DAT Cells and Organelles
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
7 components of Cell Theory
All organisms are composed of 1 or more cells.
The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms.
All cells come from pre-existing cells.
The activity of an organism depends on the combined activity of independent cells.
Cells have functional metabolisms (energy flow occurs within cells).
Cells contain hereditary genetic information, which is passed on when a cell divides or an organism has offspring.
All cells of similar species have the same basic chemical composition.
3 Things all cells contain
Plasma membrane: selective barrier that separates and protects cell contents from the outer environment.
DNA: the source of genetic information.
Ribosomes: synthesize functional proteins from DNA.
Permeability of small, uncharged, polar molecules
Can cross membrane on its own
Ex: H2O, Glycerol, Urea, Ethanol
Permeability of small, nonpolar (hydrophobic) molecules
Can cross membrane on its own
Ex: Steroids, CO2, O2, N2
Permeability of large, uncharged, polar molecules
Unable to cross on its own
Ex: Glucose, sucrose
Permeability of Ions
Unable to cross on its own
Ex: Na+, H+, Ca2+
What are the 3 types of membrane proteins?
1. peripheral
2. integral
3. transmembrane
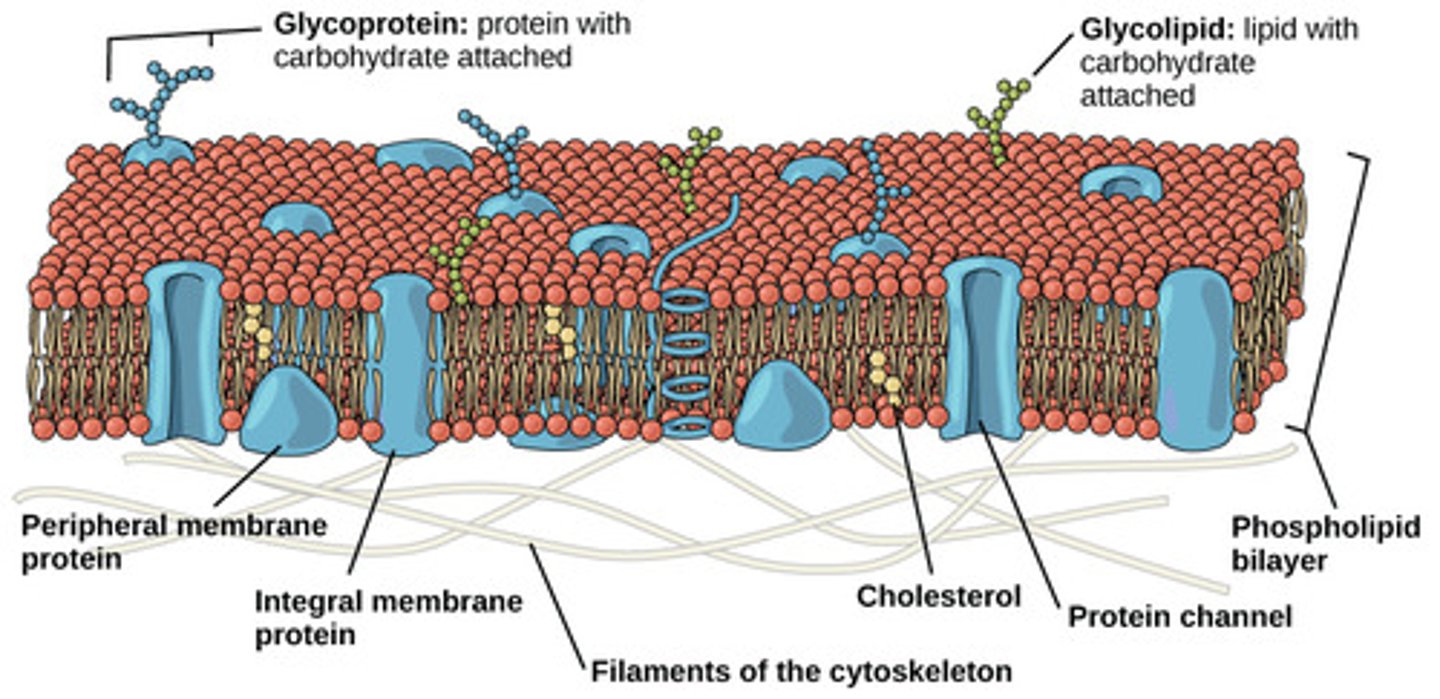
Fluid Mosaic Model
Mosaic- Composed of multiple different parts (phospholipids and proteins)
Fluid- Cell membrane components are constantly shifting arounds
Which of the following is the phospholipid bilayer most permeable to?
Small and nonpolar molecules
Besides phospholipids, the major components of the phospholipid bilayer are ________.
proteins and cholesterol (animal cells)/ sterol (plant cells)
What is the main function of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
Membrane fluidity
Which component of a phospholipid is hydrophilic?
