A Level CIE Travel and Tourism: Destination Development and Management
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
195
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
parties involved in destinations development and management
host population - local communities
visitors - people who come to visit destination for leisure or business
industry representatives - including NTOs, DMCs, NGOs that are present in the destination
tourism development
growth and maintenance of various aspects of the tourism industry e.g. creating tourist product from a basic idea to achieving the final outcome such as new hotel or resort.
policies and planning
integral to successful tourism development, as is working in partnership w diff sectors
strategies
must be made to boost and sustain tourism development in all destinations.
organisations involved in destination management:
national or local gov depts
local authorities regional tourism orgs
international companies (dmcs)
ngos
commercial orgs
what do govs, ministries and ntos do
they play an important role in encouraging tourism development. assist with development of tourist attractions and events and promote the destination as well as support development by providing essential infrastructure: access, services and amenities that allow dest to grow
strategic development
research, funding and budgets
setting priorities and objs
strategic development
govs have responsibility for managing tourism within budget
provide research, development, funding in order to fulfil successful sustainable tourism strategy for destination
aim to minimise negative impacts of tourism and maximise positive
protect envionment while encouraging investment and develop econ bens of tourism
NTOs can protect and manage areas by supporting passing of laws and by-laws such as designating area as national park or area of outstanding antural beauty (AONB).
encourage new bus and innovations to expand tourism provision to both mass and specialised/niche markets
gov mins and ntos employ key mkting strats to develop tourisma dn rpomote positive images of area.
developing strong dest image is vital to promoting it to as many tourists as possible.
retaining tourism numbers and encouraging repeat visitors essential
research, funding, and budgets
ntos rely on good research to show performance and collect data to see trends and improve prods and services by sharing w regional and local orgs. helps remain competitive.
govs fund nto and offer grants to support regional and local tourism orgs and amt depends on econ wellbeing
funds reduced if unfavourable global trends e.g. covid but other places e..g visit scotland offered support pakcages to tourism groups to help ensure survival at time hwen travel restrictions where orgs could share to receive money.
each gov and nto keeps detailedd records of income and expenditure and responsible for setting and overseeing budgets w accurate targets e.g. on r&d and liaise w other orgs lcoal and regoinal to attarct more vis and generate more income = stronger econ
gov collect taxes annually which is spent on public services + tourism industry
amt money given often fluctuates and this means that each org must carefully plan how they spend their allocated money e.g. mkting, bus dev and supporting smaller toursim orgs thru adivec and guidance.
setting priorities and objectives
govs have many priorities and objs
attempt to strengthen their economy and improve lives and wellbeing of all citizens
govs can take advantage of econ bens by encouraging tourism development and promo
ntos try to stim demand for tourism thru r&d to assess potential markets
prioritise mkting and promo work to encourage visitors to their destination.
may also include supporting recovery after natural disaster, global econ recession or terrorist activity
what do local authorities and regional tourism organisations do
gov funded orgs that provide a service to both local and visiting pops. engage in activities that help boost image of local area and serviecs thru mkting and promo campaigns. ensure services provided for locals and businesses through overseeing land use planning, planning control, infrastructrue dev and control, and visitor mgement.
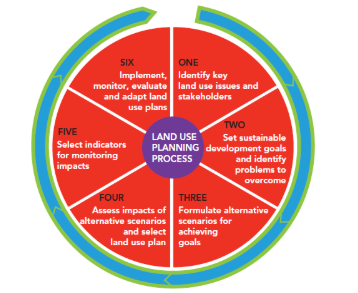
land use planning
planning control
local infrastructure and dev control
regional and local promo and mkting
visitor mgement
land use planning
process of regulating use of land
prevents undesirable use of land and helps encourage better use of environmental resources
land use planners consider both social nad environmental issues and attempt to make areas less congested and more sustainable
there are 6 objs that can be carefully monitored
prevents unwanted devs and ensures efficient use of land and resources
planning control
local authorities can approve/refuse plans req by tourism devs
oversee mgment of land and buildings to prevent inappropriate devs
usually consultation process where plans are displayed for interested groups to assess suitability of new dev or change in function or operation e.g. factory → heritage
regional tourism orgs can offer advice on completing plannig applications
planning reqs many permissions esp if dev involves tourist accom
lcoals unhappy at proposal for new hotel if near residential area as more cars and visitors
sensitive areas or environmental significant may have restrictions for any devs e.g. national park
local infrastructure development and control
major infrastructrue devs in towns and cities allow for improvements in access and amenities that could support and develop employment opportunities
tourism customers need good access to and around destinations otherwise cant visit and go elsewhere
locals liaise w gov to organise building of power supplies including gas electric water hydro solar wind and thermal (sunstaionable)
locals oversee work of waste collection, sewerage plants and sometimes destination plants
develop sustainable transport e.g. electrib buses
improve visitor and local lives
regional and local promotion and marketing
carry sig amt of marketing and promo of dest. many local authorities brand destination to create image w strong identity or perceived identity = greater customer interest and dest propserity
mkting promo forms: newspaper ads, competitions, magazines and journal ads, local or regional radio ads, public relations local stories, tv, online social media web blogs, cinema ads, billboards.
