Oral Biology Exam 1
1/263
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from tiffany_heizen on quizlet
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
264 Terms
What is growth?
-physical increase in size/number (of cellular structures)
-differential process with some parts growing more rapidly than others (different rate)
What is development?
-increase in am of organization/ “functional complexity”
physiologic and behavioral process (continues throughout life)
When is post developmental decline?
usually in 20's
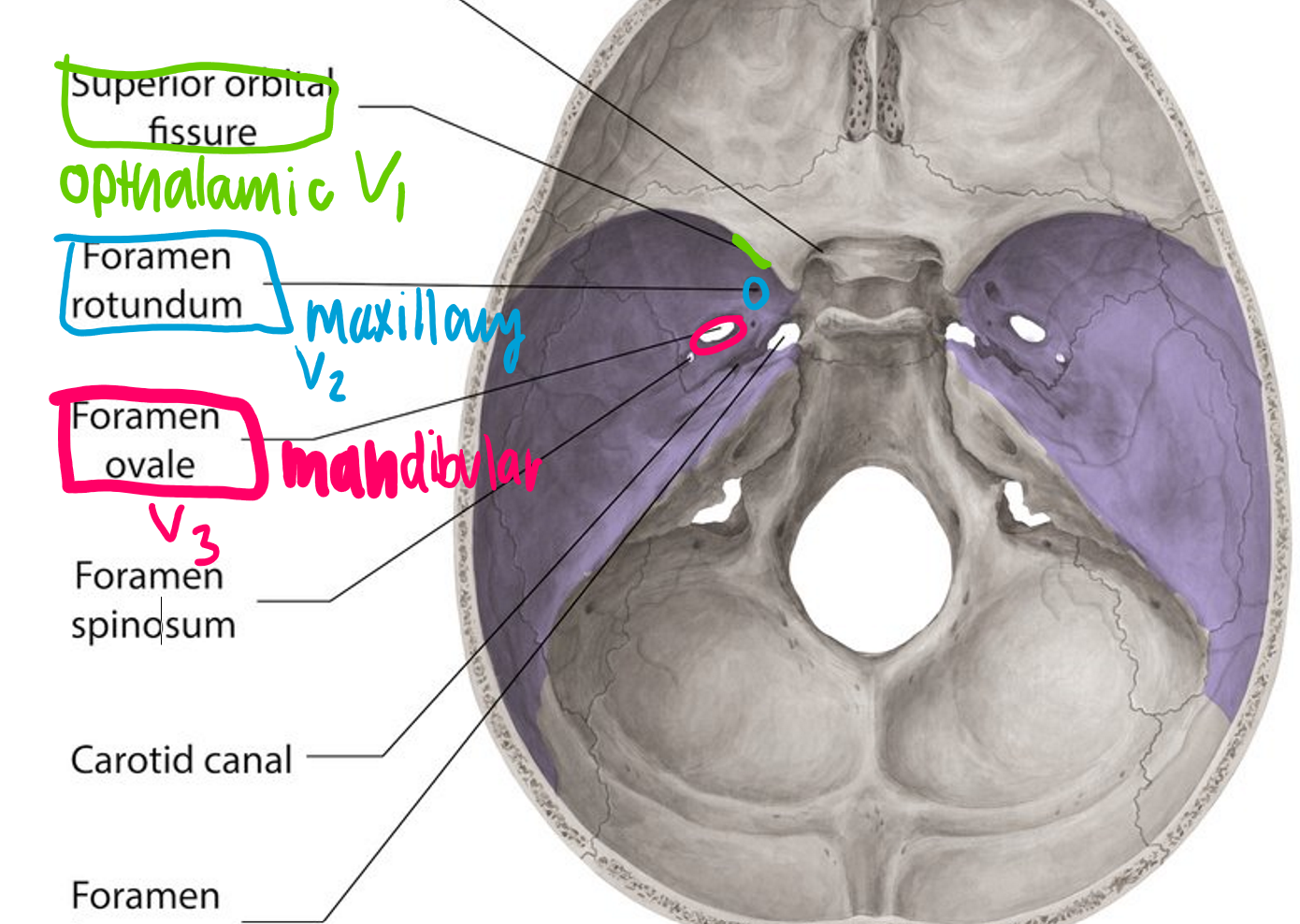
Trigeminal nerve has how many branches?
what are they?
3 branches
opthalamic, maxillary, mandibular
what’s Craniofacial morphogenesis
-complex series of events leading to formation of head and face
when is the critical period for formation of face and oral cavity
4th-14th weeks of intrauterine life
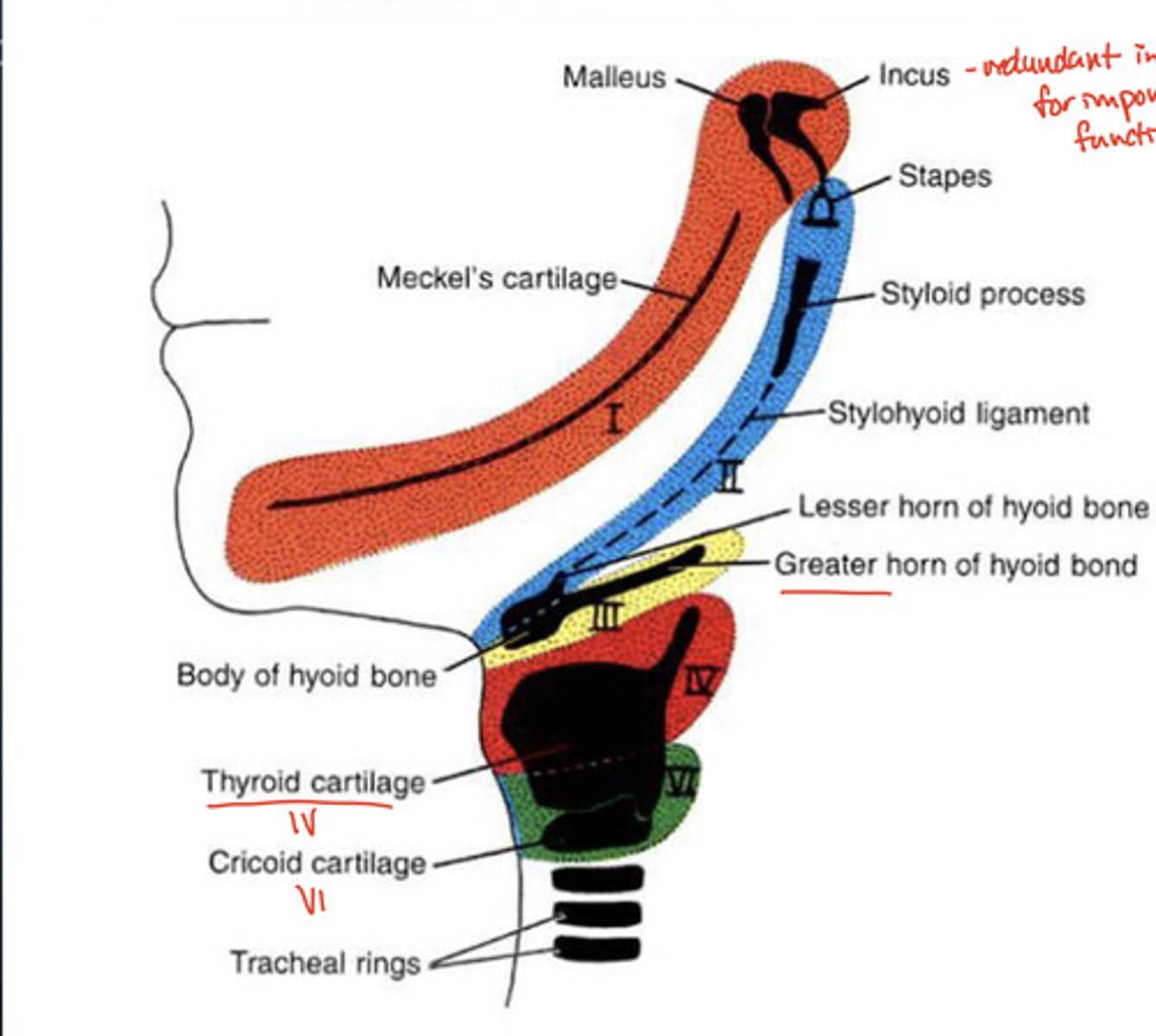
Meckel's cartilage forms what?
Mandible
What is the cartilage that forms the neck area?
Meckel's cartilage
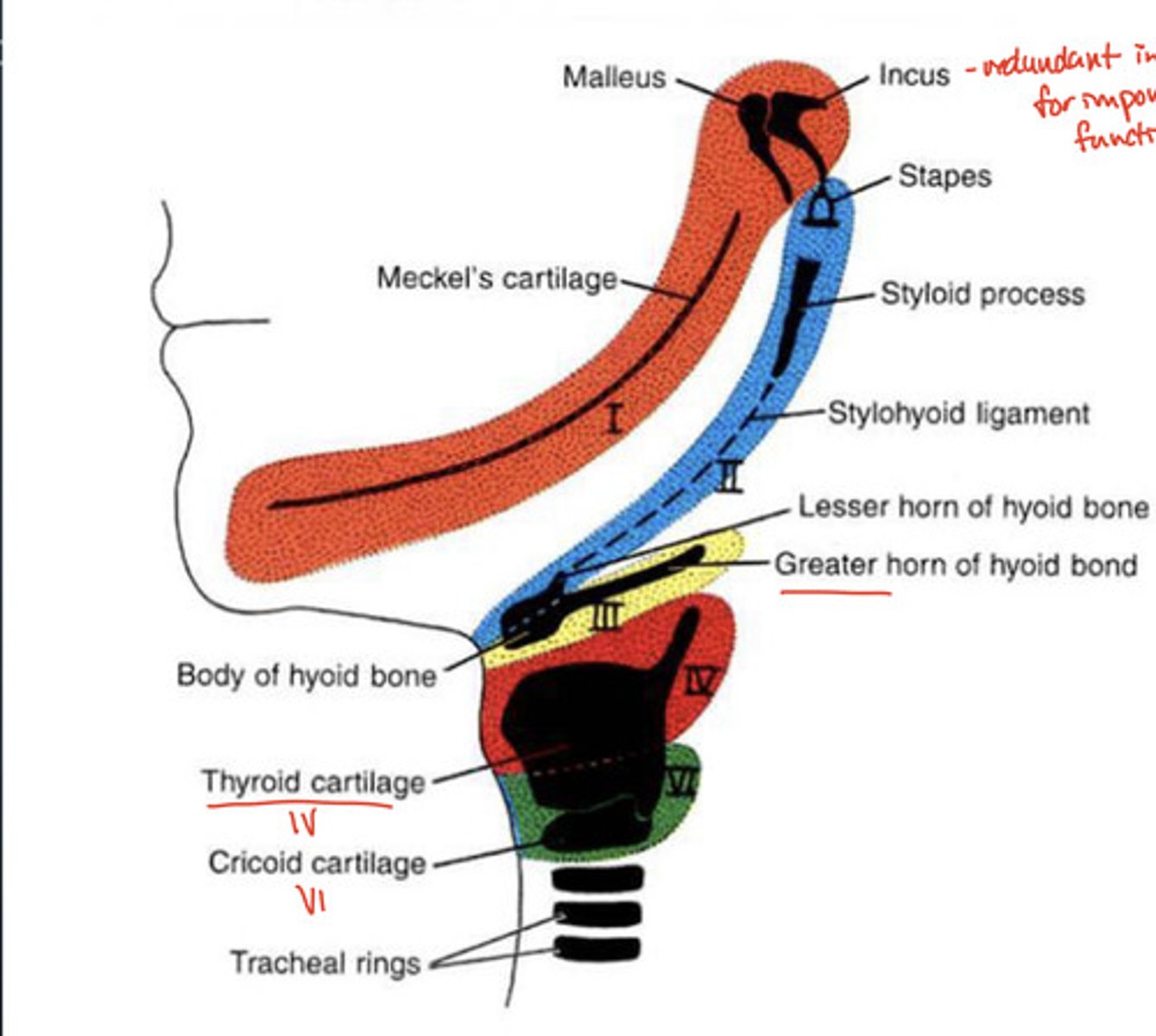
Thyroid cartilage comes from which arch?
