21 Immune system Biology DAT
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
What kind of tissue is blood?
connective
When blood is centrifuged, what make up the resulting layers?
- plasma
- buffy coat (WBC's)
- RBC's
The percentage of blood by volume of RBC's is referred to as what measure?
hematocrit level
(Note: higher in men than in women)
Plasma contains the liquid portion of blood, which is also called what?
matrix
What constituent elements make up the matrix?
water, ions, urea, ammonia, and proteins
What are the important plasma proteins?
- albumins
- immunoglobulins
- clotting factors
The plasma minus fibrinogen results in what substance?
serum
Where are the most plasma proteins located?
liver
Where is gamma globulin (used to make antibodies) formed?
lymph tissue
Plasma proteins act as a source of which building blocks for tissue protein replacement?
amino acids
All blood cells arise from stem cell precursors located where?
bone marrow
The first line of defense in human immunity is called what?
innate immunity
(Note: non-specific response)
What are the five general components of innate immunity?
- skin (physical/acidic environment)
- antimicrobial proteins (ex: lysozyme)
- cilia (in lungs)
- gastric juice (acidic environment)
- symbiotic bacteria (digestive/vaginal)
All WBC's originate from stem cells located in what?
bone marrow
(Note: but some multiply and become non-naive in the lymph node
What happens when a WBC recognizes a pathogen?
naive —> activated
What are the relative amounts of leukocytes in the blood to platelets and erythrocytes?
erythrocytes > platelets > leukocytes
What describes the second line of defense?
nonspecific and is also innate
Which type of WBC's engulfs foreign particles, bacteria, dead or dying cells via phagocytosis?
phagocytes
(Note: macrophages are
the largest phagocytes)
Which type of WBC's function in the destruction of pathogens in infected tissues drawn to the infected area by chemicals via chemotaxis?
Neutrophils
(Note: a type
of phagocyte)
By what process do neutrophils enter tissues?
diapedesis
(Note: slip between
endothelial cells of
capillary)
Which type of WBC's circulate in blood until they move into tissues via diapedesis where they develop into macrophages that phagocytize cell debris and pathogens, which are professional antigen-presenting cells?
Monocytes
Besides macrophages, what can monocytes also give rise to?
dendritic cells.
Which type of WBC's work collectively to surround and destroy multicellular parasites?
eosinophils (NOT a type of phagocyte)
Which type of WBC's are responsible for the ingestion of pathogens and stimulate acquired immunity?
dendritic cells (Phagocyte)
What is the main type of dendritic cell?
antigen presenting cell = activates T-lymphocytes
Which type of WBC's function in allergic response, inflammatory response (histamine release), and anaphylaxis?
mast cells (phagocyte located in tissues)
Which type of WBC's release histamines for inflammatory response, found circulating the blood, and are recruited into tissue when needed?
basophils
(Note: contain histamine and heparin
(which works as an anticoagulant)
and several cytokines)
Which type of WBC's attach to abnormal body cells such as tumors or pathogen-infected tissues?
natural killer (NK) cells
Of what substances does pus consist?
dead leukocytes + necrotic tissue
What system contains ~30 complement proteins that circulate the body and assist in activating the immune response?
complement system
(Note: The activation
of the complement
system results in a
cascade that attracts
phagocytes to foreign
cells and helps destroy
them by promoting cell
lysis)
What substances are secreted by cells invaded by viruses/pathogens that stimulate neighboring cells to produce proteins to defend against the virus?
interferons
What response is a series of non-specific events that occur in retaliation to injury or pathogens?
inflammatory response
In the inflammatory response, what substance is secreted by mast cells, which are white blood cells in connective tissue, and cause vasodilation?
histamine
In the inflammatory response, what action is stimulated by histamine and increases blood supply to the area, which causes a subsequent increase in temperature that stimulates WBCs that can kill pathogens
vasodilation
In the inflammatory response, what cells are attracted to injury by chemical gradients of the complement system, and engulf pathogens and damaged cells?
