Autosomal Dominant Disorders
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Expression
the severity or mildness of the phenotype
Things that influence expression
environmental factors
allelic variants in other genes
Penetrance
the chance that an individual will actually develop symptoms
Full Penetrance
fully penetrant → 100% chance of developing the disease
Partial Penetrance
partial penetrance → alleles manifest a phenotype in x % individuals
Hypomorphic AKA Loss Of Function AKA Haplo-insufficiency
produces a protein with reduced activity
neomorphic
new activity or novel protein product
antimorphic aka dominant negative
activity or product antagonises the activity of the normal gene product
hypermorphic
produces a protein with increased activity
Features of Autosomal Dominant
vertical degree pattern with multiple generations affected
each affected person normally has 1 affected parent
males and females are equally affected and likely to pass the condition on
variable expressivity and age-related penetrance
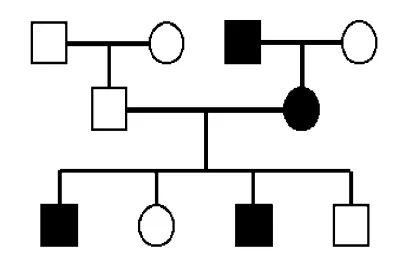
Chances of effected child
Sudden appearances of autosomal dominant disease?
de novo mutations and germline mosaicism
Expansion Repeat Disorders
dynamic mutations (increased number of repeats of a trinucleotide DNA sequence)
can cause the resulting protein to function improperly
how does slippage and mispairing during DNA replication increase repeat number?
backwards slippage
repeat expansion forms a hairpin
hairpin repeats are incorporated into DNA in the next replication
Watch video to visualise***
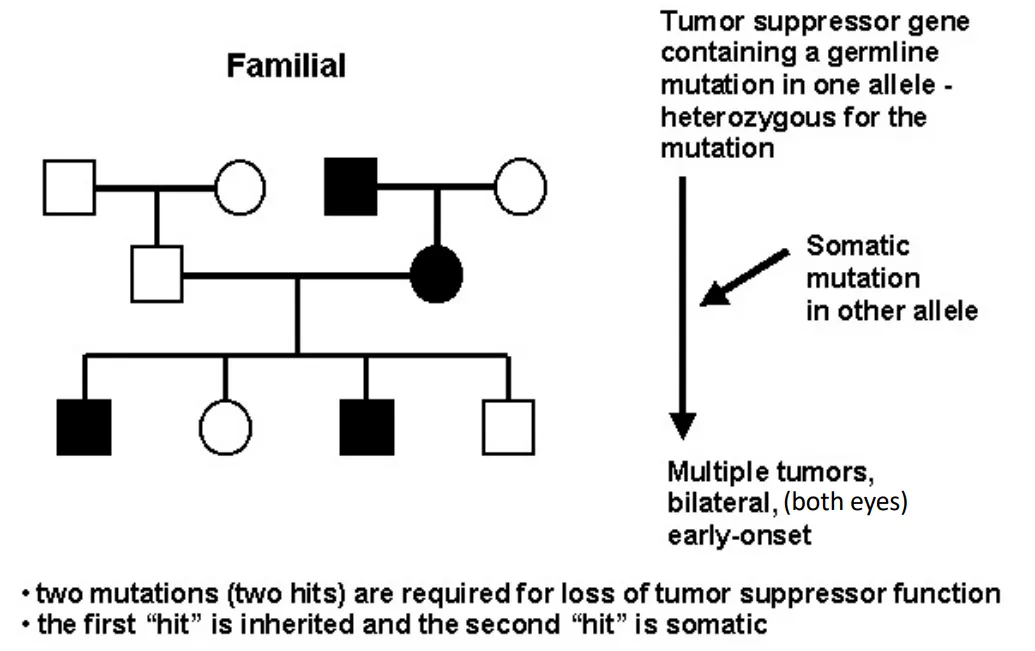
