pt will you check first - highest or lowest priority?
The highest priority patient
What are 2 irrelevant information in a prioritization question?
Age and gender (except in pediatrics)
Which information in a prioritization question is important? Most important?
Diagnosis and modifying phrase (most important!!!)
Two patients: one has angina pectoris and the other myocardial infarction. Who has the higher priority patient?
MI
Which patient is the higher priority?
a. Pt with unstable BP and Angina
b. Pt with stable vital signs and MI
a. Pt with unstable BP and Angina
What are the 4 rules for prioritization?
1) Acute beats chronic
2) Fresh post-op (12 hours) beats medical or other surgical
3) Unstable beats stable
4) Tie-breaker rule: Brain, Lung, Heart, Liver, Kidneys, Pancreas
Among the following patients: a pt 2-hour post-cholecystectomy, a pt with COPD, and a pt with acute appendicitis... which pt has the highest priority?
Pt 2 hours post-op
What words make a patient stable? (8)
- Stable
- Chronic illness
- Post-op greater than 12 hrs
- Local or regional anesthesia
- Lab abnormalities in A or B level (Creatinine, BUN, Hemoglobin 8 to 11, Bicarb, elevated Hematocrit, elevated BNP, elevated Na level, RBCs off)
- Ready for discharge, to be discharged, admitted longer than 24 hrs
- Unchanged assessment
- Experiencing the typical expected s/s of the diagnosed diseased
What word descriptions make a patient unstable? (8)
- Unstable
- Acute illness
- Post-op less than 12 hours
- General anesthesia in the first 12 hrs
- Lab abnormalities in C or D level (INR in the 4s, K in the 6s, pH in 6s, CO2 in the 50s, low O2 sat, high WBC, low ANC, low CD4, low Platelets)
- Newly diagnosed, newly admitted, not ready for discharge, admitted less than 24 hrs
- Changing/changed assessment
- Experiencing unexpected s/s
Which of the following pt is the highest priority?
a) A 16-year-old female with meningococcal meningitis who has had a temp of 103.8 ºF since she was admitted 3 days ago
b) 67-year-old male with IBS (irritable bowel syndrome) who spiked a temp of 103.4 ºF this afternoon
b) 67-year-old male with IBS (irritable bowel syndrome) who spiked a temp of 103.4ºF this afternoon
What are the four things that ALWAYS make you unstable, even if they are expected?
- Hemorrhage
- High fevers of >105 - can lead to seizures
- Hypoglycemia - can lead to brain damage
- Pulseless/breathless - asystole, V-fib
** In the case of an UNWITNESSED accident, pulseless and breathless patients are low priority, because they are likely dead.
What are the 3 things that result in a BLACK TAG in a mass casualty incident?
- Pulseless
- Breathless
- Fixed and dilated pupils (even if breathing)
"Tag them black and ship them last."
What is the tie-breaker rule?
The more vital the organ, the higher the priority.
(Brain, Lungs, Heart, Lungs, Kidneys, Pancreas)
What responsibilities can't a LPN do?
Start an IV
Hang or mix IV
Push IV meds (can maintain and document flow)
Administer blood or mess with central lines
Plan care (they can implement)
Perform or develop teaching (can reinforce)
Take care of unstable pts
Do first of anything ! (can't do admission, discharge, transfer or first assessment after change)
What responsibilities can't a UAP do?
Charting
Meds (Except topical OTC barrier creams)
Assessment (except vitals and accuchecks)
Treatments (except enemas)
CAN to ADLS but never the first
Remember doing vs evaluating
I think I heard new crackles on that guy in Room 52. Who should go assess this pt? The RN or the LPN?
The RN.
Who should the RN check? And who should the LPN check?
a. Angina with crushing substernal chest pain, 3 days ago, on nitro
b. Subtotal thyroidectomy done 2 days ago and now states "why are they watching elephants?"
RN should check (b). LPN can check (a).
How do you intervene with inappropriate behavior from staff?
a) Tell supervisor
b) Confront them and take over the staff's task ASAP
c) Talk to them later
d) Ignore it
NEVER IGNORE.
- If staff is doing something ILLEGAL, tell supervisor.
- If it's not illegal but is harmful, confront it.
- If it's not illegal or harmful, talk to them later.
** If an illegal act is also harmful to the patient, take over first... then tell the supervisor.
You suspect the RN is diverting narcotics. What do you do?
