Brain Anatomy and Function
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Temporal Lobe
This part of the brain mainly revolves around hearing and selective listening. It receives sensory information such as sounds and speech from the ears. It is also key to being able to comprehend, or understand meaningful speech.
Parietal Lobe
This part of the brain is where information such as taste, temperature and touch are integrated, or processed.
Occipital Lobe
This part of the brain is responsible for processing visual information from the eyes.
Gyrus
A ridge or fold between two clefts on the cerebral surface in the brain.
Sulcus
A depression or groove in the cerebral cortex.
Medial Longitudinal Fissure
The deep groove that separates the two hemispheres of the vertebrate brain.
Lateral Sulcus
Divides both the frontal lobe and parietal lobe above from the temporal lobe below. It's in both hemispheres of the brain but is longer in the left hemisphere in most people.
Central Sulcus
A prominent landmark of the brain, separating the parietal lobe from the frontal lobe and the primary motor cortex from the primary somatosensory cortex.
Cerebellum
A region of the brain that plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language, and in regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established.
Primary Motor Cortex
A strip of neural tissue at the rear of the frontal lobe that is specifically involved in controlling voluntary bodily movements through its control of skeletal muscles
Primary Somatosensory Area
A strip of neural tissue in each parietal lobe that receives and processes sensory information from the skin and body, enabling perception of bodily sensations (touch, pressure, temperature etc.)
Somatosensory Association Area
In the postcentral gryus; Interprets touch, and determine the size and texture of an object.
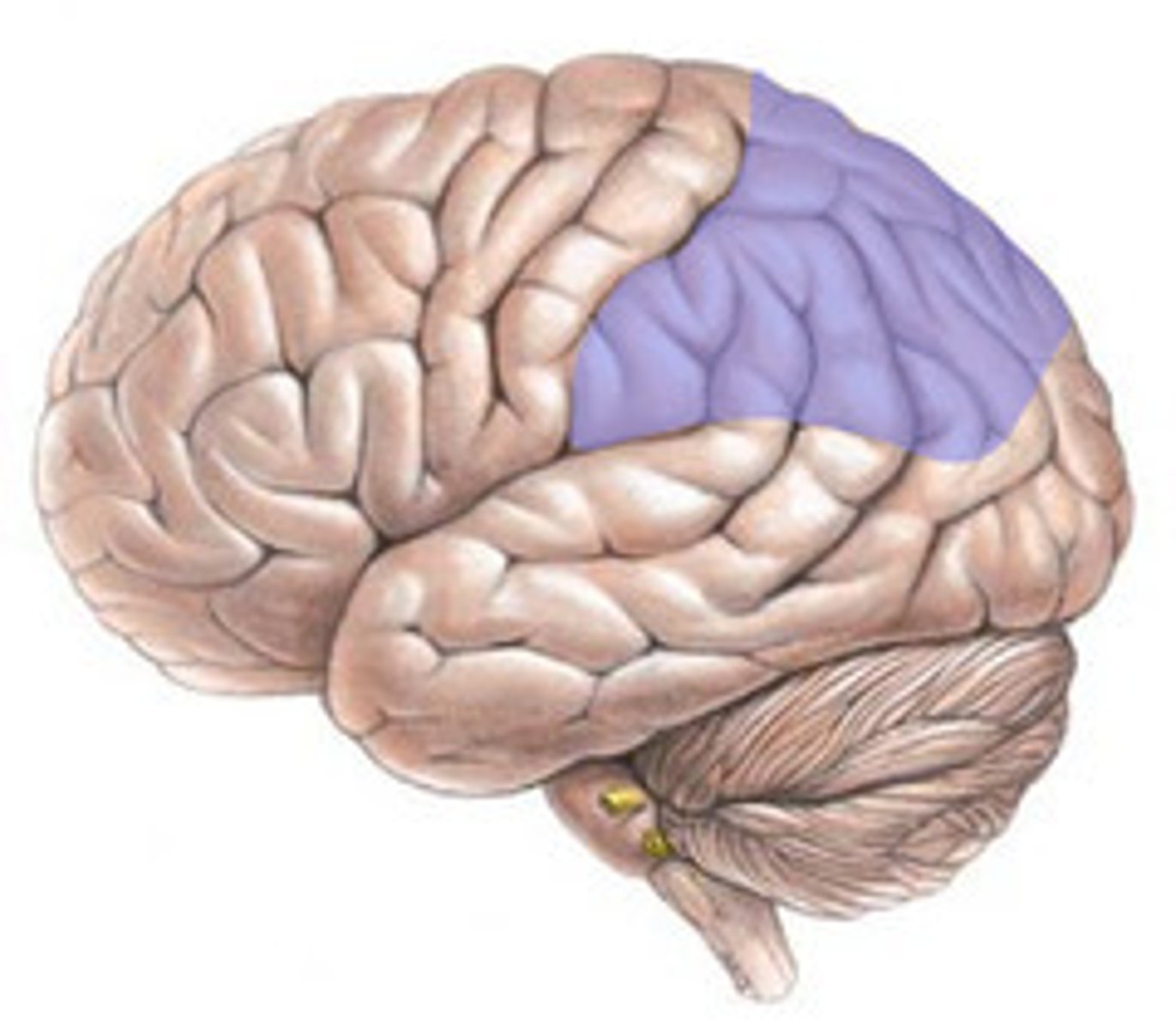
Wernicke's Area
A region of the brain concerned with the comprehension of language, located in the cortex of the dominant temporal lobe. Damage in this area causes Wernicke's aphasia, characterized by superficially fluent, grammatical speech but an inability to use or understand more than the most basic nouns and verbs.
Primary Visual Area
The part of the cerebral cortex responsible for processing visual information.
Visual Association Area
The region of the cerebral cortex occupying the entire surface of the occipital lobe and receiving the visual data from the lateral geniculate body of the thalamus.
Auditory Association Area
An area in the temporal lobe of the brain within Wernicke's area (area 22) near the lateral cerebral sulcus, which is critical for processing acoustic signals so they can be interpreted as speech, music or other sounds.
Primary Auditory Area
The region of the cerebral cortex that receives auditory data from the medial geniculate body.
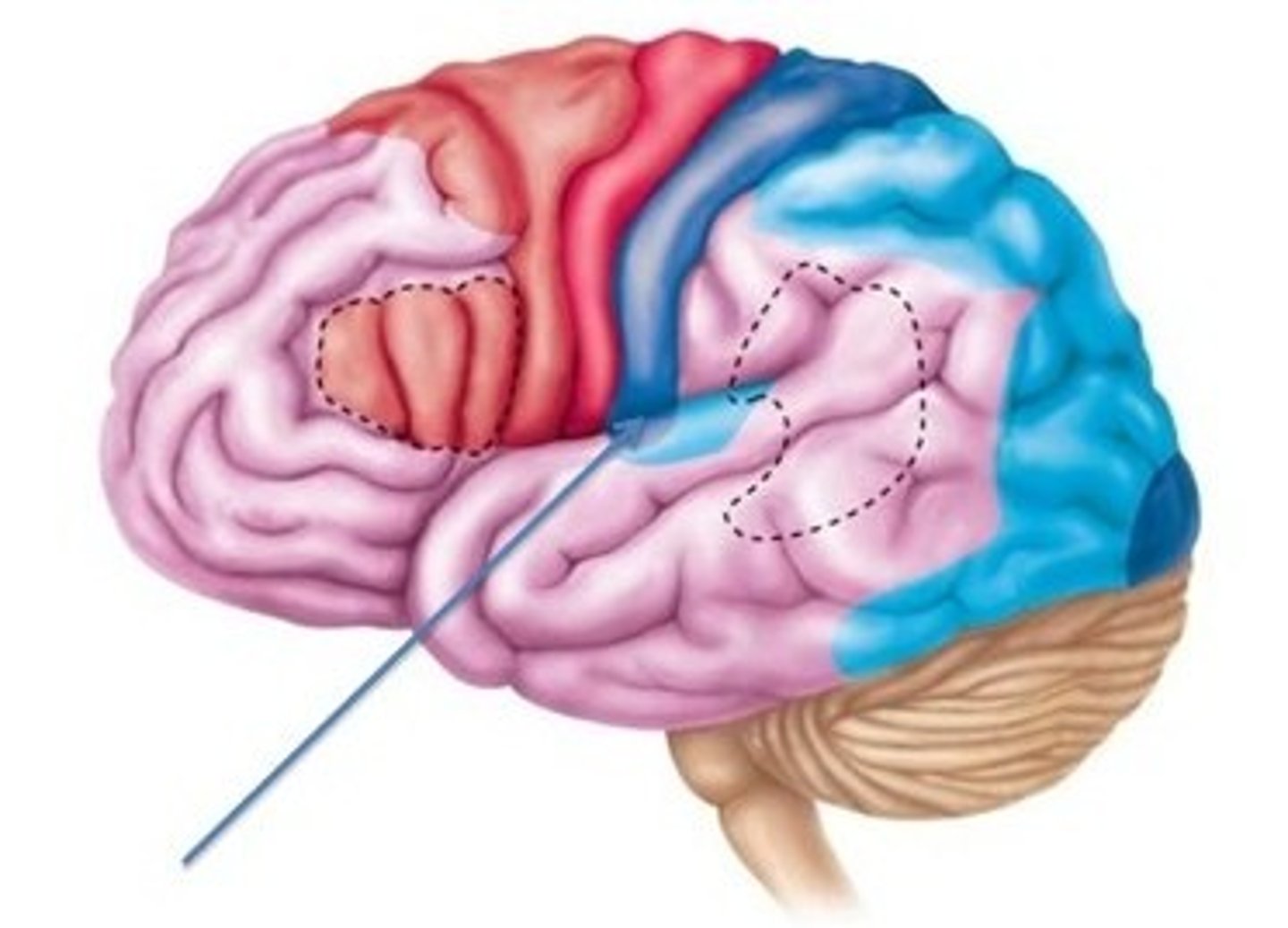
Gustatory Area
A brain structure responsible for the perception of taste.
