Understanding Queuing Theory and Waiting Line Systems
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
What is the primary goal of management regarding waiting lines in service facilities?
To avoid long lines as they may cost them business.
What is queuing theory?
A detailed mathematical analysis used to solve waiting line situations.
Who proposed the initial mathematical model of queuing theory?
Agner Kracup Erlang.
What are the two main characteristics of waiting line situations?
Fluctuating demand and formation of a queue.
What does fluctuating demand refer to in waiting line situations?
The instability of service demand during certain periods, such as paydays and product promotions.
What happens when the demand for service exceeds capacity?
A waiting line or queue is formed.
What can result from poor customer service in a waiting line situation?
Losing future sales.
How many pairs of cashiers and baggers does the supermarket employ?
16 pairs.
During weekdays, how many pairs of cashiers and baggers are typically on day off?
3 to 4 pairs.
What are the morning and evening shift hours for the supermarket?
Morning shift: 8:00 am to 5:00 pm; Evening shift: 11:00 am to 8:00 pm.
What is a suggested solution to avoid long lines at the supermarket during peak hours?
Hiring an additional pair of cashiers and baggers.
What time is identified as a peak hour that causes long lines at the supermarket?
Around 6:00 pm.
What is a potential consequence of long lines at the checkout counters?
Irate shoppers may leave the store and buy from nearby stores.
What must the manager consider when deciding to increase capacity at the supermarket?
Whether the additional cost of hiring more staff justifies the increased capacity.
What types of establishments commonly experience waiting lines?
Toll booths, banks, supermarkets, restaurants, and traffic jams.
What is one method management can use to address waiting line issues?
Adding resources to the system.
What can cause variations in the length of service in a supermarket?
The number of items bought by shoppers.
What is the impact of fluctuating demand on service facilities?
It leads to varying customer wait times and service efficiency.
How does queuing theory apply to different fields?
It has applications in emergency medical aid, passenger service in air terminals, computer systems, and more.
What is the significance of understanding waiting line characteristics?
It helps in effectively managing customer service and operational efficiency.
What can be a consequence of not managing waiting lines effectively?
Loss of customers and potential sales.
What is a typical queuing system process?
Customers arrive, wait for service, receive service, and leave.
What happens to customers who do not want to wait in line?
They leave without receiving service.
What are the main parts of a queuing system?
1. Customers and Their Source 2. Arrival Process 3. Queue (Waiting Line) 4. Service Facility and Service Process 5. Exit Process
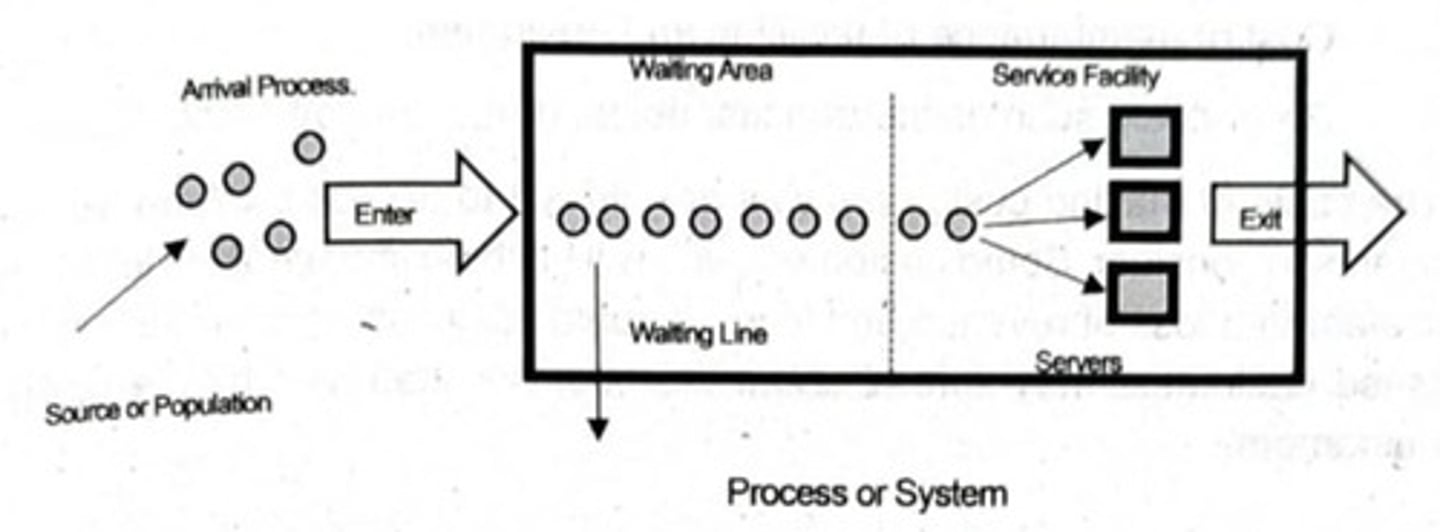
Who can be considered customers in a queuing system?
