APHG Unit 2, Population + Migration Cumulative Set
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
demography
The scientific study of population characteristics.
ethnicity
Identity with a group of people that share distinct physical and mental traits as a product of common heredity and cultural traditions.
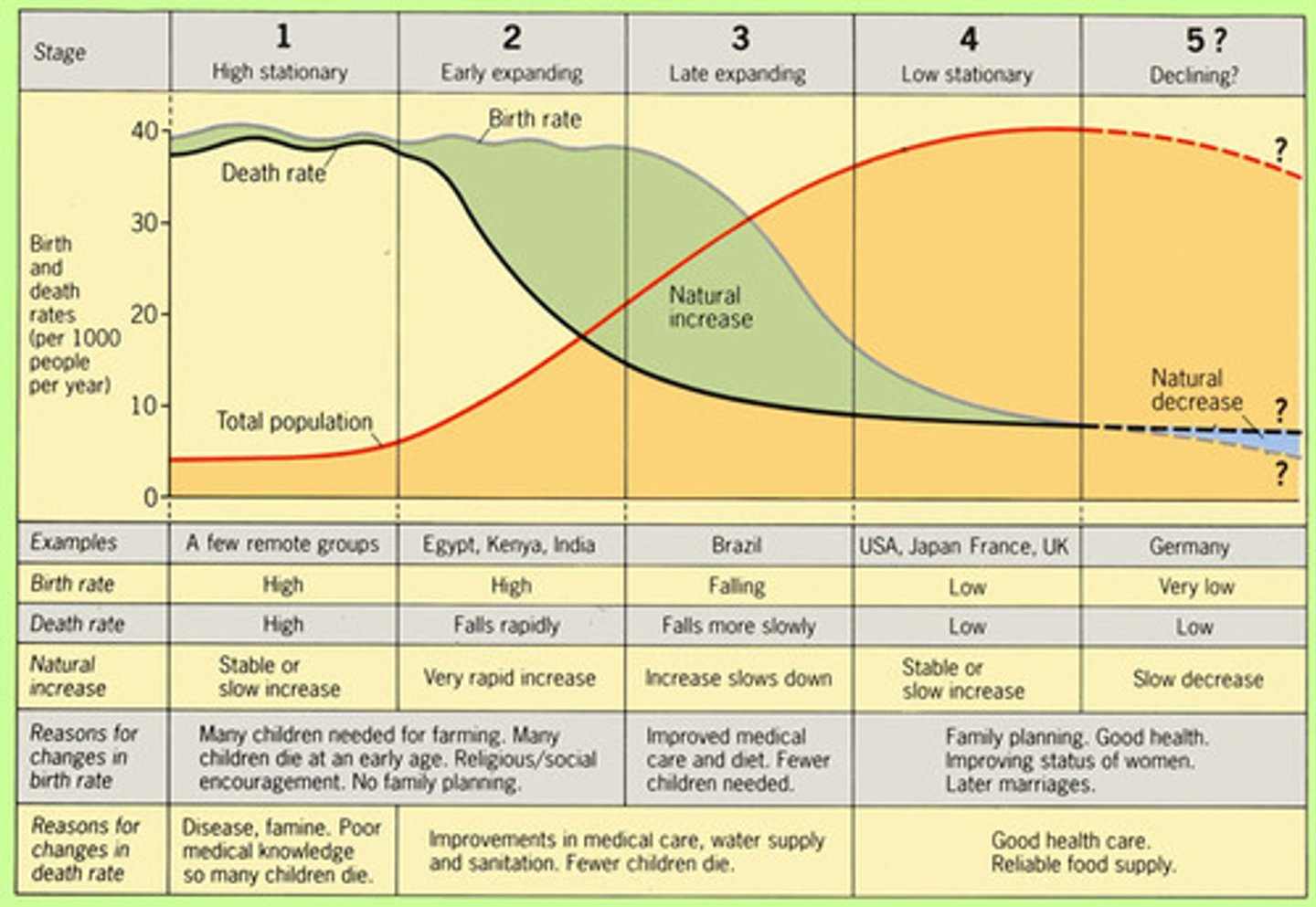
Demographic Transition Model
A sequence of demographic changes in which a country moves from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates through time.
ecumene
The portion of Earth's surface occupied by permanent human settlement.