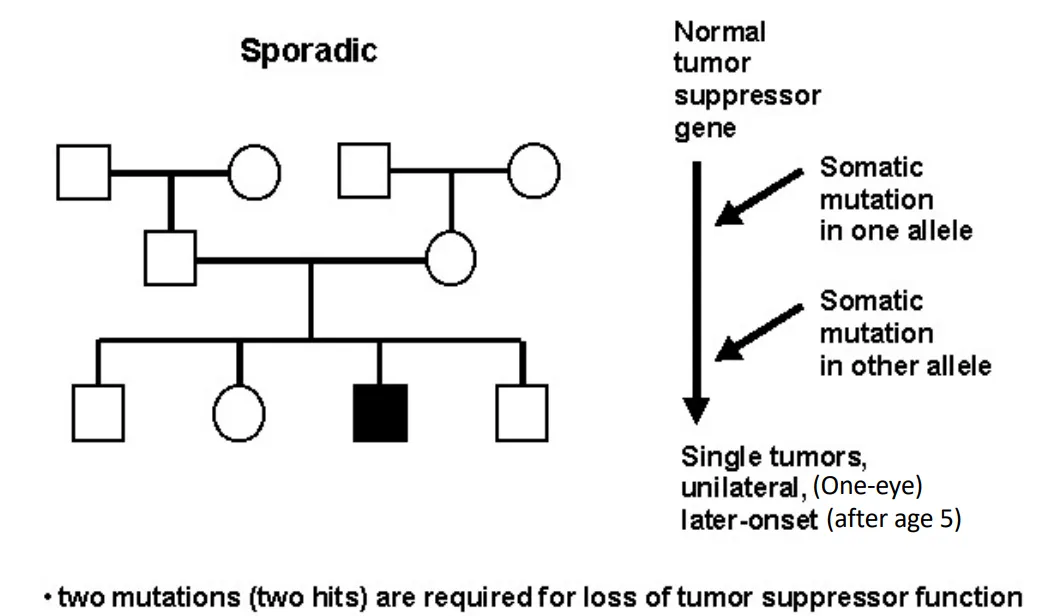
how are diseases inherited according to Knudson's two-hit hypothesis?
familial = inherit 1 mutation, 2nd develops somatically
sporadic = requires 2 somatic mutations
how is pre-symptomatic testing of family members at risk of an AD disorder done?
test an affected family member for the family-specific mutation
confirm the diagnosis of the family member at risk (acceptable if treatment is available)
offer pre-symptomatic testing or assess risk for recurrence
why does gene therapy work better for recessive traits?
replaces nonfunctioning genes with the correct version
How could gene therapy work in Autosomal Dominant disorders
→ Using anti-sense rna
antisense RNA inhibits gene expression
Process of using antisense DNA
start with antisense siRNA complementary to an mRNA target region
siRNA foms a complex that recognises target region
target region is cleaved
loss of protein synthesis (loss of function)
Achronoplasia | Hypochondroplasia → Gene and Mutation
FGFR3 (fibroblast growth factor receptor 3)
Normal Function → codes for a TKR responsible for signaling growth → limits bone formation (in long bones)
Cause of Mutation → both 80% de novo
Achronoplasia | Hypochondroplasia → How does mutaton effect function
gain-of-function (hypermorphic → receptor constitutively active)
inhibited proliferation and hypertrophy of chondrocytes in growth plate cartilage
increased endochondral ossification and cartilage matrix production
Achronoplasia | Hypochondroplasia → Penetrance
100% in both
Achondioplasia → Most common mutation
p.Gly380Arg
the achondroplasia mutation affects [what part] of the receptor?
