Chapter 11 – Acid–Base Reactions
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Brønsted–Lowry acid definition?
Proton (H⁺) donor.
Brønsted–Lowry base definition?
Proton (H⁺) acceptor.
General properties of acids?
Sour, pH <7, corrosive, conduct in solution, react with bases.
General properties of bases?
Bitter, pH >7, caustic (can burn or corrode), slippery, conduct in solution.
What’s an alkali?
Soluble base.
Examples of common acids?
HCl, H₂SO₄, HNO₃, CH₃COOH.
Examples of common bases?
NaOH, Ca(OH)₂, NH₃, Na₂CO₃.
What’s an amphiprotic species?
Can act as both acid and base.
Strong vs weak acids/bases?
Strong = fully ionise, weak = partially ionise.
Concentrated vs dilute acids/bases?
Based on amount of solute (acid/base molecules) in solution, not strength.
concentrated if a lot of acid/base molecules
dilute if there is little acid/base molecules
Neutralisation reaction definition?
Acid + base → salt + water.
Antacid purpose?
Neutralise stomach acid.
pH scale meaning?
Ranks acidity/basicity; low pH = acidic, high pH = basic.
pH calculation for strong acids/bases?
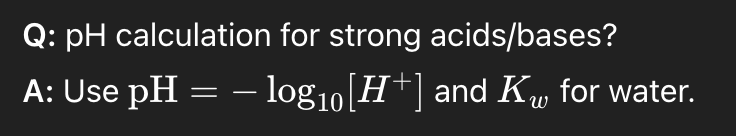
Common natural indicators?
Litmus, red cabbage.
Common commercial indicators?
Phenolphthalein, methyl orange, bromothymol blue, universal indicator.