Pulmonary Function Testing (PFT)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
what are the three indications for pulmonary function testing (PFT)
to evaluate signs/symptoms (like hypoxemia or dyspnea)
to assess progression of lung disease
to monitor effectiveness of therapy
what are the three PFT options
spirometry
lung volumes
diffusion capacity
_____________ can be performed in a clinic setting, but all other tests need to be performed in a pulmonary function laboratory
spirometry
what is a spirogram
is a graph that shows the volume of air a person breathes in and out over time
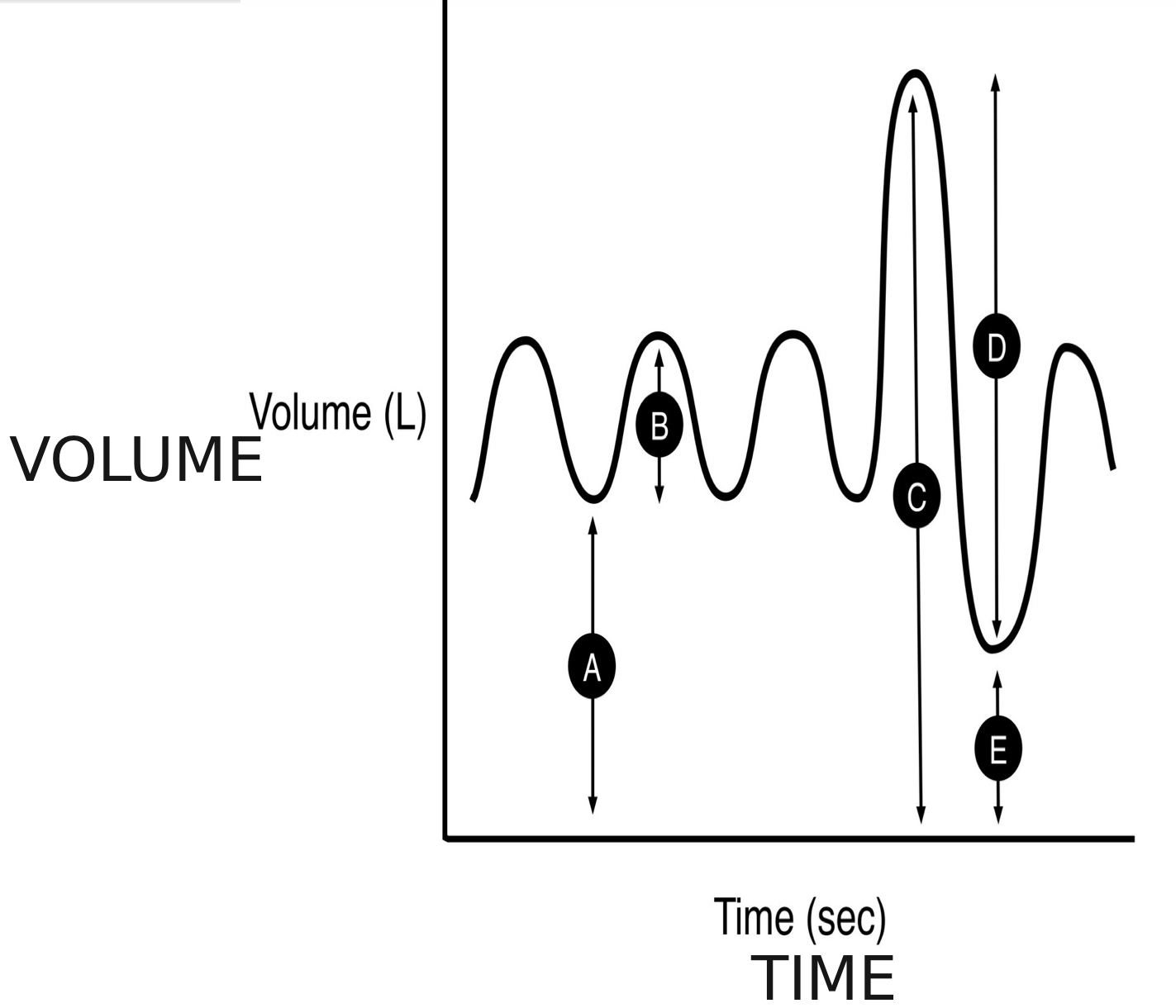
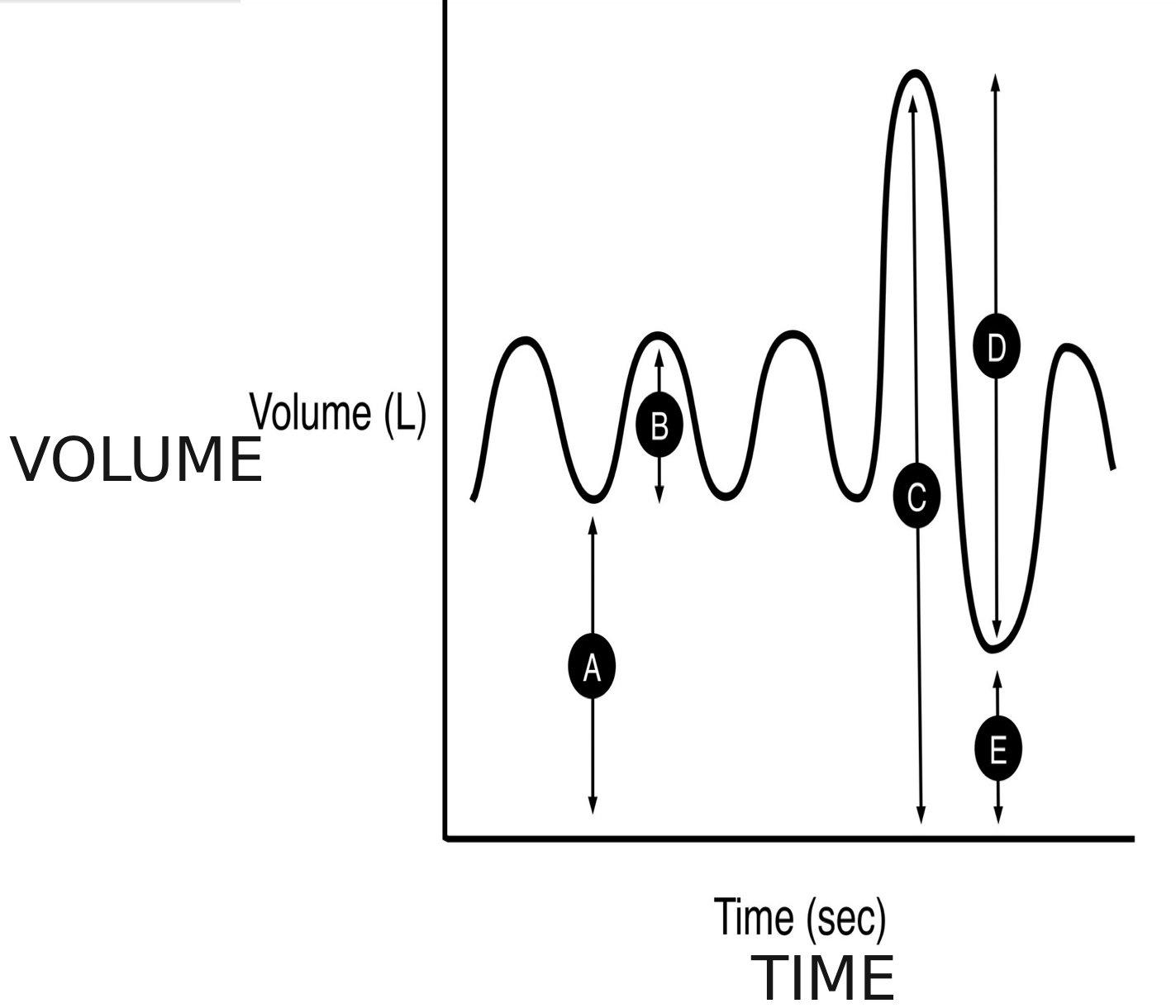
A
functional residual capacity