transmembrane domain
Achrodoplasia → If two heterozygotes have kids
2/3 affected (dwarfism)
1/3 normal height
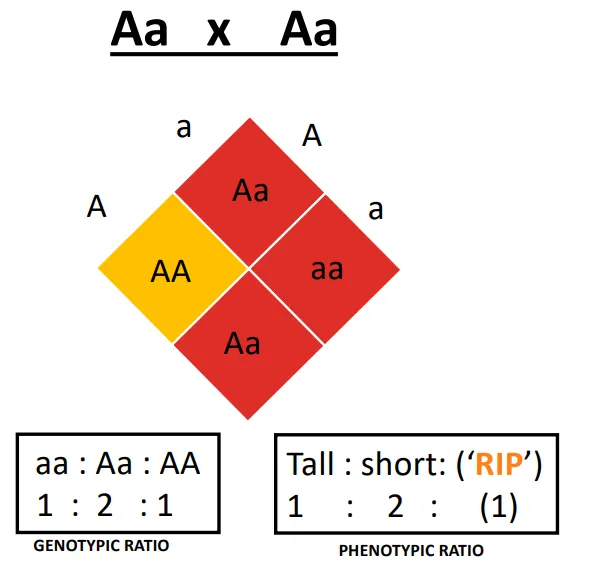
why is there a higher than normal frequency of miscarriages and stillbirths in achondroplasia?
homozygosity for the mutant allele (AA) is incompatible with life
Achondroplasia | clinical features
abnormal bone growth → short stature with disproportionately short arms and legs
large head and prominent forehead
trident hands
delayed motor development
intelligence and life span normal
with achondroplasia, why is there is an increased risk of death in infancy?
spinal cord compression/ upper airway obstruction (bone does not grow wide enough)
Hypochondroplasia | Common mutations
p.Asn540Lys
p.Lys650Met
the hypochondroplasia mutation affects [what part] of the receptor?
first TK domain
Hypochondroplasia | Clinical Features
normal birth weight and length
disproportion in limb trunk length (mild and easily overlooked during infancy)
typically present as toddlers or school-aged children with failure to grow
short stature with disproportionate limbs as they age
Difference between A and Hypo chondroplasia clinical presentation.
no trident hands or facial features in hypochondroplasia
motor milestones are usually normal in children with hypochondroplasia
HD | Gene and Mutation
HTT gene
glutamine (CAG) repeats in the HTT protein
HD | effect of phenotype
HTT protein aggregation in cells of the caudate nucleus→ cell atrophy and death
HD | Clinical Features
progressive motor disability featuring chorea (jerky involuntary movement)
cognitive decline
mental disturbances
changes in personality and/ or depression
FHx consistent with AD inheritance
HD → Number of CAG Repeats | Normal
10-26
HD → Number of CAG Repeats | With HD
36-121
HD → Number of CAG Repeats | Intermediate Alleles
27-39
the person is not at risk of developing symptoms of HD
but may be at risk for having a child with an allele in the abnormal range
HD → Number of CAG Repeats | Alleles between 36 -39
reduced penetrance for symptomatic HD (may or may not develop symptoms)
adult onset of HD if they have 40-55 repeats
Adult on onset of HD | Number of Repeats
40-55
Juvenile onset of HD | Number of Repeats
>60
Is pentreance 100% in HD?
no
need >40 repeats for 100% penetrance
Anticipation
phenomenon in which there is increased disease severity and/ or earlier age of onset in successive generations
Anticipation in HD Transmission
more likely in paternal transmission (with large expansions of >7 CAG repeats)
arises from instability of the CAG repeat during spermatogenesis
HD Treatment
no treatment or cure
potentially gene therapy (HTT gene silencing with siRNA)
Myotonic Dystrophy | Gene and Mutation
1. DMPK gene
2. >37 CTG repeats
is penetrance 100% in Myotonic Dystrophy?
no, need >50 CTG repeats for 100% penetrance
Myotonic Dystrophy | Effected Organs
skeletal/ cardiac/ smooth muscle
eyes
endocrine system
CNS
Myotonic Dystrophy | Phenotypes
mild
classic
congenital
The CTG repeats increase from mild → congenital | mild has least repeats
The age of onset decrease from mild → congenital | mild has later onset
life expectancy decreases from mild → congenital | mild has longer life expectancy
Management of Myotonic Dystrophy
assistive devices (eg. ankle-foot orthoses, wheelchairs)
symptomatic treatment
hypothyroidism
pain management
arrhythmia
cataract removal
hormone replacement therapy for males with hypogonadism
surgical excision of pilomatrixoma (benign hair follicle tumor)
Retinoblastoma | Gene and Mutation
loss of function in a tumor suppressor gene (Rb gene)
Retinoblastoma | Normal Function
Normal → Rb protein normally regulates G1 → S phase transition (cell cycle progression checkpoint)
Retinoblastoma | Mutated Function
Mutated → loss of inhibiting function → uncontrolled cell cycle progression
Tell Tale Sign of Retinoblastoma
leukocoria (white pupils, clearer in photos)
Retinoblastoma | When and How does it begin?
