Sleep Apnea and Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome (Smarty PANCE)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Define obstructive sleep apnea
Intermittent obstruction of air flow (typically level of oropharynx) produces periods of apnea during sleep
How long is the apneic period in OSA?
Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when your breathing is interrupted during sleep, for longer than 10 seconds at least 5 times per hour (on average) throughout your sleep period
Risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea?
1. Obesity
2. Structural issues
3. Family history
4. Alcohol and sedatives make this worse
S/s of sleep apnea?
- Morning headaches
- Daytime sleepiness
- Snoring
- Personality changes
- Decreased intellectual function
- Systemic HTN
- Pulmonary HTN
- Polycythemia
Diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea?
Polysomnography
Treatment of obstructive sleep apnea?
The strongest recommendations for treatment of obstructive sleep apnea include weight loss and continuous positive airway pressure devices.
Alternative treatments include positional therapy, mandibular advancement devices, and surgical interventions.
Last resort for severe or life-threatening OSA?
Tracheostomy
Complications of OSA?
1. Increase in pulmonary vascular resistance (can lead to pulmonary hypertension and for pulmonale)
2. Systemic HTN (due to increase in sympathetic tone at night)
3. Increased in RBC mass (secondary polycythemia)
One of the MC manifestations of OSA?
Daytime sleepiness (but patient tends to accommodate to this, so may not complain of it)
What is associated with a 8 to 12 fold increased risk of OSA?
Obesity is the leading risk factor for obstructive sleep apnea.
Obstructive sleep apnea can occur in children due to?
Obstructive sleep apnea can occur in children due to adenotonsillar hypertrophy.
Apnea-hypopnea index > ____ per hours confirms OSA?
5
What else may a patient with OSA have?
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome
What sleeping position is ideal for patients with OSA?
Lateral (not supine)
Common surgical procedure for OSA?
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty
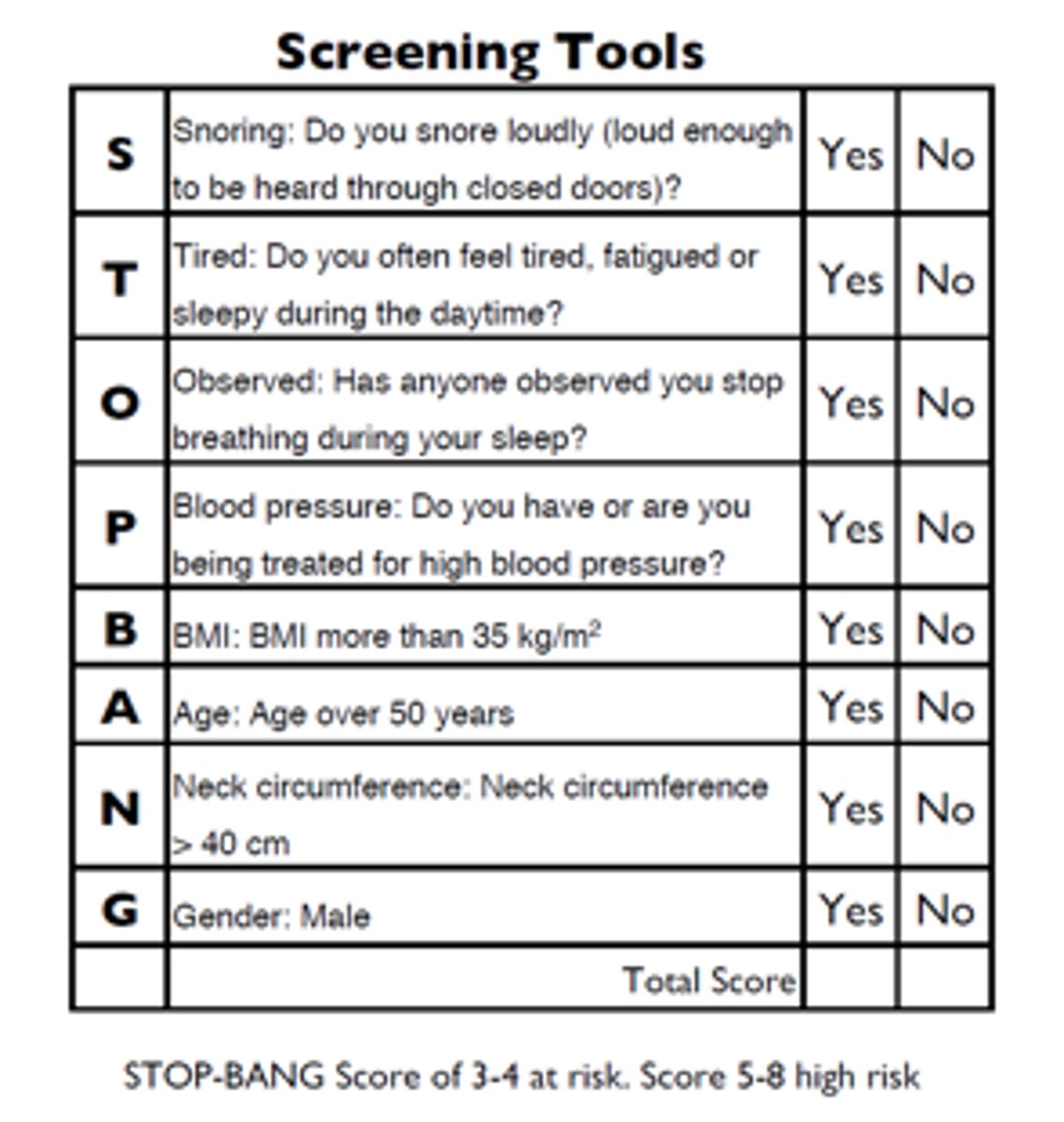
STOPBANG?
S - Snoring audible behind closed doors
T - Tired during the day
O - Observed pauses in breathing
P - blood pressure high
B - BMI >35
A - Sge >50
N - Neck circum.. >40 cm
G - Gender male
Define obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS)
Combination of obesity (BMI > 30) + awake arterial hypercapnia (PCO2 >45 mmHg) in the absence of other non causes of hypoventilation. a.k.a Pickwickian Syndrome
S/s of obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS)?
Pretty much the exact same as OSA. These two diseases are often concurrent.
What do some obese patients get OHS and some don't?
Has to do with distribution of fat (central vs. peripheral like in the hips)
T or F: Basal O2 consumption and CO2 production are increased in morbid obesity.
True.
Pathophysiology of OHS?
Thought to be a combination of these 3 main things:
1) Obesity-related changes in respiratory system
2) Alterations in respiratory drive
3) Breathing abnormalities during sleep
How does obesity change the respiratory system?
1. Excessive adipose tissue reduces lung volume
2. Fat deposits restrict diaphragmatic movement
3. Gas gets trapped due to premature airway closure (generates intrinsic, auto PEEP)
4. Atelectasis of lower lobes
Management of obesity hypoventilation syndrome?
Weight loss +/- CPAP at night
What ABG would you expect to see in a patient who has chronically been hypoventilating?
Primary respiratory acidosis with full metabolic compensation (so pH normal, CO2 very high, and bicarbonate high)
What else could help people with OHS?
- Bariatric surgery
- Tracheostomy
Ninety percent of patients with OHS have at least some coexisting ____.
obstructive sleep apnea
What type of respiratory failure do patients with OSA/OHS typically get?
Chronic hypercapnic respiratory failure (but some actually present w/ severe hypoxemic respiratory failure on top of that when they are hospitalized)
Is there typically reduced respiratory muscle strength in obesity?
Yes
Individuals with OHS adopt a pattern of breathing characterized by ___ tidal volume and ______ respiratory rate, which increases anatomic dead space leading to CO2 accumulation.
Low TV
Increased RR