4th
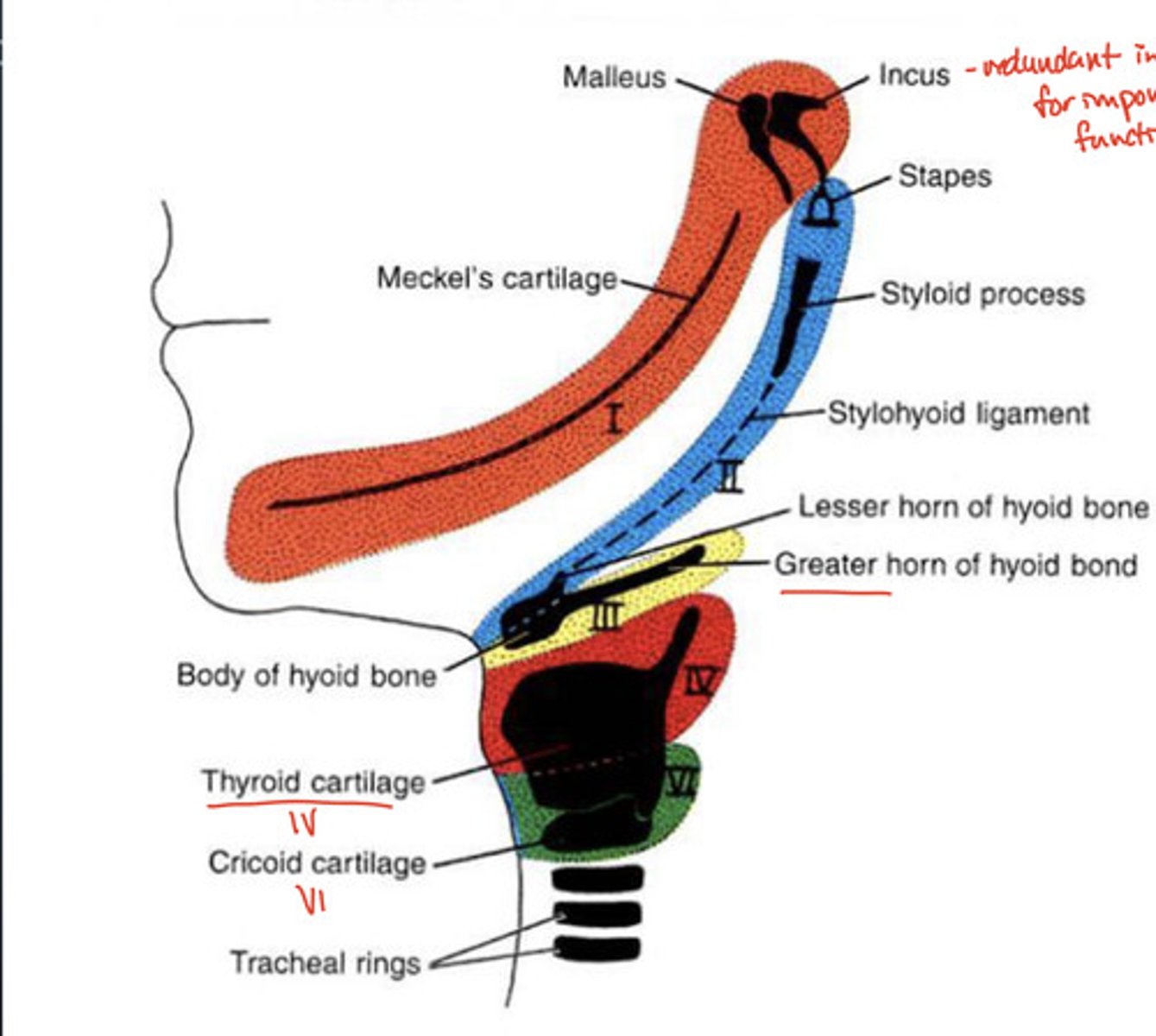
Cricoid cartilage comes from which arch?
6th
Greater horn of the hyoid bone comes from which arch?
3rd
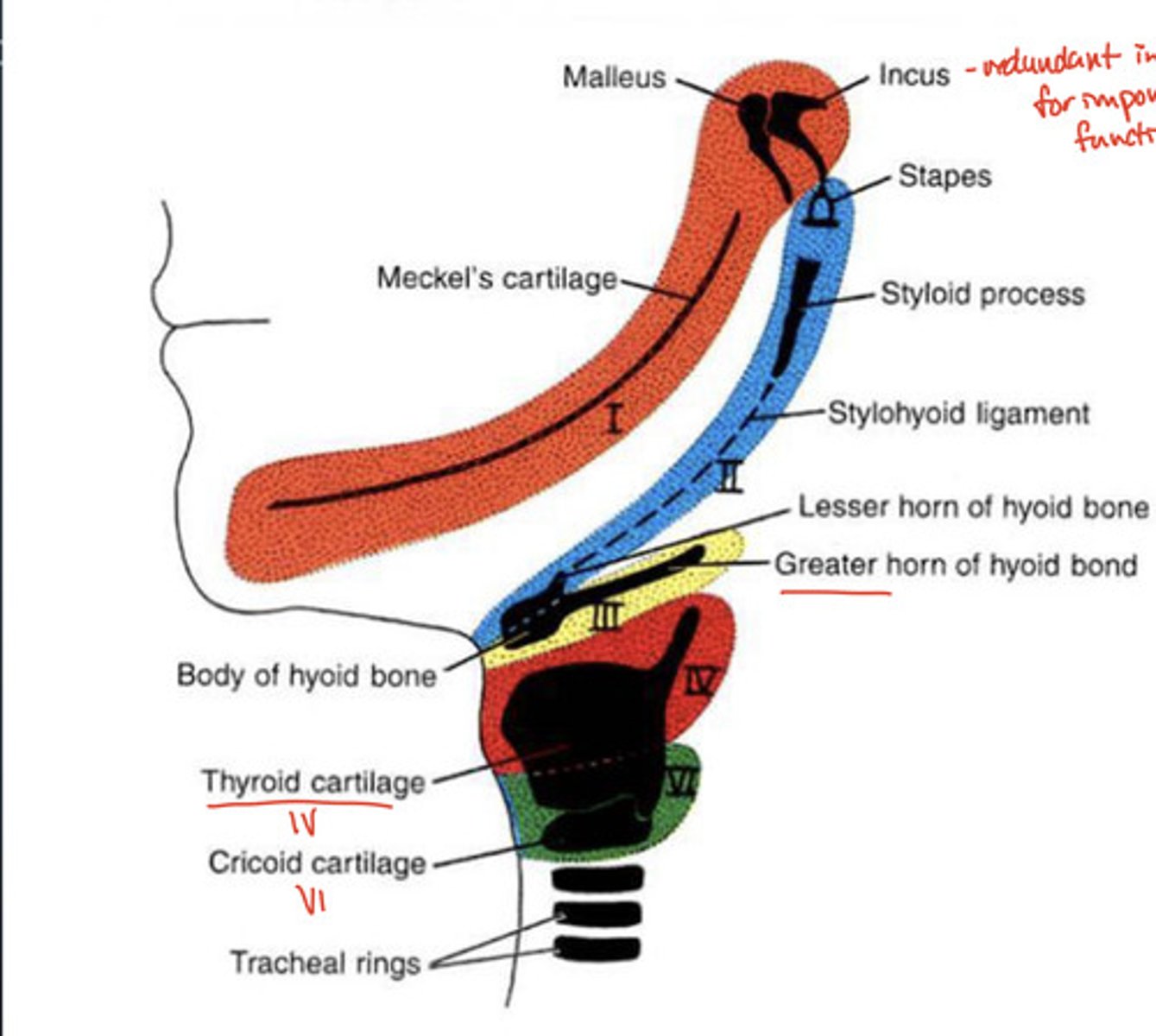
What is important about the malleus, incus, and stapes?
redundant innervation with arches 1 and 2
(redundant innervation = nerve supply from MULTIPLE sources in the 1st & 2nd pharyngeal arches)
when is the Proliferative period?
0-2 weeks
when is the Embryonic period?
2-8 weeks
when is the Fetal period?
8 weeks - birth
WHICH embryonic periods are you MOST and LEAST susceptible to malformations via environmental factors?
MOST: embryonic period (weeks 3-8) bc structures are DEVELOPING. (CNS system)
middle: fetal period (weeks 8- birth)
LEAST: proliferative period (weeks 0-2)
What important happens in the embryonic period 3rd week?
CNS is forming!!
get neural folds, CLOSE neutral tube.
What forms in the embryonic period?
primary brain vesicles: forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain, cerebral hemispheres
Forebrain includes which lobes?
frontal, temporal, occipital lobes
*NOT parietal
What weeks are most critical for serious malformations and why?
3rd-8th week: structures developing, most susceptible to environmental factors
what are the 3 steps of the proliferative period (weeks 0-2)?
1. fertilization
2. implantation
3. embryonic disk formation
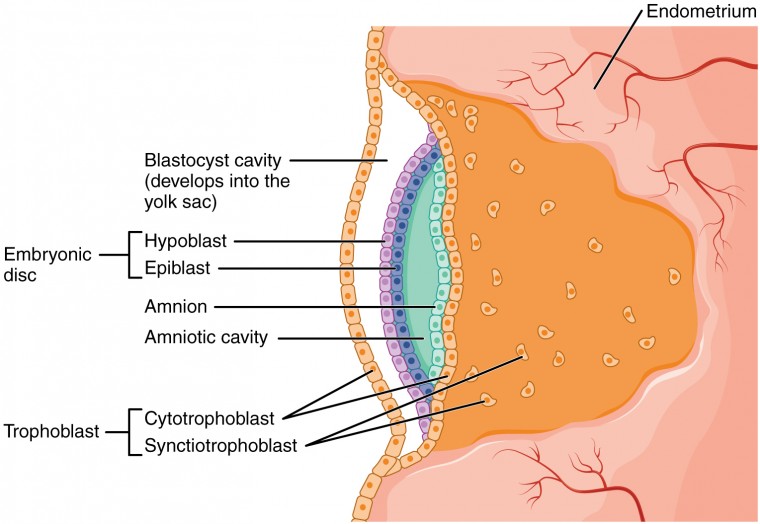
Week 1: what forms, what differentiates?
bilaminar (2 layer) disc from zygote cells → ectoderm and endoderm
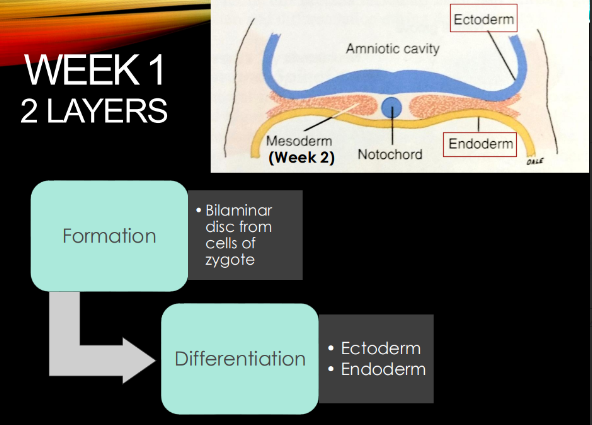
Week 2: what happens?
gastrulation → formation of mesoderm → TRIlaminar disc bc have all 3 layers now.
