Forebrain Dz
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Most important clinical signs of forebrain dz
-Behavior change
-Contralateral blindness/dec menace
-Ipsilateral head/body turn, circling
-Contralateral limb deficits
-Seizures
Dog infectious forebrain dz
-Neospora caninum
-Toxoplasma gondi
-Rabeis
-Distemper
-Cryptococcus
-Ehrlichia, Rickettsia, Borrelia, Anaplasma
-Bartonella/coccidiodomycosis in endemic areas
Cat infectious forebrain dz
-Toxoplasma gondii
-FIV
-FeLV
-FCoV
-Cryptococcus
-Coccidioidomycosis in endemic areas
CSF collection rules
-Max volume 1mL/5kg
-Sample caudal to the lesion
CSF when NOT to collect
-don't have MRI
-inc ICP
-coagulopathy
-do not collect from cervical area if chiari-like formation, AA instability, or cervical trauma
Causes of neutrophilic pleocytosis
-GME/NE
-Bacterial meningitis/meningoencephalitis
-Fungal
-FIP
-Post myelography, hemorrhage, trauma, neoplasia
-SRMA
Causes of mononuclear pleocytosis
-GME/NE
-CNS lymphoma
-Viral (CDV)
-Bacterial meningitis/meningoencephalitis
-SRMA
Causes of mixed pleocytosis
-GME
-Infarct
-Bacterial meningitis/meningoencephalitis
-Protozoal
-Fungal
-SRMA (chronic)
Causes of eosinophilic pleocytosis
-Eosinophilic ME
-Parasitic
-Protozoal
-Fungal
Causes of hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatic dz (chronic > acute), PSS
Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy
The liver can't clear ammonia, so it travels to the CNS
Diagnostic tools for hepatic encephalopathy
