Biology B1.2- proteins
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is a polypeptide
A protein
What is the general structure of animo acids
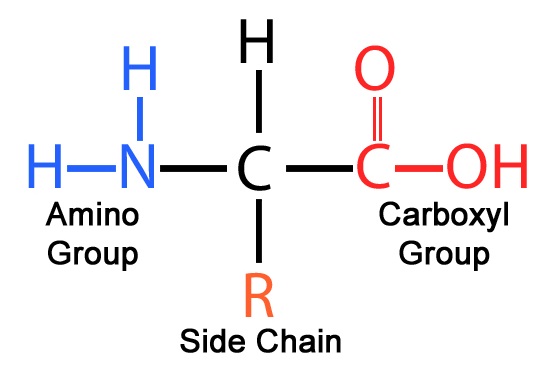
What is the R group in the structure of animo acids
variable group, changes every time
what is the carboxyl group
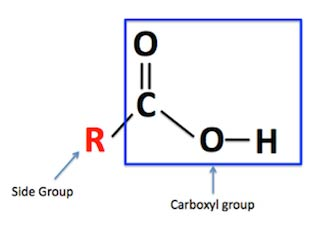
What do 2 amino acids make
Dipeptide + water
What does an amino acid and sulfur make
Disulfide bond
What is between the 2 amino acids
Peptide bond
How many different amino acids are there
20
Where are amino acids made
On a ribosome
How many amino acids can humans make
11
What are the sources of amino acids
Meat
Beans
What are genes
The code fir the sequences of animo acids
Describe fibrous proteins
Provides structure and support to cells and tissues
Collagen - skin, tendons, ligaments
Keratin- hair, nails, claws
long structural shape
insoluble in water
made up of repeated sequences of amino acids
Describe globular proteins
All enzymes - All amino acids
Eg. Hemoglobin
Do the things in the body - metabolic
tightly coiled
soluble in water
Denaturation definition
Breaking the bonds that hold a protein in shape
Proteins can be denatured by heat and a change in pH
genome definition
every complete set of genetic material in an organism and every organism has its own unique DNA
proteone definition
every organism has its own unique proteins
describe amino acids
some are hydrophobic and fold inwards
some are hydrophilic and connect with water which creates a hydrogen bond
when in a solution, they change it
some are ionized
what happens to the change of properties of the R groups
it gives rise to various bonds and the “folding” of polypeptides
does hydrophobic fold in or out
fold in
does hydrophilic fold in or out
fold out
describe primary structures
basic order of animo acids
in the linear polypeptide protein chain
coded by genes
joined by peptide bonds
first step
DNA informs the primary structure
what are the bonds in a primary structure
only polypeptide bonds
describe secondary structure
2nd level of folding
either forms of alpha helix or beta - pleated sheet
forms regular reapeating intervals
what structure are fibrous proteins
secondary level
what are the bonds in secondary structures
polypeptides
hydrogen
describe tertiary structure
3D protein shape
results from the folding of the polypeptide
sulfur is in the R group
hydrophobic fold inside since they dont like getting wet
what are the bonds in tertiary structure
hydrogen
disulfide
ionic
polypeptide
describe a disulphide bond
2 adjacent cyteine amino acids which have sulfur in the R group forming a covalent bond- leading to a folding in the chain
describe tertiary structure
not every protein gets to this level
only globular proteins get to this or tertiary level
combination of different polypeptide chains joined together
includes all level structures
what are the bonds in quaternary structure
ionic
polypeptide
disulfide
hydrogen
describe non conjugated quaternary structures
quaternary structure without a prosthetic group
describe a prostheic group
non protein molecules
has 2 alpha and 2 beta chains with a Heme group (contains ions)
what are conjugated quaternary structure
quaternary structure with prosthetic group
organisation of globular proteins
tertiary or quaternary structure
organization of fibrous proteins
secondary structure
Describe collagen quaternary structure
Secondary structure
String and stretchy but short
Building tissues that hold the body together
Fibrous proteins with polypeptide chains
Repeating sequence = regular collagen shape
Describe insulin non conjugated structure
Short genes in the human goenum
Protein hormone
describe hemoglobin conjugated structure
Large protein
Function is to reversibly to O2 in the lungs
what is the order of the structures
Primary → secondary → tertiary→ quaternary