Ectoderm is important for the formation of:
SENSORY epi:
tooth enamel
eye/ear/nose, nervous system
Mesoderm is important for the formation of:
CT derivatives!
dentin, pulp, cementum
bone, cartilage, blood
Endoderm is important for the formation of:
GI tract epithelium and associated glands
Teeth form from how many layers?
(which ones?)
2
ectoderm (outside)= enamel epi
mesoderm = dentin, cementum, pulp CT
By 4th week of embryonic period:
heart begins to beat!
what HELLA important formation happens during weeks 4-7?
formation of face and oral structures!!! *****
week 8 marks…
BEGINNING of fetal period!
what happens during weeks 8-14: (fetal)
faces takes on more of a human appearance
What happens in week 3 (embryo) and order:
1.Neurulation: neural plate → neural tube & neural crest cells differentiate.
2.migrate laterally & ventrally towards area of future face
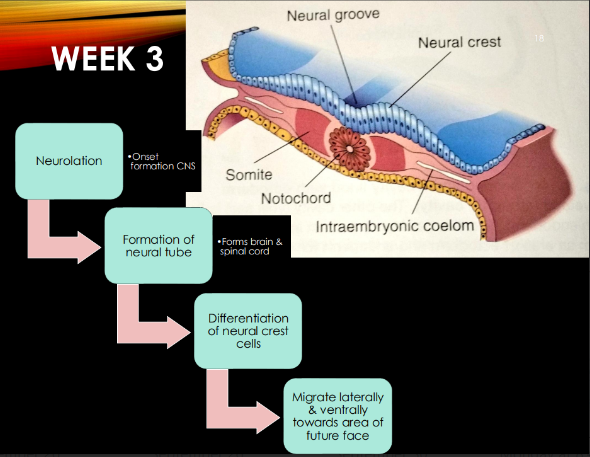
What is neurulation? where does it happen? when?
week 3: onset formation of CNS
in ectoderm
the Neural tube forms:
brain and spinal cord!
Neural tube fuses in what direction?
Fuses anterior to posterior
Once the neural tube closes, what forms? When?
Forms primary brain vesicles: forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain, cerebral hemispheres
-week 3
Weeks 4-5 of embryonic development:
cranial nerves begin development and growth into their designated tissues
-branchial arches (see cranial nerves form)
Fetal Alcohol syndrome affects which stage
stage 1: initial organization of germ layers

What happens in fetal alcohol syndrome?
first 3 ventricles of brain do NOT separate
“olfactory placodes” (tissue that’s important for sense of smell) are too close together → “deficient median nasal prominence” (nose/upper life form weirdly)
-vary from total absence of nose to midface deficiency

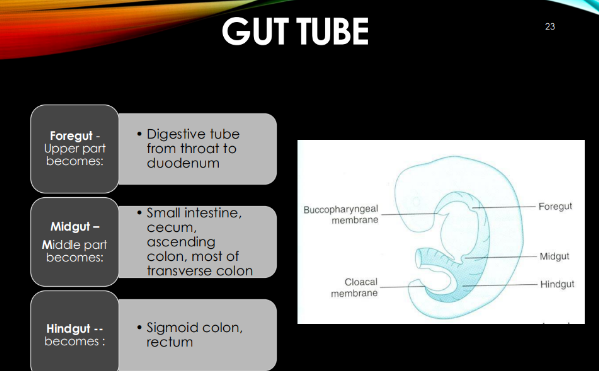
Gut tube consists of what 3 parts?
foregut
midgut
hindgut
Foregut becomes what:
digestive tube from throat to duodenum (upper part)
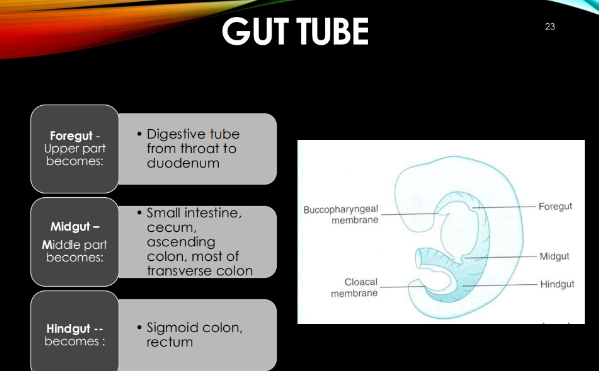
Midgut becomes what?
small intestine, cecum, ascending colon, most of transverse colon
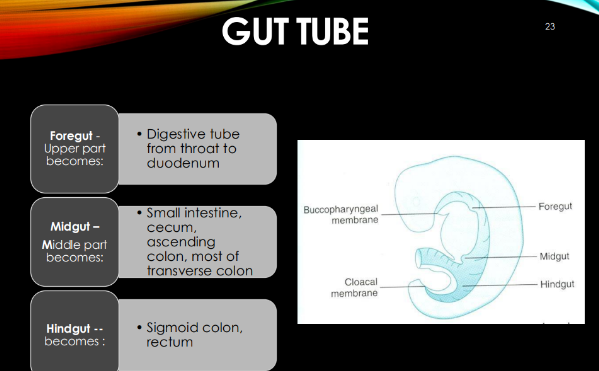
Hindgut becomes what:
sigmoid colon, rectum
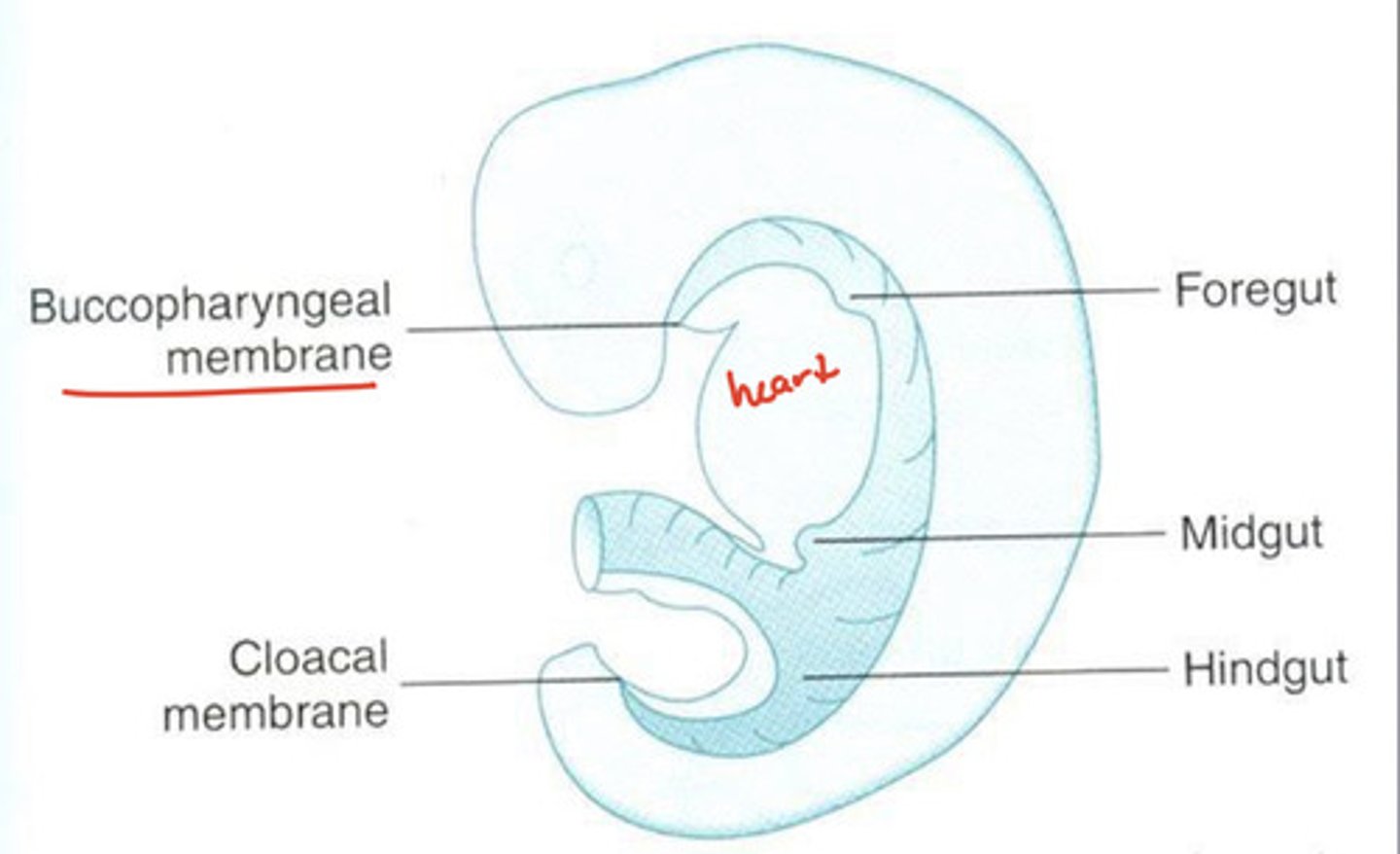
the opening between heart and branchial arches is made of?
buccopharyngeal membrane
4th week of development
frontal prominence
MX & MD processes
stomodeum
nasal pits, beginning of nasal cavity
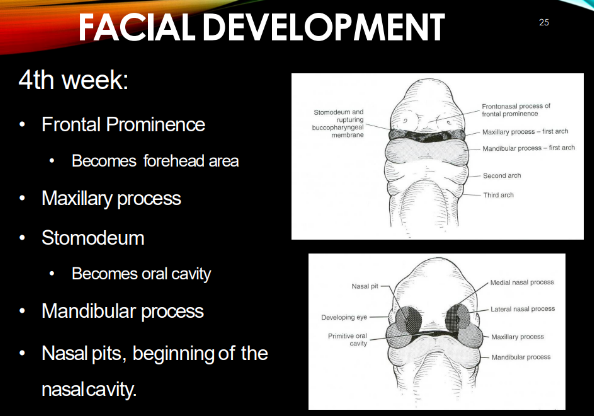
Frontal prominence becomes…
forehead area
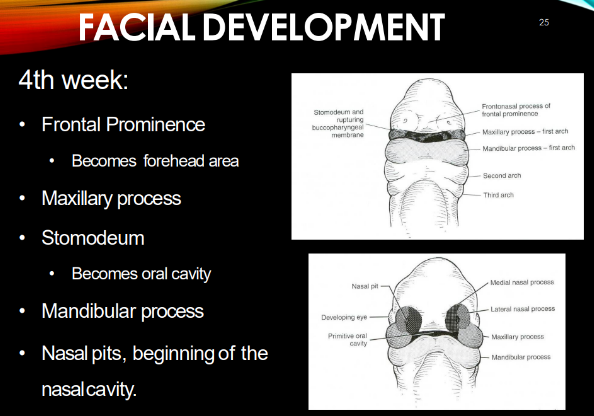
maxillary processes fuse with _______ by ______ week.
they push the ______ together.
mandibular processes fuse by the end of _____ week.