work w nat govs and nat tourist boards so no duplication of efforts
visitor management
each local and regional authority researches own area to assess and most visit places and manage environmentally sensitive sites
tics used to educate tourists abt sensitive sites and give advice on how to prevent further damage
local tourism vital to regional economy thru jobs and wealth but if too many visit can spoil resource and visitor experience
authorities anticipate tourism demand thru data collection. fluctuates naturally thru seaosns, capcity and time of day but needs to be managed flows to ensure benefits
most common managing = pricing mechanisms = entrace fees or parking. park and ride schemes → car park to bus so lses environmental impact.
carying capcity = limited no. visitors to protect env. group sizes restricted in sensitiev areas and permits needed e.g. grand canyon usa
ngos
charitable ventures that rely on donations from their various supporters. they support a particular cause e.g. animal protection, empowering women in business or supporting responsible cultural and environmental issues. can support activities that increase profile of local dest
examples of ngos
wwf - focus on protecting environment, using renewable resources and reducing pollution and they encourage more local travel for holidays by asking tourists to reduce no. flights taken and supprot socio-cultural environmental protection of landscape
other:
center for responsible travel (CREST)
destination stewardship center
green destinations
sustainable travel international
tourism cares
the travel foundation
come together to set sustainability standards, prevent negative climate change and encourage ppl and orgs to act repsonsibily and protect resources.
ngo 6 functions
research, fund raise, develop and finance projects
provide specialist knowledge and expert staff to oversee projects
provide guidance in regional planning for projcets
provide assistance w training and education of local communities
promote awareness of political, environmental, and socio-cultural issues
promote awareness of demand for specialised tourism products
provide specialist knowledge and expert staff to oversee projects
many ngos have highly qualified staff who can give advice and suggest practical solutions to new and established tourism orgs or communities
conservation experts can provide alternative strats for local community to protect endangered elephants e.g. in asia, ngos support elephant rescue centres and fight illegal elephant tourist work
ngo staff can give advice and suppport to help monitor and fund protected elephant habitats
working w experts, local comm can establish good sustianable practices and learn solutions for future to protect their land and animals
provide guidance in regional planning for projects
regional planning includes diff land use projects and activities that help to develop and grow an area including building of infrastructure to support rural or urban landscape and development of resrots,, shopping centres, offices and housing.
ngos have an interest in usch projects to assist control of devs that may have historic and environmental significance
regional planners consult ngos for guidance on preservation of buildings, landscapes or other items of arcaheological or historical significant e.g. bell towers, statues, old factories
provide assistance w training and education of local communities
focus for many ngos is social/political influence had.
role fo trainig and education is integral to main goal to spread knowledge and understanding of aims and objs which prevents possible exploitation of locals and resources e.g.:
educaiton for empowering local girls in rural dest offering them cahnce to learn how to support themselves and their families
assistance for schools thru provision of teachers, books and computer access, helping reduce illiteracy providing futures for many children
sustainable training projects including vocational skills that can be useful for dev young adults as well as children
research, fund-raise, develop and finance projects
research conducted to assess suitabliity of area for sustianable tourism
ngos offer expert knowledge of dest and may highlight negative issues affecing environment e.g. retaining important habitats for rare animals e.g. blakc rhino and snow leopard
consultation w ngos by govs and commercial orgs very common
partners, develoipers and DMCs also use ngo info to deliver sustainable prods and services
research findings often allow for niche tourism projects to flourish such as agri-tourism (farm based)
ngos may provide funding support in many LEDCs where locals given options to help poverty reduction including voluntourism (popular within africa and central america) where volunteers give assistance in setting up and running of sustainable tourism projects e.g. small guest houses which benefit locals w direct and indirect tourism employment.