Customers can be people, machines, cars, airplanes, or raw materials.
What is the arrival process in a queuing system?
The manner in which customers enter the service area.
What is the queue in a queuing system?
The line where customers wait if all service spots are busy.
What is the service facility in a queuing system?
The location where the actual service occurs, which can be a person, group, or machine.
What is the exit process in a queuing system?
The point at which the customer exits after completing the service cycle.
What are the two major costs considered in a queuing system?
1. Cost of Providing the Service 2. Cost of Making Customers Wait
What does the cost of providing the service include?
Construction Cost, Operational Cost, Maintenance Cost, Other Fixed Costs.
What are the types of losses involved in the cost of making customers wait?
1. Loss of Time 2. Loss of Goodwill 3. Loss of Sales 4. Loss of Repeat Business.
What are the three steps in the methodology of queuing analysis?
1. Establish measures of performance 2. Compute measures of performance 3. Make an analysis.
What are some examples of measures of performance in a queuing system?
Average waiting time, average number of customers in the queue, measure of busy or idle time of servers.
How can the source of customers be classified?
Into finite and infinite categories.
What is a finite source in a queuing system?
A limited number of entities, such as a repair crew for ten pieces of equipment.
What is an infinite source in a queuing system?
An unlimited number of entities, such as tourists visiting a site.
What are the two types of arrivals in a queuing system?
Batch arrivals and individual arrivals.
What are scheduled arrivals?
Customers who arrive with prior appointments.
What are nonscheduled arrivals?
Customers who arrive without advance notice.
What is the mean arrival rate (λ)?
The average number of arrivals per unit of time, calculated by dividing the total number of arrivals by the total time observed.
How is the mean arrival rate calculated in a supermarket example?
If 20 customers arrive over two hours, the mean arrival rate is 10 customers per hour (20/2).
What does the mean interarrival time represent?
The average time between consecutive arrivals.
How is the mean interarrival time calculated if the time between the first and second arrival is 11 minutes?
It can be computed as 5.45 minutes (60/11).
What type of distribution do interarrival times for nonscheduled arrivals follow?
A negative exponential distribution.
If the average arrival rate (λ) is 6 per hour, what is the average interarrival time?
10 minutes between arrivals.
What is the Poisson distribution used for in the context of arrivals?
It illustrates the arrival process, describing random arrivals over time when the mean number of arrivals is known.
What is the significance of the Greek letter λ in arrival processes?
It designates the average arrival rate.
What are the basic arrangements of service facilities?
Single service facility, multiple parallel identical facilities, multiple parallel non-identical facilities, and service facilities arranged in a series.