etal development where retinoblasts are rapidly dividing
Retinoblastoma | Inheritance Patterns
familial or sporadic retinoblastoma (Knudson's two-hit hypothesis)
due to loss of function of both alleles of the RB gene
Retinoblastoma | Penetrance
90%
Why is familial form Retinoblastoma more severe?
multiple bilateral tumors vs single unilateral tumors
Familial Retinoblastoma
Sporadic Retinoblastoma
Neurofibromatosis | Mutation
partial or complete loss of function
Neurofibromatosis | Inheritance Pattern
Knudson’s 2-hit hypothesis
1st mutated allele is inherited
2nd allele has been somatically inactivated
Neurofibromatosis | Penetrance
both 100% ( NF1 and NF2)
Lifespan for NF1 and NF2
normal for NF2 but 8 years lower for NF1
Clinical Features of NF1
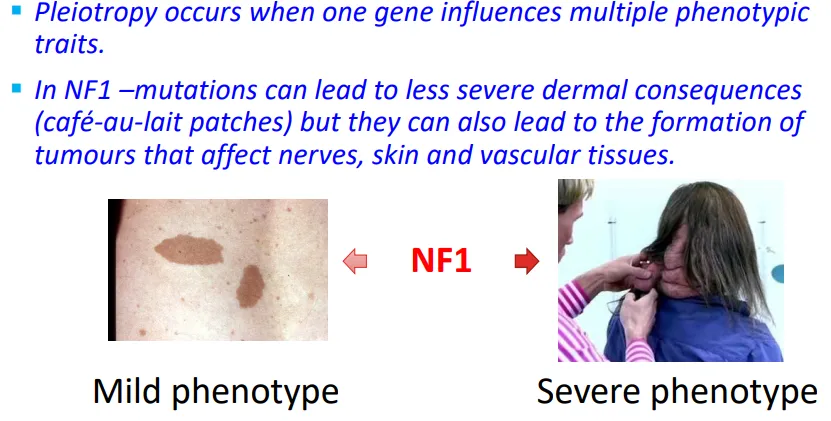
changes in pigmentation (café-au-lait)
growth of tumors along nerves in the skin/ brain
Pleiotropy in NF1 | how does pleiotropy explain the variability of features?
Gene Locus of NF1 gene
17q12
NF1 gene | Normal Function
tumor suppressor gene producing neurofibromin
prevents cell growth through inhibiting the oncogene Ras
NF1 gene | Treatment
surgical removal of disfiguring or uncomfortable discrete cutaneous or subcutaneous neurofibromas
Clinical Feature of NF2
growth of noncancerous tumours in the nervous system → hearing loss/ deafness
vestibular schwannomas (acoustic neuromas)
gene locus of NF2
22q12.2
NF2 gene | Normal Function
tumour suppressor gene producing merlin
prevent cell growth through contact-mediated growth inhibition
Treatment for NF2
surgical removal of vestibular schwannomas
awareness of problems with balance and underwater disorientation (prevent drowning)
Germline Mutations
A mutation that occurs in gametes (eggs or sperm) and is present in each cell
of the body and can be passed onto the next generation
Lethal Allele
An allele that causes death before reproductive maturity or halts prenatal
development
Proto-oncogene
genes that normally help cells grow and divide.
Upon mutation it can become turned on when it is not
supposed to be, at which point it's now called an oncogene.When this happens, the cell can start to grow out of control, which might lead to
cancer
Somatic Mutation
mutation that occurs at some time during a person’s life and is present
only in certain cells and cannot be passed onto the next generation.