MX: fuse w/ intermaxillary segment by 10th week
-push nasal pits together
MD: end of 4th week.
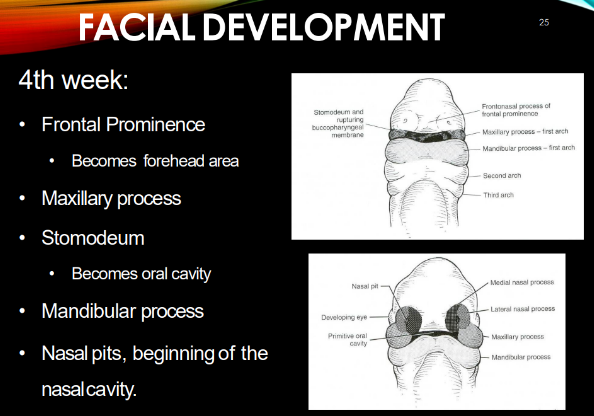
stomodeum becomes:
oral cavity!
during week 4, what are THREE important things happen that are relevant to the oropharynx?
oral pit first appears!
-stomodeum becomes oral cav btw the brain & heart.
-heart beats → supplies blood via vessels to the face, neck, brain
what stuff happens during week 5 that’s relevant to oropharynx development?
oropharyngeal membrane
-ruptures due to apoptosis → becomes the OROPHARYNX that connects the oral cavity to tubular foregut!
-the outside is lined by ectoderm that becomes the oral mucosa.
(fun fact: if this membrane doesn’t rupture → mouth is COMPLETELY or partially closed)
Mandibular arch grows [this direction] to develop into [ ]
and forms:
laterally to oral pit and will develop into MX process
-forms cheeks and mandible
Weeks 5-6 of development
facial processes continue to migrate
development of nose and nostrils!!!**
eyes and external ears become more evident
mandible begins ossification during late 6th week
Week 4 and teeth development:
neural crest interacts with other cells to form teeth!
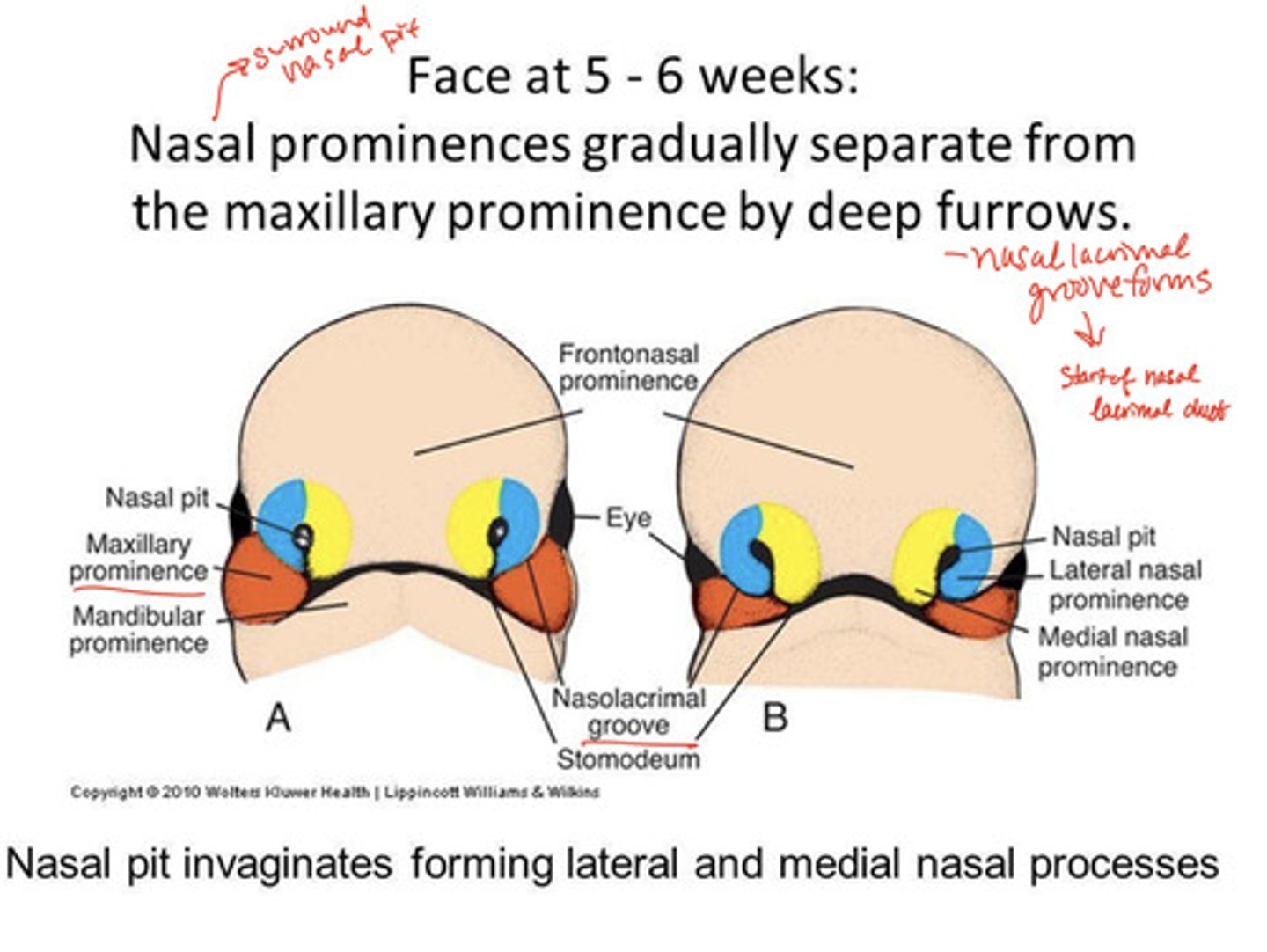
wtf happens during week 5-6 that have to do with the nose?
deep furrows SEPARATE the nasal prominences (surrounded by nasal pit) from the maxillary prominence.
-nasolacrimal groove forms = start of nasal lacrimal duct
Neural crest cells (NCC) form…
FORM tooth & periodontium via migrating to oral ectoderm & interacting w/ epithelial & mesenchymal stem cells.
-complex process: NCCs migrate to epi areas w/ high conc of homeobox genes
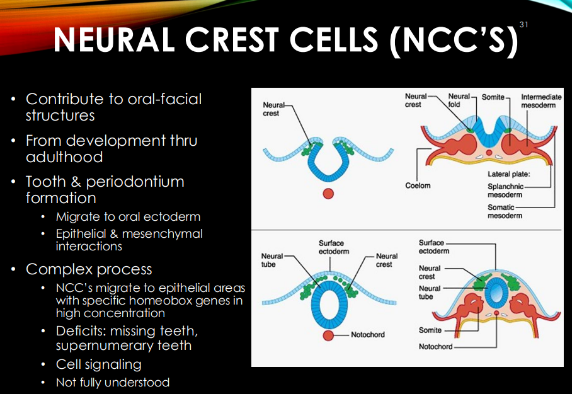
NCC’s exist when? why?
from development THROUGH adulthood bc they form oral facial structures.
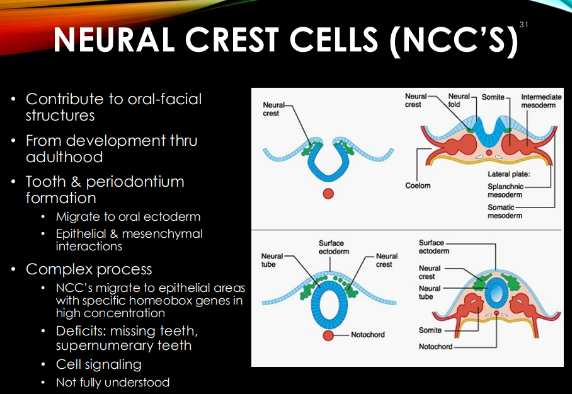
wtf is the “complex process”?
if it goes wrong….
when NCCs use cell signaling to move to epi areas w/ high conc of specific homeobox genes.
missing teeth (lacking homeobox genes), supernumerary teeth (extra homeobox genes)
Ear tubercle in development:
angle of mandible, sits rather low, associated with developmental syndromes
Pharyngeal arches are aka…
and form…
aka branchial arches/ apparatus!
form head and neck region
When would a malformation of the cranial facial complex happen?
when pharyngeal arches TRANSFORM into their adult derivative.
What’s a pharyngeal arch MADE of?
bar of cartilage w/ artery, cranial nerve, & mesodermal tissue
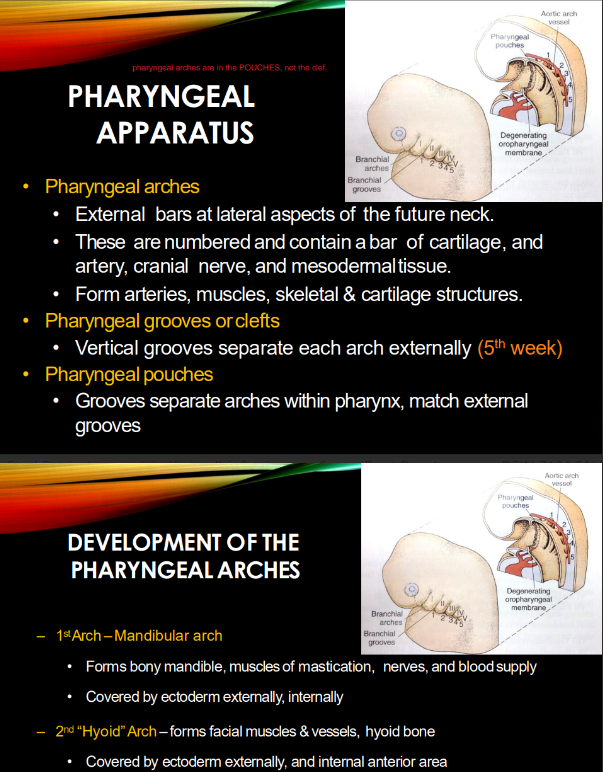
Pharyngeal arches make 4 types of structures. what are they?
arteries, muscles, skeleton, and cartilage
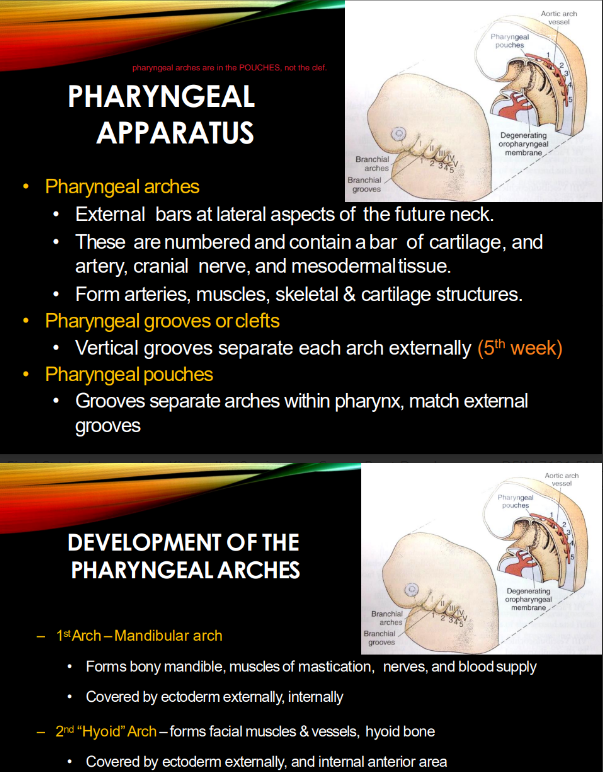
What INTERNAL & EXTERNAL sh*t separates pharyngeal arches?
how many r there?
internal = pharyngeal POUCHES
external = pharyngeal GROOVES
@ week 5, there are 5 arches/clefts.
