M9 (Sir Jerry)
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Communicable Disease
An illness due to an infectious agent or its toxic products.
Criteria:
Transmitted directly or indirectly
Susceptible host
Presence of agent, vector, or inanimate object
Examples: Rabies, UTI
TRUE
“Communicable” and “Infectious” are being used interchangeably. True or False?
TRUE
All contagious are communicable and infectious. True or False?
FALSE
All communicable and infectious are contagious. True or False?
Infectious Disease
An illness wherein there is a presence of a living microorganism in the body
May not be transmitted through ordinary contact (vector, droplets, and indirect contact)
Example: Chickenpox (respiratory droplets)
Contagious Disease
An illness that is easily transmitted from one person to another through direct or indirect means.
Chain of Infection
Causative Agent → Reservoir → Portal of Exit → Mode of Transmission → Portal of Entry → Susceptible Host
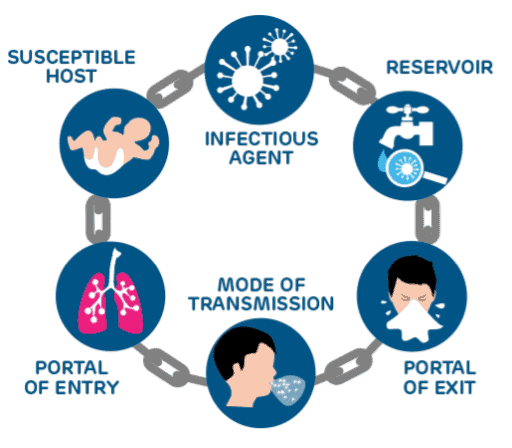
Causative Agent
Any microbe capable of producing a disease.
Bacteria
Virus
Rickettsia(e)
Chlamydia(e)
Fungi
Protozoa
Parasite
Bacteria
One-celled membrane microbes with double cell membranes that protect them from harm.
Reproduce rapidly and are considered as the most common cause of fatal infectious diseases.
Classified according to:
Shape (cocci, bacilli, spirillae)
Need for oxygen (aerobic, anaerobic)
Response to staining (gram (+) or (-), or acid-fast)
Motility (motile, non-motile)
Tendency to capsulate (encapsulated, capsulated)
Capacity to form spores (spore-forming, non-spore-forming)
Example: Tuberculosis, Syphilis
Virus
Smallest known microbes
Cannot replicate independently of the host’s cells; invade and stimulate the host’s cells to participate in the formation of additional microbes
Example: COVID-19 virus, HIV, influenza/flu
Rickettsia(e)
Small, gram (-) bacteria-like microbes that can induce life-threatening infections.
Require a host cell for replication
Usually transmitted through a bite of an arthropod carrier, such as lice, ticks, fleas
Example: rocky mountain fever, typhus fever, Q fever
Chlamydia(e)
Common cause of infection of the urethra, bladder, fallopian tubes, and prostate gland
Most common infection is transmitted through sexual contact (STI)
Bacteria: chlamydiasis
Fungi
Thrive inside or outside the body; may be harmful or beneficial
Example: athlete’s foot, candidiasis, pneumocystis carinii (most common opportunistic microbe in HIV)
Protozoa
Simple single-celled organisms of the animal kingdom
Example: malaria, amoeba
Parasite
Live on or inside other organisms (hosts), usually at the host’s expense
Do not usually kill their host but take only the nutrients they need
Example: tapeworm, ringworm, ascariasis
Variability of Pathogenicity
Pathogenicity is the ability of the causative agent to cause a disease:
Mode of Action
Infectivity
Virulence
Antigenicity
Toxigenicity
Mode of Action
How the organisms produce a pathologic process.
Infectivity
Invasiveness; ability to invade and multiply.
Virulence
Degree of the microbe’s pathogenicity
Capacity of pathogen to overcome/destroy immunity
Causes tissue damage
Antigenicity
Ability to induce an immune response to the host
Capacity of pathogen to withdraw being detected by the antibody (stealth)
Toxigenicity
Amount and destructive potential of released toxin, ability to cause a toxic effect
Toxin
Any poisonous protein that is produced by bacterial action.
Exotoxin
Exists outside of the bacteria and circulates independently of the cell body.
Endotoxin
Confined within the body of the bacteria and released only when bacteria are broken down.
Reservoir
The environment and object on which an organism survives and multiplies.
Types:
Human reservoir
Animal reservoir
Non-living reservoir
Human Reservoir
Frank cases (very ill)
Sub-clinical or ambulatory
Carriers
Incubatory Carrier
A person who is incubating the illness.
Convalescent Carrier
A person who is at the recovery stage of illness but continues to shed the pathogenic microorganism.
Intermittent Carrier
A person who occasionally sheds the pathogenic microorganism.
Chronic/Sustained Carrier
A person who always has the infectious organism in his or her system.
Animal Reservoir
Zoonotic such as rabies.
