1.8 IPv6 Addressing
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
128
IPv4 has 32-bit length addresses
IPv6 has ___-bit length addresses
Split up into 8 segments of 16 bits each
Compression rules
Groups of zeroes (0000) can be abbreviated with ::
Leading zeros are optional, can be removed
Zeros that come before a non-zero number
Ex. 0001 becomes 1
2600:DDDD:1111:1::1
2600:DDDD:1111:0001:0000:0000:0000:0001 compressed
2601:4C3:4002:BE00::66
2601:04C3:4002:BE00:0000:0000:0000:0066 compressed
6to4 addressing
Method of tunneling IPv6
An IPv6 packet is sent over IPv4, by encapsulating IPv6 within IPv4
Requires a special relay router; troublesome
Not used anymore
4in6 tunneling
Method of tunneling IPv6
Transfer IPv4 traffic over an IPv6 network, by encapsulating IPv4 within IPv6
Not used anymore
Dual-stack routing
IPv4 and IPv6 are being used at the same time
Most devices now will probably be using this
Apps can decide to use IPv4 or IPv6
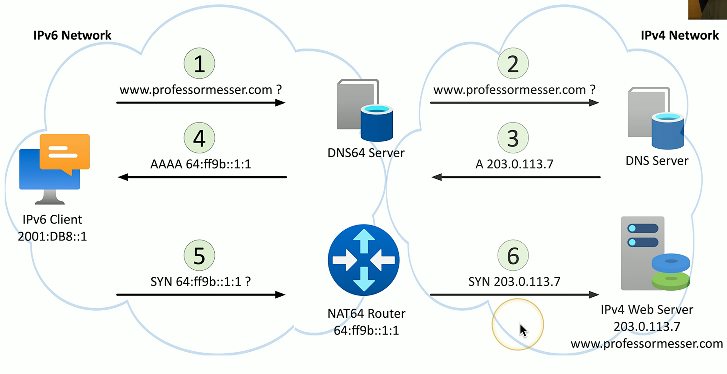
NAT64
Translate IPv4 address to IPv6
Requires a NAT64-capable router and DNS64 server
NAT is usually used to translate private IPv4 to public IPv6
NAT64 process
Client (IPv6) makes request to DNS64 server
DNS64 server makes request to destination DNS server (IPv4)
DNS server sends back IPv4 address to DNS64 server
DNS64 server sends IPv6 version of the IPv4 address to the client, which is the address to the NAT64 router
Now, when the client wants to comm with the IPv4 network, it will send a SYN to the NAT64 router
The NAT64 router will translate the IPv6 address to a IPv4 address, and then send the comm to the IPv4 network