L2 - Non covalent interactions
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
How strong are covalent bonds?
Strong
200 - 800 kJ/mol
What is a covalent bond?
Shared pair of electrons in the valence shell
How strong are non covalent bonds?
Weaker
Under 30 kJ/mol
What are non covalent bonds?
Based on unequal sharing of electrons between nuclei (polarised bonds and polar molecules)
Interaction between biomolecules and domains of biomolecules
What are intermolecular bonds?
Between biomolecules
What are intramolecular bonds?
Interactions between domains of biomolecules
What do noncovalent bonds determine?
Solubility in water
What is bond polarity to do with?
Different electronegativities of the elements
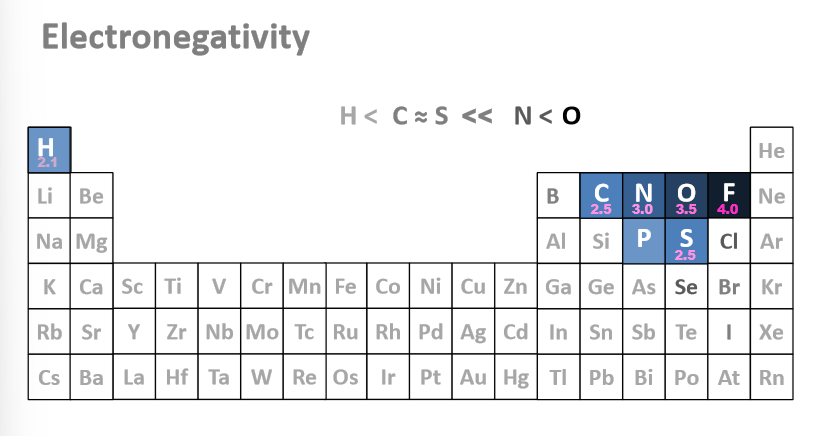
Put the most common elements in order of electronegativity
Flourine
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Sulfur and carbon
Hydrogen
What is an example of a non-polar covalent bond?
C - H
What is an example of a moderately polar bond?
S - H
What are some examples of polar bonds?

What do polar bonds have?
Partial ionic character
The electrons tend to be more on the side of the atom with a higher electronegativity
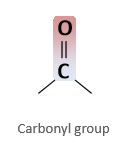
How are carbonyl groups polar?
How are amino groups polar?

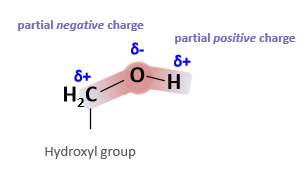
How are hydroxyl groups polar?
What does the uneven distribution of charge turn the molecule into?
An electrical dipole
What makes a molecule a dipole?
If it has a net dipole movement which depends on the geometry of the molecule
Why do polar molecules have a high BP than apolar?
Partial positive and negative attract each other so more polar molecules have a higher boiling point than apolar molecules of the same size
What are the different type of noncovalent interactions?
Dipole - dipole interactions and hydrogen bonds
Charge - charge interactions (ion pairs)
Van der Waals forces
Hydrophobic interactions
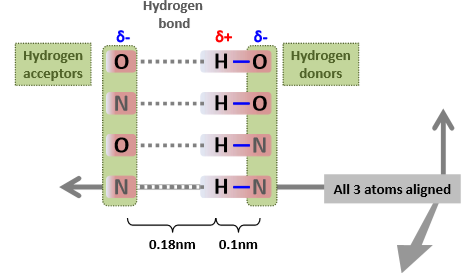
What are the criteria for Hydrogen bonds to form?
If H and H acceptor are 0.18 nm apart
If all 3 atoms are aligned
Strength of the bond will decrease the further away from the ideal
How do hydrogen bonds form between water molecules?
How many other water molecules can 1 water molecule form hydrogen bonds with?
4
2 as donors
2 as acceptors
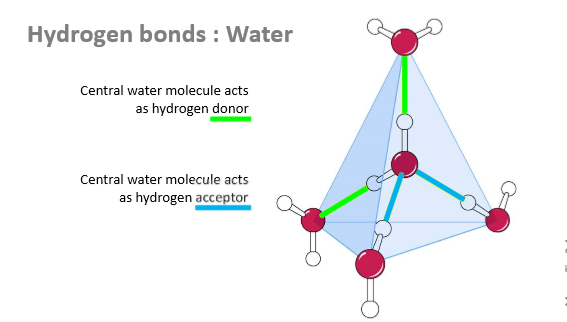
When are all 4 bonds in water realised?
When ice forms
Forming a hexagonal lattice
Why do all 4 bonds not form in water?
In liquid water, the molecules are too restless to align in the right way with 4 other molecules so they move about so hydrogen bonds are formed and broken all the time
How long do hydrogen bonds last in water?
Not longer than 10ps
How much energy is required to break a H bond?
20 kJ/mol
Why does ice have a lower density than water?
The hydrogen bonds wake the molecules space themselves further apart
What are the 2 main types of hydrogen donor in biomolecules?