ILLEGAL. Tell supervisor.
The Aide is giving perineal care to pt, not wearing gloves. What do you do?
HARMFUL. Confront and maybe take over.
The RN is going home with bulging pockets. What do you do?
ILLEGAL. Tell supervisor.
You notice surgeon contaminates her gloves. What do you do?
HARMFUL. Confront and maybe take over.
The RN always gives report, always says exasperation instead of exacerbation. What do you do?
Not illegal or harmful. Talk to them later.
If you find 2 pts involving in sexual intercourse, what is best thing to do?
Close the door..... and give them privacy.
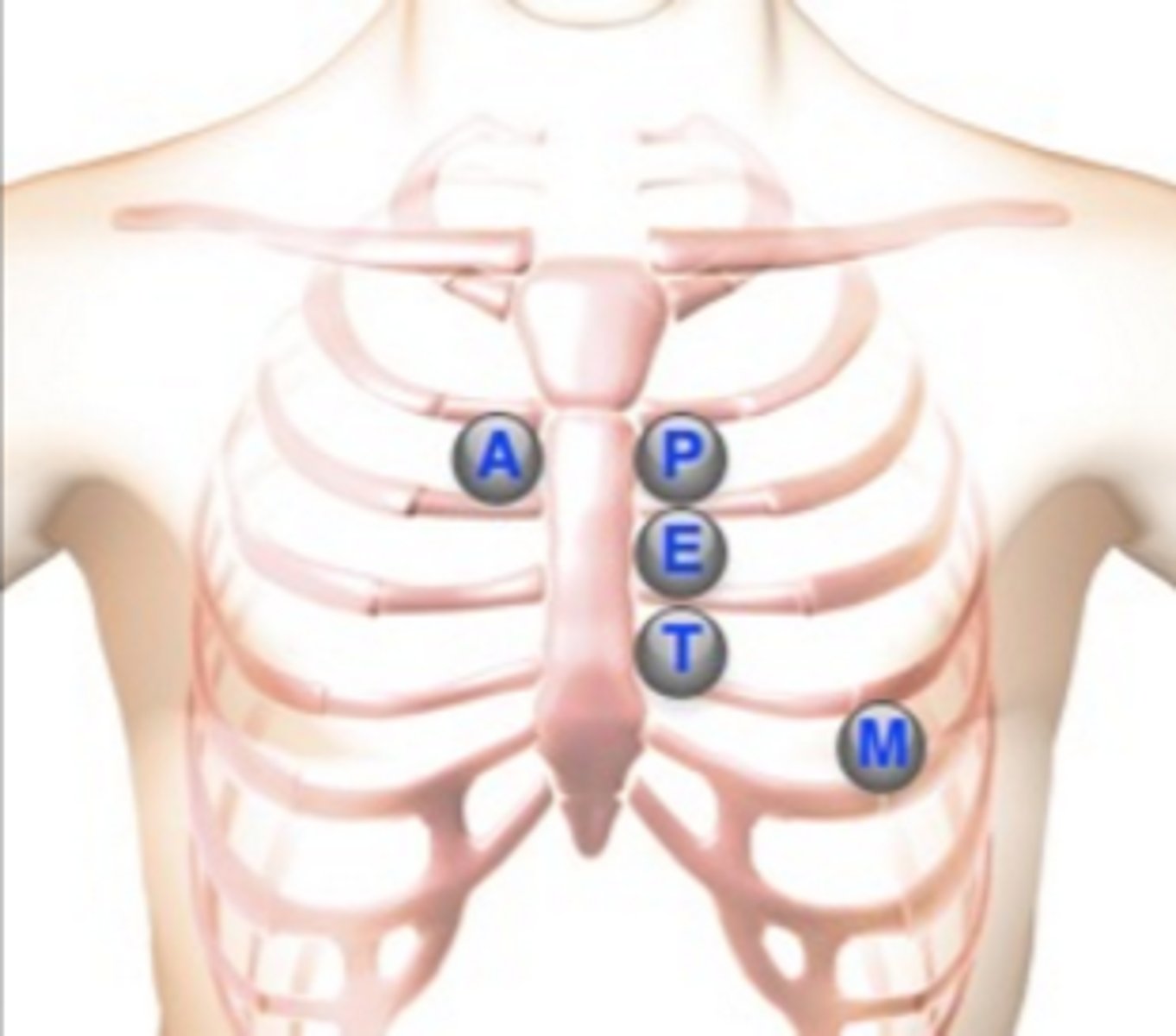
Where is the aortic valve?