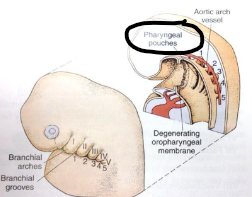
the 1st pharyngeal arch is called…
function?
Mandibular arch forms the bony mandible, muscles of mastication, nerves, AND blood supply
_____ germ layer covers the 1st & 2nd pharyngeal arches, both internally and externally.
exception?
ECTODERM.
for the 2nd arch (hyoid), ectoderm ONLY covers ANTERIOR internal part (that forms the muscles of FACIAL expression)
the 2nd pharyngeal arch is called the… and forms the…
Hyoid arch
-forms facial muscles and vessels, hyoid bone
-covered by ectoderm externally, and internal anterior area (muscles of facial expression)
what’s quirky about the 3rd, 4th, 5th pharyngeal Arches?
what do they form?
are paired bilateral bars that get divided by the BULGING heart @ the body midline.
-form hyoid bone, thyroid and cricoid cartilages
pharyngeal Arches 2-5 develop during what weeks?
what germ layer are they covered by externally vs internally?
weeks 4-7
external: ectoderm
internal: enDOderm.
Arch 1 cranial nerve, important muscles, cartilage/bone
CN V
muscles of mastication, mylohyoid, ant digastric
malleus & incus bones
Arch 2 cranial nerve, important muscles, cartilage/bone
CN VII
muscles of facial expression, posterior digastric, stylohyoid
stapes, styloid process, hyoid
Arch 3 cranial nerve, important muscles, cartilage/bone
CN IX
stylopharyngeus
hyoid
Arch 4 and 5 cranial nerve, important muscles, cartilage/bone
CN X (vagus nerve)
muscles of larynx, pharynx, soft palate
cartilages of larynx
Vascular development: each arch has what
right and left aortic arch vessel
1st and 2nd arch vessel begin to develop in the
4th week, disappear in 5th week
3rd arch vessel becomes:
prominent (taking over facial area)
-becomes common carotid arteries
As 4th and 5th aortic arches arise:
4th becomes prominent, 5th disappears
Which arch vessel becomes dorsal aorta
4th
1st arch muscles appear when and spread where
in 5th week
-spread within mandibular arch into each muscle's origin in 6th and 7th week
1st arch muscles make up what muscles
masseter, medial and lateral pterygoid, temporalis
