Enzymes, Nonenzymatic Protein Function, and Protein Analysis
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MCAT Prep: Biochemistry Part 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
enzymes
catalyst; lower the activation energy necessary for reactions. They do not alter the free energy (ΔG) or enthalpy (ΔH) change that accompanies the reaction nor the final equilibrium position
rate (kinetics)
Enzymes change the __________ at which equilibrium is reached.
Ligases
are responsible for joining two large biomolecules, often of the same type
Isomerases
catalyze the interconversion of isomers, including both constitutional and stereoisomers
Lyases
catalyze cleavage without the addition of water and without the transfer of electrons. The reverse reaction (synthesis) is usually more biologically important
Hydrolases
catalyzes cleavage with the addition of water
Oxidoreductases
catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions that involve the transfer of electrons
Transferases
move a functional group from one molecule to another molecule
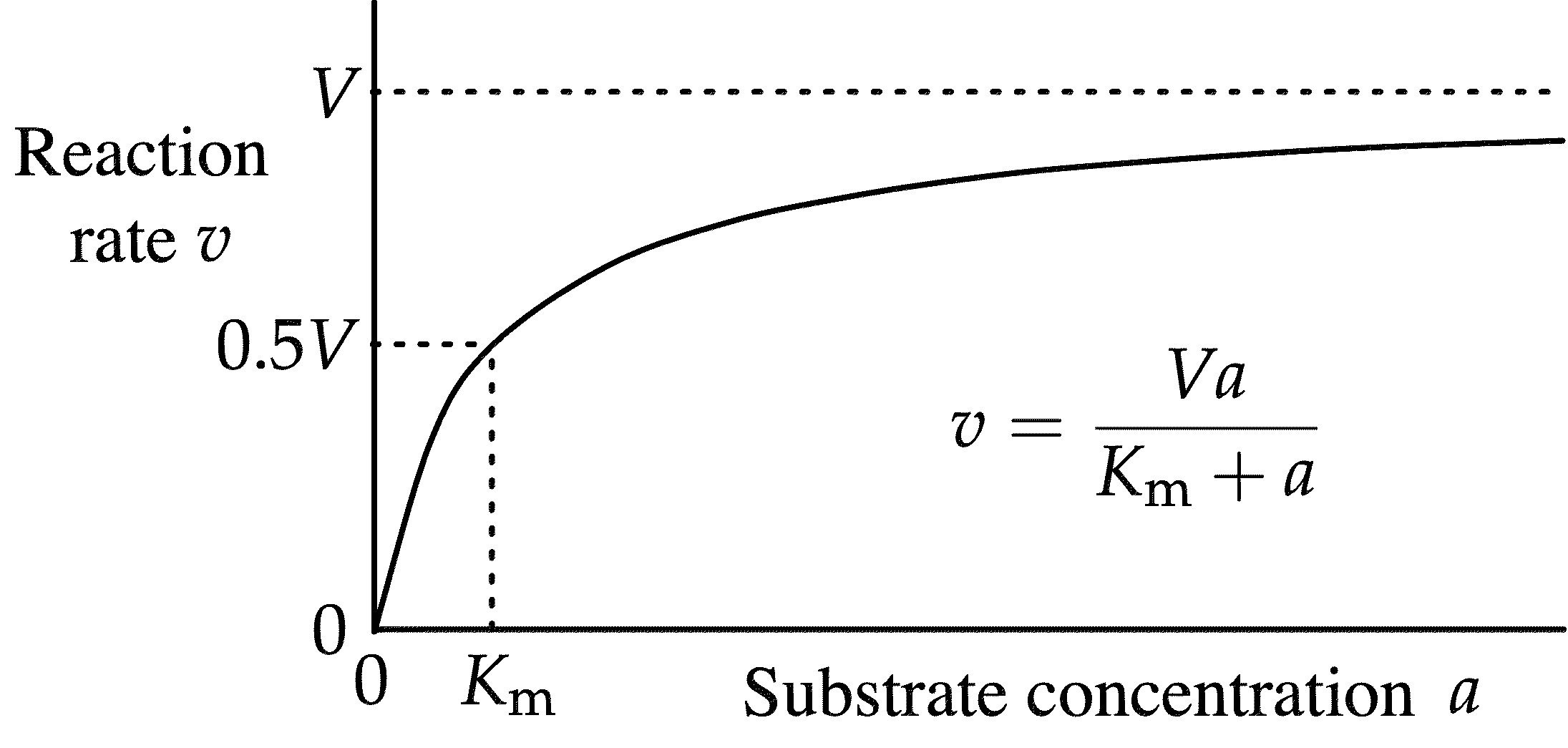
saturation kinetics
as substrate concentration increases, the reaction rate also increases until a maximum value is reached
v = (vmax [S])/(Km + [S])
Michaelis-Menten equation
[S] = Km
At one-half vmax
Michaelis-Menten
sigmoidal
Cooperative enzymes show a ________ curve.
