Ren R 210 Module 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Last updated 1:15 AM on 10/26/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
kilo
10^3
2
New cards
centi
10^-2
3
New cards
mili
10^-3
4
New cards
micro
10^-6
5
New cards
porosity
The relative proportion of a volume of soil that is filled by air and water
6
New cards
particle density
density of solid mineral material (constant)
7
New cards
bulk density
weight of soil/volume of soil
8
New cards
Db and porosity of sand
1.55 Mg/m^3 and 42% (least aggregation)
9
New cards
Db and porosity of loam
1.20 Mg/m^3 and 55%
10
New cards
Db and porosity of clay
1.05 Mg/m^3 and 60% (most aggregation)
11
New cards
cohesion vs adhesion
cohesion - water molecules form weak bonds with each other
adhesion - water molecules form weak binds with other surfaces
adhesion - water molecules form weak binds with other surfaces
12
New cards
hydrophillic
water loving (glass/sand)
13
New cards
hydrophobic
water repelling (OM)
14
New cards
water is affected by...
gravity force
matric force (adhesion/cohesion)
somatic force (salt content)
matric force (adhesion/cohesion)
somatic force (salt content)
15
New cards
evapotranspiration
Work required to move water from point a (soil) to point b (atmosphere).
16
New cards
matric potential (Ψm)
adhesion/cohesion (adhesion of water to soil particles -> cohesion)
17
New cards
osmotic potential (Ψo)
salt content (water will move from low salt content to high salt content)
18
New cards
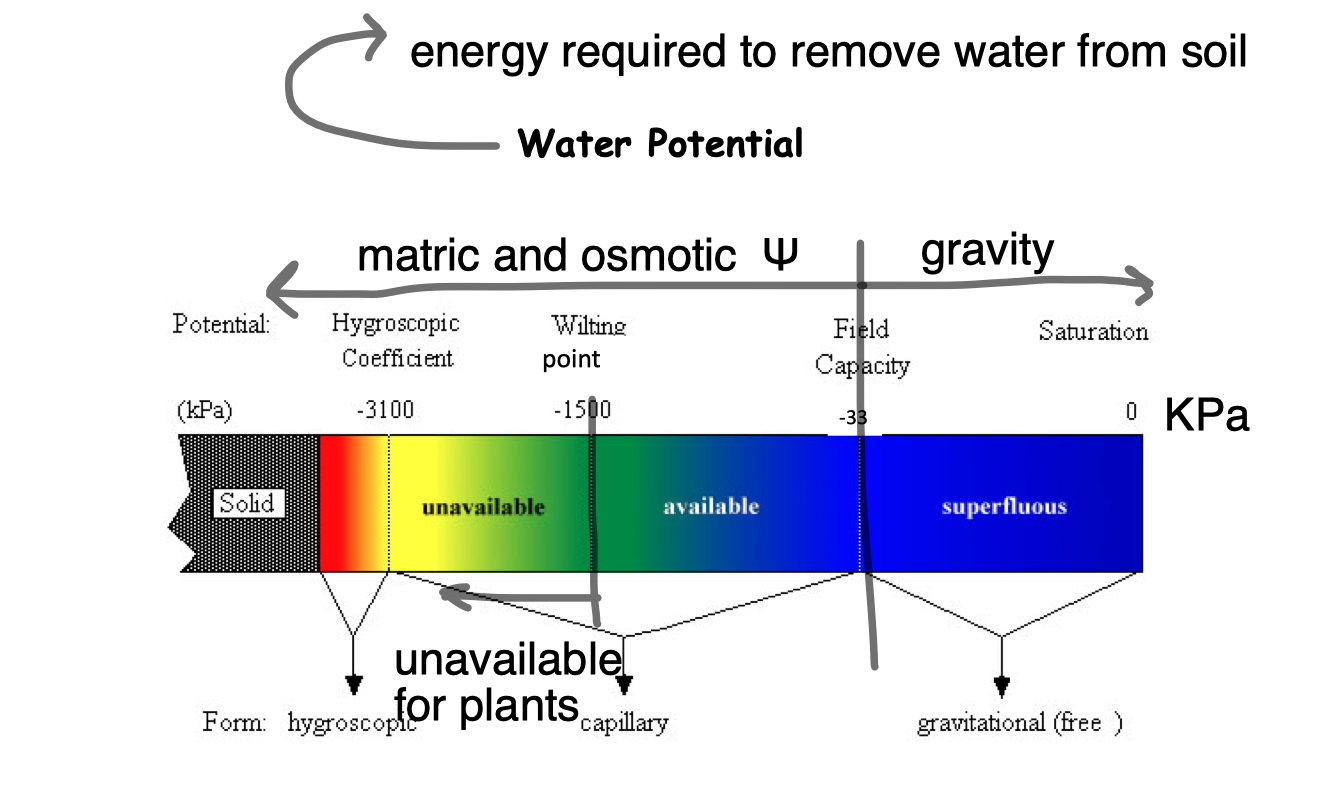
water availability to plants
grav pot (available to plants) 0.0 to -33 kPa
matric pot and osmotic pot (available to plants) -33 to -1500
matric pot and osmotic pot (unavailable to plants) -1500 to -3100
matric pot and osmotic pot (unavailable to everything) -3100 onwards
matric pot and osmotic pot (available to plants) -33 to -1500
matric pot and osmotic pot (unavailable to plants) -1500 to -3100
matric pot and osmotic pot (unavailable to everything) -3100 onwards
19
New cards
soil texture AW in descending order
loam > clay > sand
20
New cards
influence of texture on water infiltration rate (i)
coarse soil -> large particles, large pores, fast infiltration
fine soil -> small particles, small pores, slow infiltration
fine soil -> small particles, small pores, slow infiltration
21
New cards
influence of structure on water infiltration rate (i)
Granular: fast (i), small round peds
Blocky: moderate (i), angular peds
Prism: moderate (i), salt crust, osmotic potiential high
Platy: slow (i), horizontal peds
Blocky: moderate (i), angular peds
Prism: moderate (i), salt crust, osmotic potiential high
Platy: slow (i), horizontal peds
22
New cards
Saturated flow is controlled by...