-muscles of mastication
2nd arch muscles form when and spread where?
by 10th week, muscles formed thin sheet extending over face and posterior to ear
4th arch muscles:
Pharyngeal constrictor muscles in neck enclosing pharynx
1st arch cartilage
meckel's cartilage
2nd arch cartilage: what arises from here?
reichert's cartilage, rod shaped
-stapes, styloid process, lesser horn & upper body of hyoid
3rd arch cartilage form what
greater horn and lower part of hyoid body
4th arch cartilage
contribute to hyoid cartilage
5th arch cartilage
no adult cartilage deriveratives
6th arch cartilage
laryngeal cartilage
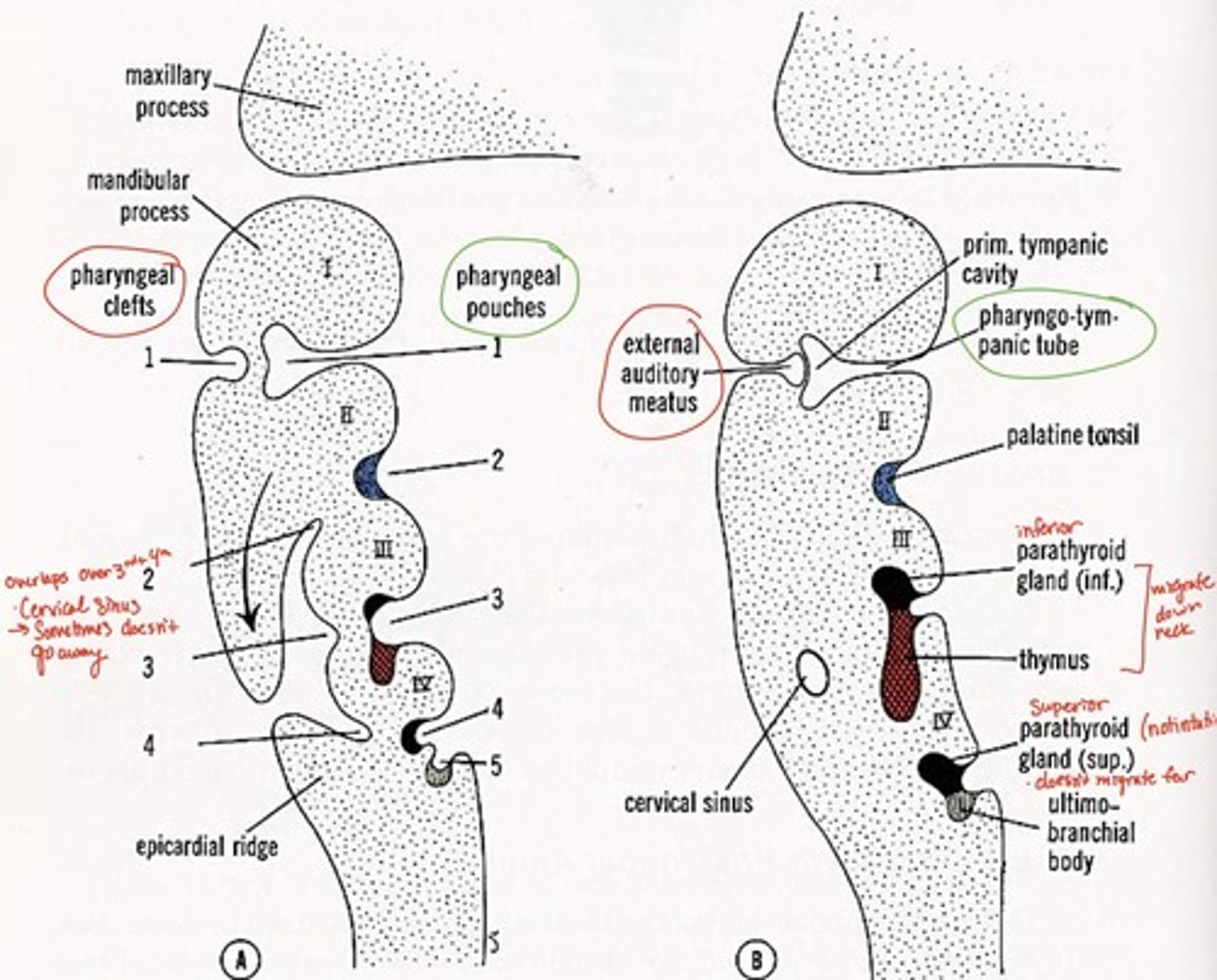
1st pharyngeal groove forms what
external auditory canal
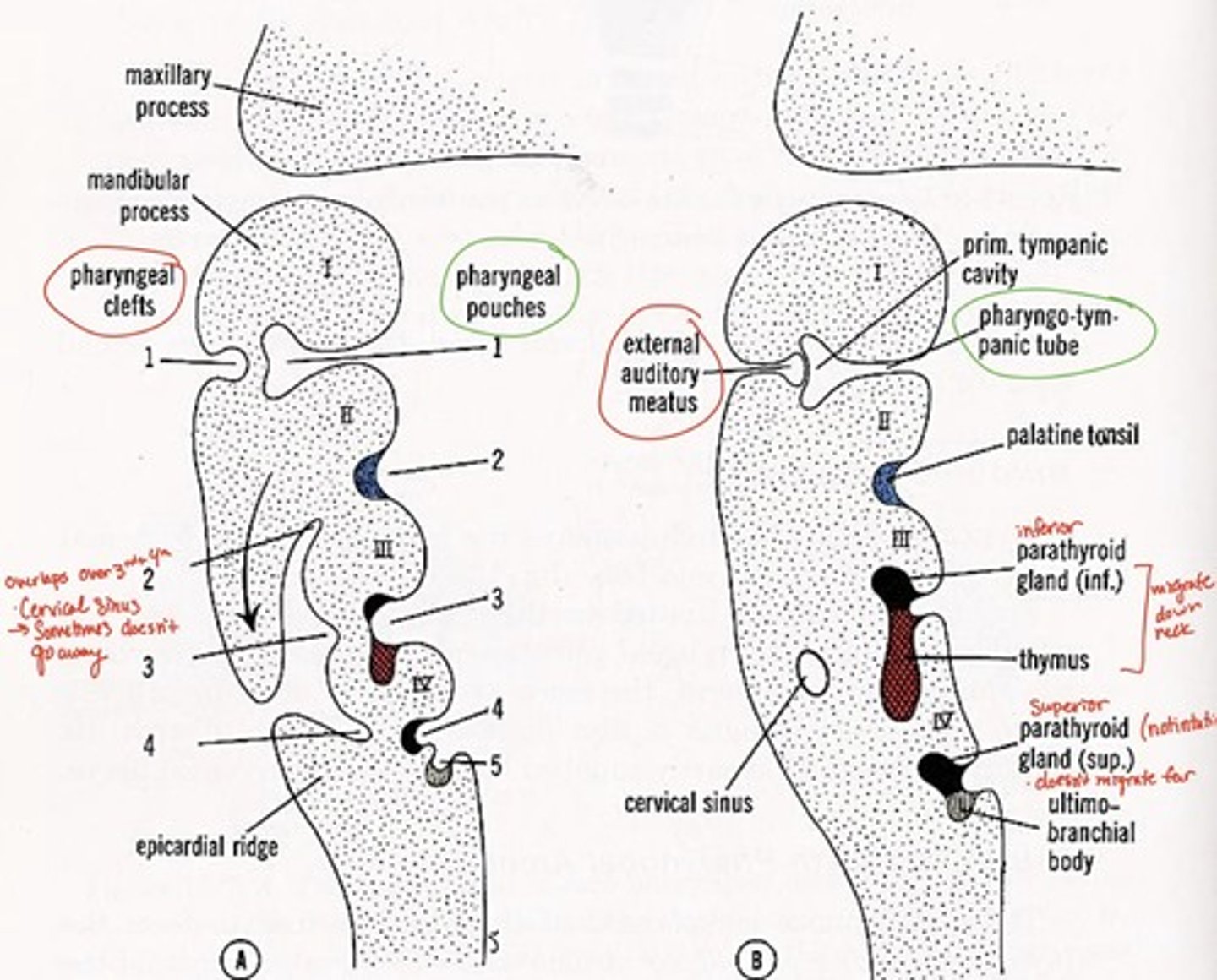
1st pharyngeal groove & 1st pharyngeal pouch forms:
tympanic membrane
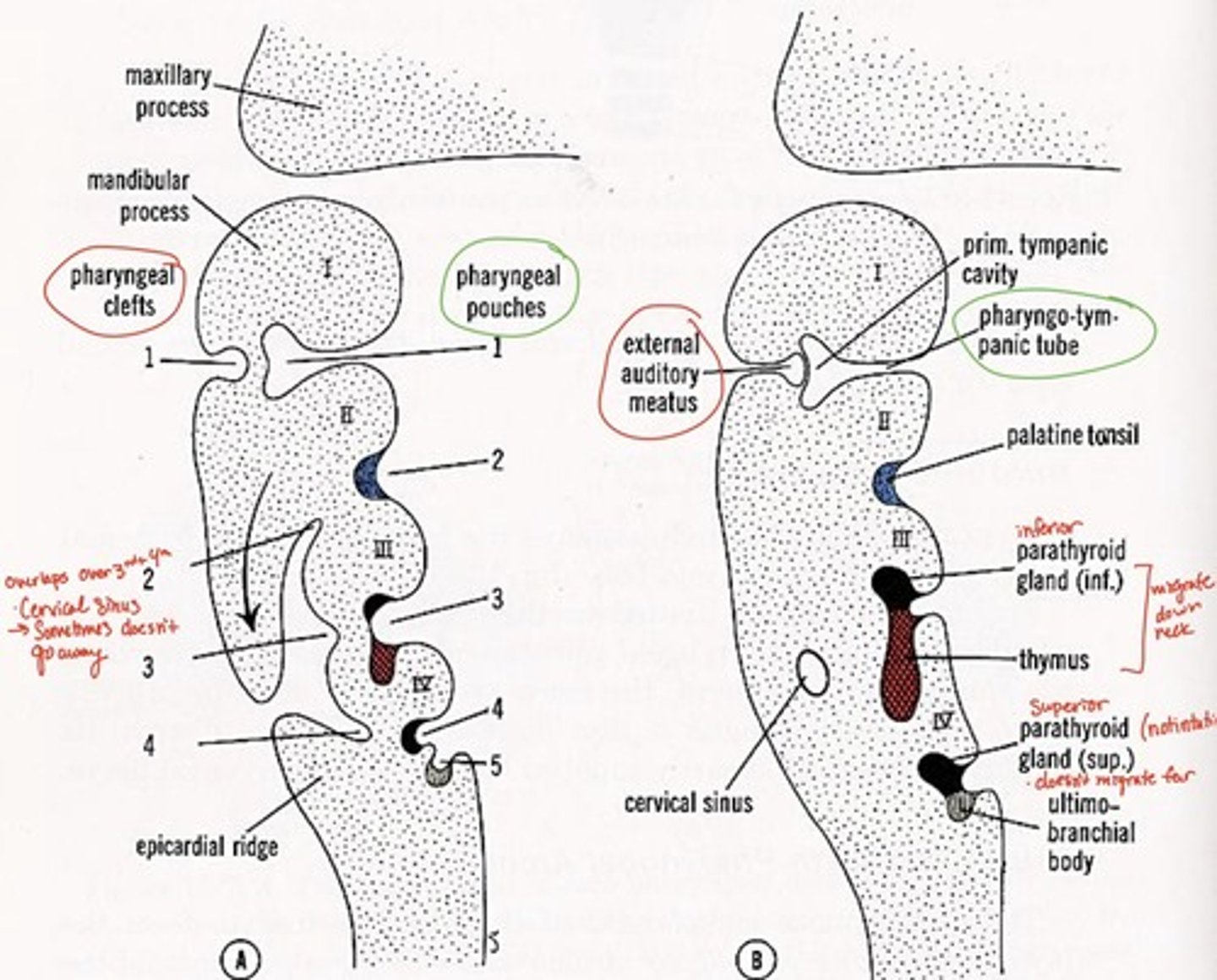
1st pharyngeal pouch forms what
middle ear and eustachian tube
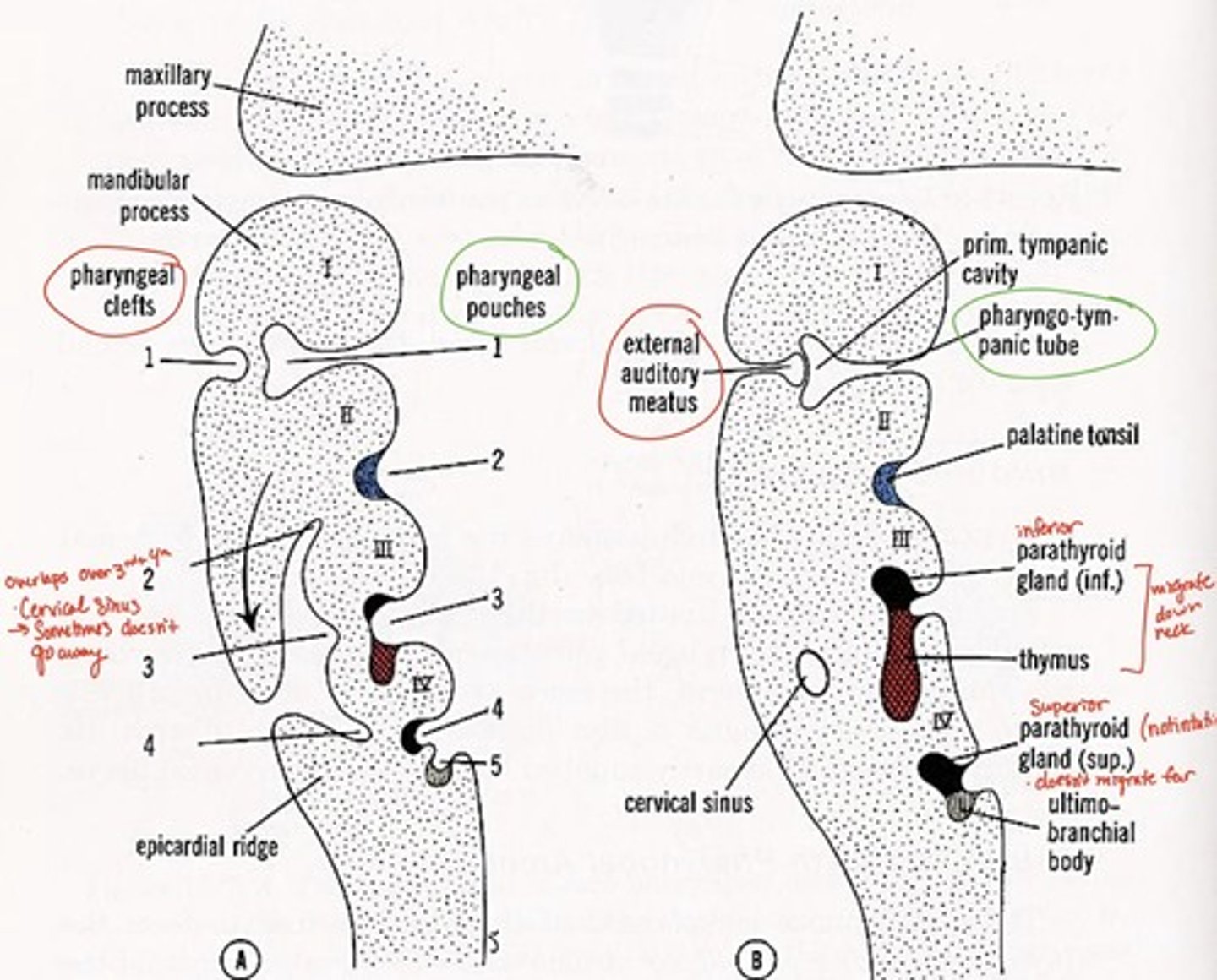
2nd pharyngeal pouch forms what
palatine tonsils
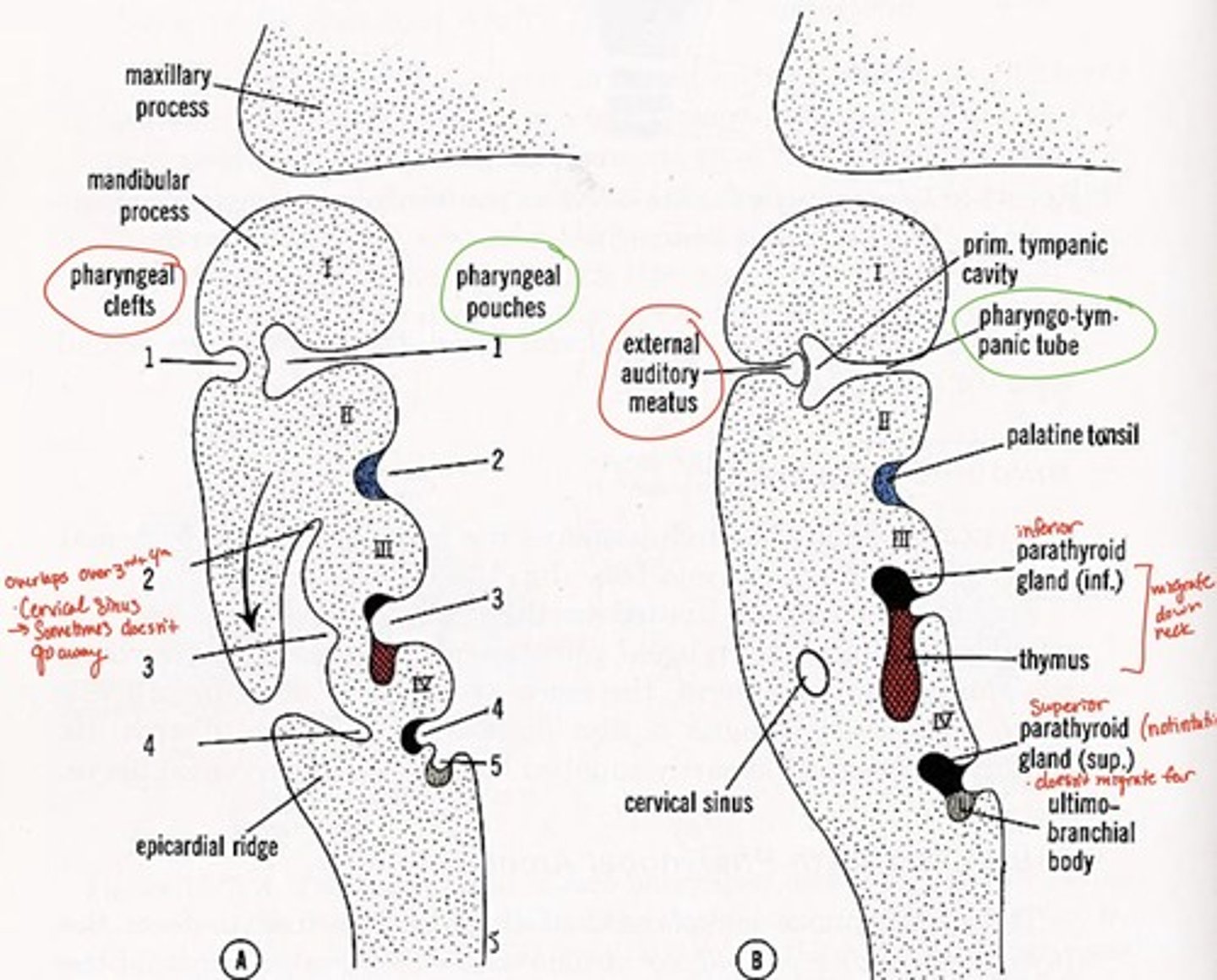