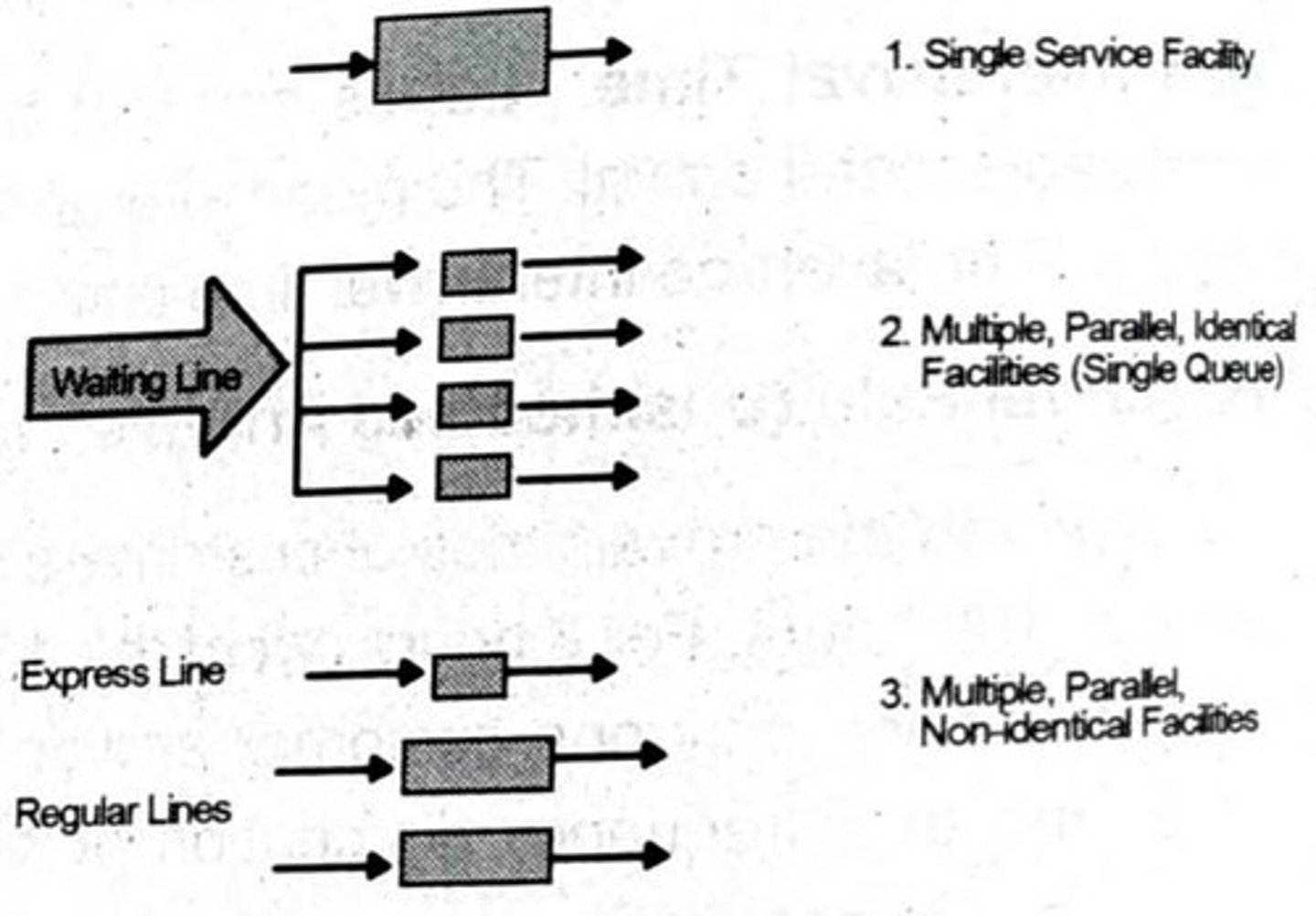
What is the difference between constant and fluctuating service time?
Constant service time is fixed (e.g., five minutes per service), while fluctuating service time varies and can be expressed as a frequency distribution.
What does the service rate (μ) measure?
The service capacity of the facility expressed in customers per unit of time.
How is the average service time calculated?
It is designated by 1/μ, representing the average length of time a cashier processes one shopper.
What are some common queue disciplines?
Priority System, Emergency (Preemptive Priority) System, and First-in, First Served (FIFS).
What is 'balking' in the context of waiting lines?
When customers feel discouraged to join a very long queue.
What is 'reneging' in the context of waiting lines?
When customers leave the queue after waiting for a period.
What is the role of queue discipline in waiting lines?
It determines the rules and regulations governing the order in which customers are served.
What is an example of a single service facility?
A doctor's chair.
What is an example of multiple parallel identical facilities?
Banks or gasoline stations.
What is an example of multiple parallel non-identical facilities?