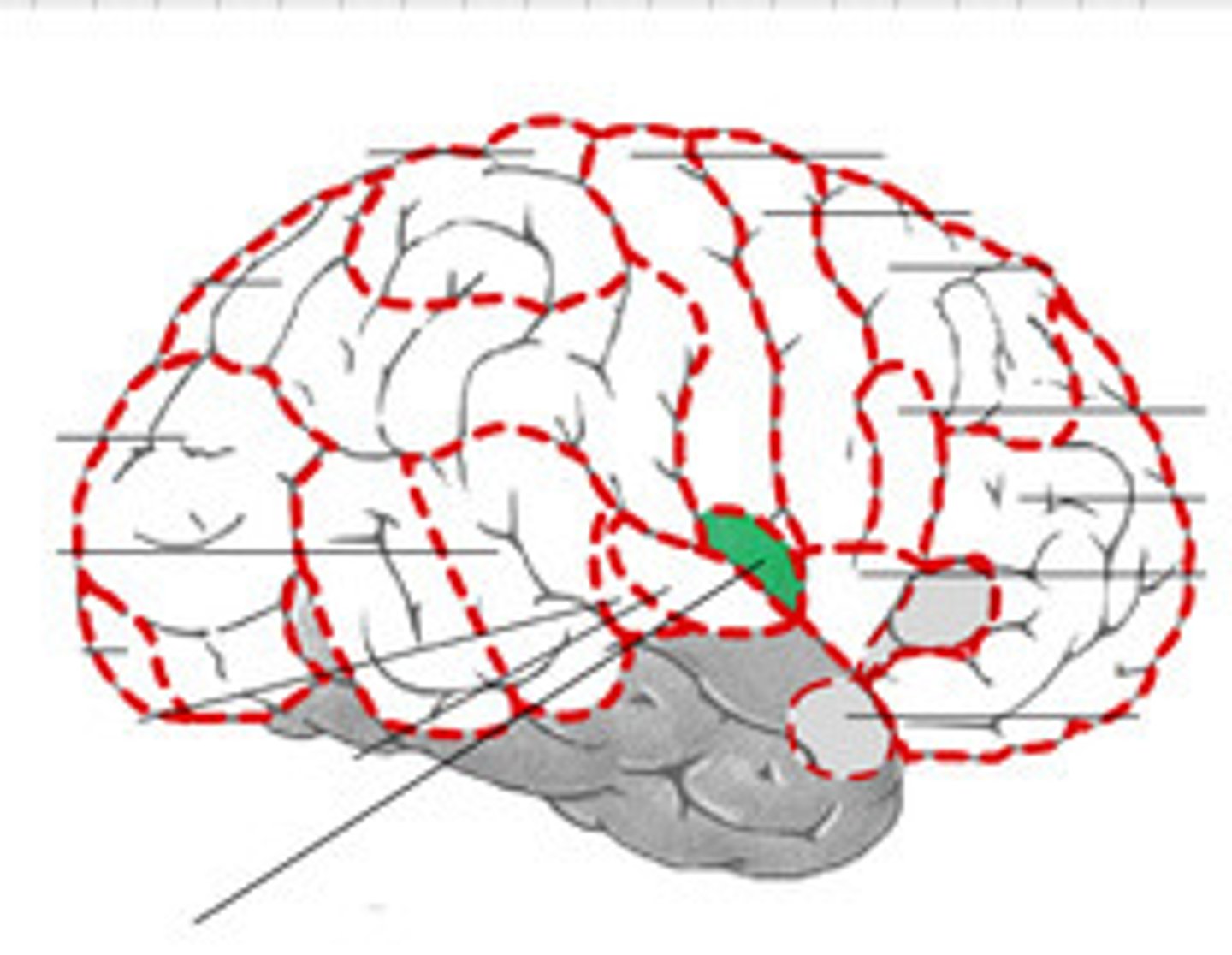
Premotor Cortex
An area of motor cortex lying within the frontal lobe of the brain just anterior to the primary motor cortex.
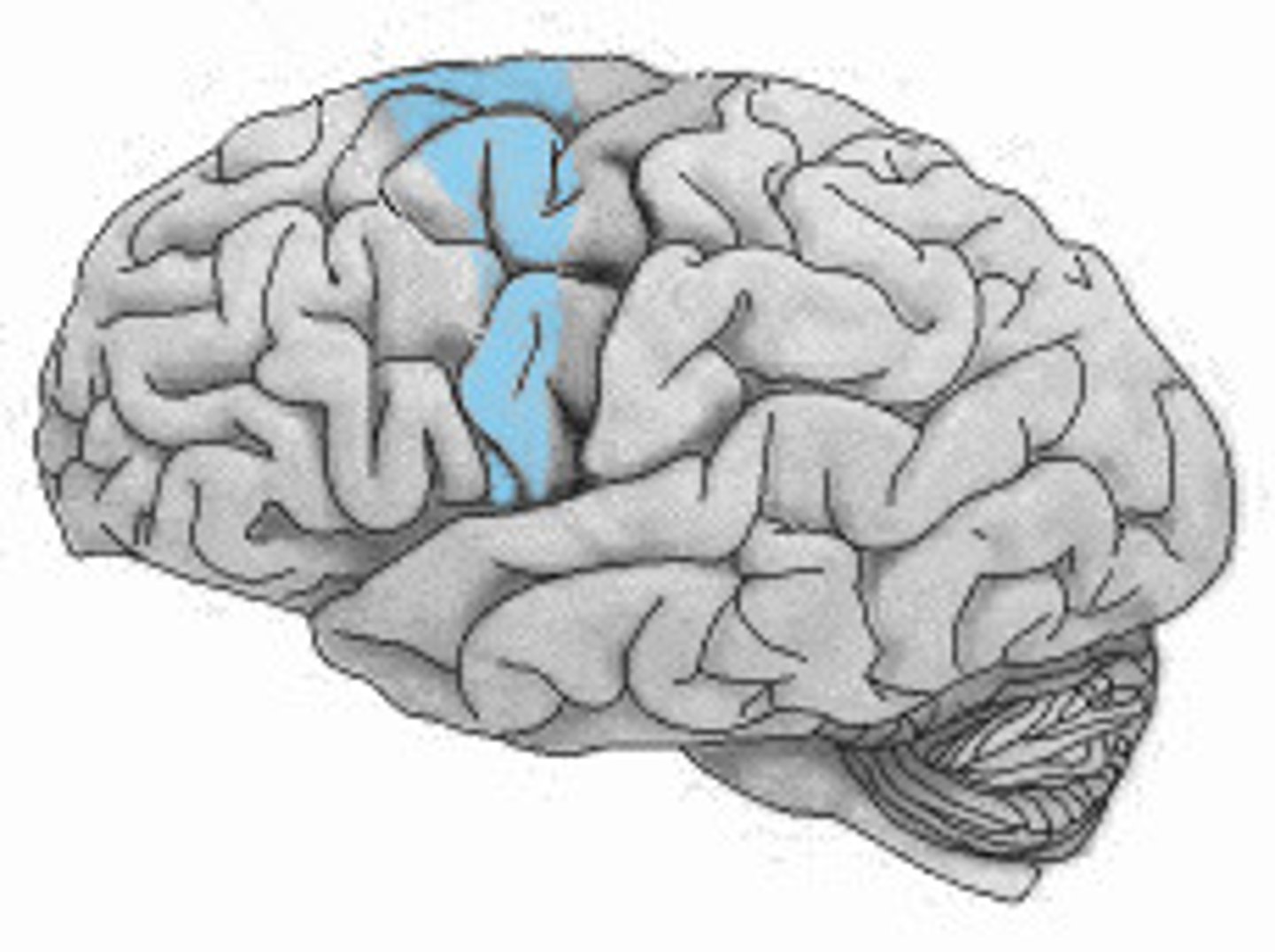
Broca's Area
A region of the brain concerned with the production of speech, located in the cortex of the dominant frontal lobe. Damage in this area causes Broca's aphasia, characterized by hesitant and fragmented speech with little grammatical structure.
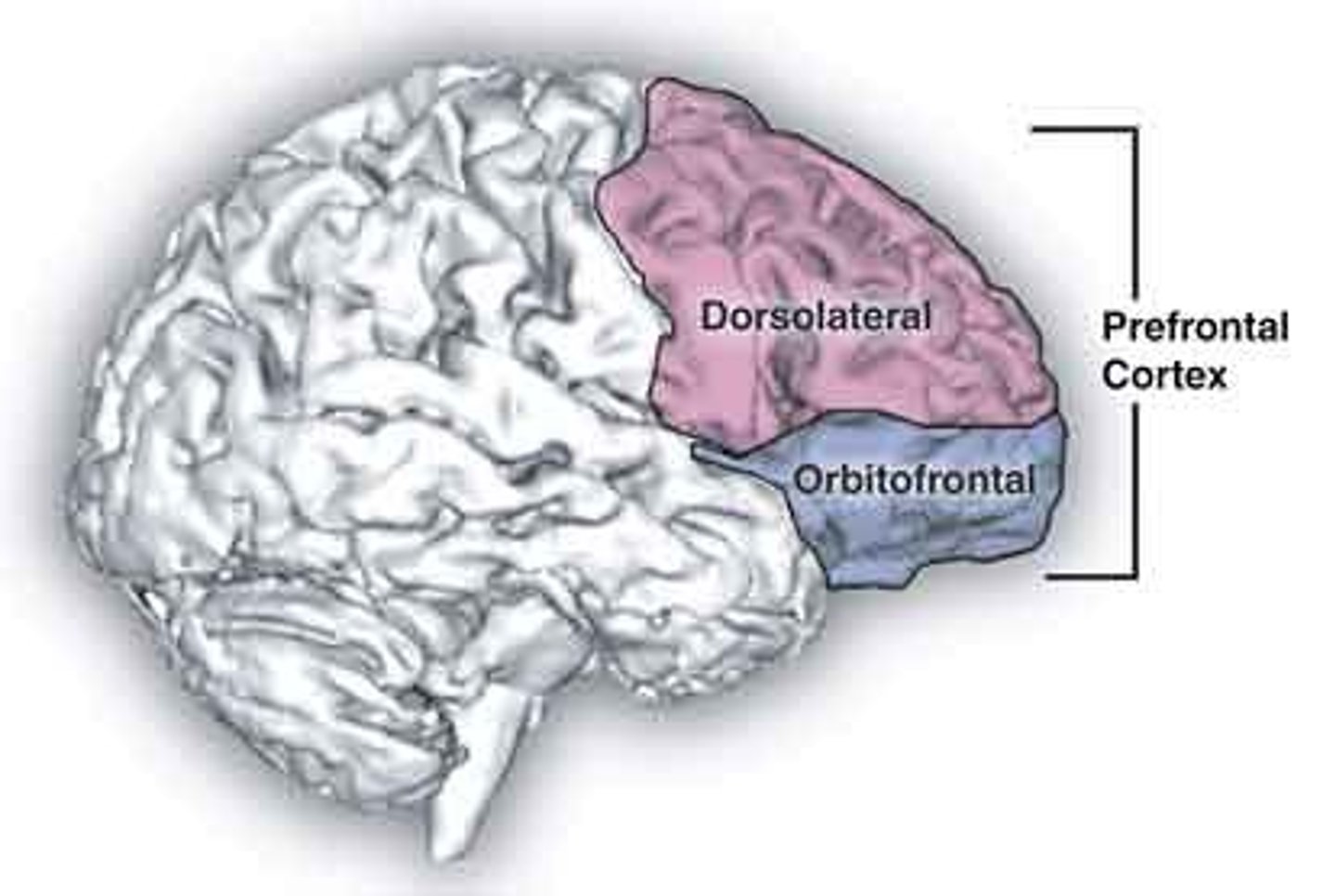
Prefrontal Area
This brain region has been implicated in planning complex cognitive behavior, personality expression, decision making, and moderating social behavior.
Medulla Oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
Spinal Cord
The cylindrical bundle of nerve fibers and associated tissue that is enclosed in the spine and connects nearly all parts of the body to the brain, with which it forms the central nervous system.
Pons
A hindbrain structure that connects the medulla to the two sides of the cerebellum; helps coordinate and integrate movements on each side of the body.