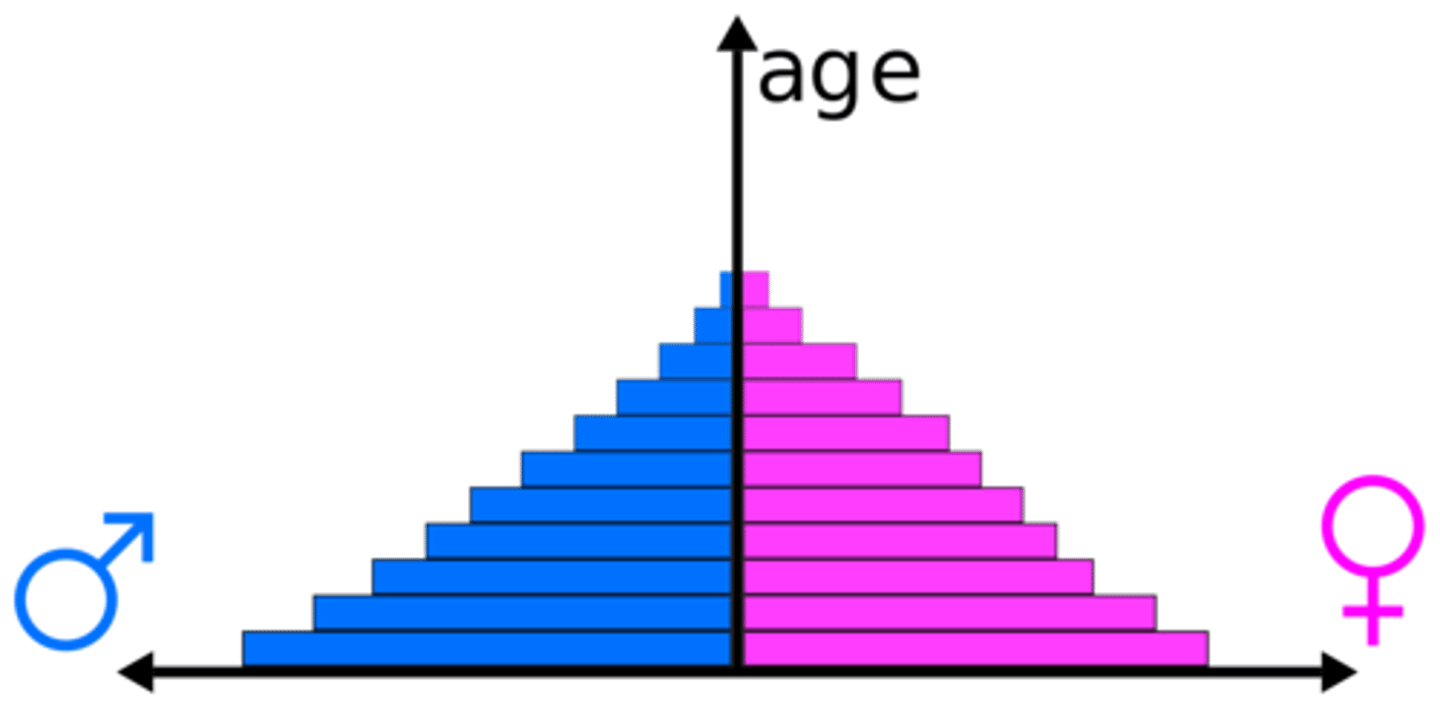
Population Pyramid (Age-Sex Pyramid)
A bar graph representing the distribution of population by age and sex.
Stage 1 Demographic Transition Model
low growth - high birth rate, high death rate, (birth and death rate cancel each other out), and low population growth
NO COUNTRY IS IN THIS STAGE; only a few ISOLATED regions in the world
cohort
a group of people from a given time period/age group
social stratification
a system by which a society ranks categories of people in a hierarchy
Stage 2 of Demographic Transition Model
high growth - high birth rate, falling death rate, high population growth (society: from agricultural to urbanized, raising quality of life)
Ex: Egypt, Kenya, India
Industrial Revolution
A series of improvements in industrial technology that transformed the process of manufacturing goods and allowed for an increase in population
birth deficit
The bars of a population pyramid representing children born during conflict are often significantly shorter than the bars immediately above and below them.