Amino group
Hydroxyl group
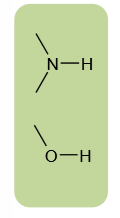
What are the 3 main hydrogen acceptors?
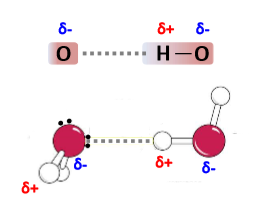
What type of interaction is a hydrogen bond?
Dipole - dipole
(the most common one in biology)
Describe a hydrogen bond
H atom bonded to electronegative atom can hydrogen bond to another electronegative atom with lone pair electrons
How strong are hydrogen bonds?
30 kJ/mol
What are charge - charge interactions also known as?
Electrostatic interactions
What do electrostatic interactions occur between?
Opposite charges
Are electrostatic interactions stronger than H bonds?
Yes
How are electrostatic interactions different to other noncovalent interactions?
Can extend over greater distances than other noncovalent
Doesn’t depend on molecular geometry like H bonds
Potentially strongest non-covalent interaction
What is a salt bridge / ion pair?
Charge- charge interaction between acidic and basic amino acids in proteins
What happens if salt bridges/ ion pairs are on the surface of proteins?
If they are on the surface of proteins the interaction is sometimes weakened by shielding or screening effect by water molecules that arrange themselves around the ionized groups
Ions in solution can also screen charged groups
Why are ion pairs stronger if they are buried in the hydrophobic interior of a protein?
There is no screening so bridge is much stronger than between solvent exposed ion pairs on the surface
More stable
What are Van der Waals forces?
Act between stable dipoles in polar molecules or inducible dipoles
eg permanent dipoles or inducible dipoles
How do VDW forces induce dipoles?
Even completely non-polar bonds (eg C-H) are sometimes temporarily polarised because of random asymmetries in the distribution of electrons around the nuclei in a chemical bon
If there is asymmetry in one place, it has a knock-on polarising effect on its neighbour - flickering back and forth quickly
If 2 carbonyl groups are stacked head to tail in the right orientation and right distance, what will there be?
attractive Van der Waal forces of about 10kJ/mol
Why do results in attractive forces between 2 atoms depend strongly on the distance between them?
When theyre too close, there is a repulsive force because negatively charged electron clouds repel each other - results in the curve
Trough = where Van der Waals attraction is greatest
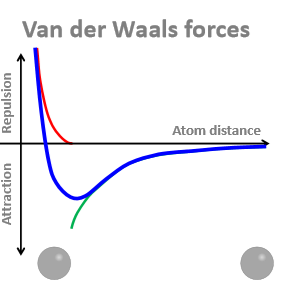
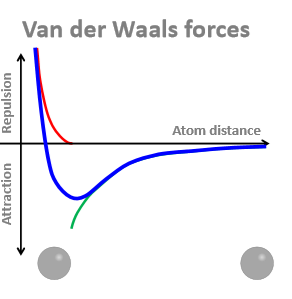
What is the distance between the 2 atoms at the trough?
The sum of their Van der Waal radiis
How big are Van der Waals radiis?
0.12 - 0.19 nm
In large clusters of atoms tightly packed in biomolecules, what stabilises them?
A large number of Van der Waals interations stabilises the molecule
eg In DNA, the stacked base pairs are also held together by VDW forces
Why are VDW forces important?
These interactions add up to a quite significant contributing factor to macromolecular structures
What distances do VDW forces work?
At very short, optimal distance
Are VDW strong?
No much weaker than other dipole interactions but add up
Why can hydrophobic molecules not engage in hydrogen bond with water molecules?
Few or no polar bonds
What do hydrophobic molecules do when they dissolve?
They force the water molecules around them into a specific arrangement so the bulk water is free to form H bonds in all directions
By clustering the hydrophobic molecules, fewer water molecules are forced into a more ordered arrangement
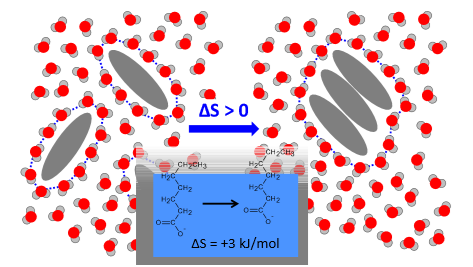
Why is the right more favoured?
Increase in entropy
For every CH2 group of a hydrocarbon that is moved out of the water, __kJ/mol are gained in entropy
3
What is this gain in entropy enough to do?
It is enough to screen the hydrophobic group from interactions with water (huddling together with other hydrophobic molecules)
What are hydrophobic interactions?
Association of non-polar groups with most energy attributed to the exclusion of water
How strong are VDW?
0.4 - 4 kJ/mol
How strong are hydrophobic interactions?
3 - 10 kJ/mol
How strong are H bonds?
2 - 30 kJ/mol
How strong are electrostatic interactions?
40 - 200 kJ/mol