The Multi-Store Model of Memory
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Multi-Store Model
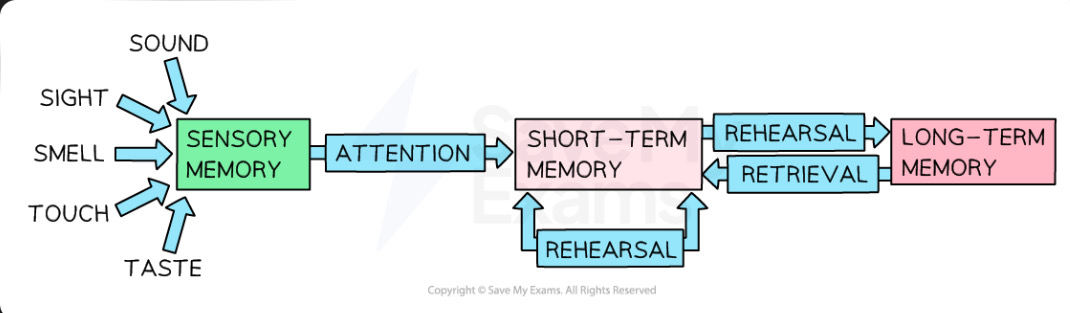
What is the multi-store model of memory?
MSM was proposed by Atkinson and Shriffin in 1968
Capacity
A measure of how much information can be held in the memory. Represented in terms of bits of information, such as the digits of numbers
Duration
A measure of how long information can be stored for, before it isn’t available
Coding
The way information is changed for it to be stored in your memory. Information enters the brain via sense. Stored in various forms, acoustic codes or semantic codes
Sensory register
Where all sensory information from the environment is held. There are stores within the brain for each sense
Sensory register - coding
Depends on the sense involved, modality specific
Sensory register - capacity
Very high, constantly receiving information
Sensory register - duration
Only holds sensory information for milliseconds. The brain can’t retain all of the data that is received
Attention
Connects the SR to the STM and if attention is paid to the information, it is passed to the STM
Short term memory
Information held in the STM is used for present and immediate tasks
Short term memory - coding
Normally acoustic (sound)
Short term memory - capacity
Limited, only a certain number of items can be remembered
Short term memory - duration
Limited, around 18 secs unless rehearsed. Temporary memory store
Rehearsal
Information to be passed from the STM to LTM
Maintenance rehearsal
A surface-level repetition of the information
Elaborative rehearsal
Involves deeper processing
Long term memory
A permanent memory store. To recall information passed into LTM it must be accessed and transferred to STM - retrieval
Long term memory - coding
Coded semantically
Long term memory - capacity
Unlimited
Long term memory - duration
Thought to be for the lifetime of each individual and items in LTM may be prone to forgetting