promote awareness of political, environmental and socio-cultural issues
main obj to to fulfill ethical/moral change by highlighting inequalities and attempting to improve lives of million
ngo work e.g. planning native rainforest trees in brazil, protecting indigenous in south america.
by bringin awareness of environmental or scoial injustices, ngo integral to dest dev and management
promote awareness of demand for specialised tourism products
ngos support and work for benefit diff causes
have influence to promote specialised tourism products that are associated w their philosophies
some of most popular are nature absed oturism, community tousim and agri tourism.
products aim to have long term viability thru their sustianable approach.
hope is to make dest offering specialised prods successful and competitive.
commercial organisations
privately owned businesses and their main concern is generating profit to pay dividends to owners or shareholders. they take part in all types of activity that adverties and promotes brand, raises awareness among potential customers and lead to increase in sales to boost revenues
e.g. tour operators, travel agents, accom providers, transport operators, attractions and guiding services. these put together packages that they market to public and sell
commercial org types
overseas travel agents and inbound, outbound or specialist tour operators
local businesses
overseas travel agents and inbound, outbound or specialist tour operators
role of tour operator is put together the different components for a holiday and sell them as package to customer
inbound and outbound tour operators such as TUI research destinations carefully and choose accom and transport methods suitable for each of their markets
then package these products, set prices and undertake marketing and promotional work to sell their holioday prods to wide variety of customers
specialist tour operators plan and organise tours that follow trends in industry
catery for smaller markets and give advice and guidance on each products they sell.
specialist operators are similar to larger tour operators in that htey must be financially stable hav egood management structures and be able to effectively promote and sell products. they have expert knowledge and are educatosr as well as holiday providers. spend time collecting and researching appropriate activities. these are then placed online or in brochure ready to be targeted to specific niche market such as adventure, eco and culture
each operator offers packages that theyve selected and checked. they then market holiday packages online. may be ancillar services associated e.g. activties, insurance, and car hire.
local businesses
tt industry made up of many diverse orgs from very small 1 person guiding companies to large multinational hotel chains. comoplex industry
hundreds of diff accom providers in tourism industry from camping yurts to 7 star hotelsn, some local bus.
give customers place to rest and stay and may also provide food, cleaning and activtieis
money made used to pay staff, maintain establishment and make profit.
sometimes accom work w local enterprises to support wellbeing of host population and may have missions to be ecofriendly
transport operators are integral to travel and tourism industry. without them industry wont funcntion bc passengers need to be moved from and within destination so local bus profit from doing this e.g. water taxis venice, tuktuk thailand, bike thailand and vietnam - local knowledge helps go faster.
some operators funded by gov e.g. bus in luxembourg and others private e.g. greyhound usa so depends on customer price, timing and competition
loca bus also icnlude attractions. commercial attractions support dest and can be purpose of visit and satisfy range of interests and cultures including historic, cultural, sporting and entertainment venues. may also be local carnis or festivals
guiding services may be provided by local bus often as part of organised trip. local guides have a detailed knowledge of area
commercial orgs keen to dev and provide new p&s that keep them updated in competitive industry to satisfy new customers and offer current more choice.
by expanding cusomter base, more chance of success and therefore economic benefits. indsutry has always been easily affected by trends, global events and new fashions, therefore dynamic approach to developing new prod and services prevents stagnation and offers chance of staying relevant particularly in struggling market
dmc
company that uses extensive local knowledge and resources to offer professional service including organising and runing events, assisting with transport, activities and sourcing accomodation. can organise meetings and book accom and restaurants to particular requirements.
by coordinating all plannign elements and logistics for any service required, such as excursions, conference,s events, dmcs can offer competitive fees as have established contacts within industry. through these services, visitors can experience unique, cultural, historic sites of interest
dmc roles
providers of ground services
conference and event organisers
providers of ground services
holiday begins w airport - large commercial ventures w shops, restaurants, cafes, toilets, showers, car park, prayer rooms and must accomodate passaengers while waiting w safety measures and checks on luggage and indiviudla
ground oeprations involves all aspects of aircraft handling at airporst e.g. refuelling, cleaning, catering and aircraft mogvement. air traffic control supervise craft for takeoffs and landnigns
dmcs understand airport procedures at airports and this helps them provide range of ground services for cusomters at airport including norganising ticketing, easy check in, advising on oversized baggage handling and lost baggage.