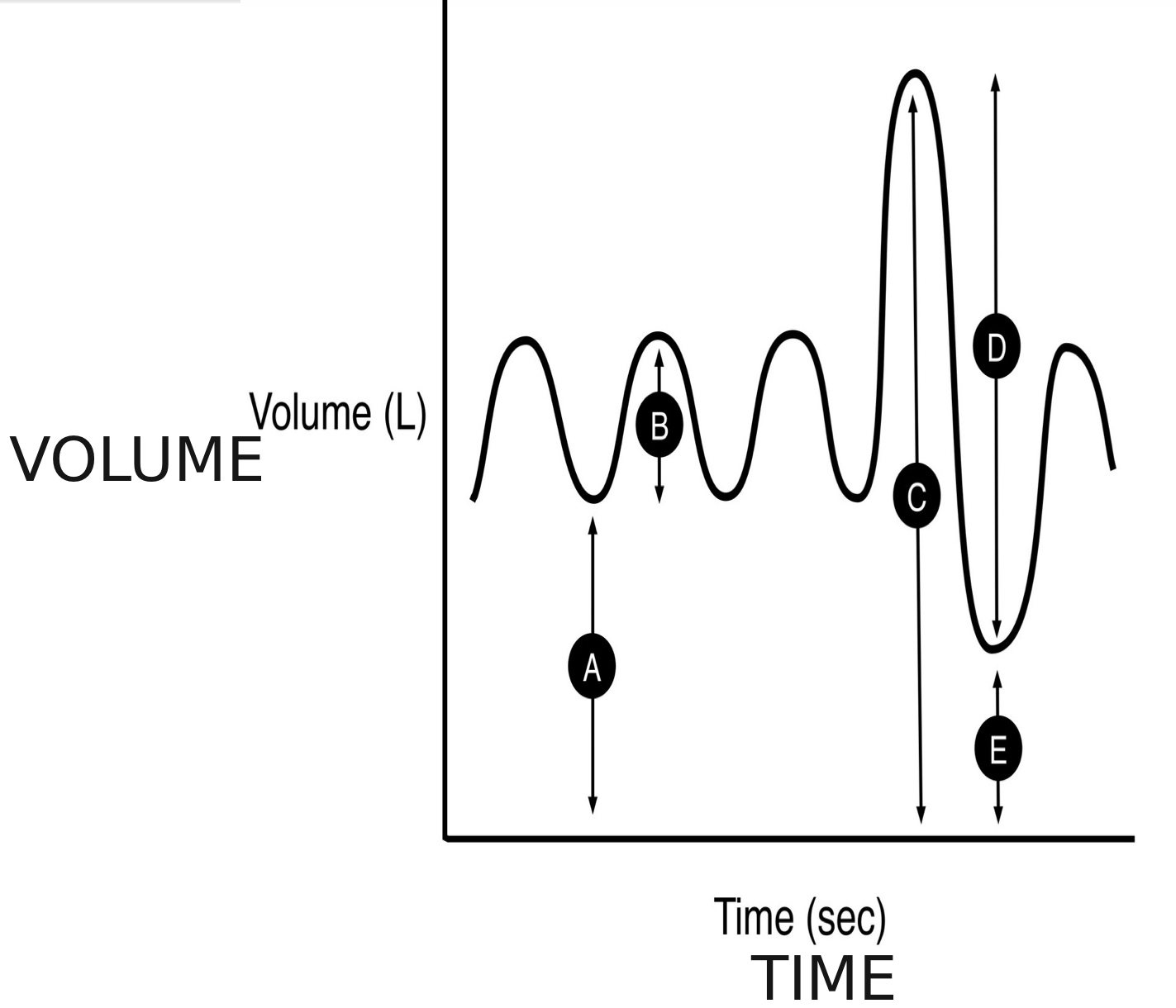
B
tidal volume (TV)
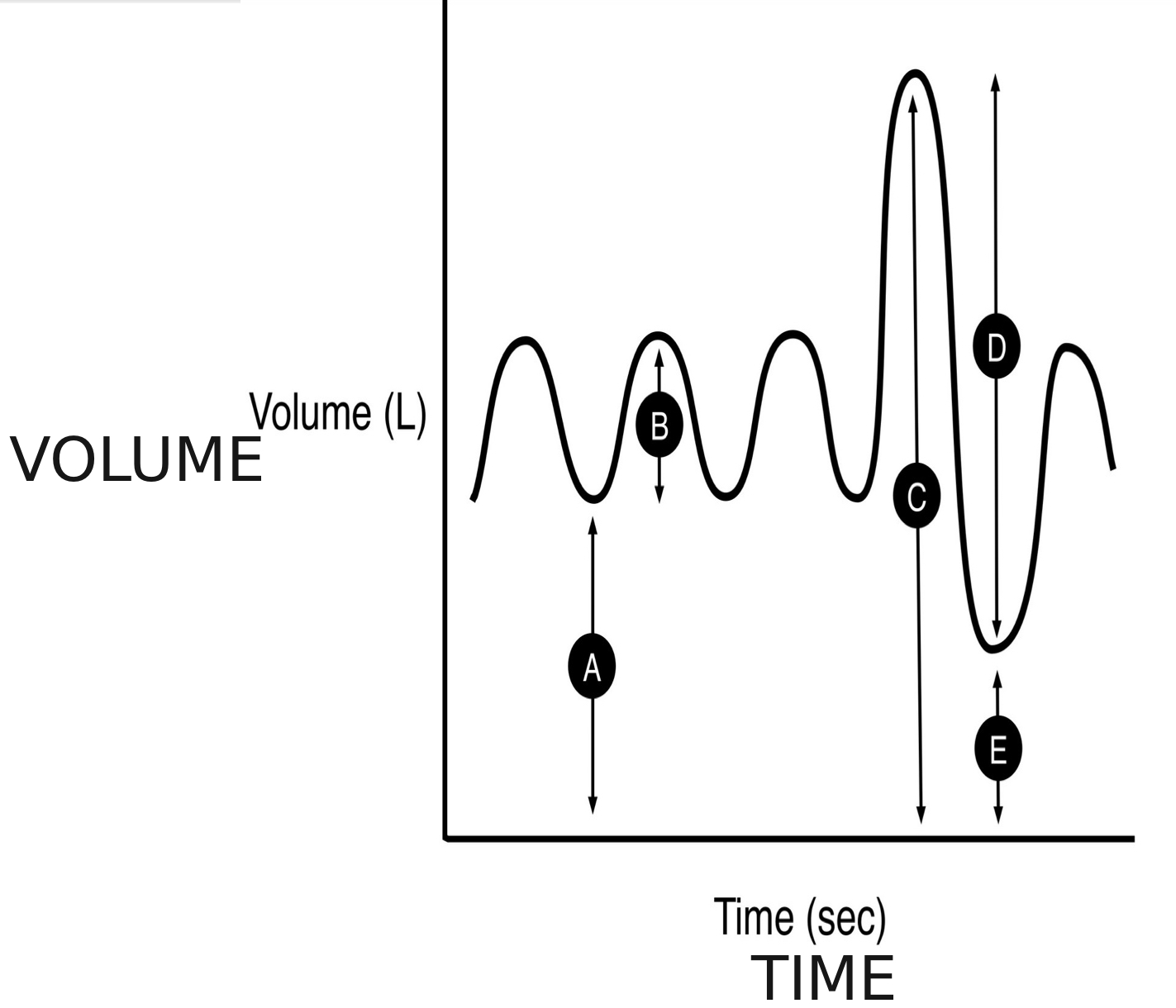
C
total lung capacity (TLC)
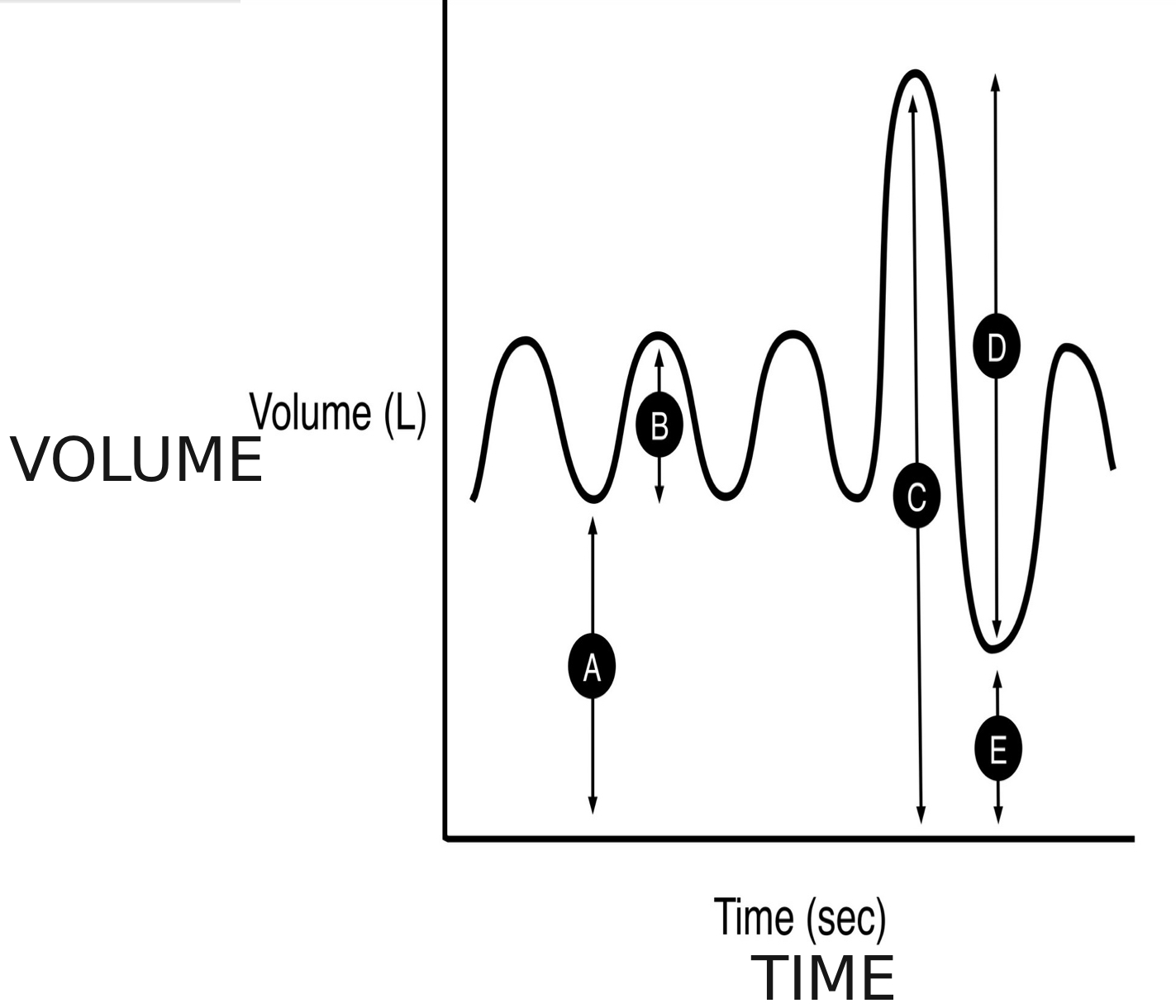
D
forced vital capacity (FVC)
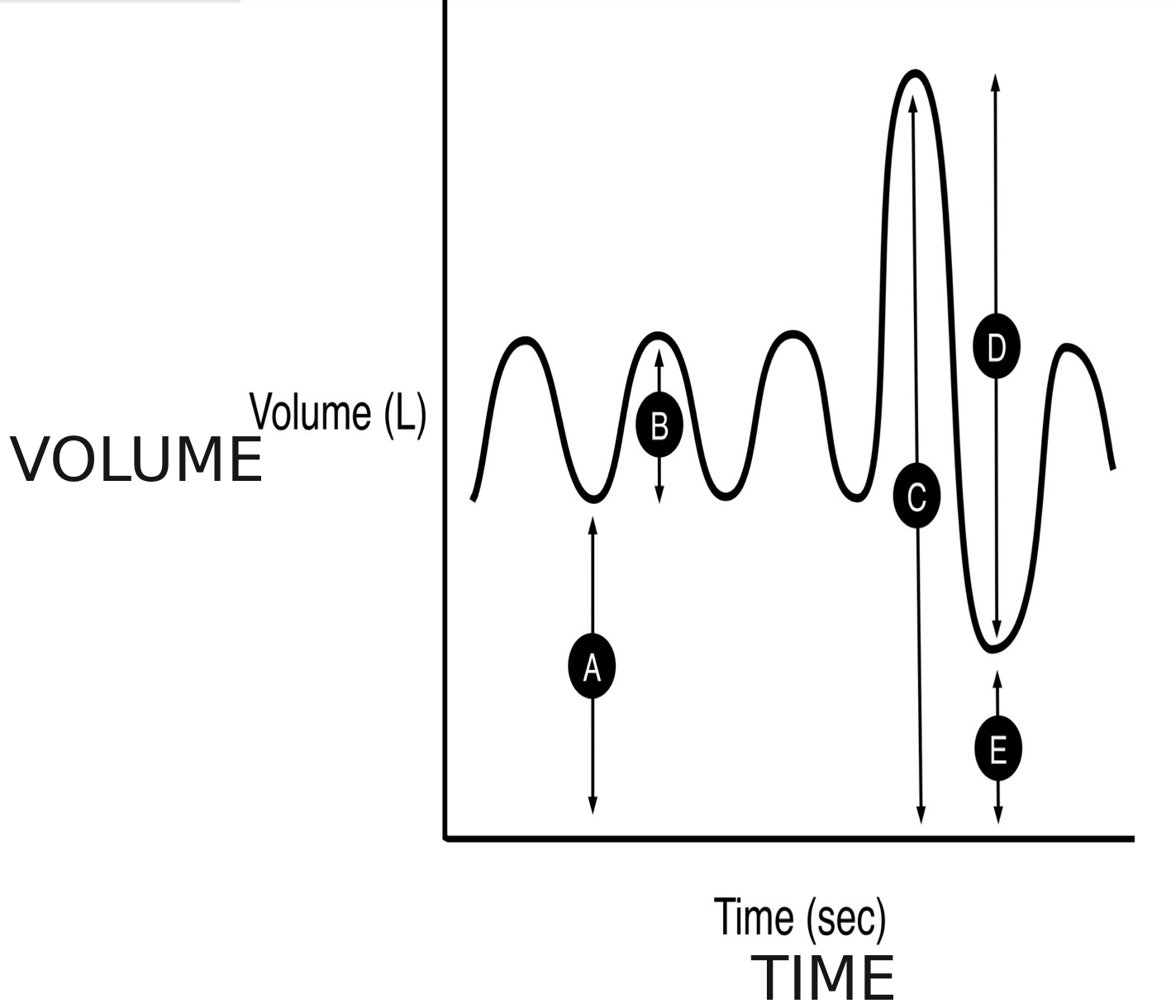
E
residual volume (RV)
what is spirometry
can see lung function represented as volume vs time just during theforced exhalation from maximal inhalation from minimal exhalation
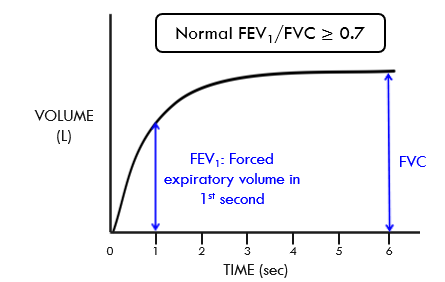
what is FEV1
the volume of air that comes out in the first second
what is FRC
resting point at the end of a normal breath and represents the balance between the outward recoil of the chest wall and the inward recoil of the lung