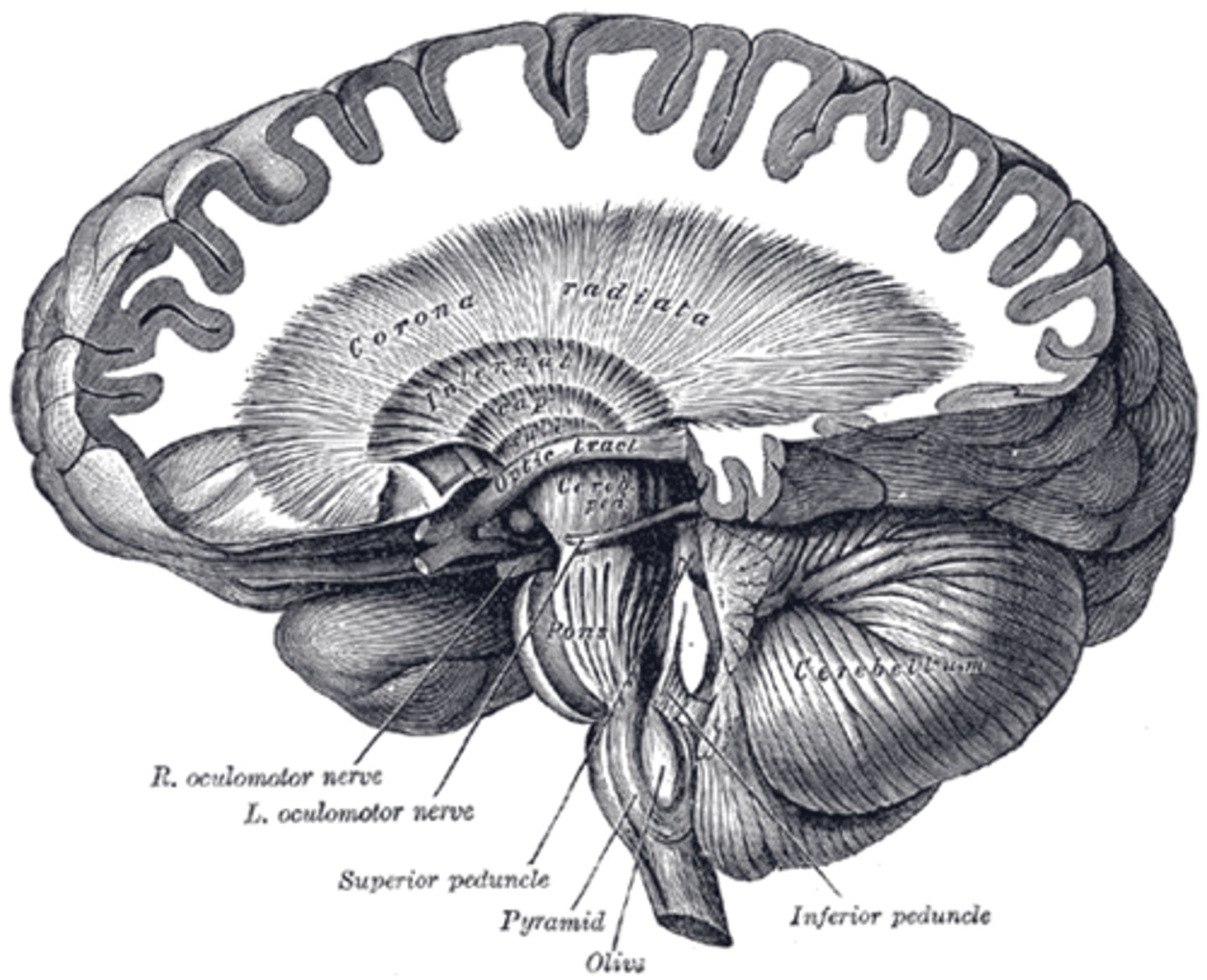
Optic Nerve
A paired nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. The optic nerve is derived from optic stalks during the seventh week of development and is composed of retinal ganglion cell axons and glial cells.
Optic Tract
Conveys visual information exclusive to its respective contralateral half of the visual field.
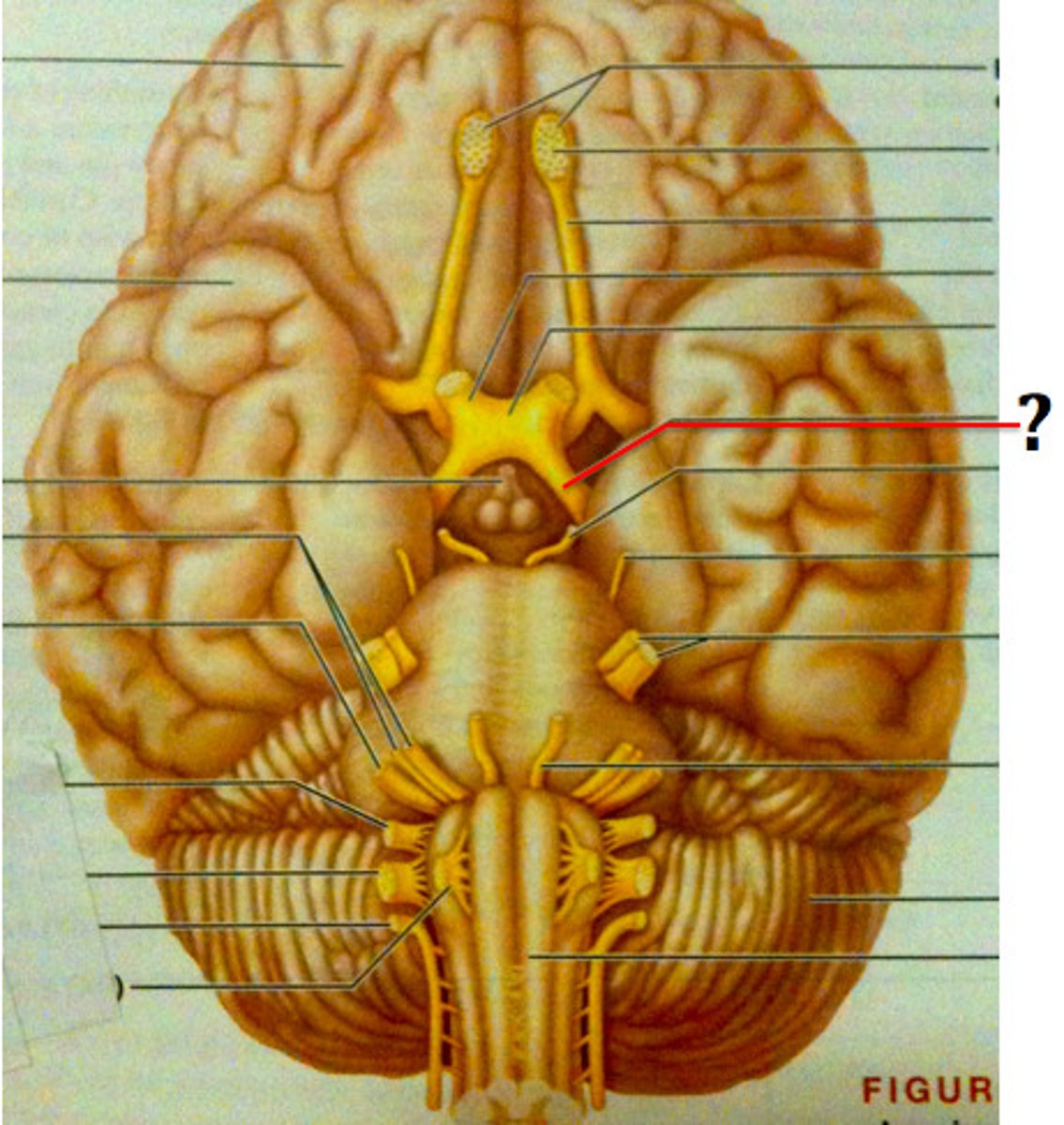
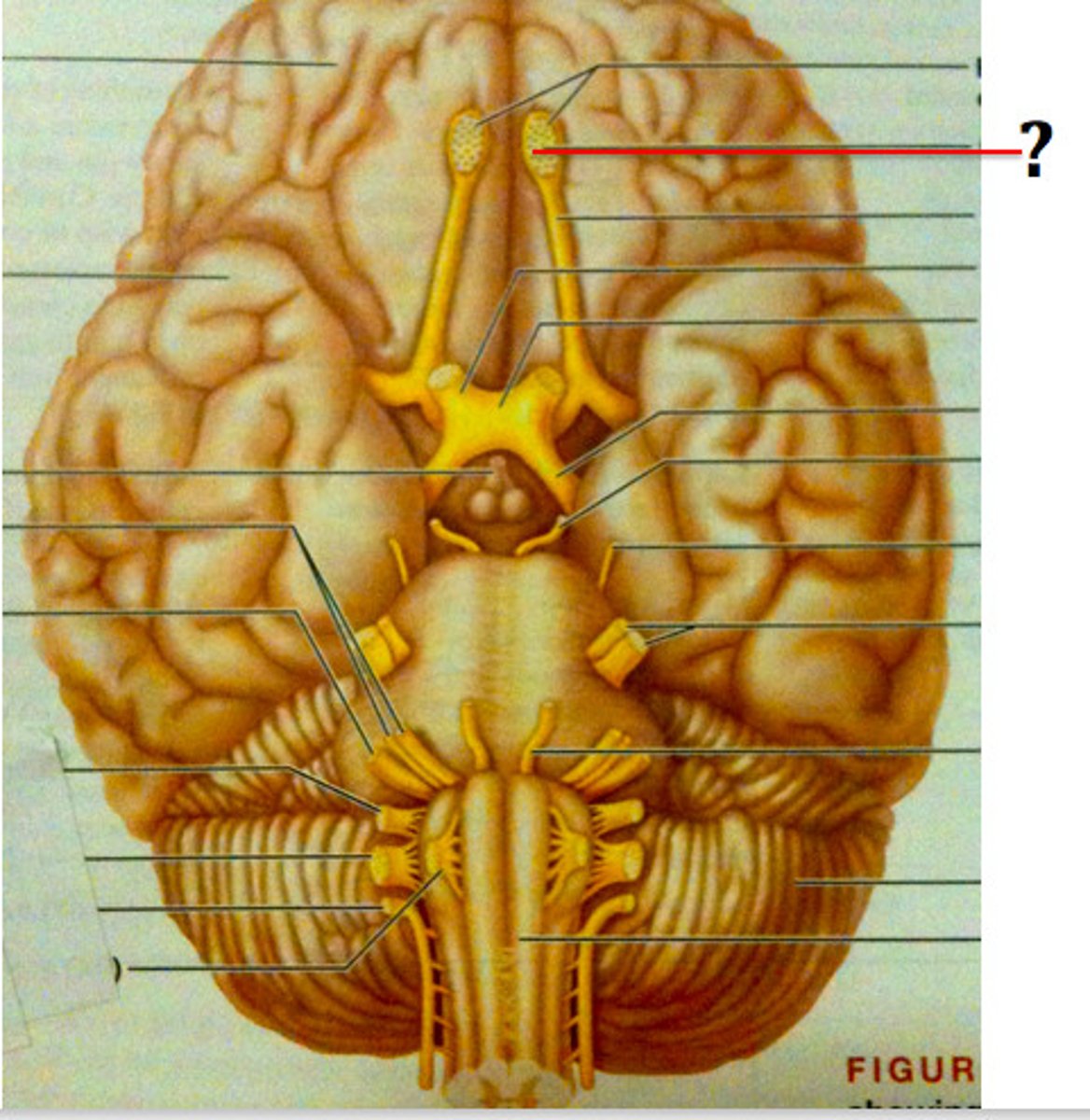
Olfactory Bulb
A neural structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, or the sense of smell.