dms organise all aspects of ground services to ensure the smooth running of the holiday experience.
customers use dmcs as they can rely on their experience to transport them safely to their destination and provide accom and catering services.
offer range of excursiosn that customers can book.
these companies have plenty of experience within dest and it is this expert knowledge that creates successful planning and trips all customer types
conference and event organisers
dmcs can organise conferences and evnetson global scale
Meetings, incentives, conferences, exhibition industry will be worht estimatied 14,293 billion USD by 2025.
dmcs have many contacts w venues and orgs to assist w providing for needs of business tourist
venues important for staging conference
should have lal facilities and amenities to host many ppl w option of small meeting rooms
bus customers have diff needs and wants to leisure customres and many of top destinations can facilitate bus centres, wifi, computer access, printing, audio, and visual equipmemnt
dmcs also need to be able to include entertainment nad leisure activites for bus customers and their spouses.
destination management activities
sustianable tourism policies and practices
dev of new prods
vis and traffic mgment
dest branding and marketing as mass/specialisdew market
partnership of commercial and non commercial orgs, local community and vis
investment in long term bens for local community and tourism econ
community involvement, community projects, education, training and employment of locals
planning control
widening access to facilities
regular environmental impact auditing (EIA)
comm and liason w vis and providers and provision of vis info’
monitoring and eval of how dest is being managed
encouraging responsible and ethical tourist behavior
sustainable tourism definition (WTO)
development requires informed participation of all relevant stakeholders as well as strong poli leadership to ensure wide particip and consensus buidling. continuous and needs constant monitoring of impacts w/ necessary preventive or corrective measures when necessary
needs high lvl of tourist satisfaction and ensure meaningful experience to tourists, raising awareness abt sustainability issues and promoting sustainable tourism practices amongst them
sustianable tourism policies and practices
forefront of most industries
includes holidays that positively impact local comms, env, holidaymakers and tourism bus
tourism dev are heavily influenced e.g. derelict areas regeneration, new approaches to building hotels and visitor attractions, staging of events, minimising neg impacts of large groups on env
new or rejuvenated places subject to strict building and planning regulations to prevent poor use of mats, safeguard dest image and enhance built env
govs can influence dev policies and issue guidelines to tourist devs
bus need to meet cus demands and protect resource that future depends on
good practices shld boost local economies and employment opps while improving quality for holidaymaker
carrying capacity definition
no. individuals who can be supported in given area within natural resource limits, and w/o degrading natural social, cultural, and econ env for present and future
carrying capacity
sustainable toursim policies involve identifying max carrying cap of dest
if exceeded = change in physical env = decline in qual of consumers experience
keeping tourists happy important but shouldnt be deteriment to landscape and locals
limits to no. restaurants, bars, and hotels dest requires
if tourism so pop that area tries to dev more facilities to cater to greater no. visitors = impact on env so when is saturatoin
exceeding phys capacity damages native plants and wildlife
overcrowding and congestion limits enjoyment and experience of adventurous activites reducing remotenes and uniqueness of experience
responsible tourism
more bus are developing this
emphasises that all stakeholders responsible for kind of tourism they dev or engage in to imrpove tourism without causing harm or degrading culture/environment of dest and ppl
for cape town declaration on responsible tourism:
minimises neg econ, env, and scoail impact
gens greater econ bens for locals and enhances wellbeing of host comms, improves worknig conds and access to industry
improves locals lives and life chances
makes positive contribs to conservation of natural and cultural heritage to maintenance of worlds diversity
provides enjoyable experience for tourists w/ meaningful connections w locals, understanding of local cultural social and env issues
access for ppl w disabilities
culturally sensitive rpomoting respect betw tourists and hosts building local pride and confidence
dev of new prod and serv
competitive environment so this is necessary (can be niche, accom, equipment, instruction, insurance, holiday risks)
factors needed to be considered:
dest location and accessibility (comp)
price
hours of operation (new prod or serv available 24/7 during season or seasonal)
mkting and promo (how to sell to cust, how easy to buy)
visitor and traffic management
methods depend on bus (whether in natural or urban area)
overcrowding and traffic can deter future customers
successful methods of vis management used:
creating park and ride schemes
seasonal/temporal limitation of vis no.