Lineweaver-Burk
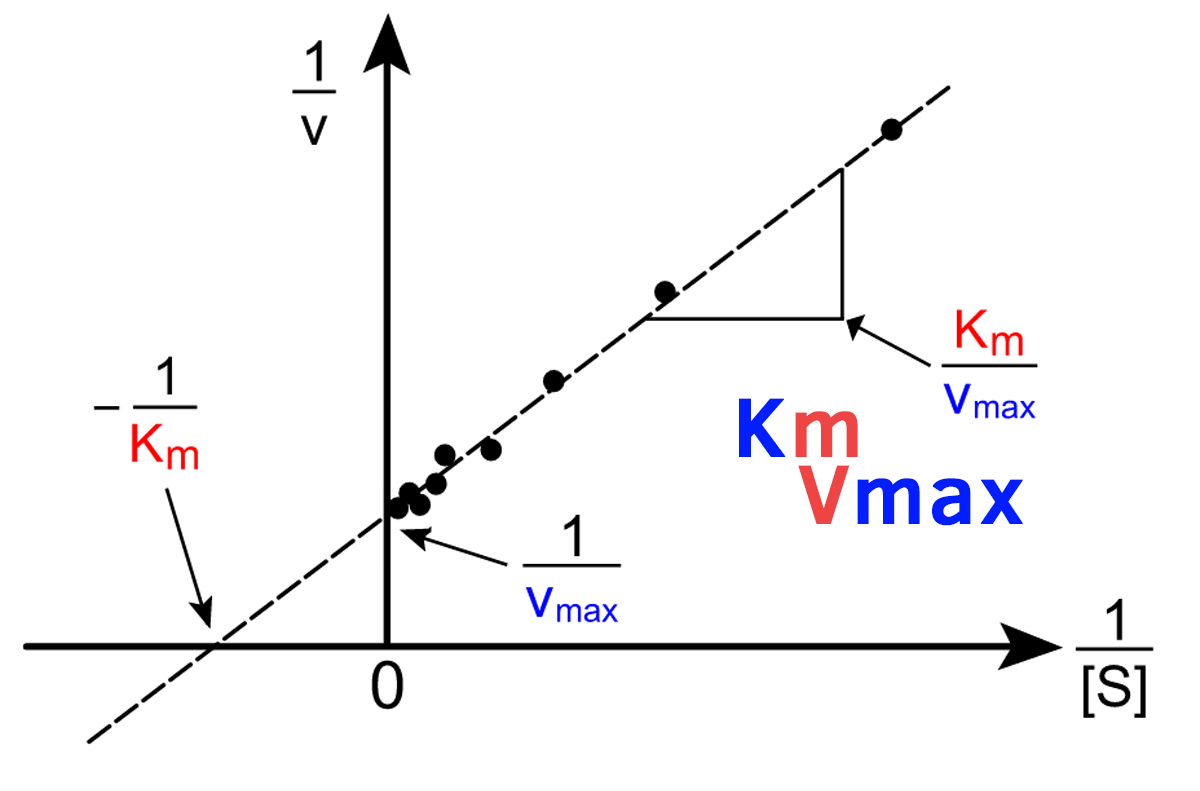
kcat = (vmax)/([enzyme])
equation for the turnover number for an enzyme
(kcat)/(Km)
catalytic efficiency equation
Competitive
Binding site: active site
Impact on Km: increases
Impact on vmax: no change
Noncompetitive
Binding site: allosteric site
Impact on Km: no change
Impact on vmax: decreases
Mixed
Binding site: allosteric site
Impact on Km: increases or decreases
Impact on vmax: decreases
Uncompetitive
Binding site: enzyme-substrate complex
Impact on Km: decreases
Impact on vmax: decreases
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE)
proteins migrate through porous matrix according to size and charge
Native PAGE
is used to analyze the protein in folded state
SDS-PAGE
uses detergent to break all noncovalent interactions and analyzes the unfolded state
Reducing
_________ reagents can be used to break covalent disulfide bonds.
Structural proteins
generally fibrous. Include collage, elastin, keratin, actin, and tubulin
Motor proteins
capable of force generation through a conformational change. Include myosin, kinesin, and dynein
Cell adhesion molecules (CAM)
bind cells to other cells or surfaces. Include cadherins, integrins, and selectins
Ion channels
can be used for regulating ion flow into or out of a cell. There are three main types: ungated channels, voltage-gated channels, and ligand-gated channels
Enzyme-linked receptors
participate in cell signaling through extracellular ligand binding and initiation of second messenger cascades
G protein-coupled receptors
have a membrane-bound protein associated with a trimeric G protein. They also initiate second messenger systems