Pyramids of Medulla
Paired white matter structures of the brainstem's medulla oblongata that contain motor fibers of the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts.
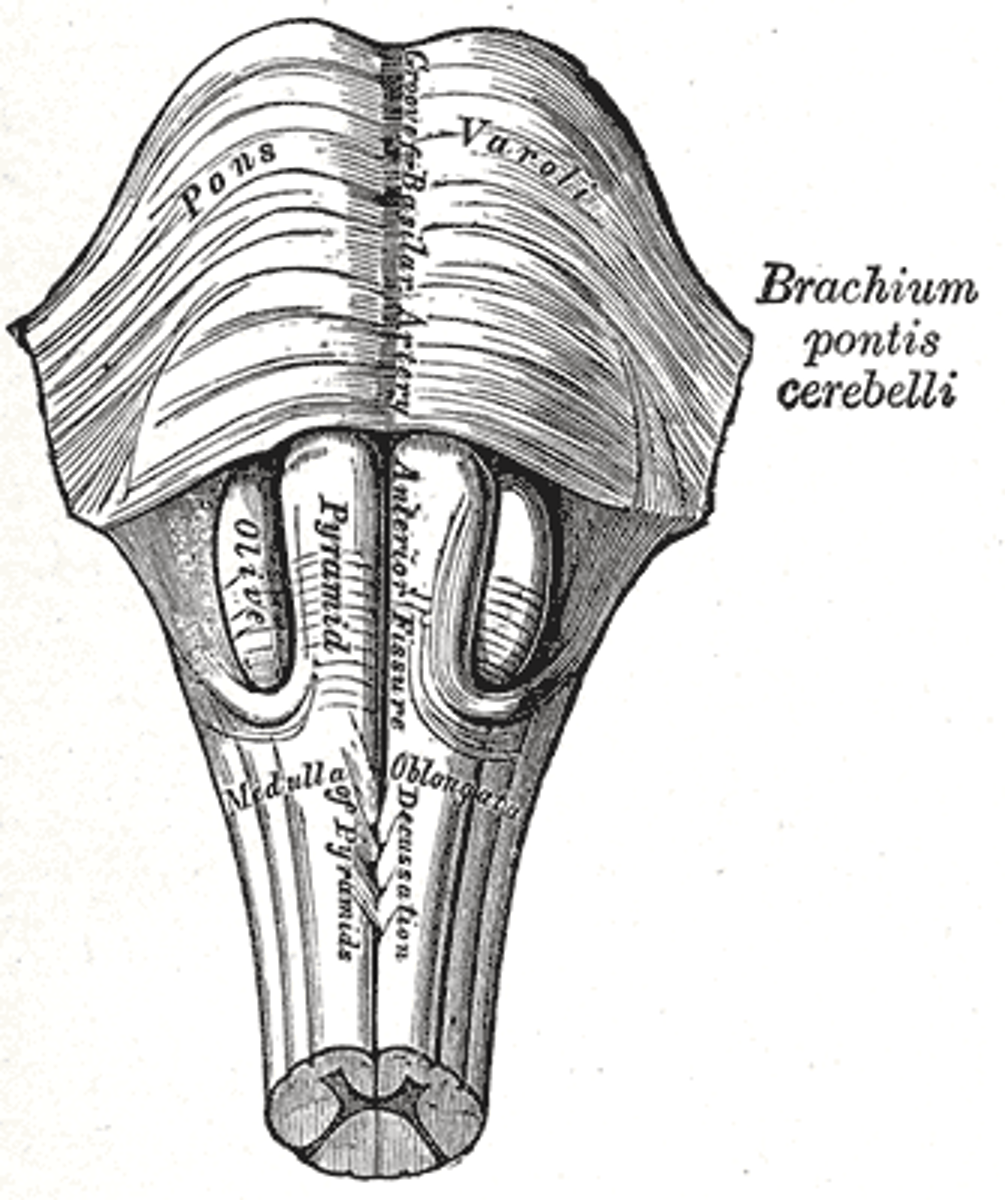
Mammillary Bodies
Hypothalamic structures that are most important in the limbic system. The hippocampus, amygdala, the cingulate cortex, and the prefrontal cortex.
Cerebral Peduncles
Structure that connects the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord and connects the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum via the pons.
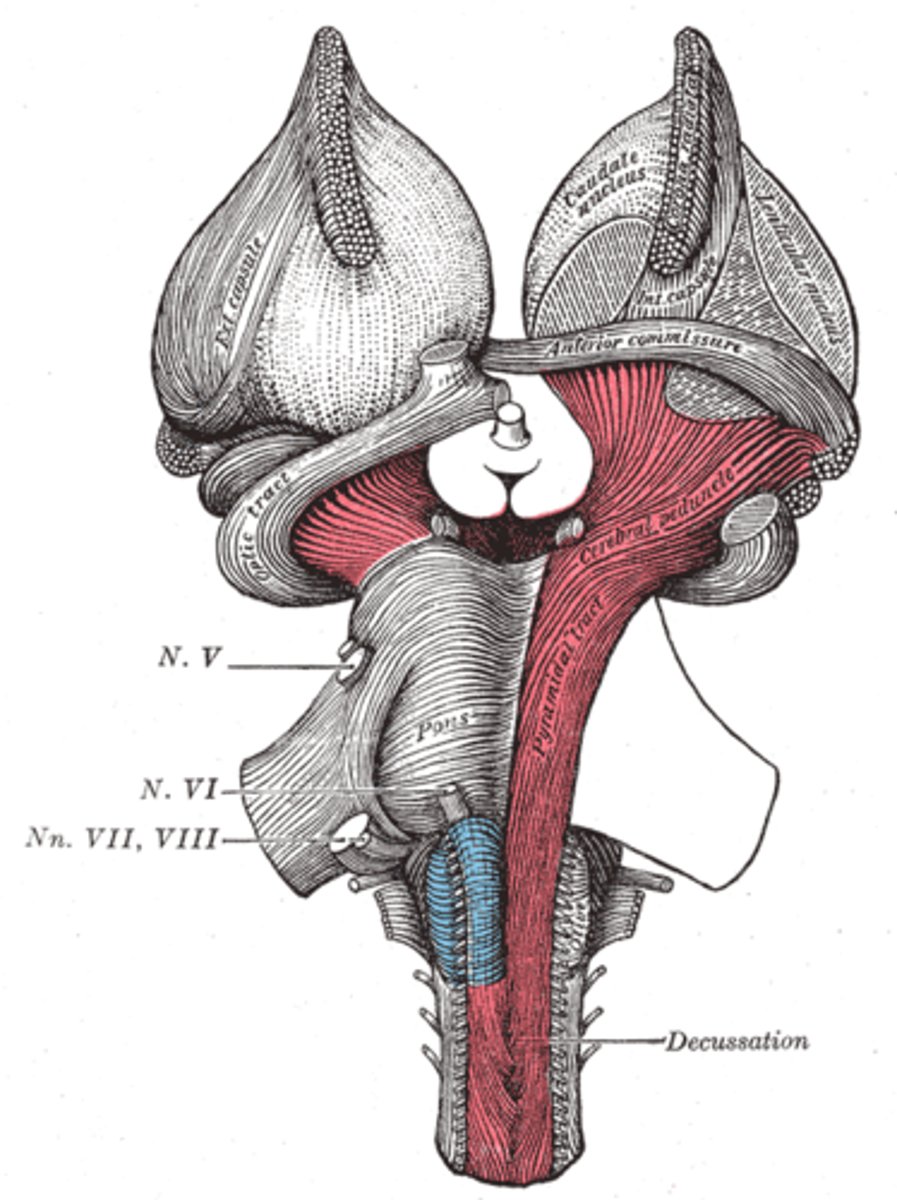
Infundibulum
A stalk that attaches the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus.
Third Ventricle
One of four connected fluid-filled cavities comprising the ventricular system within the human brain. The central cavity of the brain, lying between the thalamus and hypothalamus of the two cerebral hemispheres.
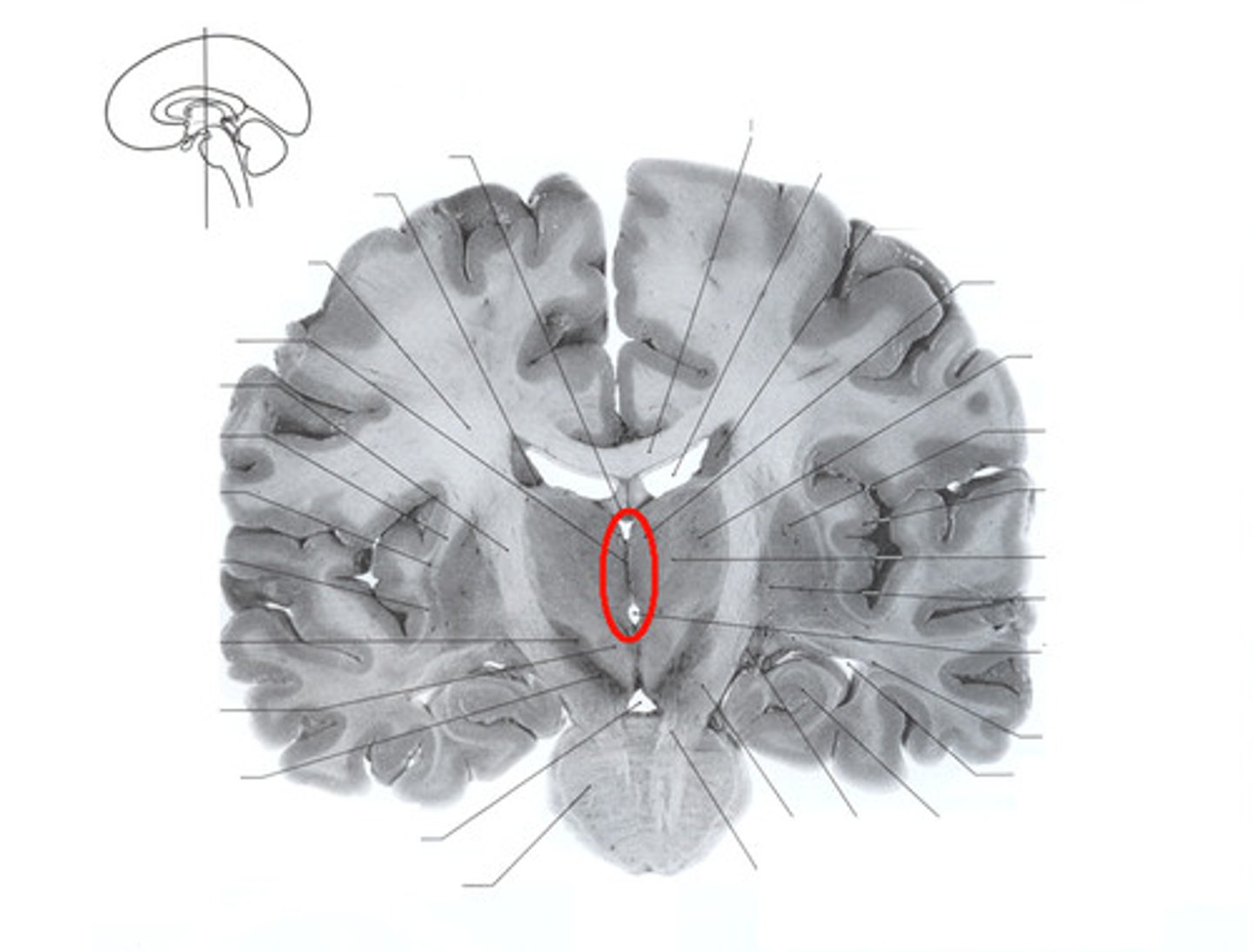
Cerebral Aquaduct
A fluid-filled canal that runs through the midbrain connecting the third and fourth ventricles.