zoning areas
pedestrian areas
using interpretation boards, signage, maps, brochures, leaflets
restricting use by diff groups - ages/genders/heights/size etc.
steering vis flows w natural features e.g. pathways, trails, roads, etc
use of tech for e-tickets, fast passes etc.
use of pricing mechanisms to encourage and discourage cust usage at diff times seasonally/daily etc.
dest branding and mkting as mass/specialised mkt
strong brands enable potential visitors to know product and can act as strong pull factor/differentiate esp in mass tourist mkt
can focus on segments e.g. accor - movenpick, ibis, novotel etc. focused on diff
partnership of commercial and non commercial organisations, the local community and visitors
dmcs must invovle all involved parties to ensure their activities successful.
work with locals to provide accurate and authetnic experiences
helps w prod dev, training, educational events, sales support, incentives and joint mktign
investment in long-term bens for locals and tourism economy
tourism can have long lasting benefit to locals through funds gained invested into projects that benefit e.g. infrastructure (park, community centre).
ensures ppl can enjoy socio-cultural and ecconomic benefits e.g. doctors, football grounds. must be discussed and willl also beenfit tourists e.g. theatre
community involvement, community projects, education, training and employment of locals
local community involvement integral to successful sustainable tourism
dmcs wish to have strong links to communities bc without that, local customs and knowledge lost and difficulties may arise if poor comms and lack of understanding of dest
dmc needs support and invovlement of locals for events so if objections = extra costs and bad relationsihps
dmcs help comm projects e.g. small tourism enterprises e.g. food and accom bus by booking their facilities rather than using larger multinational orgs
tourism brings a wealth of opps for staff training, education, personal dev from mgment to cust service (large variety of areas where new skills benefit holiday makers and employees)
tourism jobs need face-to-face
good training bens the rep of any tourism orgs - increase rev for local community who benefit from direct or indirect tourism roles, appropriate training also essential for health and safety aspects of tourism industry.
govs have sponsored trainign shcemes to assist w this and more tourism qualifications available
many ledcs look for tourism for new job opps
dest management can boost no. vis received and can dev new employment roles e.g. guides, craft makers, souvenir sellers. can improve whole area and for locals and have more managerial positions.
planning control
prevents unsightly and inappropriate building as large scale devs without sensible restrictions can spoil the aesthetics of a dest and put strain on facilities and amenities. planners consider:
sustainability of dev (include green spaces and support ecosystems)
size of dev must be within limits and consider proximity to other
considering local habitats e.g. land and marine animals protected
tree preservation
use of materials sympathetic to area (e.g. local instead of improted)
prevention of building in conservation or World Heritage site
height of dev (can’t exceed certain heights depends on area)
widening access to facilities
vis mgment must consider all types of customers and accessibility (specific needs - physical e.g. wheelchair, illnesses, limited vision, impaired hearing, educational needs)
poor dev = inacessible = barrier for all types of customers maybe bc lack of investment or bc dest dev too rapid. bad coping = beaches closing or limits on vis no.
regular environmental impact auditing (EIA)
useful tool to allow policy makers and mgers to assess and predict the environmental impacts of any proposed dev and may reveal + or - impacts
assits decision makers on whether to proceed w project e.g. new resort, pool, mall
using eia can reduce loss of natural resources and env deg or social disruption that can accompany tourism devs
subject to public consultation to allay fears by locals but most eia strongly linkedto carrying cap of area
must be continualyl reviwed and monitored (anually or seasonally) (sometimes required by law) which shows amt of damage to env overtime so action can be taken after inspections
inspections will show damage to footpaths, evidence of pollution which = maintenace and clean ups allowniog tourists and locals to enjoy env
communicaiton and liason w visitosr and providers and provission of visitor info
dest mgment activities continually evolve and ensure effective comm w vis and providers hapens before, during and after any visit.