A supermarket with express lanes and regular lanes.
What does a frequency distribution of arrival times for nonscheduled arrivals resemble?
It may look like a Poisson distribution.
What is the average service time if the service rate is 20 customers per hour?
3 minutes per customer (1 hour / 20 customers = 60 mins / 20 customers).
What happens to customers who feel irritated and tired of waiting in a queue?
They will leave the queue without being served.
What is 'jockeying' in the context of queuing?
Customers transfer from one waiting line to another.
Define 'cycling' in queuing situations.
Cycling refers to returning to the queue immediately after being served, similar to children in a playground.
What does 'combining or dividing' refer to in queuing?
It includes combining or dividing the lines at certain queue lengths, as seen in supermarkets.
How are queuing situations named?
They are named based on the X/Y/Z notation, where X indicates the arrival process, Y refers to the service process, and Z tells the number of servers used.
What are the two basic approaches to solving queuing problems?
The two approaches are the Analytical Approach and Simulation.
What is the Analytical Approach in queuing?
It utilizes formulas to determine measures of performance, though it can be impractical for complex situations.
When should simulation be applied in queuing problems?
Simulation should be applied when the analytical approach is not appropriate.
What are the three inputs in most queuing models?
Mean arrival rate (λ), mean service rate (μ), and number of servers (K).
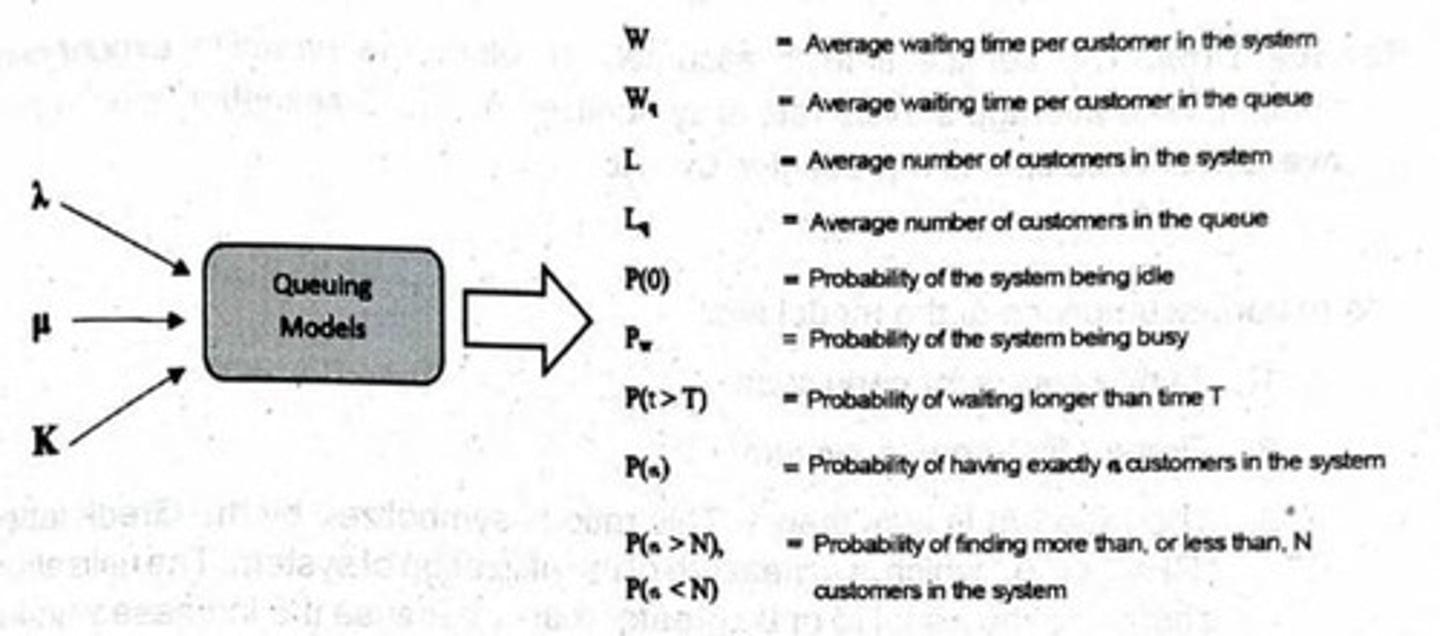
What characterizes a Deterministic Queuing System?