Stage 3 of Demographic Transition Model
moderate growth - falling birth rate, low death rate, steady population growth (urbanized and more industrialized families have less children)
Ex: Brazil
Irish Potato Famine
A famine in 1845 when the main crop of Ireland, potatoes, was destroyed by disease. Irish farmers grew other food items, such as wheat and oats, but Great Britain required them to export those items to them, leaving nothing for the Irish to live on. As a result, over 1 million Irish died of starvation or disease, while millions of others migrated to the United States.
Stage 4 Demographic Transition Model
low/stationary growth - low birth rate, low death rate, steady/stationary population growth
Ex: USA, France, UK
baby boom
In general, birth rate spikes
Specifically, a cohort of individuals born in the United States between 1946 and 1964, which was just after World War II in a time of relative peace and prosperity. These conditions allowed for better education and job opportunities, encouraging high rates of both marriage and fertility.
Stage 5 Demographic Transition Model
Slowly falling death rate,
Low birth rate
Slowly declining population
Ex: Japan
baby bust
In general, lower birth rates post baby boom
For example, the period of time during the 1960s and 1970s when fertility rates in the United States dropped as large numbers of women from the baby boom generation sought higher levels of education and more competitive jobs, causing them to marry later in life. As such, the fertility rate dropped considerably, in contrast to the baby boom, in which fertility rates were quite high.
Black Plague
A disease that engulfed Europe during the Middle Ages. It killed about one-third of the population and was carried by fleas. Because of this, the feudal system died out.
overpopulation
The number of people in an area exceeds the capacity of the environment to support life at a decent standard of living.
echo
increase in births due to an earlier boom
4 regions of population concentration
East Asia
South Asia
Europe
Southeast Asia
Zero Population Growth (ZPG)
A decline of the total fertility rate to the point where the natural increase rate equals zero.
Countries with negative natural increase
North America
Japan
Europe (continent, I know)
Australia/New Zealand
potential workforce
people ages 15-64 that are expected to be the society's labor force
Epidemiological Transition Model
The theory by Abdel Omran that says that there is a distinct cause of death in each stage of the demographic transition model. It can help explain how a country's population changes so dramatically.
Stage 1 of Epidemiological Transition
HIGH CDR: the stage of pestilence and famine; infectious and parasitic diseases; attacks by animal and other humans; "natural checks" on population growth
Ex: Black Plague
dependent population
those people that rely on others for support for the goods and services they consume, usually the very young (15 and under) and very old (65+)
Arithmetic Density
The total number of people divided by the total land area.
mortality
a measure of the number of deaths in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time
Stage 2 of Epidemiological Transition
RAPIDLY DECLINING CDR: stage of receding pandemics; primarily due to poor nutrition, low sanitation and few available medicines in the environment
Cholera--water sanitation (London in 1800s, Haiti more recently)
Physiological Population Density
The number of people per unit area of arable land
Stage 3 of Epidemiological Transition
MODERATELY DECLINING CDR: degenerative, human caused diseases; decrease in deaths caused by infectious diseases and an increase in deaths associated with chronic diseases caused by aging; cardiovascular diseases and various forms of cancer
total fertility rate (TFR)
The average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years.
Agricultural density
The ratio of the number of farmers to the total amount of land suitable for agriculture
crude birth rate (CBR)
the number of births per 1,000 individuals per year
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that an environment can support without damage to the environment
Stage 4 of Epidemiological Transition
LOW BUT INCREASING CDR: delayed degenerative diseases; people still have the degenerative diseases but are able to expand their life expectancy through medical advances
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
The total number of deaths in a year among infants under 1 year old for every 1,000 live births in a society.
Stage 5 of Epidemiological Transition Model
POSSIBLE Reemerging infectious and parasitic disease through Globalization (EX: Malaria, TB, SARS, AIDS)
Child Mortality Rate (CMR)
-Number of deaths of children from the age of 1 to 5 per 1,000 live births in that year
natural increase rate (NIR)
The percentage growth of a population in a year, computed as the crude birth rate minus the crude death rate.
infrastructure
the basic physical and organizational structures and facilities (e.g., buildings, roads, and power supplies) needed for the operation of a society or enterprise.
Infant mortality rate (IMR)
The total number of deaths in a year among infants under 1 year old for every 1,000 live births in a society.
Higher in developing regions, lower in developed regions
doubling time
The number of years needed to double a population, assuming a constant rate of natural increase.