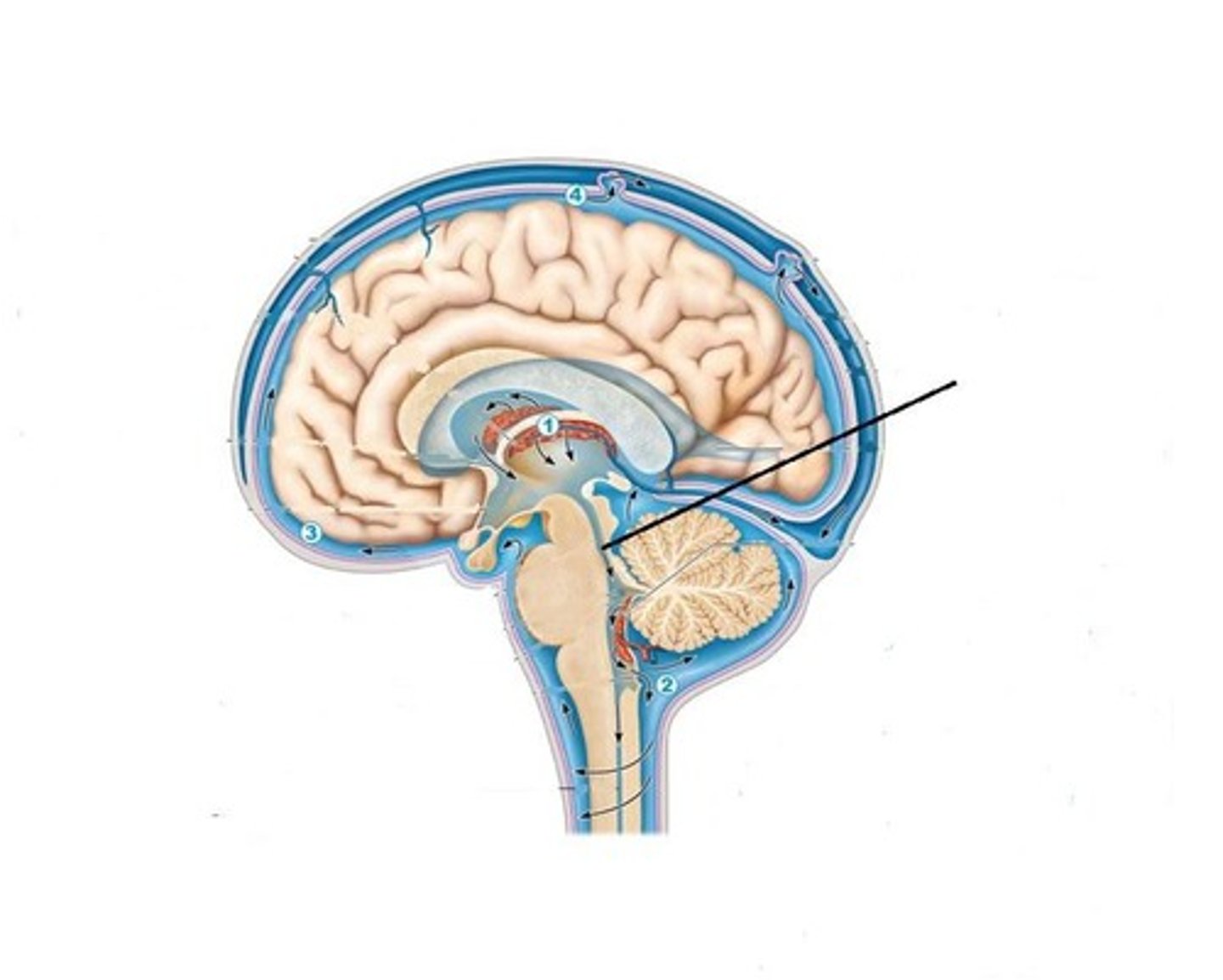
Fourth Ventricle
One of the components of the ventricular system in the brain, along with the lateral and third ventricles. It extends from the cerebral aqueduct (of Sylvius) to the obex and is filled with CSF.
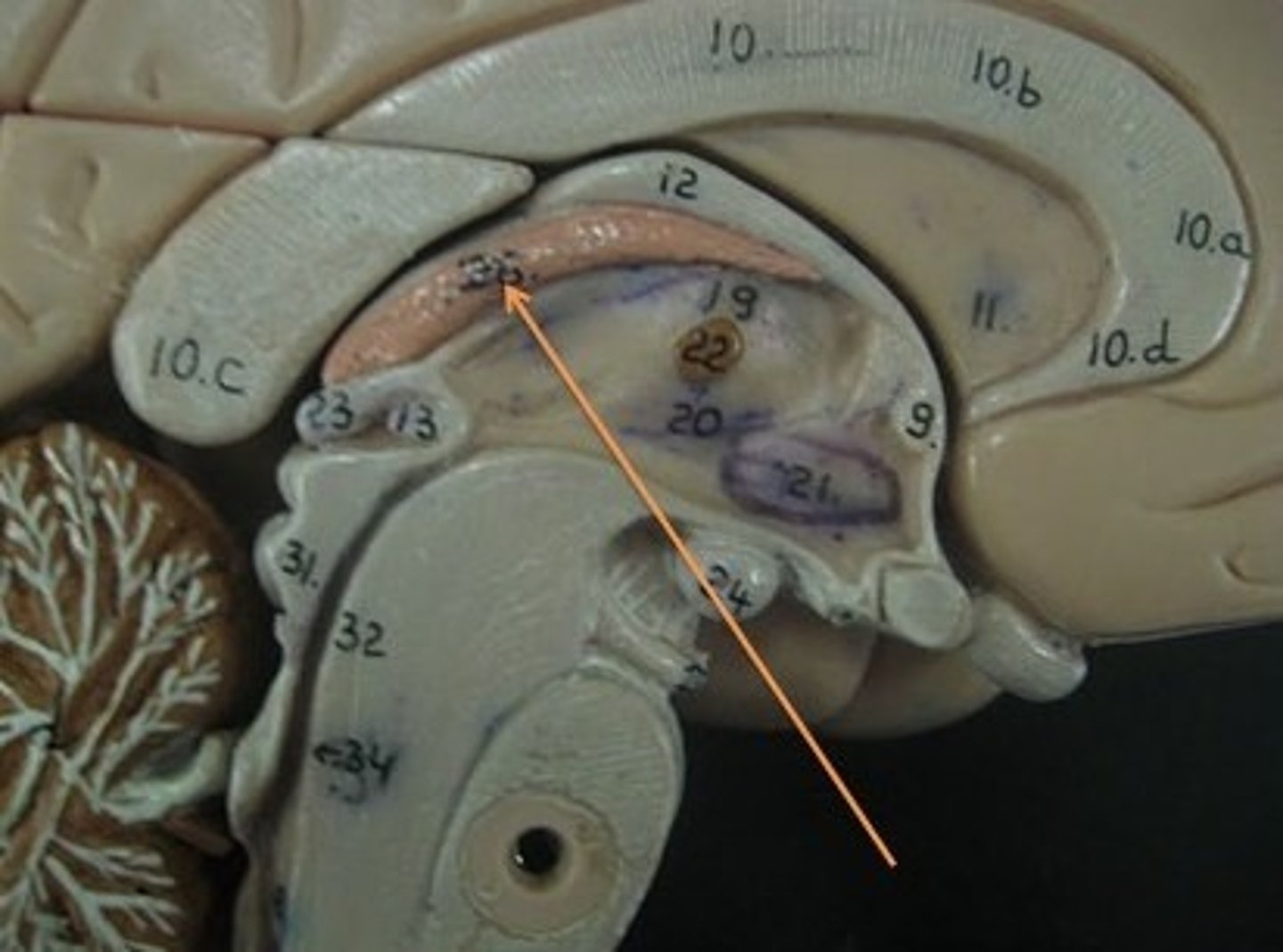
Pineal Body
A small endocrine gland in the vertebrate brain. It produces melatonin, a serotonin derived hormone, which affects the modulation of sleep patterns in both seasonal and circadian rhythms.
Choroid Plexus
A highly vascular portion of the lining of the ventricles that secretes cerebrospinal fluid.
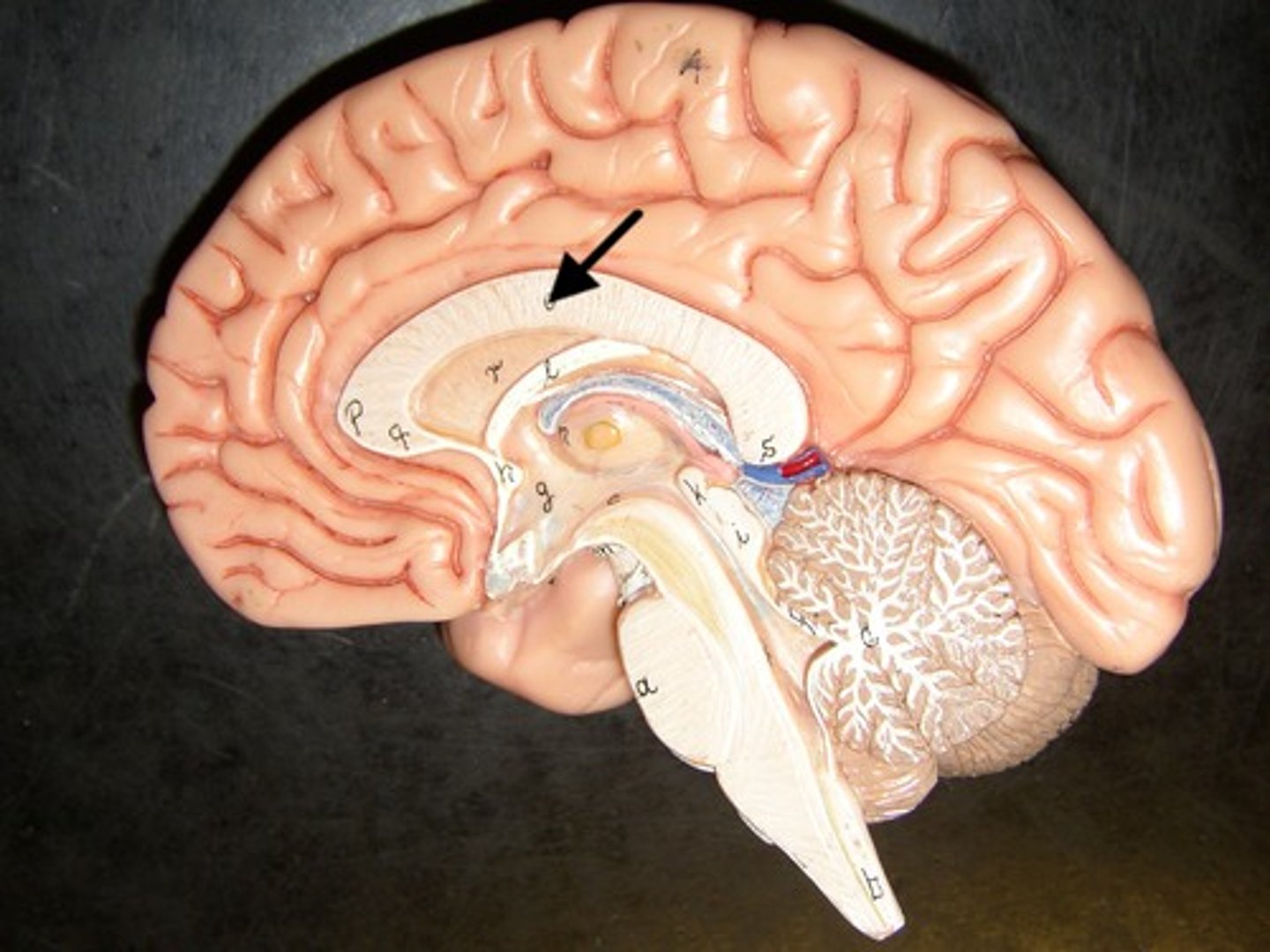
Thalamus
A structure in the forebrain through which all sensory information (except smell) must pass to get to the cerebral cortex.