2nd intercostal space, right sternal border
Where is the pulmonic valve?
2nd intercostal space, left sternal border
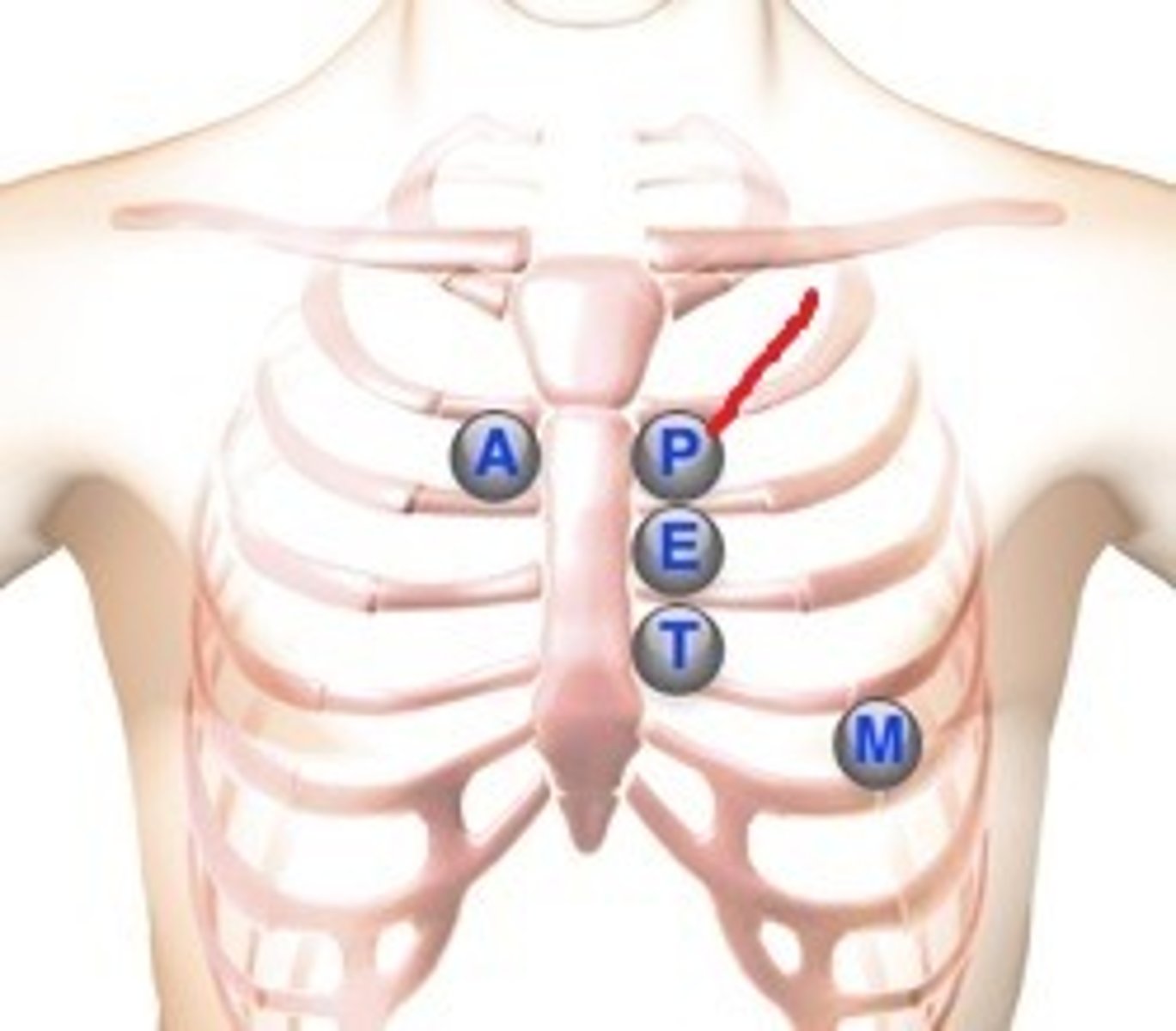
Where is Erb's point?