what is FVC
the forced exhalation until the pt cannot blow out anymore air
what is RV
volume of air that is left in the chest after maximal exhalation
how to get TLC
add FCV and RV together
what is the normal range in spirometry
normal FEV1/FVC >/= 0.7
describe a flow-volume loop
black dots demonstrate what we predict the loop to look like for the pt based on population norms
inhalation is at the bottom while exhalation is at the top
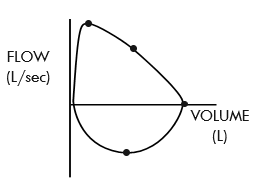
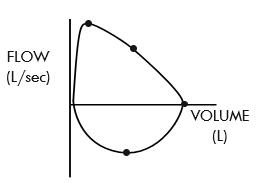
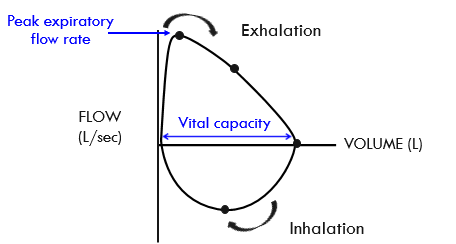
what are the two important things that can be pointed out on a flow-volume loop
peak expiratory flow rate
vital capacity
what is the peak expiratory flow rate on a flow-volume loop
the highest point on the expiratory curve — it's the maximum speed at which air is exhaled from the lungs after a full inhalation
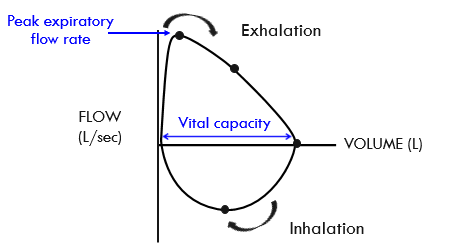
what is vital capacity on a flow-volume loop
the volume of air exhaled form maximal inhalation to exhalation
any PFT value is abnormal if it is less than the (LLN) lower limit of normal (defined as the 5th percentile), corresponding to what Z-score
<-1.645
some PFT values can be abnormal if elevated (TLC, RV, DLCO) or greater than the (ULN) upper limit of normal (>95th percentile), corresponding to what Z-score
>1.645
what are the three main step sin approaching PFTs