Life expectancy
The average number of years an individual can be expected to live, given current social, economic, and medical conditions. Life expectancy at birth is the average number of years a newborn infant can expect to live.
Higher in developed regions, lower in developing
Arithmetic Growth (Populations)
Situation where a population increases by a constant number of persons (or other objects) in each period being analysed.
A steady change in population numbers due to addition, with equal changes in population over equal increments in time (i.e. 2+2+2+2...)
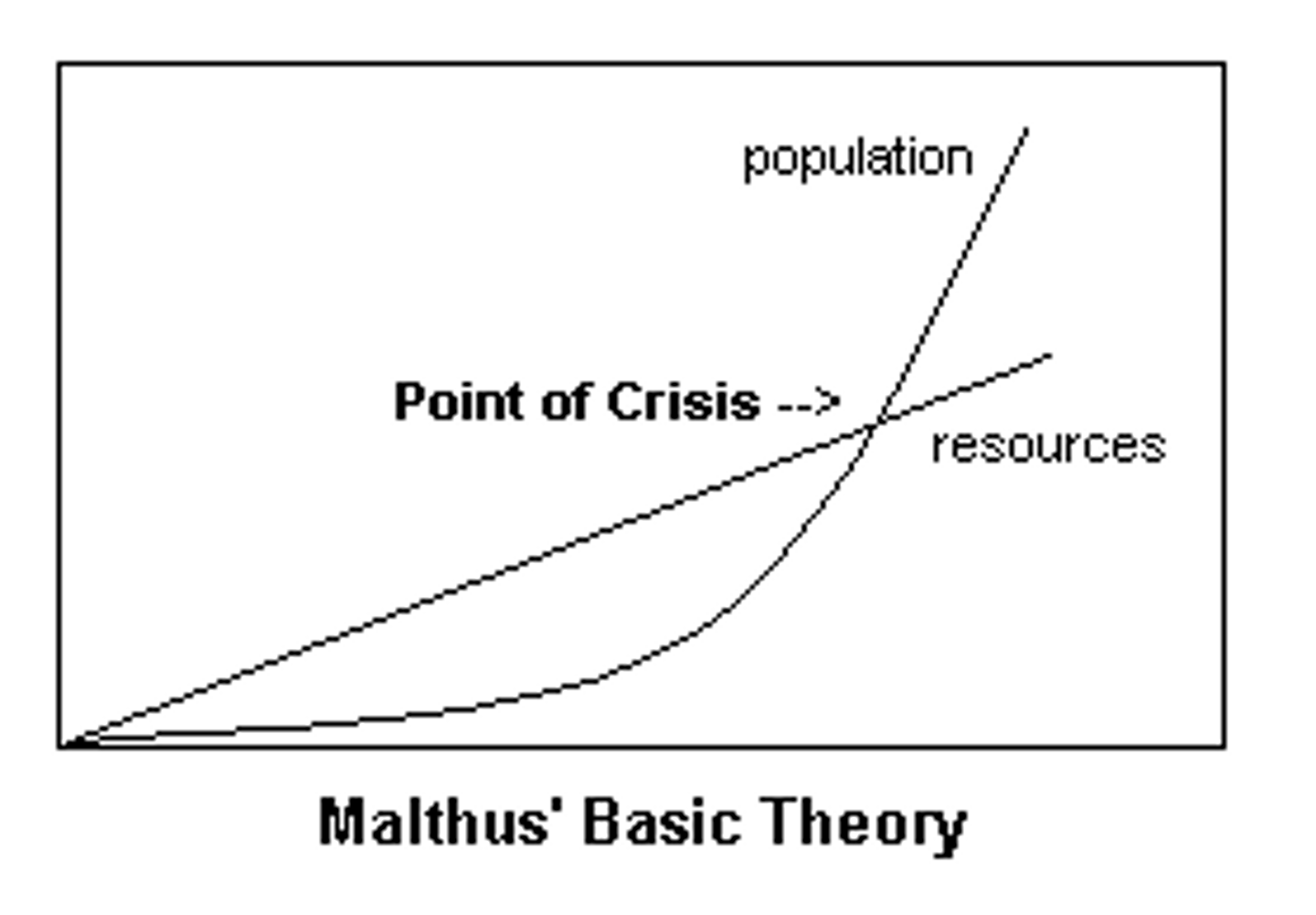
Thomas Malthus
Eighteenth-century English intellectual who warned that population growth threatened future generations because, in his view, population growth would always outstrip increases in agricultural production.