-microcytosis
-ALT/ALP
-bile acid stim
-AUS, liver biopsy
Treatment plan for hepatic encephalopathy
-IVF, enemas to flush out ammonia
-lactulose to bind NH4+
-highly digestible protein
-antibiotics to decrease urease producing bacteria
Causes of hypernatremia
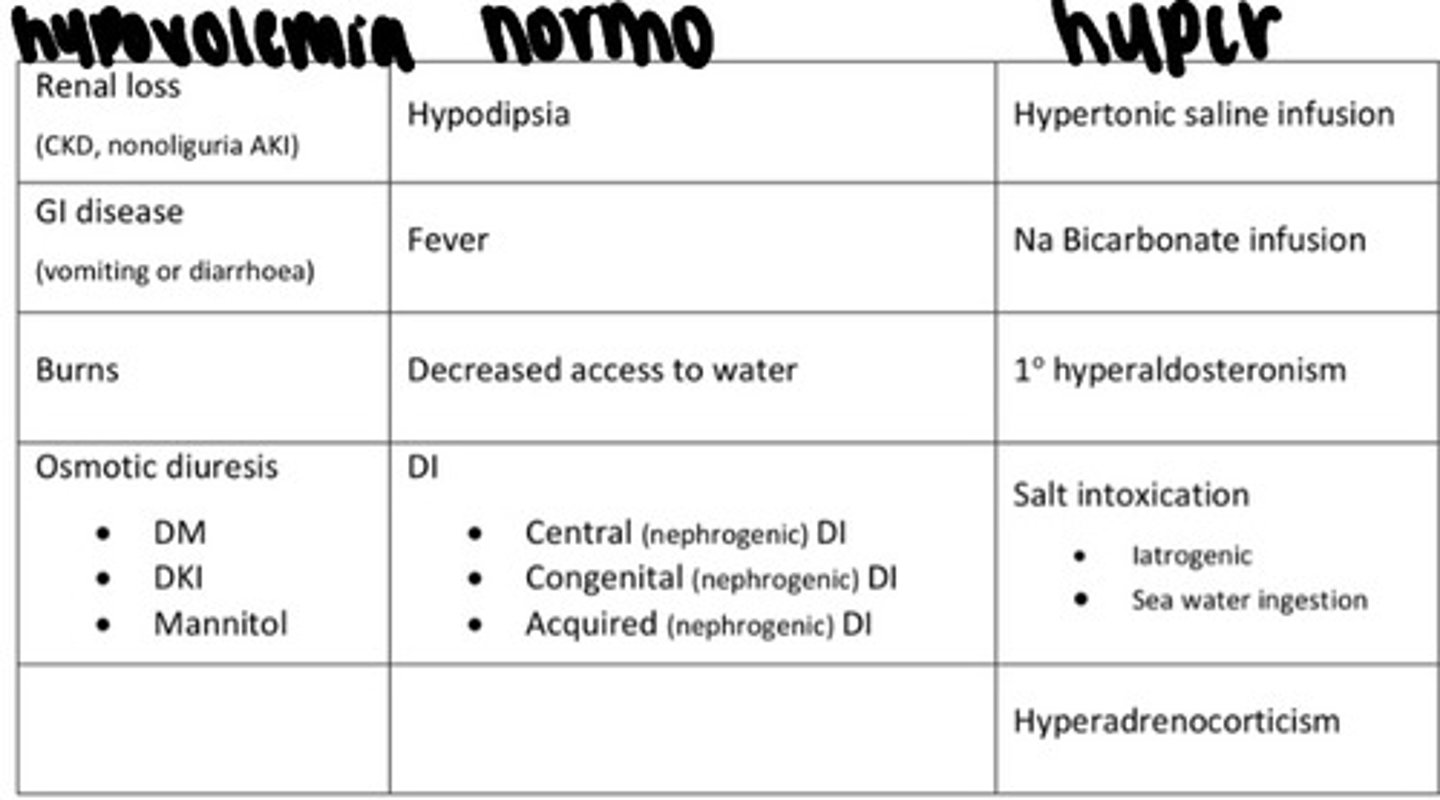
Pathogenesis of hypernatremia
Acute hypernatremia causes shrinkage of brain cells that can lead to rupture of cerebral vessels
Treatment for hypernatremia
Correct slowly over 48-72hrs, not faster than 0.5mEq/L/hr. Need to evaluate sodium levels every 4 hours!

Pathogenesis of hyponatremia
-acute>chronic will cause brain edema
-must correct slowly to prevent cell shrinkage and irreversible nerve damage
Causes of hyponatremia