3rd pharyngeal pouch forms what
inferior parathyroid and thymus glands
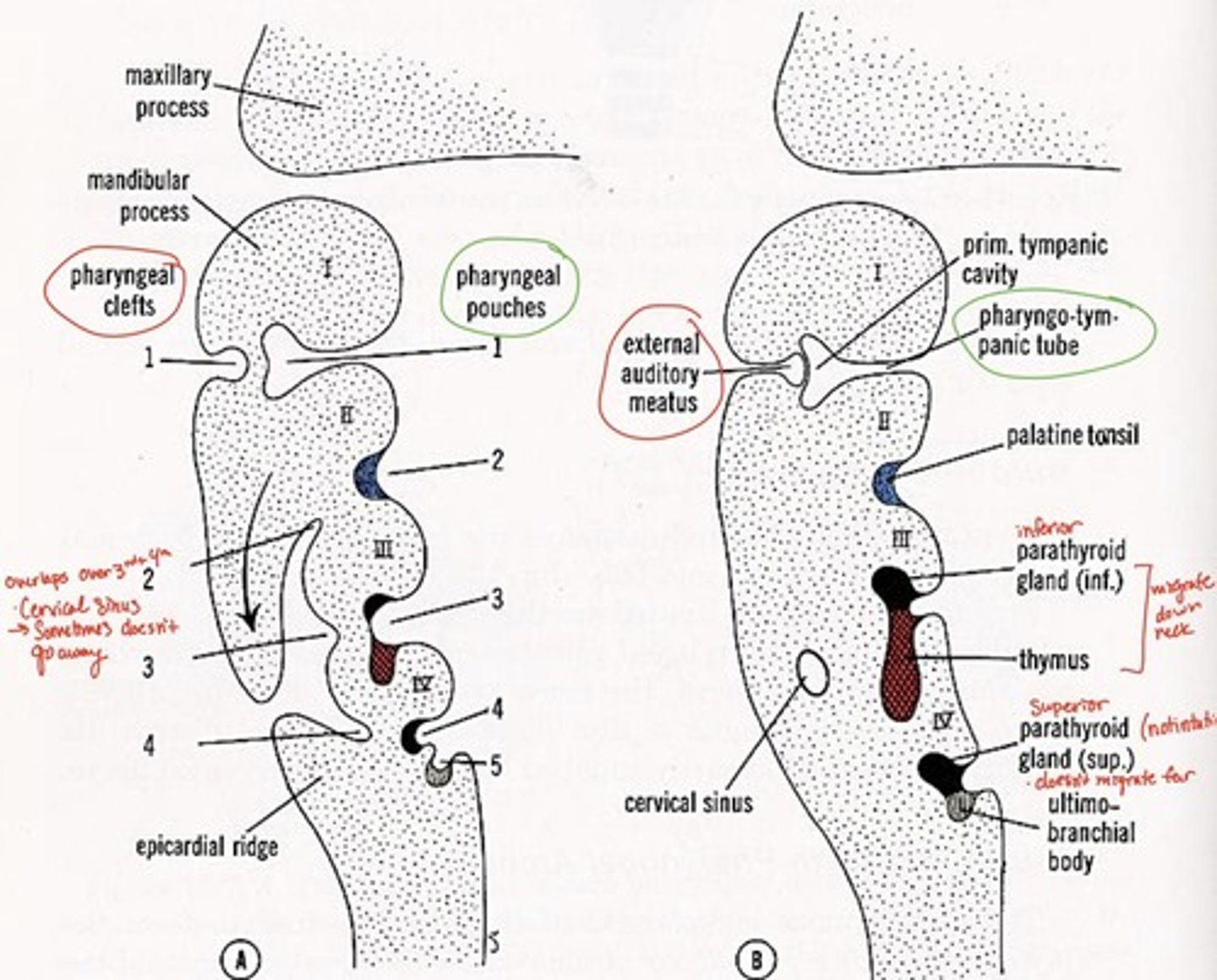
4th pharyngeal pouch forms what
superior parathyroid glands
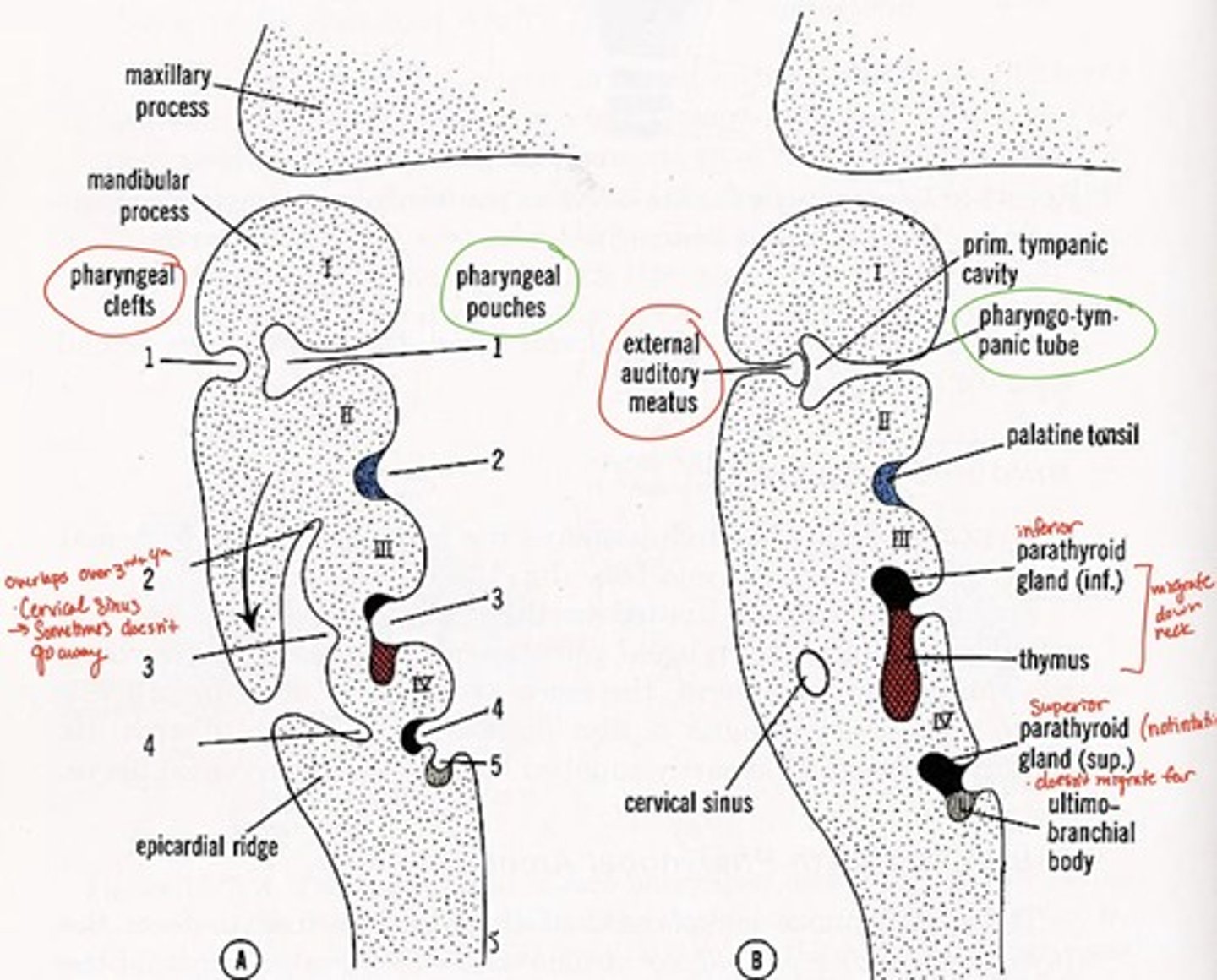
5th pharyngeal pouch forms what
ultimobranchial body--> fuses with thyroid gland, provides parafollicular cells to thyroid
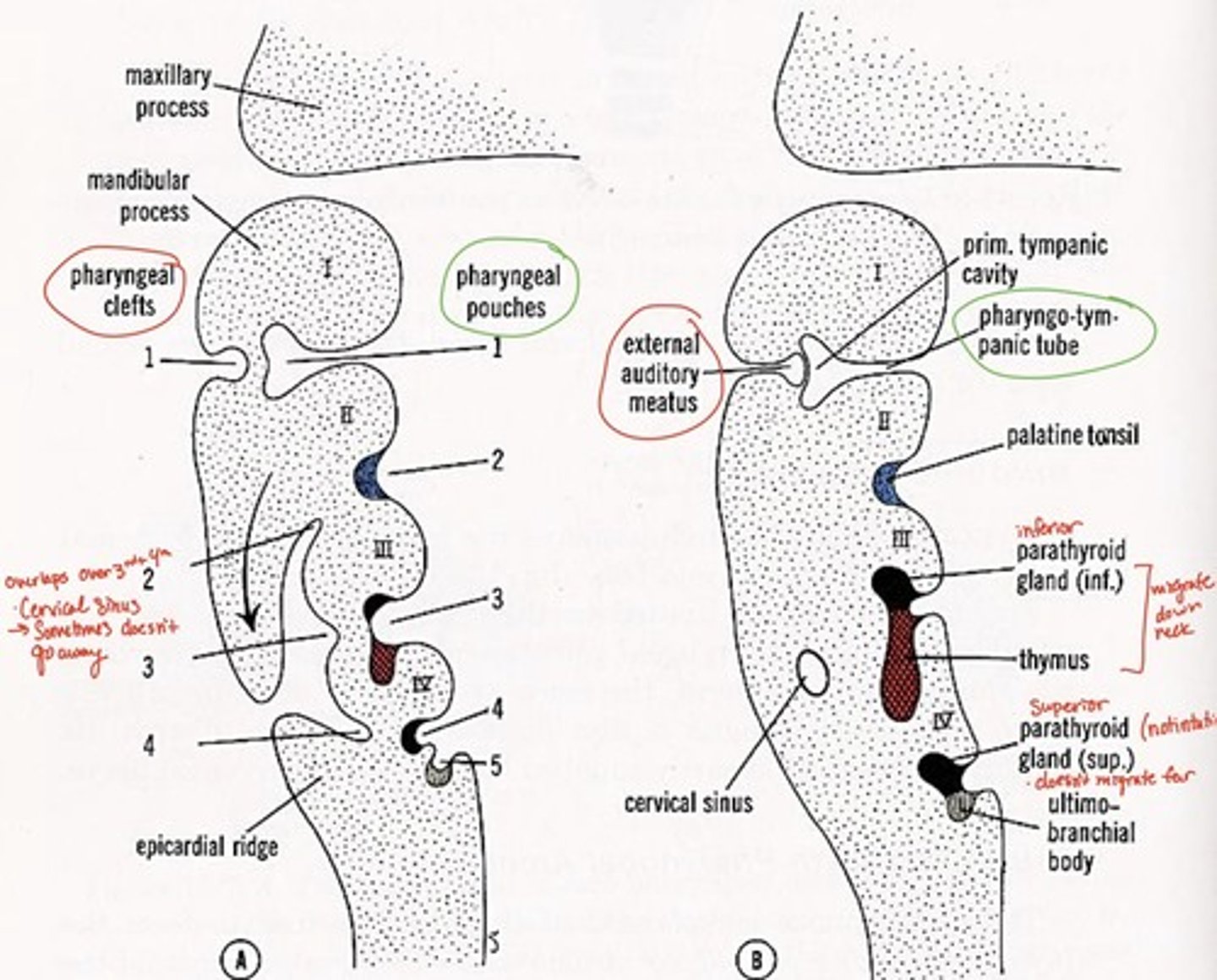
Pharyngeal grooves 2-4 covered by
arches 2 & 5 after 5th week
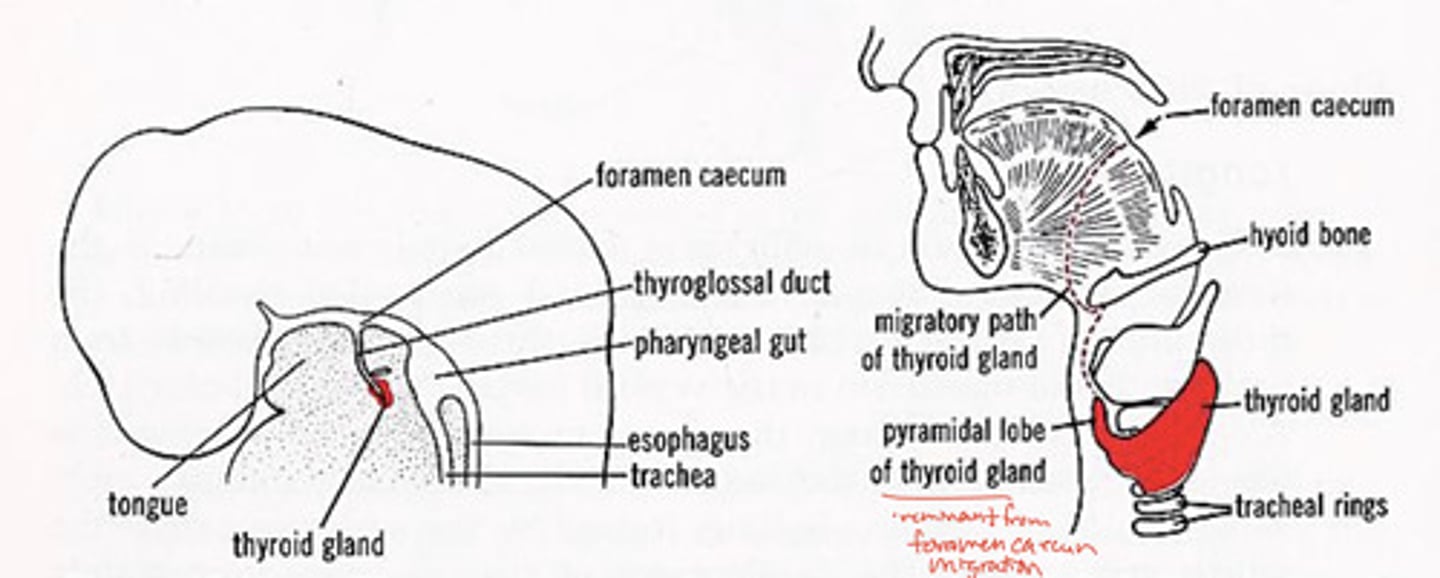
foramen caecum in development:
leaves pit in tongue, some thyroid gland sometimes left
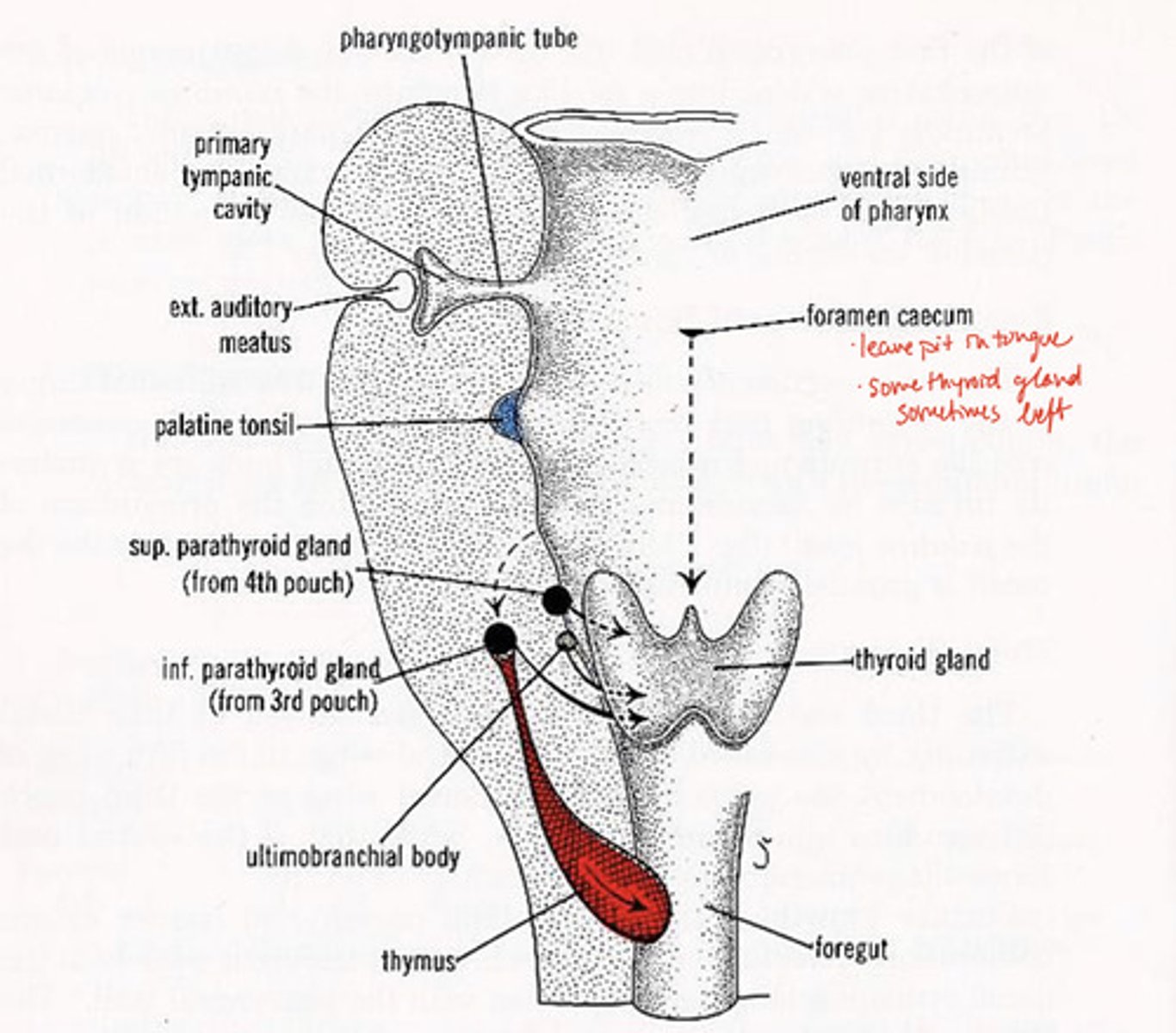
Tongue formation:
-lateral lingual swellings, tuberculum impar, copula
pyramidal lobe of thyroid gland
remnant from foramen caecum migration
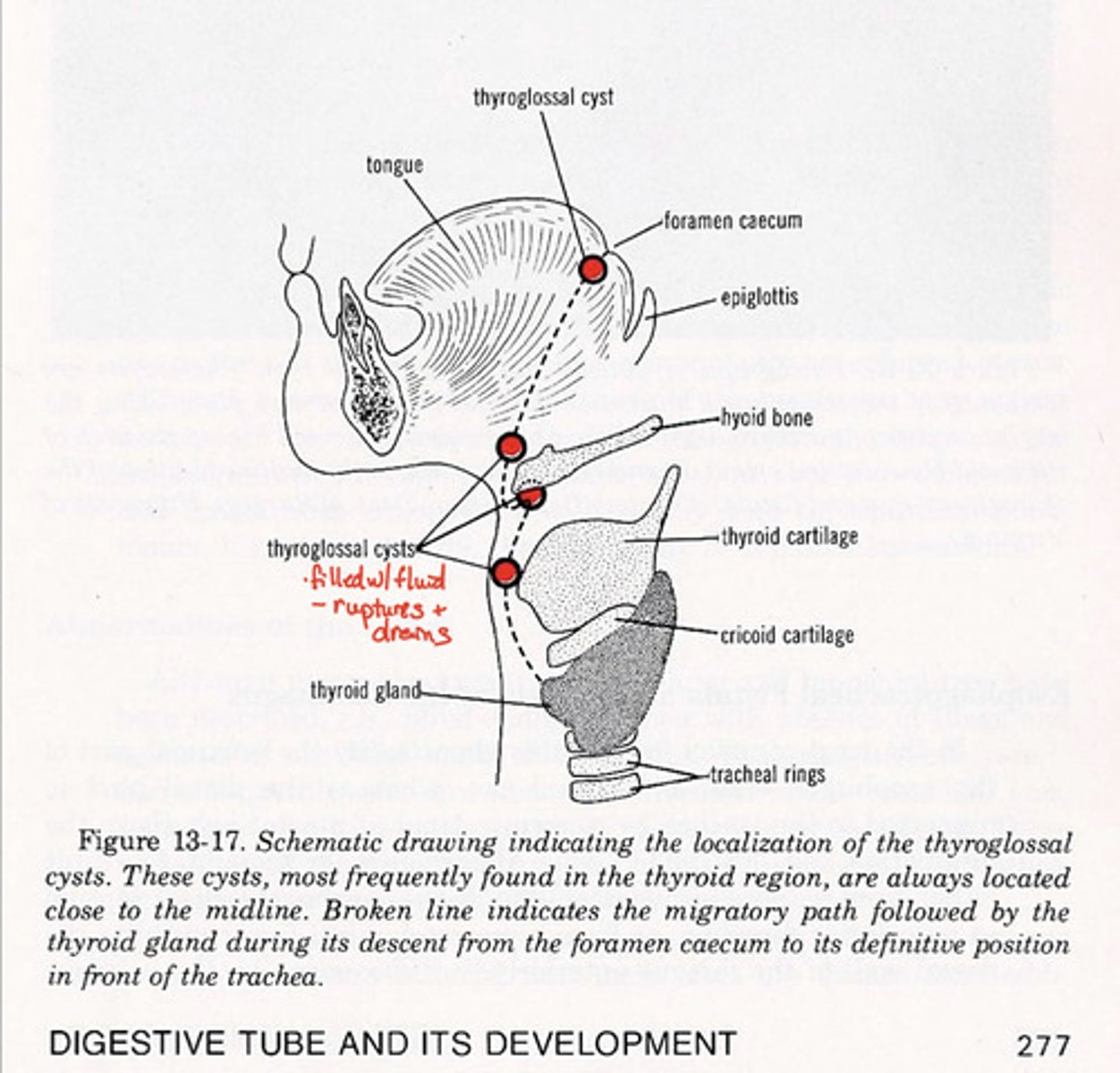
Thyroglossal cysts and fistulas
left over bits of thyroid gland as cysts
-fistula after cyst bursts
Branchial grooves/clefts adult derivative with arch number
external auditory meatus (arch 1-mandibular)
cervical fistula (arch 3)