3rd intercostal space, left sternal border
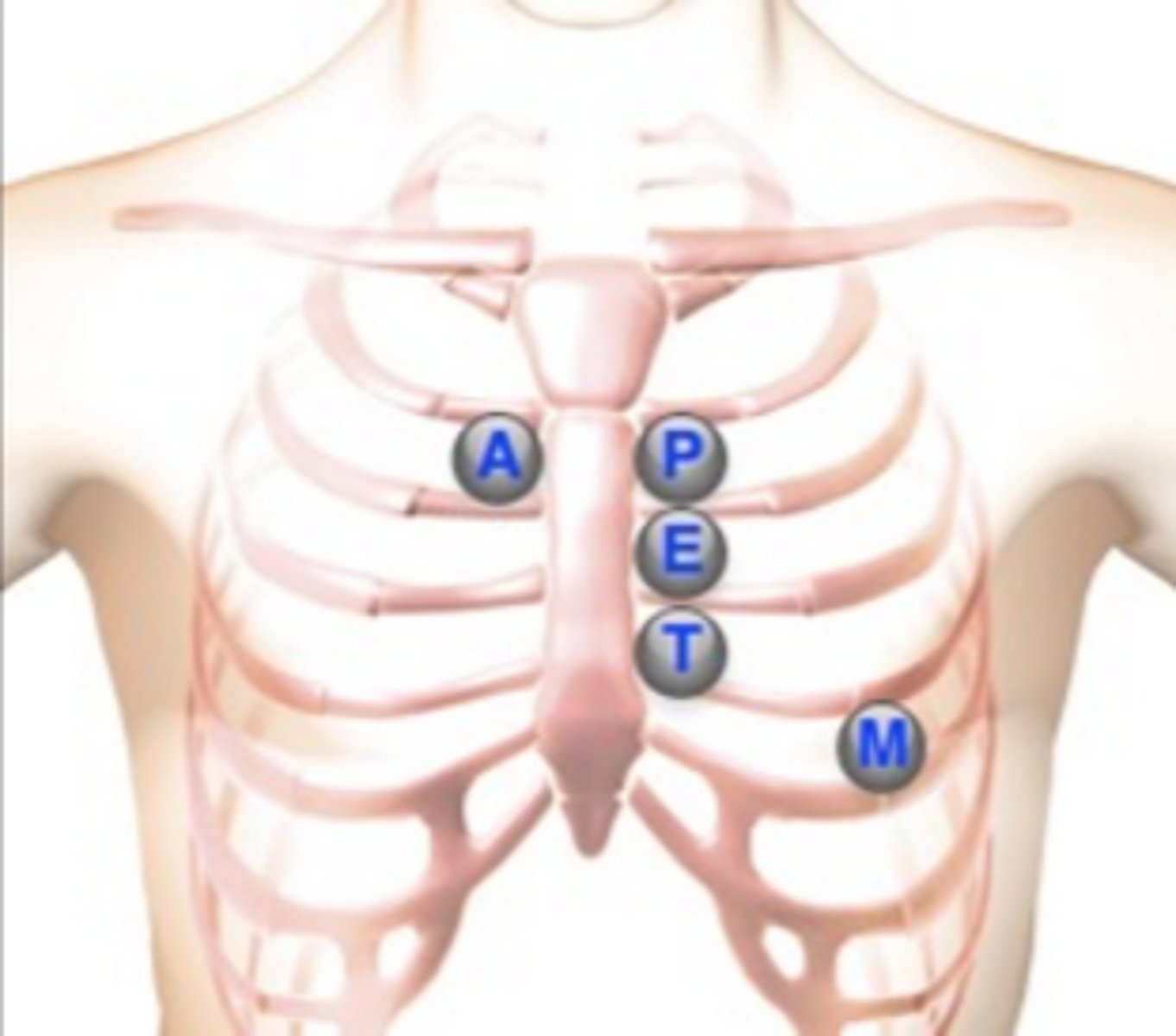
Where is the tricuspid valve?