Corpus Callosum
A thick band of axons that connects the two cerebral hemispheres and acts as a communication link between them.
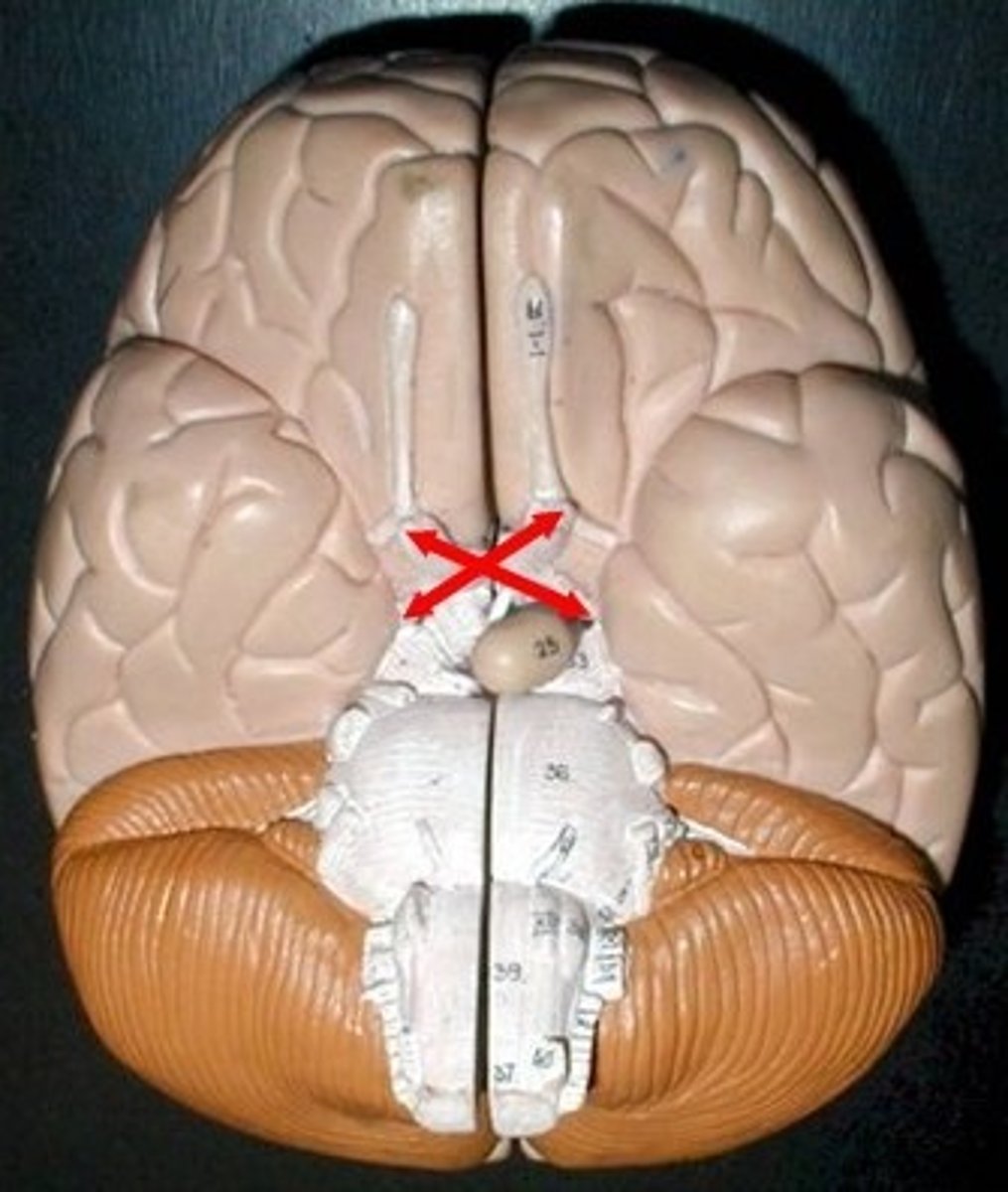
Optic Chiasm
The part of the brain where the optic nerves (CN II) partially cross. The optic chiasm is located at the bottom of the brain immediately below the hypothalamus.
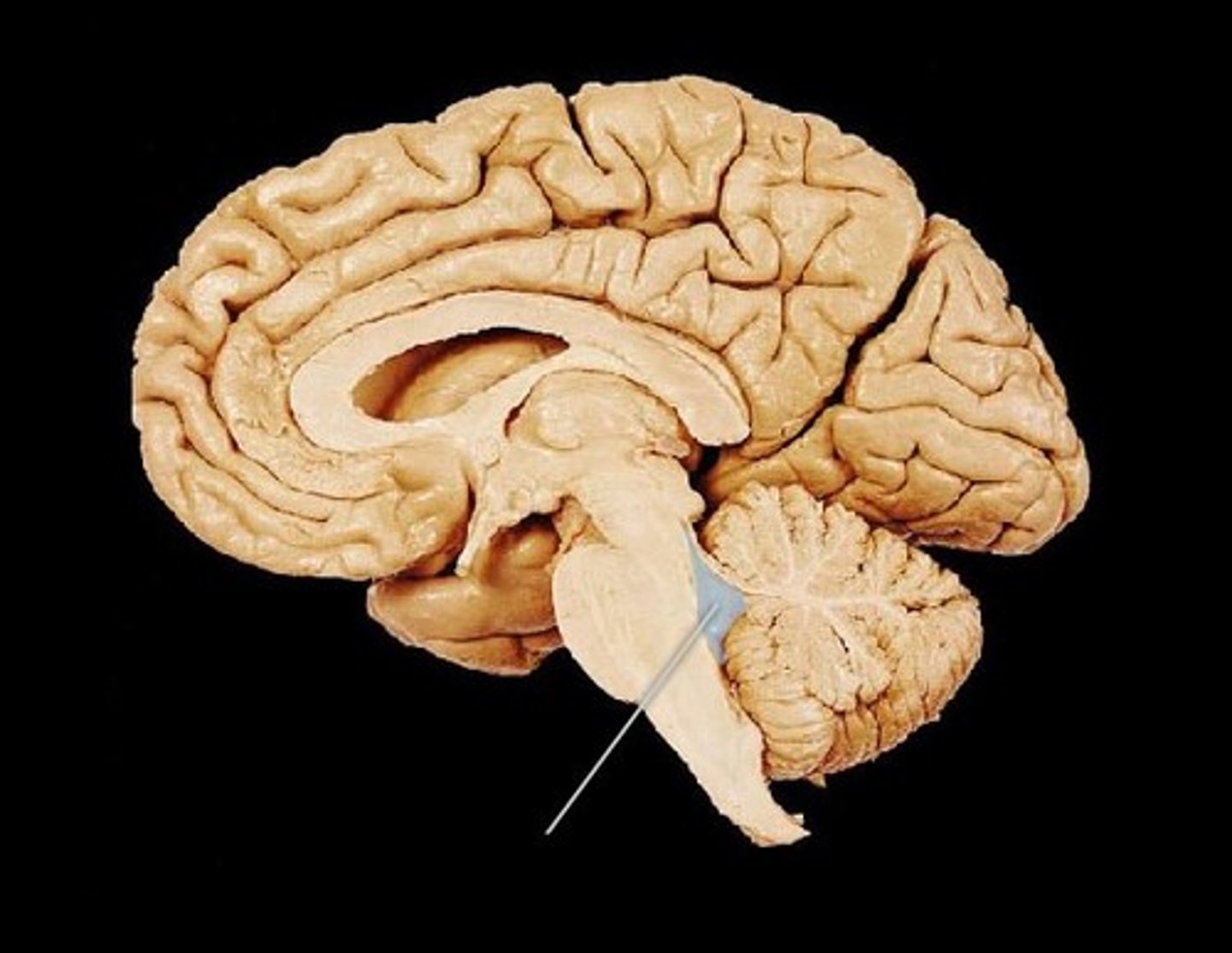
Fornix
A fiber tract that extends from the hippocampus to the mammillary body.