Malthusian Theory
Starvation is the inevitable result of population growth, because the population increases at a geometric rate while food supply can only increase arithmetically

Checks on the population
War, disease and famine
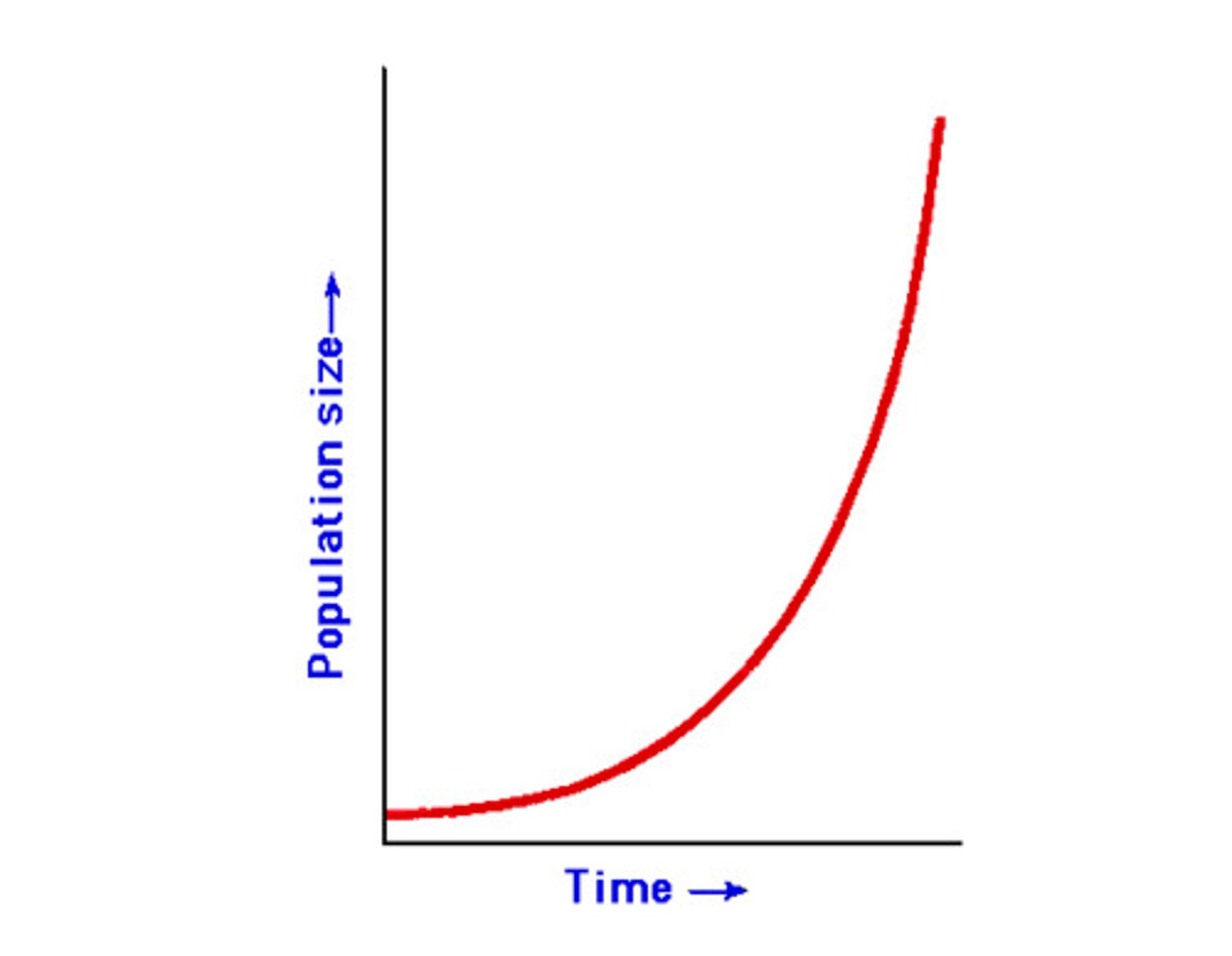
J-curve
a growth curve that depicts exponential growth
Malthusian trap
Malthus's prediction that a rapidly increasing population will overuse natural resources, leading inevitably to a major public health disaster
Neo-Malthusians
group who built on Malthus' theory and suggested that people wouldn't just starve for lack of food, but would have wars about food and other scarce resources
Malthus Critics
Many geographers consider Malthusian beliefs unrealistically pessimistic because they are based on a belief that the world's supply of resources is fixed rather than expanding and some critics disagree with Malthus's theory thinking that a larger population could stimulate economic growth and therefore, the production of more food.