Non-Living Reservoir
Examples are tetanus (soil, wood, rust), hepatitis, cholera (infected water), AGE (water; long-standing food), Clostridia (soil)
Portal of Exit
The path or way in which the microorganism leaves the reservoir.
Respiratory system
GU tract system
GI system
Skin and mucous membranes (Integumentary)
Placenta
Mode of Transmission
The means by which the infectious agent passes through from the portal of exit of the reservoir to the susceptible host
Modes:
Contact
Air-Borne
Vehicle
Vector-Borne
Contact Transmission
Direct
Indirect
Droplet spread
Direct Contact Transmission
Person-to-person transfer
Indirect Contact Transmission
Occurs when the susceptible host comes in contact with a contaminated object.
Droplet Spread
Bigger; more than 5 mm
3-feet caution; equivalent to 1 yard
Heavier, lesser travel tendency
Contact with respiratory secretions when the infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks
Air-Borne Transmission
Occurs when fine microbial particles or dust particles containing microbes remain suspended in the air for a prolonged period.
Less than 5 mm; smaller, and have high travel tendency
Vehicle Transmission
Transmission through articles or substances that harbor the organism until it is ingested or inoculated into the host.
Vector-Borne Transmission
Occurs when a reservoir such as fleas, flies, mosquitoes, ticks, snails, transfers the microbes to another living organism
Example: dengue, filariasis, elephantiasis
Portal of Entry
Venue through which the organism gains entrance into the susceptible host.
Susceptible Host
A person presumably not possessing resistance against a particular causative agent.
Depends on factors that increase or decrease host vulnerability:
age (young/old), sex, and genes
Geographic and environmental factors
General condition (physical, emotional, and mental states)
Underlying diseases (DM, lymphoma, leukemia, neoplasm, uremia)
Treatment (antimicrobial, corticosteroids, radiation, immunosuppressive drugs)
Stages of Infection
Incubation period
Prodromal stage
Illness stage
Convalescent stage
Incubation Period
Time from the invasion of the disease to the period before the appearance of first symptoms.
Asymptomatic
Example: chickenpox - 10-14 days, HIV and hepatitis - 2-6 months
Prodromal Stage
Interval from the onset of nonspecific signs and symptoms to more specific manifestations
Malaise, low-grade fever, fatigue
Growth and multiplication of microorganisms; capable of spreading to others
Illness Stage
Time when the client manifests signs and symptoms specific to type of infection.
Convalescent Stage
Containment of infection, progressive elimination of pathogen
Recovery, but still (+) presence of pathogen
Sporadic
Diseases that occur occasionally and irregularly with no specific pattern
Absence or presence of disease
Endemic
Constant presence of a disease or infectious agent within a geographical area
Example: malaria in palawan
Epidemic
Occurs in greater numbers (population, particular region, or community) than what is expected in a specific area over a specific time
Example: bird flu, FND, swine flu, polio, SARS
Pandemic
Epidemic that affects several countries or continents.
Example: SARS ,HIV, COVID-19, Spanish flue, plague
Immunity
The body’s ability to resist infection afforded by the presence of circulating antibodies and WBC.
Types of Immunity
Natural
Artificial
Sub-Clinical
Natural Immunity
Inherent to the body; not brought by immunization
Passive: acquired through placental transfer (IgG); breastmilk (IgA)
Active: acquired through recovery from a certain disease, with exposure (IgM)
Artificial Immunity
Passive: acquired through the administration of antitoxin, antiserum, and/or gamma globulin; has shorter and immediate effect
Active: acquired through the administration of vaccine and toxoid; give time to build antibodies; has longer effect and cannot be given for immediate use (IgM)
Sub-Clinical Immunity
Acquired through constant exposure to a particular disease or organism
Types of Antigens
Inactivated
Attenuated
Inactivated Antigen
Killed microorganisms; does not mutate
Characteristics
Not long lasting
Multiple doses needed
Booster doses needed
Example: flu vaccine, DPT, hepatitis vaccine
Attenuated Antigen
Live organism but weakened; can mutate
Characteristics
Single dose needed
Long-lasting immunity
Example: BCG, MMR, chickenpox, OPV
Isolation Precautions
Standard precautions
Transmission-based precautions
Standard Precautions
First level which apply to all patients at all times.
Signs and symptoms of infection are not always obvious and therefore may unknowingly pose risk for a susceptible person.
Inclusions:
Hand hygiene
Personal protective equipment
Injection safety
Environmental cleaning
Medical equipment
Respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette
Transmission-Based Precautions
Second level which are intended for individuals who have a known or suspected infection with certain organisms
Inclusions:
Contact precautions
Droplet precautions
Airborne precautions
Seven Categories Recommended in Isolation
Strict isolation
Contact isolation
Respiratory isolation
Tuberculosis isolation
Enteric isolation
Drainage/secretion isolation
Universal isolation
Strict Isolation
Done to prevent highly contagious or virulent infections
Patient’s things are considered as infected
5 Moments of Hand hygiene
Articles used → discarded, bagged, labeled before decontamination
Negative pressure
Contact Isolation
Done to prevent the spread of infection primarily by close or direct contact.