need to know abt new p&s e.g. launch of new hootel, restaurant or cruise
networking w providers allows for exhcange of current ideas and social media easy and quick to interact/liase w new and established providers
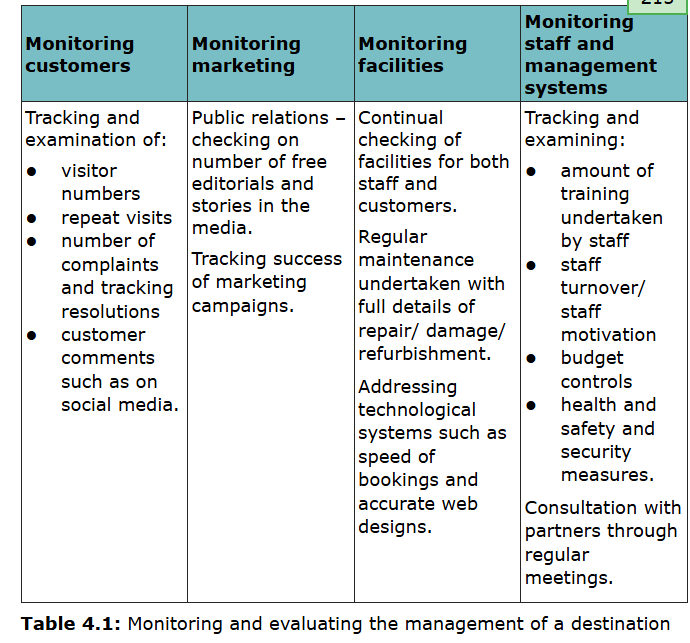
monitoring and eval of how dest is being managed
once toursit dest dev, monitoring and eval essential
dynamic industry so cant stagnate
must be up to date w tech and changing needs of cust to be viable
planning for new devs or refurbishing regen of current projects shld also be considered
several ways to monitor and eval
encouraging responsible and ethical tourist behavior
responsibel tourism creates and maintains positive impacts at a destination while encouraging ethical behavior
when practised good behavior by both tourist and tourism provider can provide excellent sustainable econ bens
promoting respect for locals and customs and env
responsible tourism aims topromot respect for locals and customs
good bheavior is vital to protect and have good relationships
educated and informed tourists can bring positive messages abt tourism to areas they are visiting
respectufl clothes, atittudes and behavior should be researched.
tour operators have potential to ensure appropriate behavior at dests is understood by tourists by providing info in brochures and online
supporting the locals and encouraging prod of local produce
responsible tourism encourages vis to make sust choices to support local ppl and buy local produce
homestays more popular and allow vis to enjoy experience of seeing directly hwo diff cultures live and work
gives locals direct econ bens from tourists
buying local produce e.g. fruit and veg supporst local farmers and encourages more production
production of local souvenirs cna support econ and prvent illegal trrade of animal souvenirs e.g. ivor
objectives of tourism dev and mgment:
econ
env
socio-cultural
political
2 econ objectives of tourism dev and mgment
maximisation of retention of visitor spending
investment of tourism income in public and social projects for local community
maximisation of the retention of visitor spending 3
growing and retaining visitor spendings is vital for longterm econ security so to do this must know cust needs and wants and adapt prods and serv
dests have to evolve to keep up so must be clear vision and asses what vis experience needs or lacks and respon appropriately e.g. extend season with MICE or overseas cust segs
employ well trained and qualified staff who can deal w range of cust queries from complaints to advice and may also take op to dev skills w training
investment of tourism income in public and social projs for local comm
tourist sector major investment contributor benefiting locals and tourists as ethical travel orgs employ local guides and invest in bus start ups and social projects e.g. fair trade, education
varies between countries depedning on tourist dependency
helps to develop infrastructure and community facilities e.g. car parks, toilets, cycle paths, well-lit streets
3 environmental objectives
minimisation of negative impacts of tourism
preservation, conservation, regen of local env and nautral dests, their flora and fauna
sust use of resources
minimisation of negative impacts of tourism 5
aim to work towards sustainable practices by educating visitors, staff and local community
done by introducing entry fees to sites and charging for car parking
local authorities introduce zoning of areas allowing for diff activities to be undertaken safely at diff times of day
segregated areas where skiing, mountaing biking, hiking, and abseiling all compete for mountain access
tourists restricted from areas or may be rerouted on new paths to allow for sites to be maintained and prevent further damage
preservation, conservation and regen of local env, natural dests, their flora and fauna
ensuring tourism causes as little damage as poss within dest
can support conservation work e.g. protecting sea turtle nest sites or protecting improtant meadows, prairies or savannas
possible to regen environment through this
new form of travel building on sust ecotoruism (regenerative travel) promotes lowering travel carbon footprint but also makes more pos changes to dest visited
may be restoration of countryside area or assisting w setting up education programmes for disadv groups
sust use of resources
stimulate improvements for ben of locals and vis
using renewable resources e.g. water, wind, solar, wave energy
unesco have sust tourism dev goals promoting careful use of env resources while maintaining ecological integrity to conserve natural heritage and biodiversity (all stakeholders must b involved)
6 socio-cultural objectives
protection of local culture
community involvement and empowerment
widened access for all to facilities and assets
provision of employment and staff development
promotion of tourism education for the local population
education of tourists to be environmentally and culturally aware
protection of local culture
can sustain traditional festivals, customs, and traditions, UNESCO dedicated to this, world heritage list
world heritage list ubpdated everyear and wants to recognize outsanding and international importance of sites around world. given legal rpotections to ensure preservation and enjoyment for future
many areas locally can dev and promote culture and heritage by reusing buildings and redefining places.