4th intercostal space, left sternal border
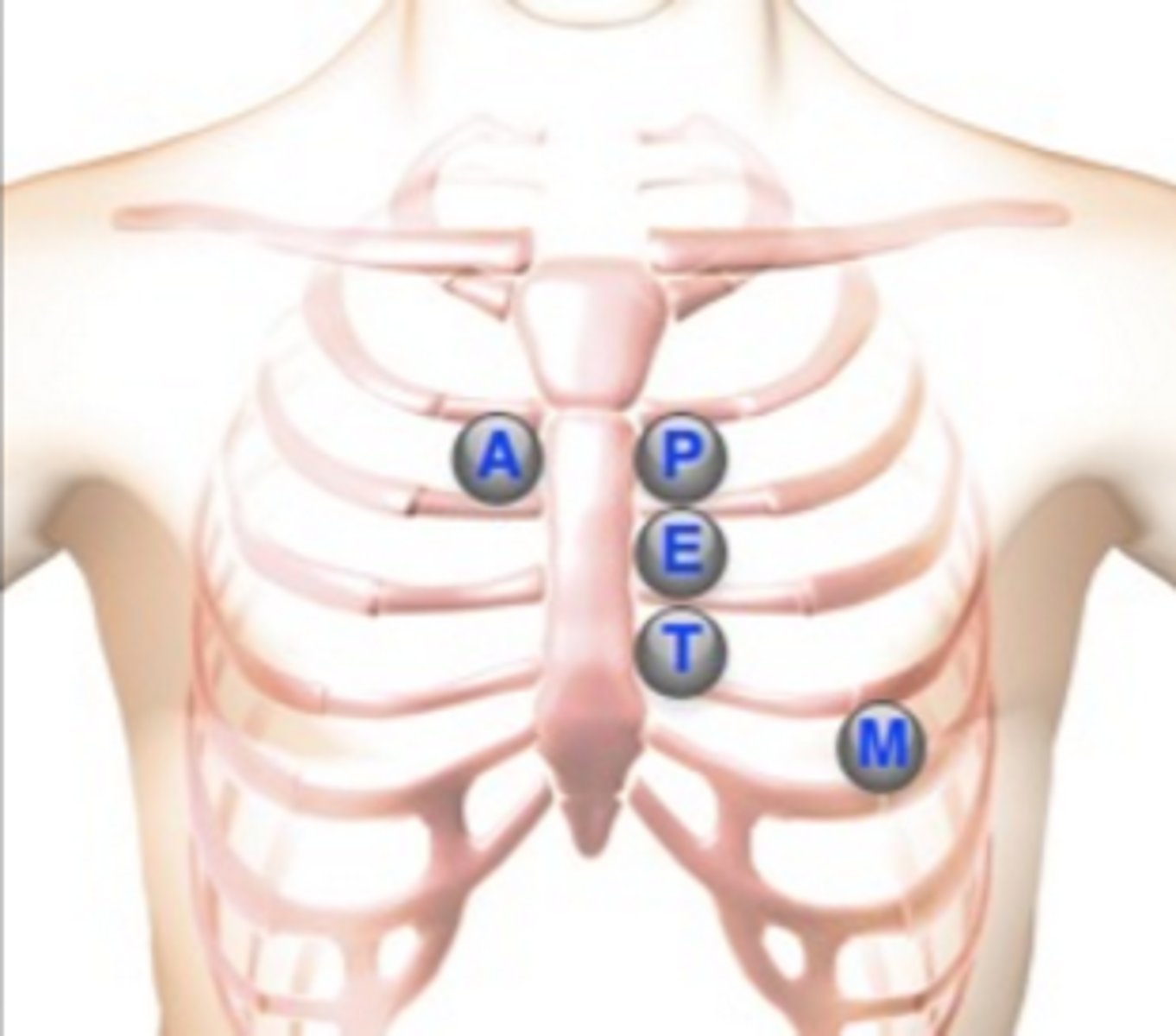
Where is the mitral valve?
5th intercostal space, left midclavicular line (apical pulse)
What is countertransference?
Refers to the nurse's behavioral and emotional response to the client
For a toddler, pick ______ food.
finger food
For a preschooler, ____ meal a day is ok!!!
ONE meal (they aren't growing as fast)
In med/surg, what is the FIRST thing to assess?
LOC. Then ABC.
In med/surg, what is the FIRST thing to DO?
Establish an airway
For growth and development in pediatrics, what are the three rules that can help you narrow down your answers?
- When in doubt, call it normal. Some six year olds can read. Some can't. "Give the child more time..."
- When in doubt, pick the "older age" in the 2 that it could be. What age can a child walk, 12month or 14? Choose 14.
- When in doubt, pick the "easier task." At 6 months, a baby can roll over or sit with support? Pick "roll over."
NORMAL, OLDER, EASIER!!