Respiratory Isolation
Done to prevent transmission of infectious diseases over short distances through air.
Tuberculosis Isolation
For TB patient with positive smear or with chest x-ray which strongly suggest active TB
Confirmatory test: sputum (PTB)
3 specimen tabs, done first thing in the morning
Treatment
6-12 months
2 weeks as non-contagious, but needs continuity of medical compliance
Enteric Isolation
For infections that are spread through direct contact with feces.
usually affects pediatric patients
Drainage/Secretion Isolation
Done to prevent infections that are transmitted by direct or indirect contact with purulent materials or drainage from an infected body site.
Universal Isolation
Applied when handling blood and body fluids.
Applied for patients with HIV/HCV
Intended to prevent parenteral, mucous membrane, and non-intact skin exposure to healthcare workers to `blood-borne pathogens
Necessary to prevent infections that are transmitted by direct contact (body fluids)
Alcohol-Based Hand Rub
Used when the hand is visibly not soiled; ideal
Soap and Water
Used when hands are visibly soiled, or after caring for patients with known or suspected infection.
Aseptic Technique
What technique is utilized in preparing medications?
Cleaning
Removal of visible soil and organic contamination from a device or environmental surface using the physical action of scrubbing with a surfactant or detergent and water, or an energy-based process (e.g., ultrasonic cleaners) with appropriate chemical agents.
Disinfection
A less lethal process of microbial inactivation (compared to sterilization)
Eliminates virtually all recognized pathogenic microorganisms but not necessary all microbial forms (e.g., bacterial spores)
Do not use disinfectant products as cleaners unless labeled suitable for such use
Reusable Medical Equipment
Accompanied by instructions for cleaning and disinfection or sterilization as appropriate.
Example: endoscopes
Single-Use Devices (SUDS)
Labeled by the manufacturer for only a single use and do not have reprocessing instructions
Reusable Medical Equipment Classification
Critical items
Semi-critical items
Noncritical items
Environmental surfaces
Critical Items
Objects that enter sterile tissue or the vascular system and must be sterile prior to use
Example: surgical instruments
Semi-Critical Items
Contact mucous membranes or non-intact skin and require high-level disinfection (at a minimum) before reuse
Example: endoscopes (upper endoscopy and colonoscopy)
Noncritical Items
May come in contact with intact skin but not mucous membranes
Should undergo low or intermediate-level disinfection depending on the nature and degree of contamination
Example: BP cuffs
Environmental Surfaces
Generally do not have contact with the patient during the delivery of care
Cleaning may be all that is needed for the management of these surfaces
If disinfection is indicated, low-level disinfection is appropriate
Example: floors, walls
Hand Hygiene
Reduce the risk of spreading infections in ambulatory care settings.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Intended to protect the HCP from exposure to or contact with infectious agents.
Injection Safety
Prevent transmission of infectious diseases during preparation and administration of parenteral medications.
Respiratory Hygiene/Cough Etiquette
Element of standard precautions
Highlights the need for prompt implementation of infection prevention measures at the first point of encounter with the facility/ambulatory settings
For patients with accompanying family members/friends with undiagnosed transmissible respiratory infections
Applies to any person with signs of illness
Contact Precautions
Applied to patients with:
Stool incontinence (norovirus, rotavirus, clostridiuum difficile), draining wounds, uncontrolled secretions, pressure ulcers
Ostomy tubes and/or bags draining body fluids
Generalized rash or exanthems
Placed in an exam room (prioritize stool incontinence, draining wounds, skin lesions that cannot be covered/uncontrolled secretions)
utilize gloves, gown, and hand hygiene; disinfect exam room
Use separate bathroom
Droplet Precautions
Applied to patients known or suspected to be infected with a pathogen that ca be transmitted by droplet route:
Respiratory viruses (influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, human metapneumovirus)
Bordetella pertussis
For first 24 hours of therapy: neisseria meningitidis, group A streptococcus
Placed in a closed exam room (prioritize excessive cough and sputum production); if not available, provide face mask and separate area far from other patients; avoid coming into close contact; respiratory hygiene; disinfect exam room
Utilize face mask, gloves, gown, goggles, hand hygiene
Airborne Precautions
Applied to patients known or suspected to be infected with a pathogen that can be transmitted by airborne route
Tuberculosis
Measles
Chickenpox (until crusting over of lesions)
Localized (immunocompromised patient) or disseminated herpes zoster (until crusting over of lesions)
Separate entrance; place in airborne infection isolation room (AIIR); If not available, provide face mask
Placed in closed exam room; instruct patient to keep facemask on—change when it becomes wet; same procedure as other precautions
Utilize fit-tested N-95 or higher-level disposable respirator, gloves, gown, goggles, face shield, hand hygiene
Vacant the exam room for generally one hour.