phagocytes
In the inflammatory response, what system helps phagocytes engulf foreign cells, stimulate basophils to release histamine, and lyse foreign cells?
complement system
prostaglandins and lymphokines can be causative agents of what response?
inflammatory response
What is the specific third line of dense that develops after the body has been attacked?
adaptive immunity
(Note: Here, the immune response targets specific antigens, rather than doing a broad sweep like in the complement system or inflammatory response)
Which component of the adaptive immunity response constitutes the mechanism by which the immune system is able to differentiate between self and non-self
major histocompatability complex (MHC)
What response does a foreign MHC trigger?
T-cell attack
What kinds of molecules make us MHC's?
glycoproteins
(Note: exist on the membrane of cells)
MCH presents what agents?
antigens
What is the main part of the daptive immunity that carries out the immune response
lymphocyte
Where do lymphocytes originate?
bone marrow (as leukocytes)
Where do lymphocytes concentrate?
lymphatic tissue such as lymph notes, thymus gland, and spleen
Which component of the adaptive immunity response produce antibodies?
B cells
Where do B cells originate and mature?
bone marrow
How are B cells activated?
response to antigens
Which component of the B cells contain antigen-receptor antibodies?
plasma membrane
What are proteins that are specific to each antigen?
antibodies
(Note: Y-shaped proteins
with constant and variable
regions, and disulfide
bonds connect heavy chains to
each other, and to light
chains.)
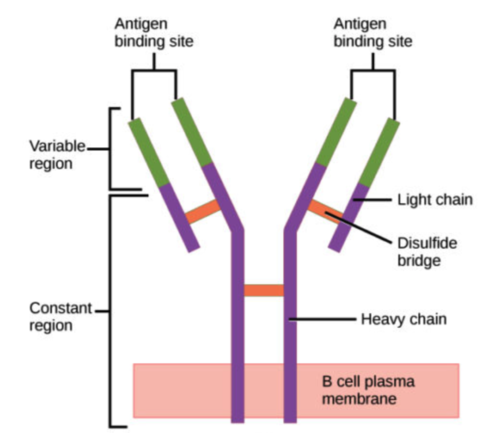
What are the 5 classes of antibodies?
IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, IgD
Which antibody class is most abundanto in serum and extravascular spaces. Can cross placenta and are most important in protecting the fetus?
IgG\
“Gross”
Which antibody class is found in breast milk and other bodily secretions (most abundant Ig in secretions)?
IgA
googoo gAgA
Which antibody class is the first antibodies produced after initial exposure to antigen?
IgM
“Mono”
Which antibody class is related to allergies?
IgE
snEeZe
Which antibody class is produced in low amounts, and the function is not well known?
IgD
“Diminished”
In fetuses, in what organ do B cells mature?
liver
When an antigen binds to a B cell, what term describes the expansion of the B cell population-forming daughter B cells?
proliferation
What is the name for B cells that circulate in blood and release specific free antibodies that dispose of antigens?
plasma cells
How can the free antibodies produced by plasma cells dispose of antigens?
- preventing virus from binding to host cell
- opsonization
- pore formation
- agglutination
- chemical inactivation
- release histamine after attaching to mast cells
What is the process of marking the antigen for phagocytosis via macrophage, neutrophil, or natural killer cell called?
opsonization
What action produces a pore in a membrane?
lysis by complement proteins
What is agglutination?
clumping of particles
What are long lived B cells that do not release antibodies in response to immediate antigen invasion?
memory cells
(Note: circulate the
body, proliferate,
and respond quickly
(via antibody synthesis)
to eliminate subsequent
invasion by the same antigen)
Why does the body's secondary response take less time (~5 days) compared to the initial infection?
memory cells
Where do T cells originate and mature?
originate: bone marrow
mature: thymus
Which component of the adaptive immunity response have antigen receptors yet do not make antibodies?