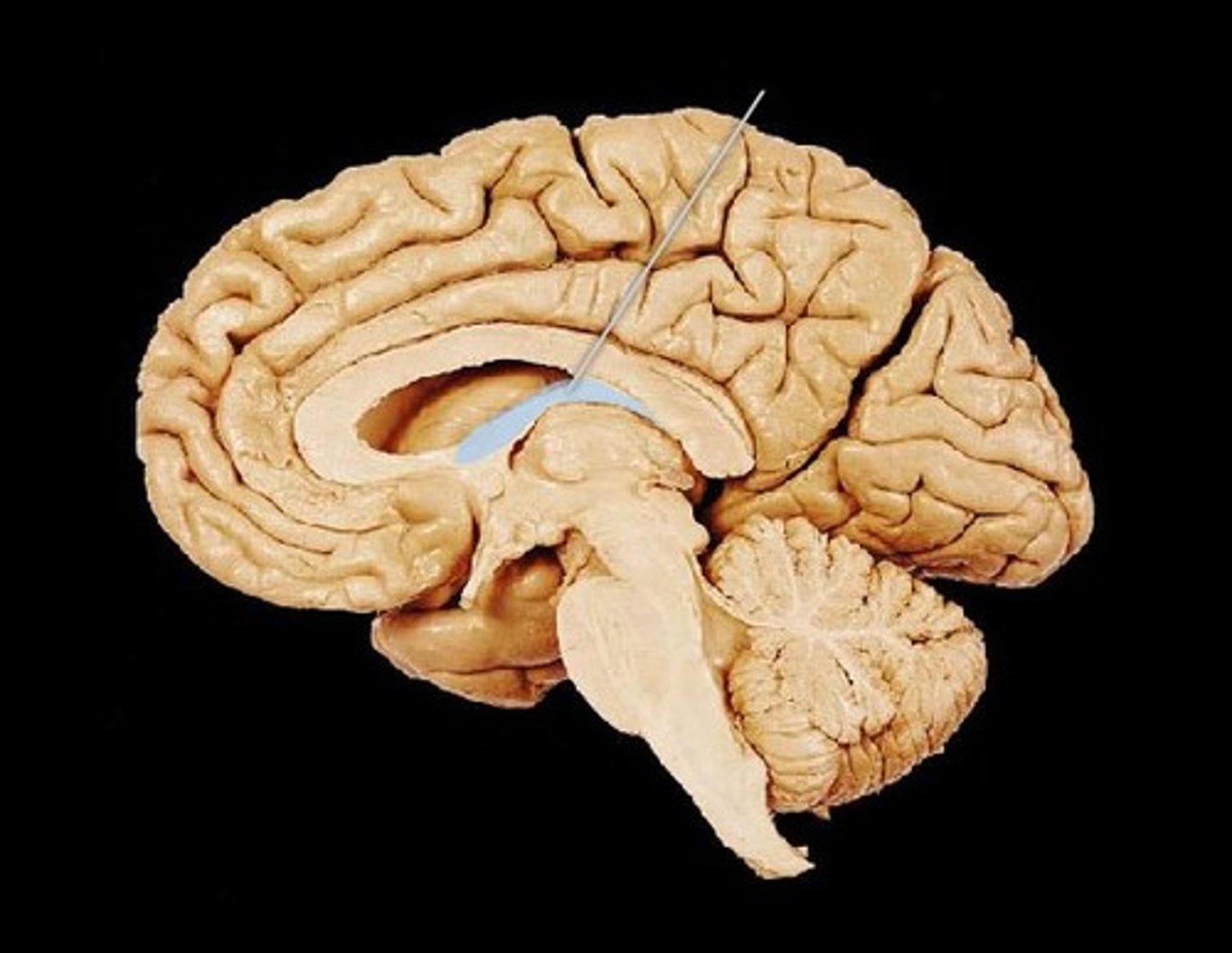
Arbor Vitae
The cerebellar white matter, so called for its branched, tree-like appearance. In some ways it more resembles a fern and is present in both cerebellar hemispheres. It brings sensory and motor information to and from the cerebellum.
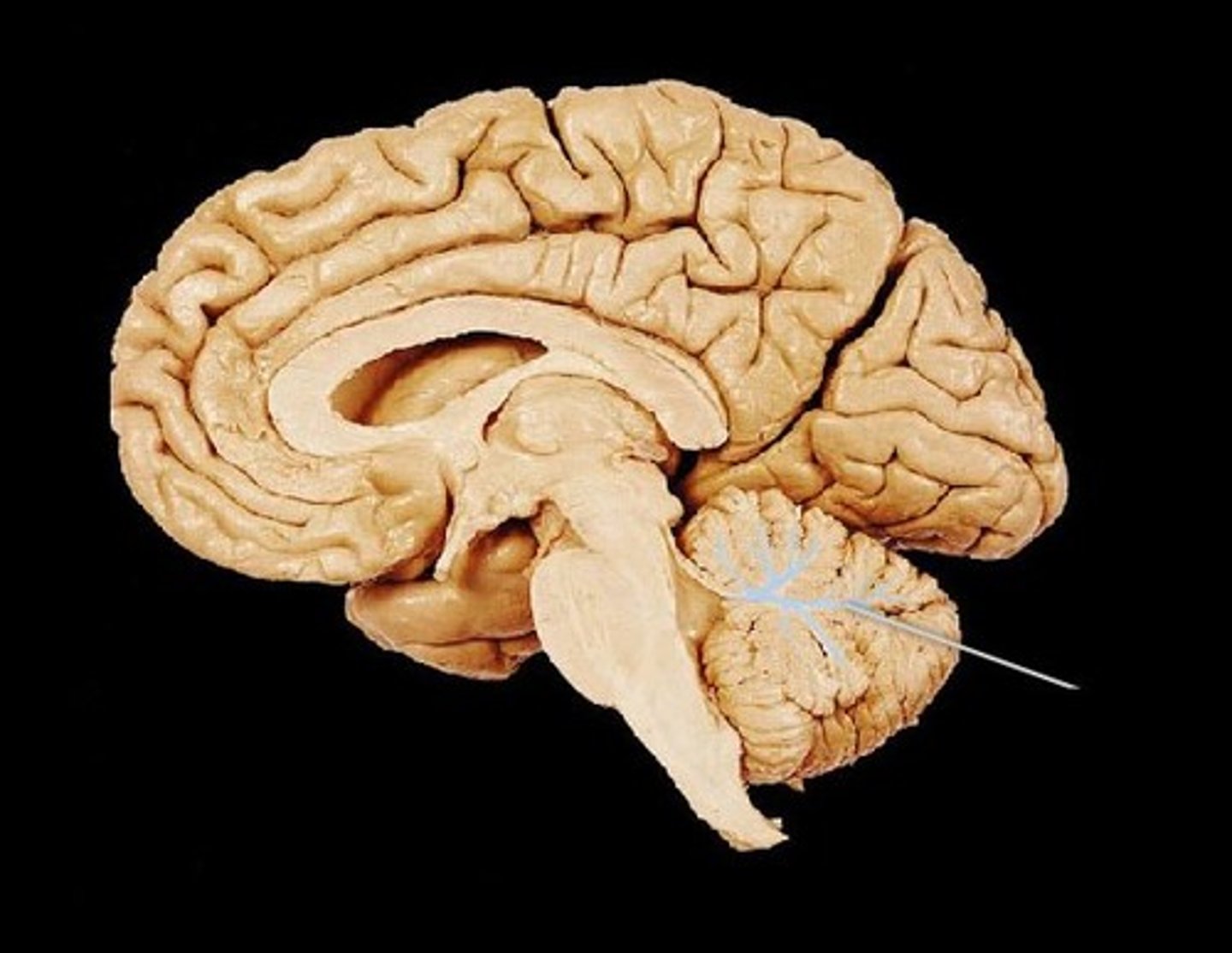
Superior Colliculus
Located in the Midbrain. Controls involuntary eye movements and the targeting of the eyes.
Inferior Colliculus
The principal midbrain nucleus of the auditory pathway and receives input from several peripheral brainstem nuclei in the auditory pathway, as well as inputs from the auditory cortex.
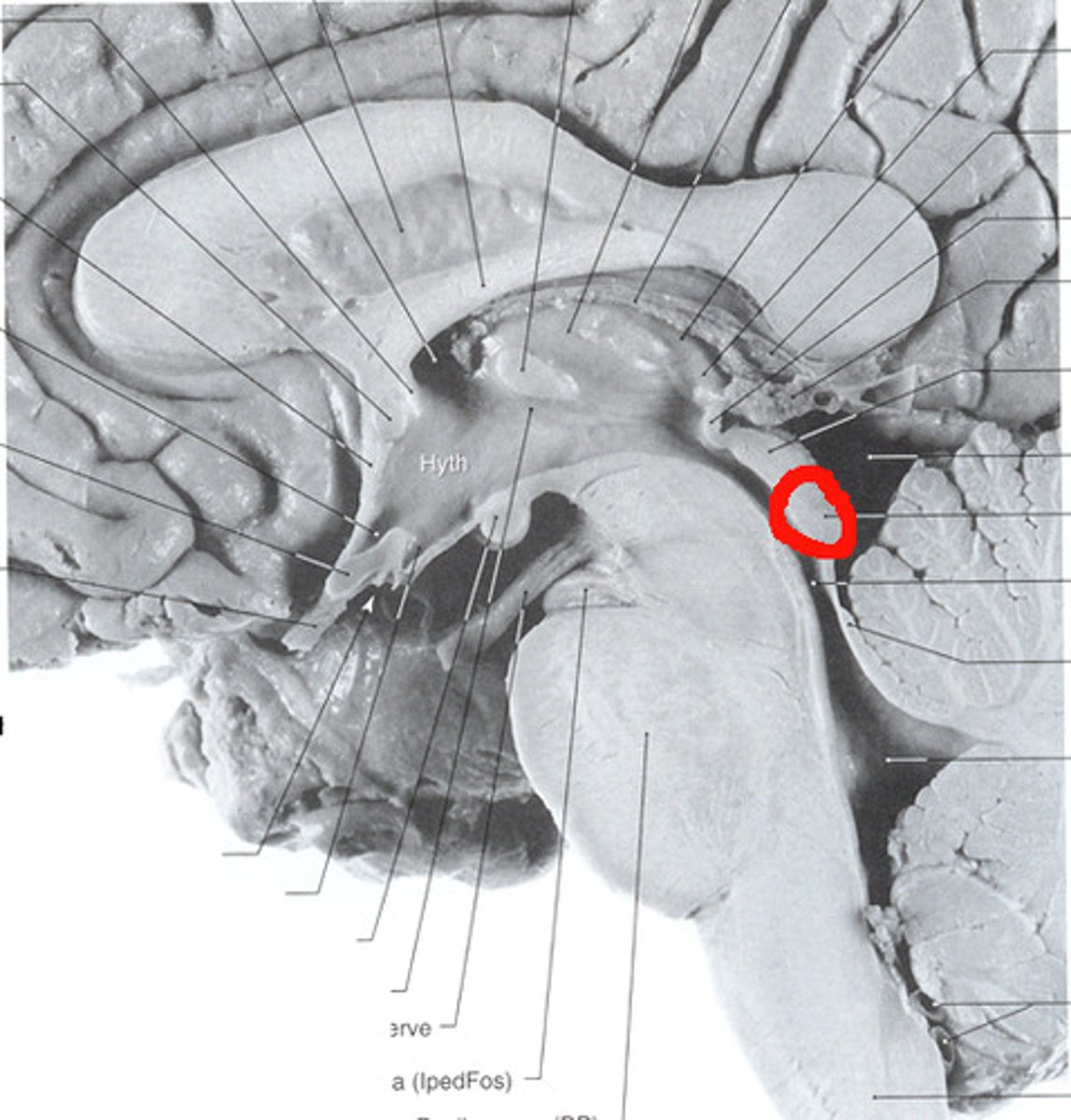
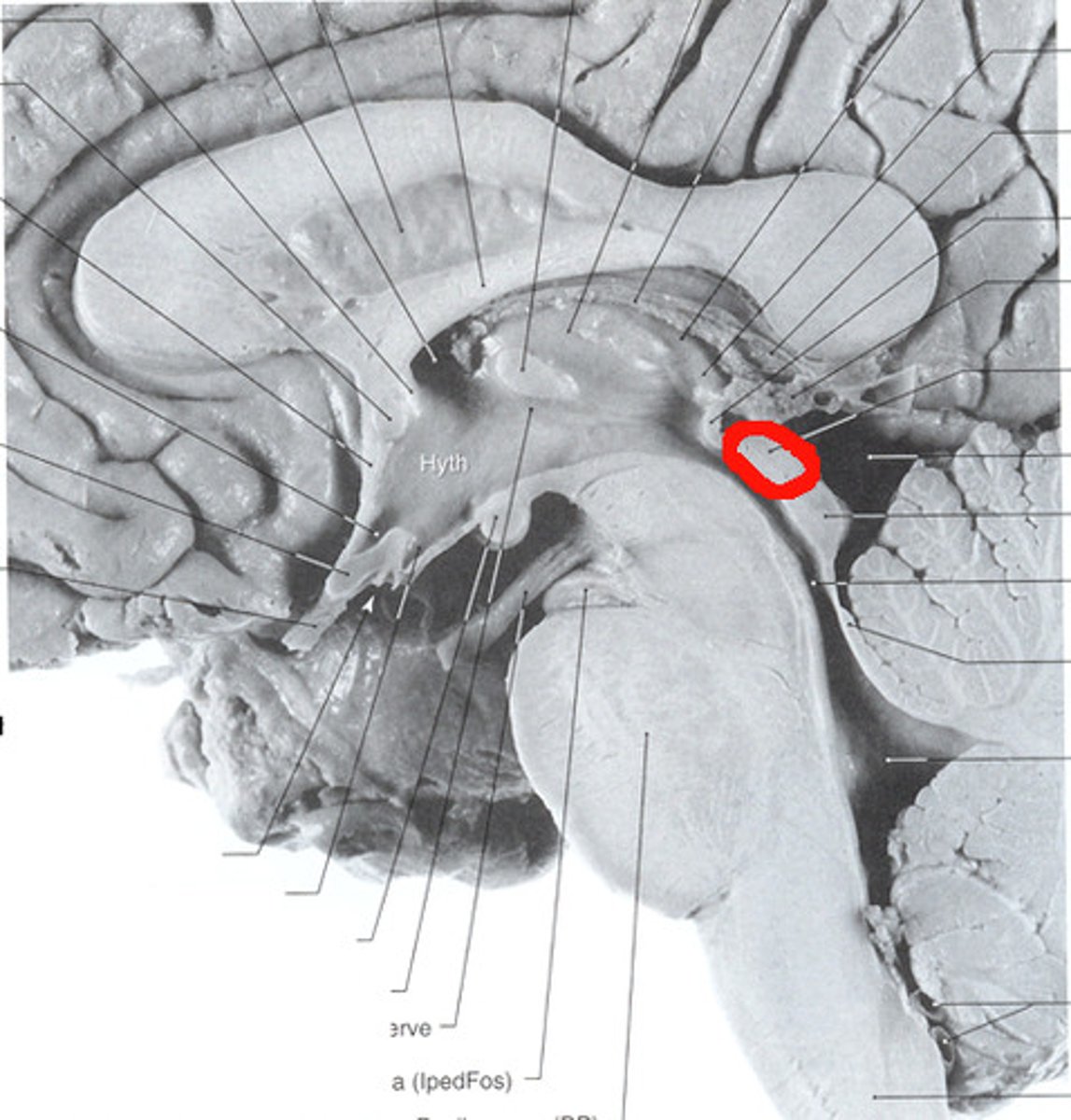
Hypothalamus
A region of the forebrain below the thalamus that coordinates both the autonomic nervous system and the activity of the pituitary, controlling body temperature, thirst, hunger, and other homeostatic systems, and involved in sleep and emotional activity.
