Munson 2
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Drug Product Performance
= function of drug, the formulation, and the body
ability of drug to elicit therapeutic response
ability of drug to stay in a safe therapeutic range during dosing
non-toxic and effective
The Goal of Formulation
transfer new, promising therapeutic compound + develop reproducible dosage form
going from small batches to being created in large batches
release from dosage forms has to balance how the body processes medicine
define reproducible
each dosage form containing same amount of drug
same performance in body
define absorption rate (kabs)
drug properties, excipient/drug composition, physiological barriers between GI tract and systemic circulation
What is the Typical Blood Level vs Time Curve used for?
accessing performance and reproducibility
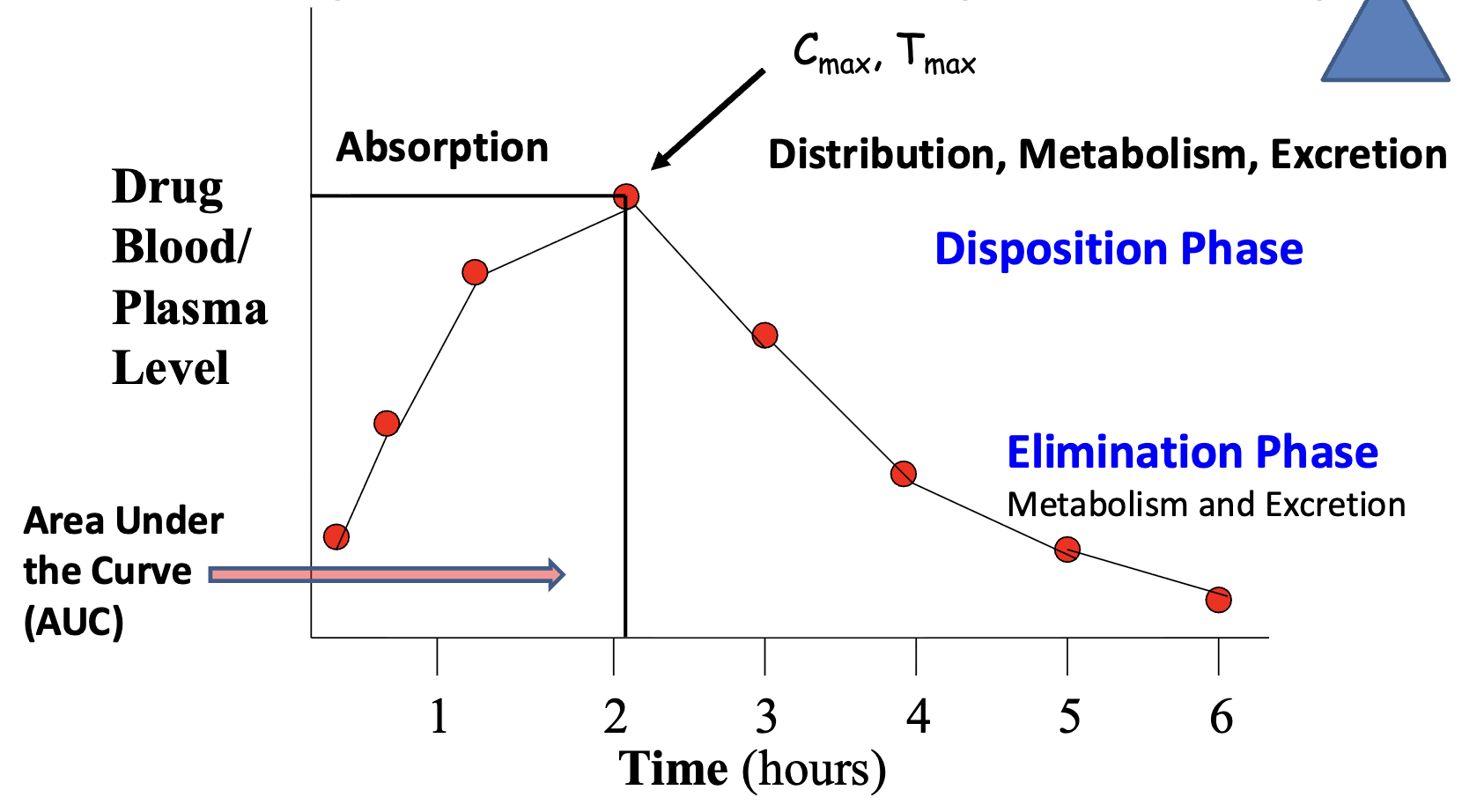
as absorption begins declining, diposition begins to ______
increase
Druggability refers to
discovery stage
assesses the ability to bind to the drug target
vivo models used to assess (tested within animals or humans)
Developability refers to
drug product performance
factors like biorelevant solubility and dissolution
formulation factors related to ADME/T incorporated
define Druggable genome
genes that encode disease-related proteins that can be modulated by drug-like molecules
subset of genomes that express proteins that bind to drug-like molecules
define Druggable protein
proteins that can bind drug-like compounds with binding affinity below 10 mM
druggable genes are identified by _______ methods
pharmacogenetics
Why are new chemical entities generated?
to fit a pharmacophere
What do new chemical entities demonstrate?
assess the ability for each agent to act like a drug aka druggability
candidates that perform best advance
What two indicators are used to test dafe and efficacious use?
