Sources of Power to the Farm - Heat Engine
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
189 Terms
A_______is an external combustion engine.
steam engine
_________have completely replaced the steam engine for all types of agricultural power applications.
Internal combustion engines
Most farm works are accomplished by machines powered by the_______
Internal Combustion Engine (ICE).
___________has completely replaced the steam engine (or External Combustion Engine) for all types of farm power applications.
Internal Combustion Engine (ICE).
The fuel or combustible fuel mixture is placed inside the cylinder in a_________and compressed before it is ignited. gaseous condition
gaseous condition
Since the is ignited and burned inside, the gas engine and all engines that operate in similar manner are called ICE.
fuel
The term "____" is often used synonymously with cylinder blocks.
engine block
Contains the______in SI engines and the fuel injectors in Cl engines and some SI engines
spark plugs
Between the head and the block, a______seals the combustion chambers, and water and oil passages.
cylinder head gasket
The______of an engine constitutes the basic and supporting portion of the engine power unit.
cylinder
The top of the piston is called the_____and the sides are called the skirt.
crown
The face on the crown makes up one wall of the combustion chamber and may be a_____or highly contoured surface.
flat
The piston is closed at one end and open on the other end to permit______attachment of the connecting rod and its free action.
direct
Counting from the top of the piston, the first and second rings are______, whose task is to control blowby.
compression rings
The middle ring is the_______, which keeps excess oil from the combustion space.
scraper
The last ring is the______, which is serrated to deliver oil to the bore.
oil ring
The connecting rod is connected to the piston through the_______.
piston pin
The end connecting the piston is known as the______and the other end is known as the _______.
The offset from the axis of rotation is sometimes called___________
crank throw or crank radius.
Has a harmonic balancer, or vibration dampener, mounted on the front where it muffles___________.
torsional vibration
The_______consists of the valves, camshaft, and other associated parts.
valve train
The valves control the flow of the incoming________and the outgoing exhaust gasses.
air-fuel mixture
The_______are larger than the exhaust valves, and many engines today have two intake and two exhaust valves per cylinder to improve efficiency and performance.
intake valves
The valves are operated by the action of the______, which has separate cams for the inlet, and exhaust valves and iIt rotates at half the speed of the crankshaft.
camshaft
The cam_______the valve against the pressure of the spring and as soon as it changes position the spring closes the valve.
lifts
The cam gets driven through either the______and chain system from the crankshaft.
gear or sprocket
It is marked with_____all around its perimeter.
tiny increments
The_____correspond to degrees of timing from the straight-up timing position of the camshaft and crankshaft.
marks
The electric ignition engine utilizes an_____produced by a spark plug located inside the combustion chamber to ignite the compressed air and fuel mixture.
electric spark
Fuel used is gasoline, and metering is done by a device called a_____.
carburetor
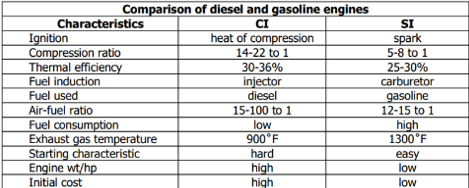
Comparison of diesel and gasoline engine
The events that occur in a 4SCE are:
These events (except ignition) occur over one stroke of the piston or _____of the crankshaft.
½ revolution
_______requires 4 strokes of the piston or 2 revolutions of the crankshaft.
One cycle
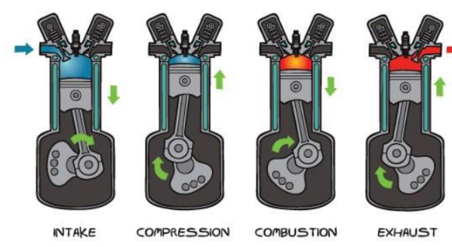
Four stroke cycle engine
_______engine is one in which two strokes of the piston are required to complete the necessary series of events required to produce one power stroke.
two-stroke-cycle
The stroke compressed air in the cylinder to ignite the______.
fuel oil
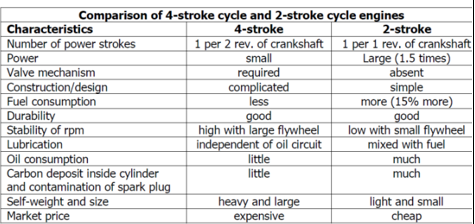
comparison of 4 stroke cycle and 2 stroke cycle engine
Small engines,________or engines used in motorcycles and even small cars have one, two or three cylinders.
stationary engines
Meter correct amount of fuel as demanded by the_______
engine load
The main difference between the turbocharger and the supercharger lies in the______.
power supply
turbocharger uses the_______for its energy. The exhaust will run through a turbine that will itself spin the compressor
exhaust stream
Turbochargers and superchargers are known as______. It means that either will compress the air flowing into the engine, which provides more power to the car.
forced induction systems
This creates a considerable amount of boost, which can be as much as more power into the engine.
50%
A_______is designed to improve the power output of an engine beyond its normal operating capacity. A normally aspirated engine uses a mixture of air and fuel that is pulled into it from vacuum created by the cylinders.
turbo charger
It increases the amount of air injected into the engine, which also allows more fuel to be injected and increases higher power______.
30%
______function is the same with turbo chargers except that they are engine driven rather than exhaust-gas driven.
Supercharger
The source of the power for the supercharger is in a belt connected _____to the engine. A supercharger will compress air of the atmospheric pressure, and create the boost by forcing air into the engine.
directly
it is used in spark ignition (gasoline engines) since the power from exhaust gases is low as a result of low compression ratio.
Oil pump
Oil filter
Oil lines
Sump tank