T cells
What is the process called when T cells check molecules displayed by non - self cells, and if a T cell binds to a self antigen in the thymus, it is destroyed?
Negative selection
What occurs if T cells do not bind to self antigens in the thymus?
they are released to circulate in lymphoid tissue, blood, or lymph
What are the ways T cells can distinguish between self and non-self
1. MHC markers on plasma membrane of cells
2. non-self pathogen presents self + non-self pathogens, which is interpreted as non-self (cancer and tissue transplants are often like this)
When a T cell encounters a non-self cell, it divides and produces which four kinds of cells?
1. cytotoxic T cell
2. helper T cell
3. suppressor T cell
4. memory T cell
Which T cell derivatives are killer T cells that recognize and destroy by releasing perforin protein that punctures cells (lysis)?
cytotoxic T cells
(Note: these can attack
many cells because they
do not phagocytize their victims)
Which T cell derivatives stimulate activation of B cells, cytotoxic T cells, and suppressor T cells?
helper T cells
(Note: Are also the target
for the virus that causes AIDs (HIV))
Which T cell derivatives play a negative feedback role in the immune system?
suppressor T cells
Which T cell derivatives are similar in function to Memory B cells?
memory T cells
Which component of the innate immunity response attack virus-infected cells or abnormal body cells (tumors)?
natural killer cells
Which cells are involved in both specific and non-specific branches of immunity and engulf antibody-coated antigens?
Macrophages
What process occurs when an antigen binds to a B cell, or when a non-self cell binds to a T cell, and the B or T cells divide into daughter cells that bear a "selected" effective antigen receptor?
Clonal selection
In clonal selection, which cell reproduces repeatedly to make clones?
cell with the selected copy of the receptor
What are the two Responses of Acquired/Adaptive Immune System?
- cell mediated
- humoral
The cell-mediated response of the acquired immune system uses mostly what kind of cell?
T cells
The cell-mediated response of the acquired immune system is effective against which structures?
Non-self and infected self cells
In the cell mediated response of the acquired immune system, what chain of events follows after the non-self cell binds to a T cell?
1. clonal selection
2. produce cytotoxic T cells/helper T cells
3. helper T cells bind macrophages
4. macrophages engulf pathogens
5. Helper T cells produce interleukins
6. proliferation of T cells, B cells, and macrophages
The humoral response of the acquired immune system is also known as what?
antibody-mediated response
The humoral response of the acquired immune system responds to what stimuli?
antigens or pathogens that circulate in lymph or blood
In the humoral response of the acquired immune system, what events occur?
- macrophage/helper T cells stimulate B cell production
- B cells produce plasma cells
- B cells produce memory cells
What is the general progression of B cells?
naive —> mature —> plasma —> antibody
Antibodies are specific for how many antigens?
one
A single B-lymphocyte produces how many antibody types?
one
How are B and T cells different in how they interact with antigens?
- B cells can directly bind intact antigens at their receptor sites
- T cells must have the antigen presented as fragments from other cells
Which cells (B or T) undergo positive selection, which ensures the cell can recognize self cells to some extent?
T cells
What are chemicals derived from bacteria and fungi that are harmful to other microorganisms?
antibiotics
What agents stimulate production of memory cells from inactivated viruses or weakened bacteria (artificially active immunity)?
vaccines (viruses and bacteria)
Which type of vaccine consists of an inactivated pathogen that has been destroyed?
inactivated vaccine
Which type of vaccine contains live pathogens but are disabled in some way to prevent virulence?
attenuated vaccine
Which type of vaccine can be made from inactivated toxic compounds that cause illness rather than the pathogen itself?
toxoid vaccine
Which type of immunity occurs when antibodies are transferred from another individual (for ex: newborns from mother)?
passive immunity
How fast is passive immunity acquired?
immediately
What substance can confer temporary protection against hepatitis and other diseases?
Gamma globulin (blood containing antibodies)
The primary response requires how much time to reach its full potential?
~20 days