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Drug formulation should consider…
physicochemical properties of drug
physicochemical properties and composition of formulation
biological factors that influence performance (ADME and Toxicity)
How are dosage forms able to reach a clinic?
be properly balanced
Physicochemical drug properties that affect absorption
solubility
drug stability in solution
lipophilicity
molecular size and shape
pKa of ionizable groups
physical state of drug (amorphous, crystalline, polymorphism, etc)
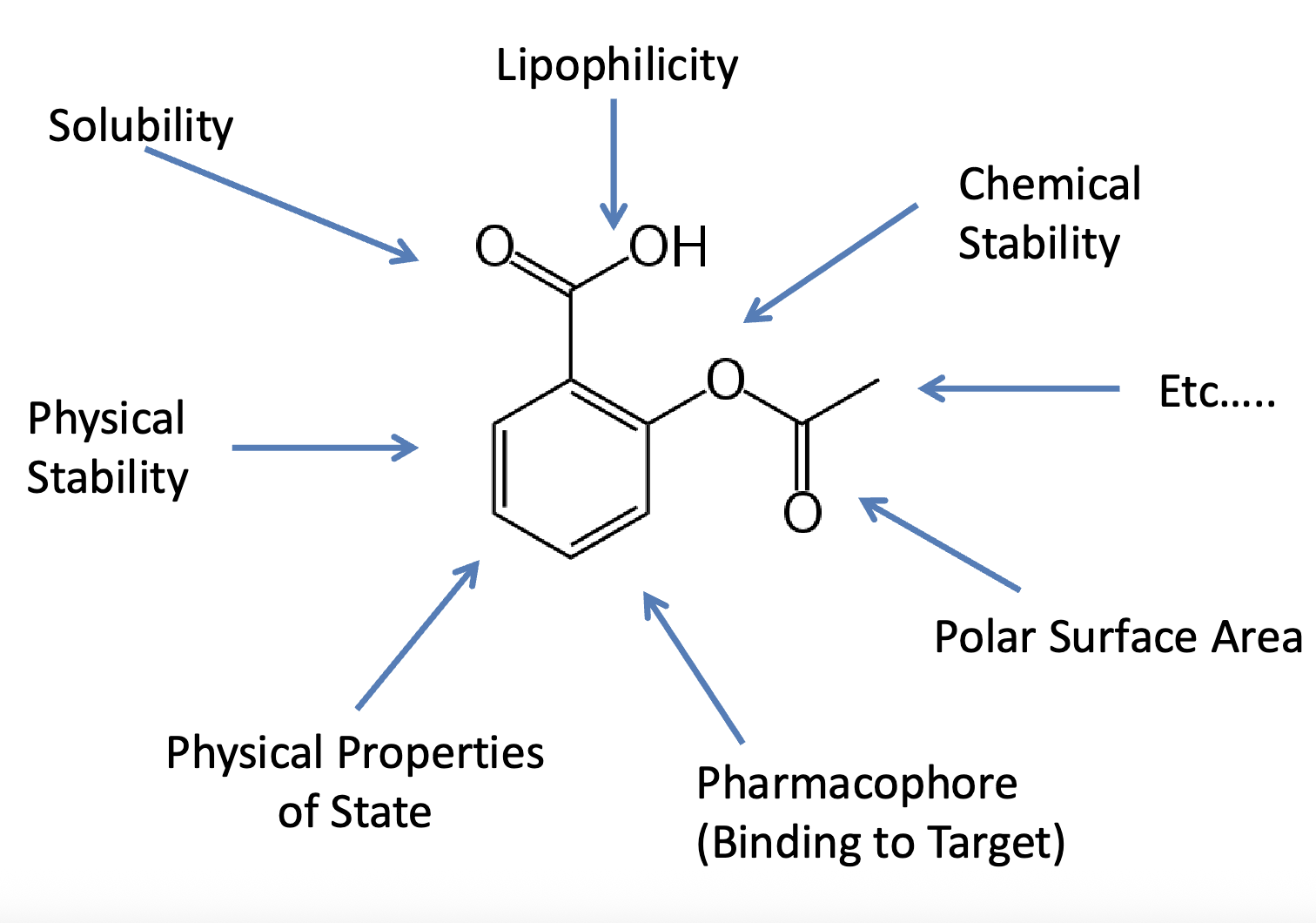
Solubility depends on…
molecular structure
physical state
composition of solvents
measurement methods
Physical state
solid: amorphous, crystalline, polymorphic form
liquid: predissolved in a solvent
Composition of solvent
type of solvent
co-solvent percentages
solution components (salts, ions, lipids)
pH, temperature
Measurement mehtods
equilibrium time
detection method
Partition coefficient
ratio of concentrations in two immiscible solvents (eg: octanol and water)
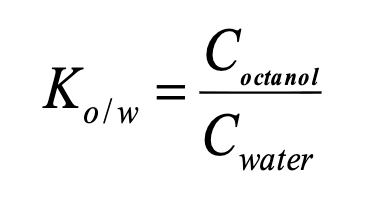
pH-Partition hypothesis
for drugs absorbed by a passive, transcellular mechanism
permeability depends on fraction of unionized drug at intestinal pH
generally, as Ko/w increases, solubility _____
decreases
Different _____ and ______ pHs can affect drug transport
extracellular and intracellular
How do you functionalize the compound?
changing its pKa
What is prodrug strategy
modify the charged moeity
modify the molecule to be recognized by a transporter
What is salt selection?
ion pairing effective in improving permeation
salt form may alter unionized fraction
Define excipients
inert ingredients that are added to therapeutically active compounds to improve appearance, bioavailability, stability, palatability
Cellulose-based excipients
microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), SMCC, HPMC, ethylcellulose
Sugar-based excipients
surcrose, lactose, mannose
Synthetic polymer excipients
polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP), polyethylene oxide (PEO)
How is excipient compatibility tested?
binary or formulation blends
binary or formulation blends with 10-20% w/w water
suspension/solution of excipients and drug
mechanical stress (milling drug)
Solid Dosage Form Requirements
content uniformity (every tab has approx. 85-115% API)
stable shelf life of 2 years
cannot break into smaller pieces