pronatalist
a government policy that encourages or forces childbearing, and outlaws or limits access to contraception
EX: Singapore, Denmark, Russia
refugee
A person who has been forced to leave their country in order to escape war, persecution, or natural disaster
labor force
the total number of workers, including both the employed and the unemployed (usually ages 15-65)
antinatalist
Policies that discourage people from having children (China's One Child Policy)
Homestead Act of 1862
this allowed a settler in the US to acquire 160 acres by living on it for five years, improving it and paying about $30
Internally Displaced Person (IDP)
Someone who has been forced to migrate for similar political reasons as a refugee but has not migrated across an international border (staying within the same country)
One Child Policy
A program established by the Chinese government in 1979 to slow population growth in China.
dependency ratio
The number of people under age 15 and over age 64 compared to the number of people active in the labor force
asylum seeker
Someone who has migrated to another country in the hope of being recognized as a refugee
transnational migration
regular movement of a person between two or more countries resulting in a new cultural identity
total fertility rate
The average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years.
transhumance
The seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pastures.
xenophobia
a fear or hatred of foreigners or strangers
push factor
Factors that induce people to leave an area and migrate to another
EX: your homeland is war-torn, and you do not want your family to live there anymore due to safety concerns
internal migration
Permanent movement within a particular country.
family planning
the practice of regulating the number or spacing of offspring through the use of birth control
pull factors
Factors that draw people to a new location
EX: The place to which you are migrating has a lot of job opportunities, making you want to go there
chain migration
migration of people to a specific location because relatives or members of the same nationality previously migrated there
emigration
movement of individuals out of an area
step migration
Migration to a distant destination that occurs in stages, for example, from farm to nearby village and later to a town and city
guest worker
a foreign laborer living and working temporarily in another country (frequently from N. Africa or Asia to Europe)
immigration
Movement of individuals into a population
Rural-urban migration
the movement of people from the countryside to the city
forced migration
Permanent movement compelled usually by cultural factors.
Types of push and pull factors
economic, social/cultural, environmental, political, demographic
Wilbur Zelinsky's Model of Migration Transition
Migration trend follow demographic transition stages. People become increasingly mobile as industrialization develops. More international migration is seen in stage 2 as migrants search for more space and opportunities already in stages 3 and 4. Stage- 4 countries show less emigration and more intraregional migration.
Atlantic Slave Trade
Lasted from 16th century until the 19th century. Trade of African peoples from Western Africa to the Americas. One part of a three-part economical system known as the Middle Passage of the Triangular Trade.
displaced person
someone who is forced to leave his or her home, community, or country
Syrian Civil War
An ongoing armed conflict in Syria between forces loyal to the Syrian Ba'ath Party government and those seeking to oust it. The conflict began on 15 March 2011, with popular demonstrations that grew nationwide by April 2011. Protesters demanded the resignation of President Bashar al-Assad, whose family has held the presidency in Syria since 1971.
intervening obstacle
An environmental or cultural feature of the landscape that hinders migration.
ethnic enclave
a small area occupied by a distinctive minority culture
Intervening Opportunities
The presence of a nearer opportunity that greatly diminishes the attractiveness of sites farther away.
intervening obstacles
Any forces or factors that may limit human migration.
Ravenstein's Laws of Migration
1. Short distances→ distance decay (time-distance decay)
2. Urban areas→ gravity model of migration
EX: Cuban migration to US around 1959--specifically FL
3. Multiple steps→ step migration
4. Rural to urban→ thanks, Industrial Revolution
5. Counter migration→ some return migration
6. Youth
7. Gender→ used to be men, women growing in #
brain drain
Large-scale emigration by talented people.
Events that produce refugees
1. Armed conflict (Syria)
2. Generalized violence (S/Central America with government/cartels)
3. Violations of human rights
4. Disasters
5. Fear of persecution (race, religion, nationality, membership in a social group, political opinion)
Rust Belt
The northern industrial states of the United States, including Ohio, Michigan, and Pennsylvania, in which heavy industry was once the dominant economic activity. In the 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s, these states lost much of their economic base to economically attractive regions of the United States and to countries where labor was cheaper, leaving old machinery to rust in the moist northern climate.