heritage centre instead of museums have become educational and preservation effort and interesting to tourists
success depends on econ conds in world. attractions can be operated and owned by public priv or voluntary sectors and these work tgt for sust dev to:
create benefit to local, regional, and nat econ
provide vis satisfaction
improve and sustain quality of life for the locals
create profit for those involved
community involvement and empowerment
tt orgs support conservation programmes and try to promote need for maintaing communities that struggle thru under dev
wants to ensure maximum local benefit e.g. initiatives for climate change resistant variety of rice for farmers and feeding without asking for aid
direct assistance from carefully planned holidayts involving locs for guiding, accom and produce.
holidays help locals access basic healthcare, security and education
communities control and dev projects that help revive local crafts and traiditonal activiteis
widened access for all to facilities and assets
tourism dev planners must consider access for locals and visitors
must be political support and balance between planning and funding for physical access
easy access to info and up to date advice is vital to give a destination the opportunity to compete w others, allowing potential visitors to gain good insight into opps available
good internet coverage and info sources are therefore essential.
all benefit from inclusive devs
provision of employment and staff development
tourism devs must retain local population in employment roles within dest.
employment opps exist in travel agencies, hotels, tour operations, airlines, coach companies, and built and natural attractions (directly or indirectly e.g. support, food suppliers, insurance, retail). tending to be customer-facing, managerial or administrative
most is part-time, seasonal = flexibility for workers
staff must be cared for and given ops to dev personally and professionally as it = happy, skilled, and motivated staff who can demonstrate knowledge in safety, values and standards of tourism org. reflects well on reputation and retain staff.
needs regular discussions, meetings, training ops should be identified for both team and personal objs and linked to orgs vision ormission statement
dev in tt enhances transport, agri and construction as need for new networks, more supply, and more accom
promotion of tourism education for the local pop
vital so that locals can support devs and be educated about econ devs they gain by helping rerduce damage to sensitive sites e.g. recycling plastics to protect oceans
can be done through signage on beaches w info about dangers of dropping litter, lighting fires and leaving dog waste. locals pass on their knowledge and understanding
locals can see value of personal dev and cna be encouraged to support tt industry by taking adv of ops available. trainig and education + community empowerment are strong predictors of community participation and involvement in tourism planning and dev
education of tourists to be environmentally and culturally aware
tourists need to be educated before and during visit so theyre sensitive towards surroudnings and respectful of culture
tour operators have advice and guidance in brochures and online outlining appropriate behavior e.g. photos not allowed in some places
many orgs taht focus bus principles on sust and responsible toursim.
holidays and tours packaged tg with good behavior in mind and attempt to give back to community, taking away little leaving as untouched as possible
2 poltiical objectives of tourism dev and mgment
enhancing image and reputatoin
international relatiosn
enhancing image and reputation
tourism helps enhance image of area esp LEDCs or negatively perceived countries due to natural disasters or wars
language an dculutre seen as essential for strong national identities and often more important that dests seen as safe and secure as tourists risk is key to decide on return or visit and repeats important to economies
some govs attempt to improve countrys rep thru policies e.g. set clear goals for sust devs bc of fear over culutral and env losses caused govs to reconsider policies and commit to these
these policies counter issue of mass and overtourism and allow dests to be more resilient and improve their rep
international relations
having good inter rels enhances perception of area and increases mkting and promotional appeal
good understanding between countries helps ease tourism movement between them e.g. reciprocal visa arrangements = good relations between govs
extending options for foreign investors encourages work based travel and gives good op for diff nationalities to meet
tourists may prefer booking internationally recognized hotels
4 positive economic impacts
income generation and increase in foreign exchange
job creation and training
econ dev and dev of infrastructure
multiplier effect