2 Relations on Statements, Negation of Statements, The Conditional, Valid and Invalid Arguments (Theory)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What are relations?
(1) are conditional or biconditional statements that are materially true in the real world
Implication (Notation and Description)
(1) p ⇒ q
(2) "if, then"
Equivalence (Notation and Description)
(1) p ⇔ q
(2) "if and only if"
What does it mean to negate a statement?
(1) to find a way to make the expression false
Negating Simple Mathematical Statements
(1) we add the word "not" when appropriate
(2) ~p
Simple rule to negating statements.
(1) distribute the negation and flip the operation
6 Equivalent Forms of the Conditional Statement
Recall: Conditional is "if, then;" "if p, then q;" "p ‒> q"
(1) q if p
(2) p only if q
(3) p is sufficient for q
(4) q is necessary for p
(5) All p are q
(6) Either not p or q
Conditional of p and q
p→q
Converse of p→q
q ‒> p (switch order)
Inverse of p→q
~p ‒> ~q (negate)
Contrapositive of p→q
~q ‒> ~p (switch and negate)
Tautology
(1) logically true statement that is true in all circumstances
Negation Equivalence: ∼ (p ∧ q)
∼ (p ∧ q) ⇔∼ p ∨ ∼ q
Negation Equivalence: ∼ (p ∨ q)
∼ (p ∨ q) ⇔∼ p ∧ ∼ q
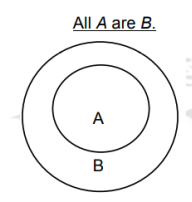
Euler Diagram for the Quantifier: All
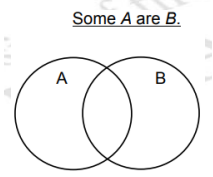
Euler Diagram for the Quantifier: Some
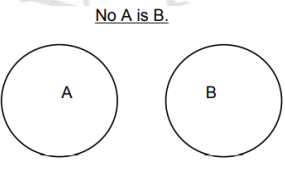
Euler Diagram for the Quantifier: No
Validity of Arguments: If an argument is valid, there should only be…
(1) one possible conclusion
Modus Ponens
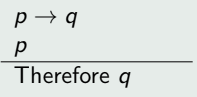
Modus Tollens
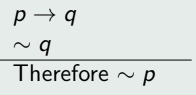
Syllogism
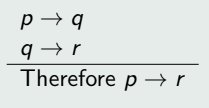
3 Types of Valid Argument Forms
(1) modus ponens
(2) modus tollens
(3) syllogism
Fallacy of the Converse
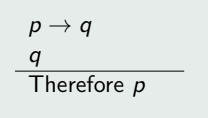
Fallacy of the Inverse
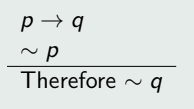
2 Types of Invalid Argument Forms
(1) Fallacy of the Converse
(2) Fallacy of the Inverse
What are the 7 types of fallacies?
(1) fallacy of the converse
(2) fallacy of the inverse
(3) ad hominem
(4) ad populum
(5) appeal to authority
(6) false cause
(7) hasty generalization
Ad Hominem
(1) attack the character instead of the argument itself
(2) hominem = human
Ad Populum
(1) when the argument is valid since many people believe it
(2) populum = population, populous, people, nation
Appeal to Authority
(1) because a famous person, who is not an expert in the pertinent field, supports it
(2) advertisements
False Cause
(1) correlates two events, even if unrelated
Hasty Generalization
(1) a generalization is made based on a few examples supporting the claim
(2) trap of inductive reasoning
What is Deductive Reasoning?
(1) bottom-up thinking
(2) general to specific
What is Inductive Reasoning?
(1) top-down thinking
(2) specific to general
Traps of Inductive Reasoning
(1) prone to error
(2) establish theorems, axioms, known facts before concluding
2 Step Process to Avoiding the Traps of Inductive Reasoning
(1) abstraction
(2) generalization