Lateral Ventricle
Located in each hemisphere of the cerebrum, C shaped located in the hemisphere of the cerebrum and contains CSF.
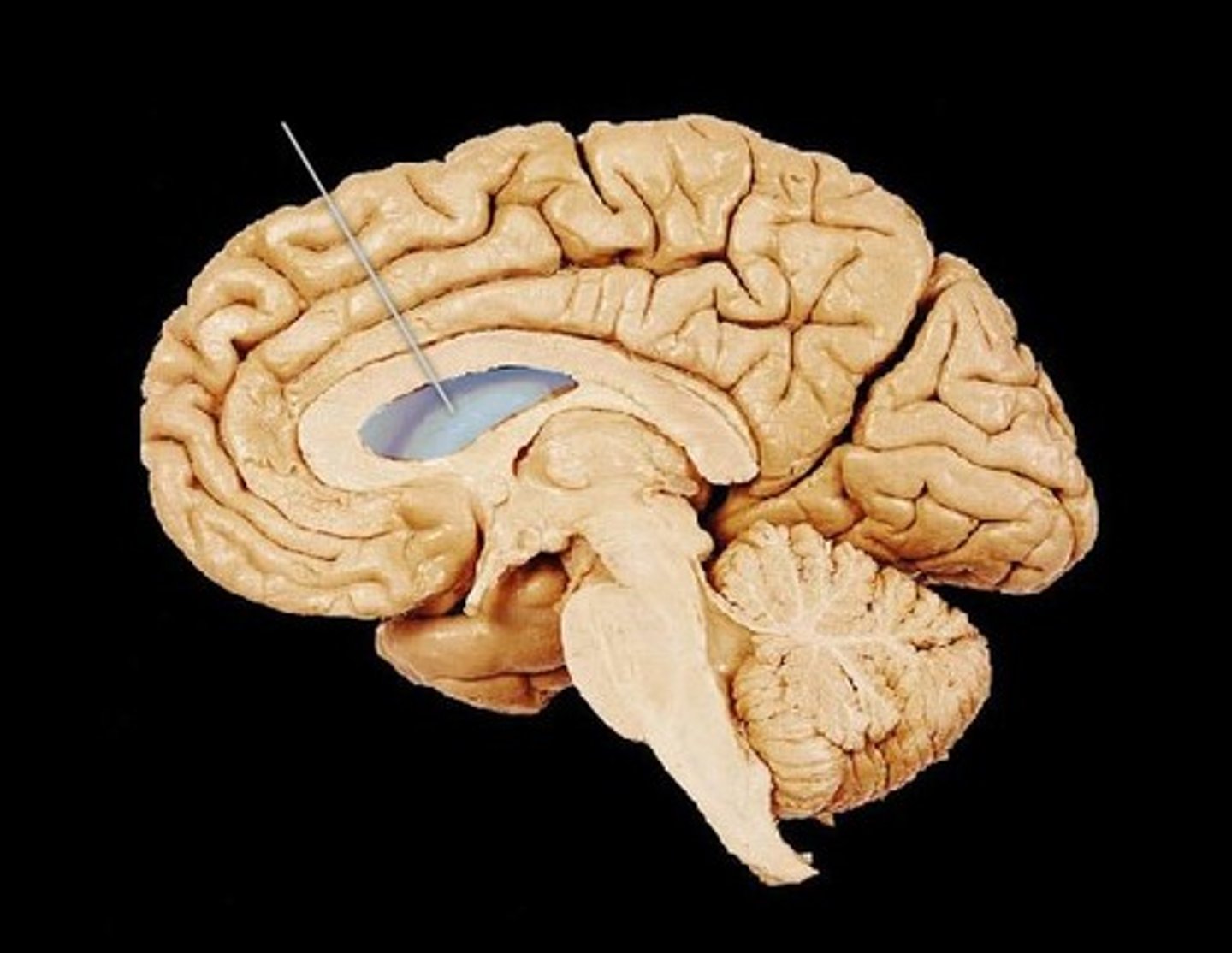
Internal Capsule
A white matter structure situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of brain. It carries information past the basal ganglia, separating the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the globus pallidus.
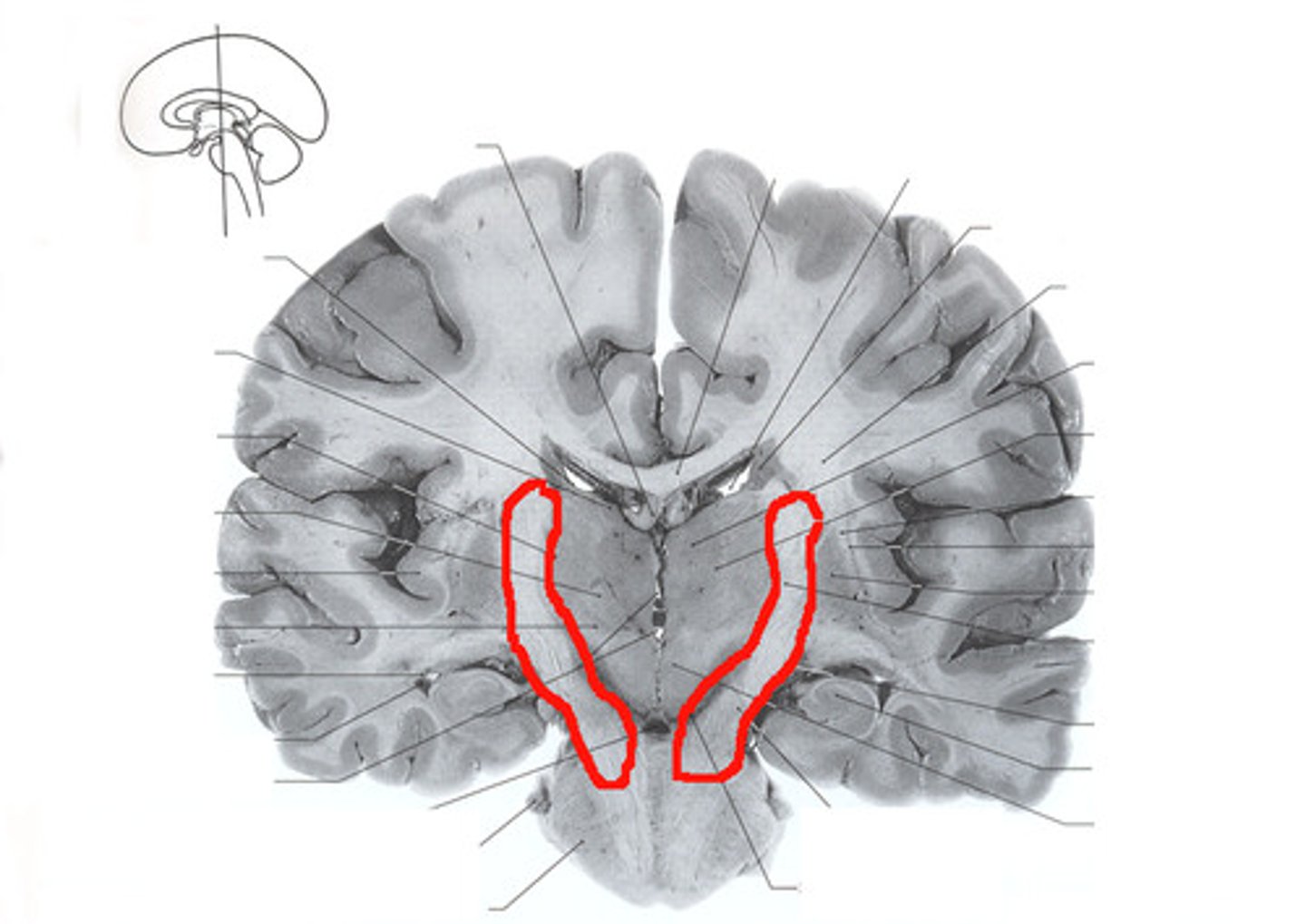
Corona Radiata
A white matter sheet that continues ventrally as the internal capsule and dorsally as the semioval center. This sheet of axons contains both descending and ascending axons that carry nearly all of the neural traffic from and to the cerebral cortex.