The arrival rate equals the service rate, such as customers arriving every five minutes and being served in five minutes.
What occurs when the arrival rate is larger than the service rate in a queuing system?
Customers arrive more frequently than they can be served, leading to longer wait times.
What is the Basic Poisson-Exponential Model (M/M/1)?
It is a classical queuing model characterized by random arrival rates following a Poisson distribution and service times following a negative exponential distribution.
What symbol represents the average arrival rate in queuing models?
The Greek letter lambda (λ).
What symbol represents the average service rate in queuing models?
The Greek letter mu (μ).
What is the significance of the ratio λ/μ in queuing models?
It should be less than 1 to avoid an 'explosive' situation, indicating the system's utilization.
What are the major assumptions of the Basic Poisson-Exponential Model?
1. Infinite source of population, 2. First-in, first-served system, 3. λ/μ < 1, 4. Steady state must be achieved, 5. Unlimited waiting space.
What are the two components of total cost (TC) in a queuing system?
Facility cost (CF) and total cost of waiting customers (CW).
How can waiting cost (CW) be expressed?
It can be expressed by the waiting time before being served (Wq) or the total time in the system (W).
What does facility cost (CF) include?
It includes fixed costs (rent, insurance, taxes) and variable costs.
How many students can an online math tutor attend to in one hour according to the notes?
The tutor can attend to 10 students.
What is the average waiting time (W) in a queuing system?
The average time a customer stays in the system, including waiting and being served, calculated as W = 1 / (μ - λ). For the given values, W = 0.2 hours.
How is the average waiting time in the queue (Wq) calculated?
Wq = λ / (μ(μ - λ)). For the given values, Wq = 0.1 hours.
What does L represent in queuing theory?
L is the average number of customers in the system, including those in the queue and those being served. For the given values, L = 1 student.
How is the average number of customers in the queue (Lq) calculated?
Lq = λ / (μ(μ - λ)). For the given values, Lq = 0.5 students.
What is the probability of an empty facility (P(0))?
P(0) = 1 - (λ / μ). For the given values, P(0) = 0.5.
How is the probability of the system being busy (Pw) calculated?
Pw = 1 - P(0). For the given values, Pw = 0.5.
What is the formula for the probability of being in the system longer than time T (P(t > T))?
P(t > T) = e^((λ - μ)T). For T = 0.5 hours, P(t > T) = e^(-2.5) = 0.0821.
How is the probability of finding exactly n customers in the system (P(n)) calculated?
P(n) = (λ^n / μ^n) * (1 - (λ / μ)). For n = 4, P(4) = 0.0312.
What does P(n > N) represent in queuing theory?
P(n > N) is the probability that the number of customers in the system, n, will be larger than a specified number of customers, N.
What is the relationship between the number of customers in the system (L) and the average time per customer (W)?
L = λW, indicating how many are using the system.
What does Lq = λWq signify?
It represents the number of customers in the queue, indicating how many are waiting.
How is the total time per customer in the system (W) calculated?
W = Wq + 1/μ, representing total time per customer including waiting and service.
What is the average arrival rate (λ) of students?
The average arrival rate is 5 students per hour, calculated from students arriving every 12 minutes.
What is the service rate (μ) of the system?
The service rate is 10 students per hour.
How do you convert the arrival time of students from minutes to hours?
To convert from minutes to hours, divide the number of minutes by 60. For example, 12 minutes = 1/5 hour.
What is the significance of queuing theory in management?
Queuing theory is used to compute the performance measures of a service system, aiding in the design and improvement of service operations.
What is the formula for calculating the average number of customers in the system (L)?
L = λ / μ, where λ is the arrival rate and μ is the service rate.
What does the term 'service facility' refer to in queuing theory?
The service facility refers to the system where customers receive service, such as a tutoring platform.
What is the impact of increasing the service rate (μ) on the average waiting time (W)?
Increasing the service rate (μ) generally decreases the average waiting time (W) in the system.