Darcy's law
23
New cards
saturated flow vs. infiltration rate
saturated flow - measure of how fast water moves through a soil
infiltration rate - rate at which water moves into a soil
infiltration rate - rate at which water moves into a soil
24
New cards
ground water
saturated zone
25
New cards
water table
upper limit of ground water (can fluctuate seasonally)
26
New cards
vadose zone
zone of unsaturated material above the water table
27
New cards
capillary fringe
zone of capillary rise (can fluctuate seasonally)
28
New cards
what changes porosity of a soil
aggregation increases porosity. texture alone changes surface area, but not porosity. however, finer textures (i.e clay) have more aggregates).
29
New cards
rock types
igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary
30
New cards
primary vs secondary minerals
sand+silt -> primary minerals
clay -> secondary mineral
secondary minerals are primary minerals that have weathered
clay -> secondary mineral
secondary minerals are primary minerals that have weathered
31
New cards
colloids
homogenous mixture of ultramicroscopic particles of one substance dispersed through a second substance. particles do not settle and can’t be separated (ex: gels, soils, and emulsions)
32
New cards
dominant colloid in AB soils
crystalline silicate clays = phyllosilicates = aluminosilicates
33
New cards
central cation replacement
isomorphic substitution
can take place during weathering
can take place during weathering
34
New cards
1:1 type mineral structure
1 tetrahedral to 1 octahedral
35
New cards
2:1 type mineral structure
1 octahedral between 2 tetrahdral
(generally have more isomorphic substitution, therefore more charge)
(generally have more isomorphic substitution, therefore more charge)
36
New cards
4 types of silicate clays
Kaolinite (dominant in australia)
Montmorillonite, illite and chlorite (dominate in AB)
Montmorillonite, illite and chlorite (dominate in AB)
37
New cards
Kaolinite structure
1:1
38
New cards
Montmorillonite, illite and chlorite structure
2:1
39
New cards
d spacing
distance from the top of one platelet to the top of the next platelet
0.72 nm in kaolinite
~ 1.0 - 2.0 nm in montmorillinite
1.0 nm in illite
1.4 nm in chlorite
0.72 nm in kaolinite
~ 1.0 - 2.0 nm in montmorillinite
1.0 nm in illite
1.4 nm in chlorite
40
New cards
Platelets are held together by hydrogen bonding in...
Kaolinite
41
New cards
Uses of Kaolinite
No shrink/swell so...
construction (bricks)
ceramics
glossy coating on magazines
construction (bricks)
ceramics
glossy coating on magazines
42
New cards
no attraction between platelets in...
montmorillinite
43
New cards
Montmorillinite good for...
High shrink/swell so
good nutrient retention (higher isomorphic substitution and higher CEC compared to kaolinite)
construction (sealant)
good nutrient retention (higher isomorphic substitution and higher CEC compared to kaolinite)
construction (sealant)
44
New cards
K+ in interlayer causes cation bridging in...
illite
45
New cards
Mg^2+ in interlayer causes cation bridging in...
Chlorite
46
New cards
No shrink swell
Kaolinite
47
New cards
Min shrink/swell
Illite and chlorite
48
New cards
Max shrink/swell
Montmorillinite
49
New cards
CEC
property of a soil that describes it's capacity to supply nutrient cations to the soil solution for plant uptake.
increased CEC = increased fertility
increased CEC = increased fertility
50
New cards
Typical CEC values
CEC increases as texture becomes finer
CEC = mont > illite and chlorite > koal
Clay and OM have CEC
CEC = mont > illite and chlorite > koal
Clay and OM have CEC
51
New cards
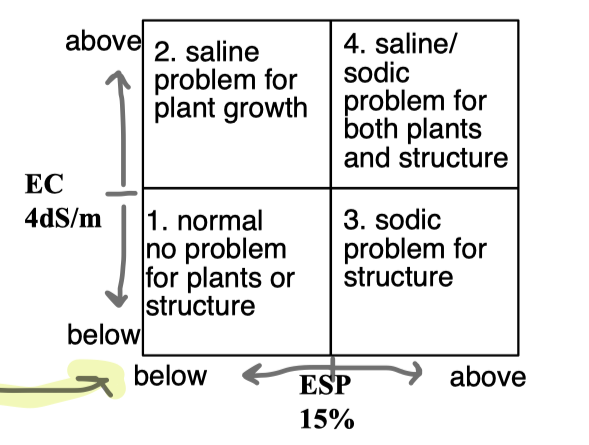
If ESP is >15%...
problem for soil function due to soil sodicity and clay deflocculation
52
New cards
General order of cation replacement
(looser) Li+< Na+ < K+ < Cs+ < Be+2 < Mg+2 < Ca+2 < Ba+2 < Al3+ < Fe3+ (tighter)
based on...
valence (higher valence cations can replace cations of lower valence)
ion size (cations with smaller hydrated radius have greater replacement power)
based on...
valence (higher valence cations can replace cations of lower valence)
ion size (cations with smaller hydrated radius have greater replacement power)
53
New cards
EC and ESP affect on plant growth and structure