check spirometry to evaluate for obstruction
check lung volumes to evaluate for restriction
check diffusing capacity
what is obstruction defined as
FEV1/FVC < LLN
FEV1/FVC Z-score < -1.645
pts w obstructive airflow will get less air out in the…
first one second (FEV1) of exhalation
describe what a flow-volume loop looks like in a pt that has an obstruction
inspiratory limb looks normal
peak expiratory flow is lower (indicated lung funx is worse)
scooped out shape due to differential emptying of lung units
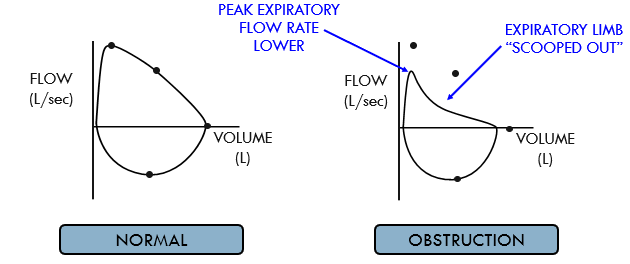
there is more rapid emptying of lung units w __________ (higher/lower) elastic recoil and __________ (faster/slower) emptying of more diseased lung units
higher; slower
what other clues, other than FEV1/FVC, can give us clues of obstruction
if TLC>ULN or RV>ULN
TLC>ULN can signify
hyperinflation
RV>ULN can signify
air trapping
what is restriction defined by
TLC < LLN
TLC Z-score < -1.645
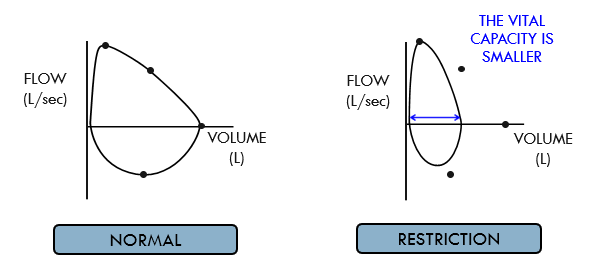
describe what a flow-volume loop look like in a pt w restriction
normal peak expiratory flow
no scooping out of the expiratory limb
dec in vital capacity
what are the two main causes of restriction
intrapulmonary and extrapulmonary
what is intrapulmonary restriction
diffuse parenchymal lung disease
what is extrapulmonary restriction
chest wall diseases
pleural diseases a
abdominal distension
neuromuscular weakness
what is hyperinflation of the lungs
when the lungs retain too much air, causing them to over-expand
what is air trapping
when air gets stuck in the lungs during exhalation due to narrowed or collapsed airways; is a big contributor to hyperinflation and makes it harder to fully breathe out
describe how a spirogram would look in a person w hyperinflation and air trapping
curve would shift right due to inc TLC
Inc RV
Scooped-out Expiratory Curve; expiratory limb of the flow-volume loop would show a concave or scooped shape, due to reduced airflow from obstructed airways
why does emphysema have a lot diffusion capacity
Emphysema has a low diffusion capacity (DLCO) because of destruction of the alveolar wall