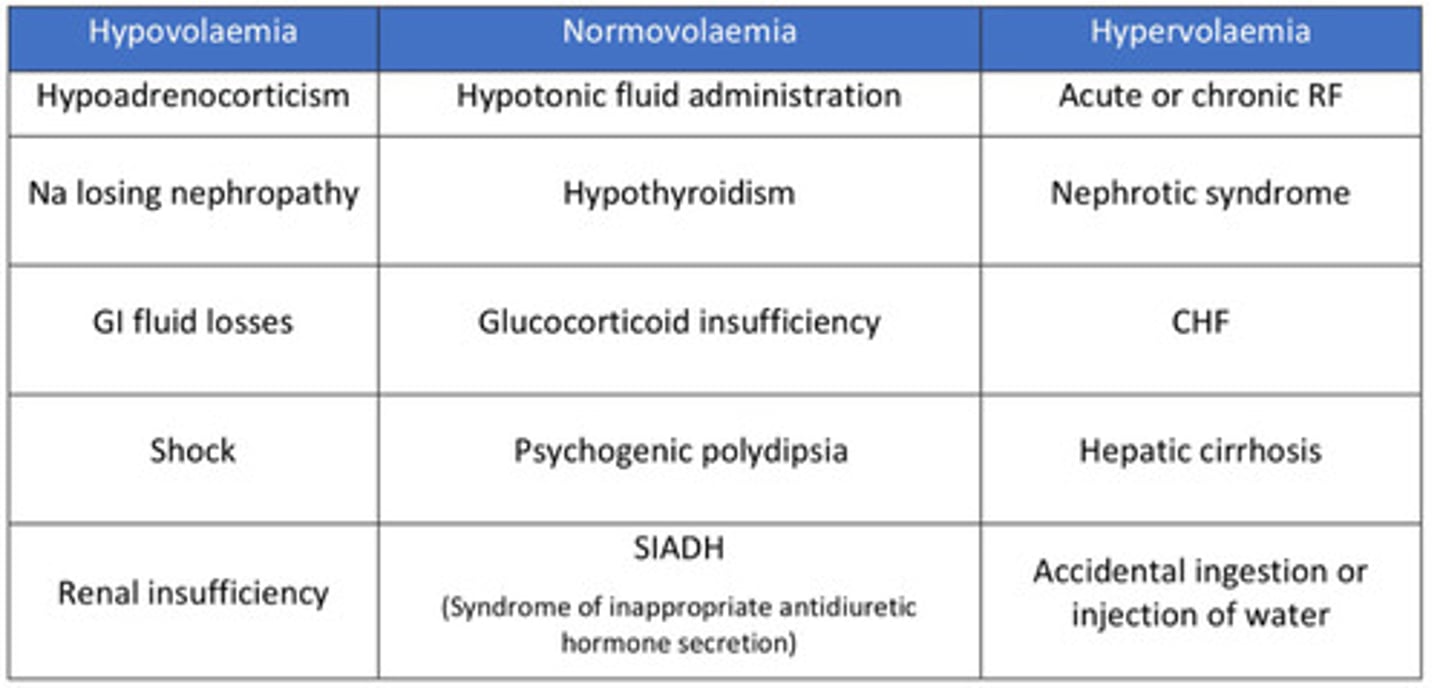
Treatment of hyponatremia
slow correction 0.5-1mEq/L/hr

Hypoglycemia treatment
0.5-1ml/kg 50% dextrose diluted with saline to minimize phlebitis/hemolysis
Neoplasia prevelance
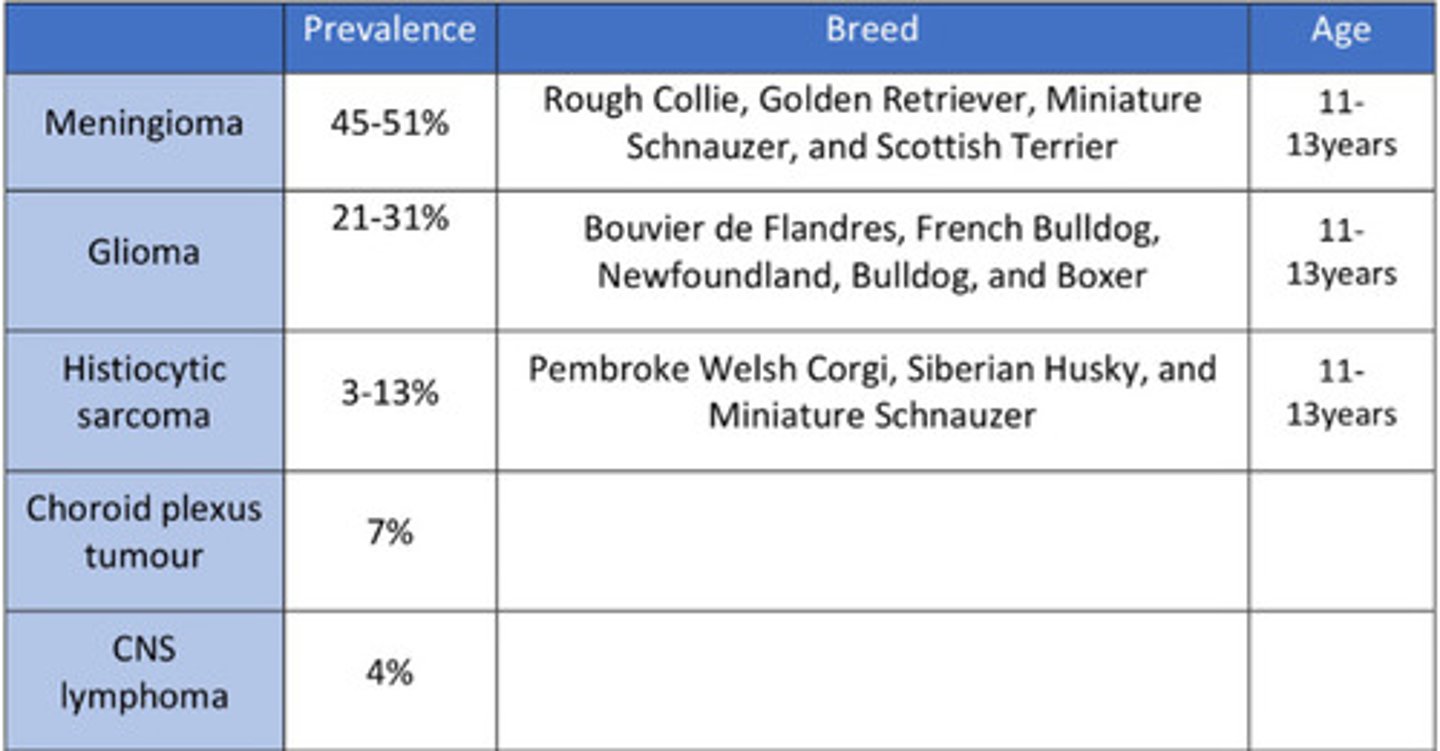
Neoplasia diagnosis
MRI, histopath (only way to definitively diagnose)
Hydrocephalus breed disposition
Maltese, yorkie, eng bulldog, chihuahua, lhasa apso, pom, toy poodle, boston, pug, pekignes
Hydrocephalus treatment
-glucocorticoids
-furosemide
-omeprazole
-acetazolamide
-SX
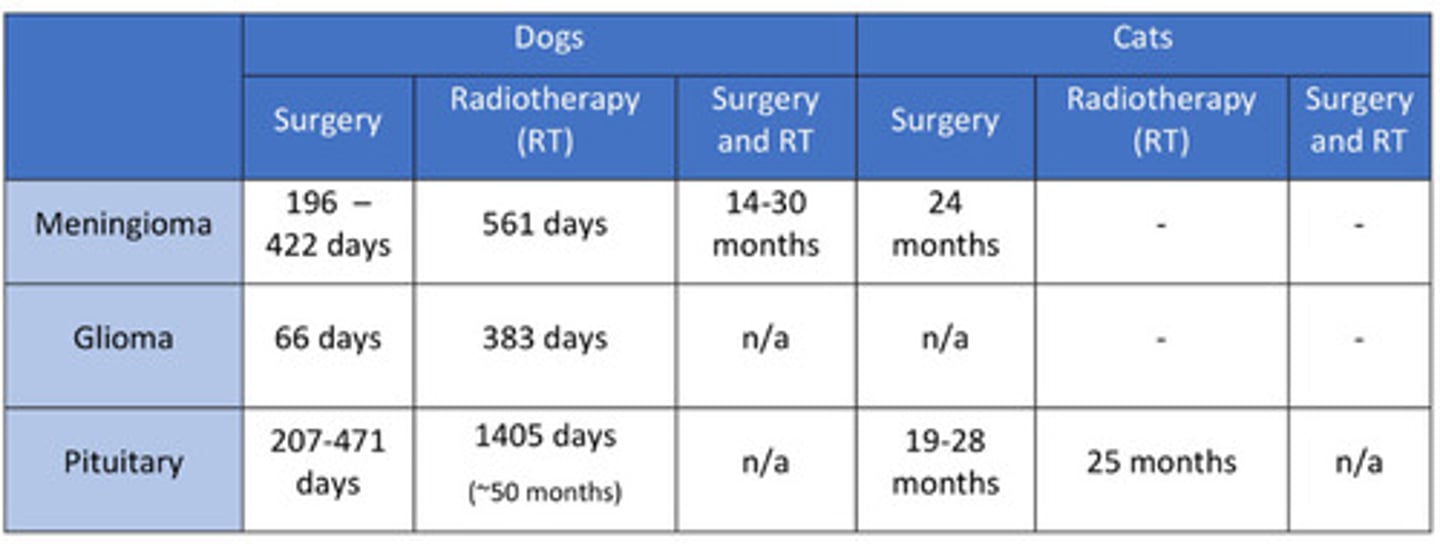
Neoplasia treatment/prognosis
Give palliative prednisone 0.25-0.5mg/kg BID
Canine cognitive dysfunction treatment
-add MCT to diet
-selegiline
-cognitive enrichment