Cotton Belt
The term by which the American South used to be known, as cotton historically dominated the agricultural economy of the region. The same area is now known as the New South or Sun Belt because people have migrated here from older cities in the industrial north for a better climate and new job opportunities.
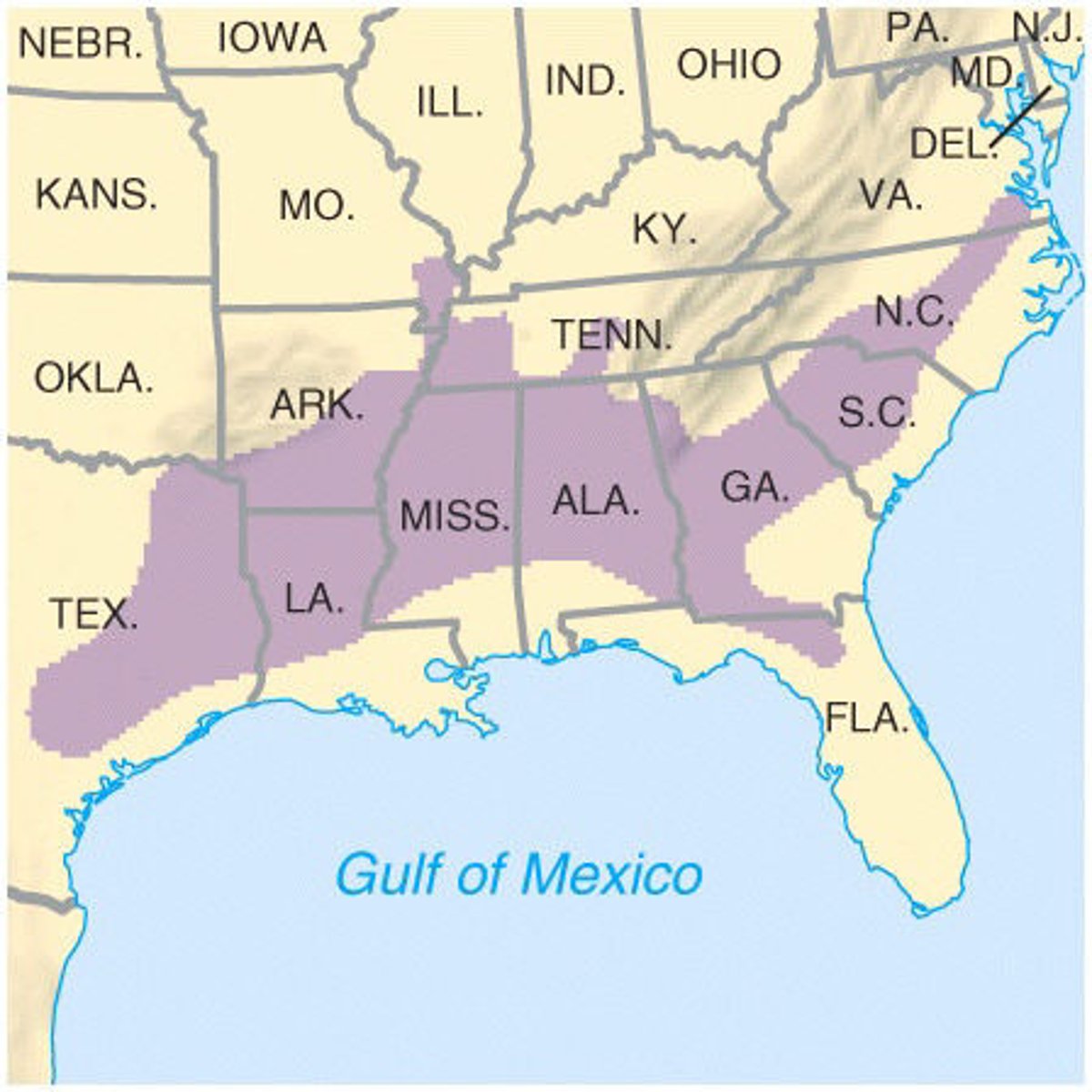
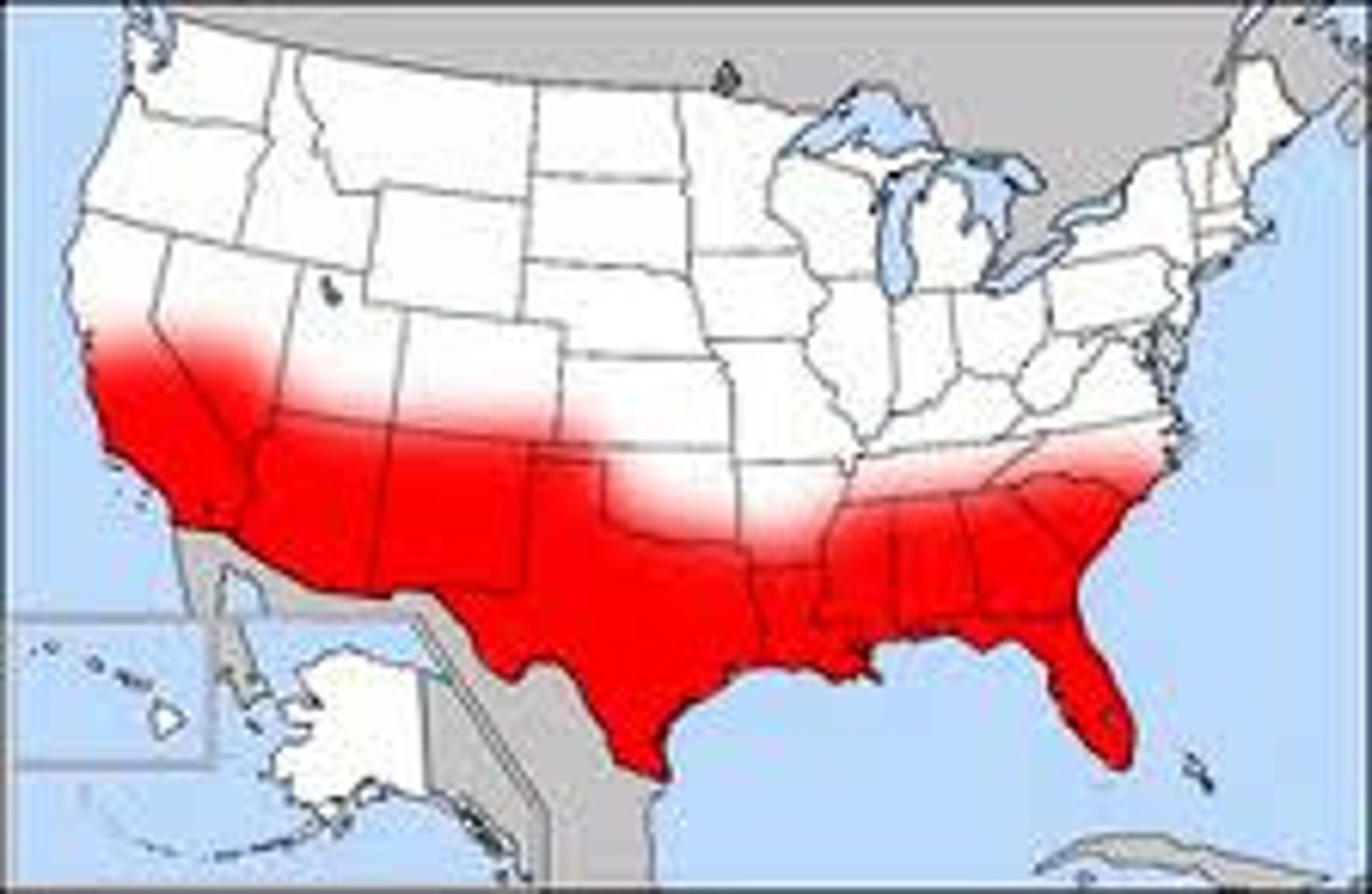
Sun Belt
U.S. region, mostly comprised of southeastern and southwestern states, which has grown most dramatically since World War II.
Transhumance
The seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pastures.
remittances
Money migrants send back to family and friends in their home countries, often in cash, forming an important part of the economy in many poorer countries
Demographic momentum (population momentum)
this is the tendency for growing population to continue growing after a fertility decline because of their young age distribution. This is important because once this happens a country moves to a different stage in the demographic transition model.