The phosphate head
Since the cell membrane is semi-permeable, all of the following can passively diffuse across EXCEPT for one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
Glucose
All of the following characteristics would allow a substance to freely cross the cell membrane EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
Charged
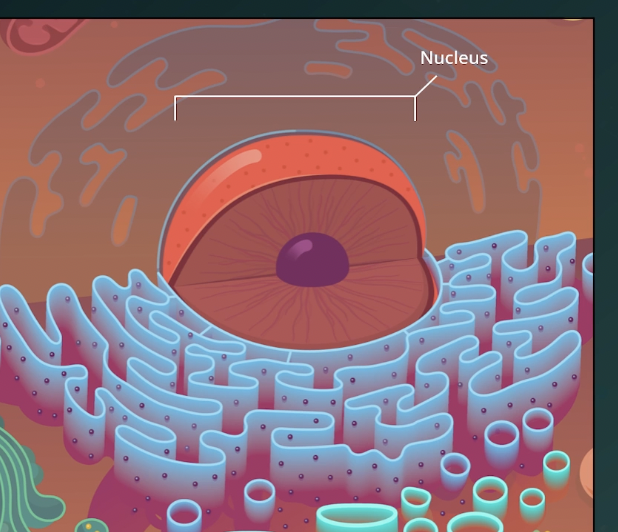
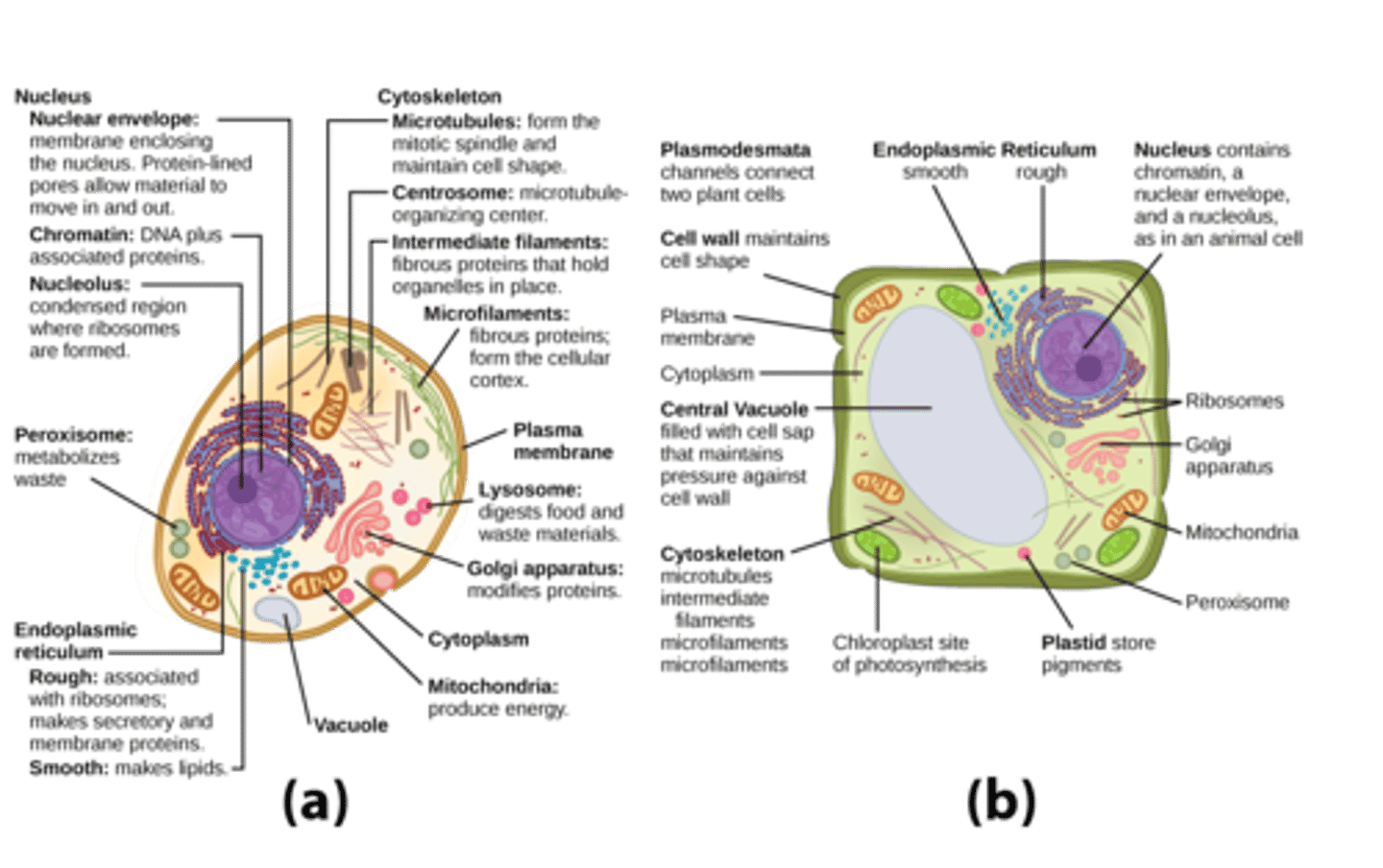
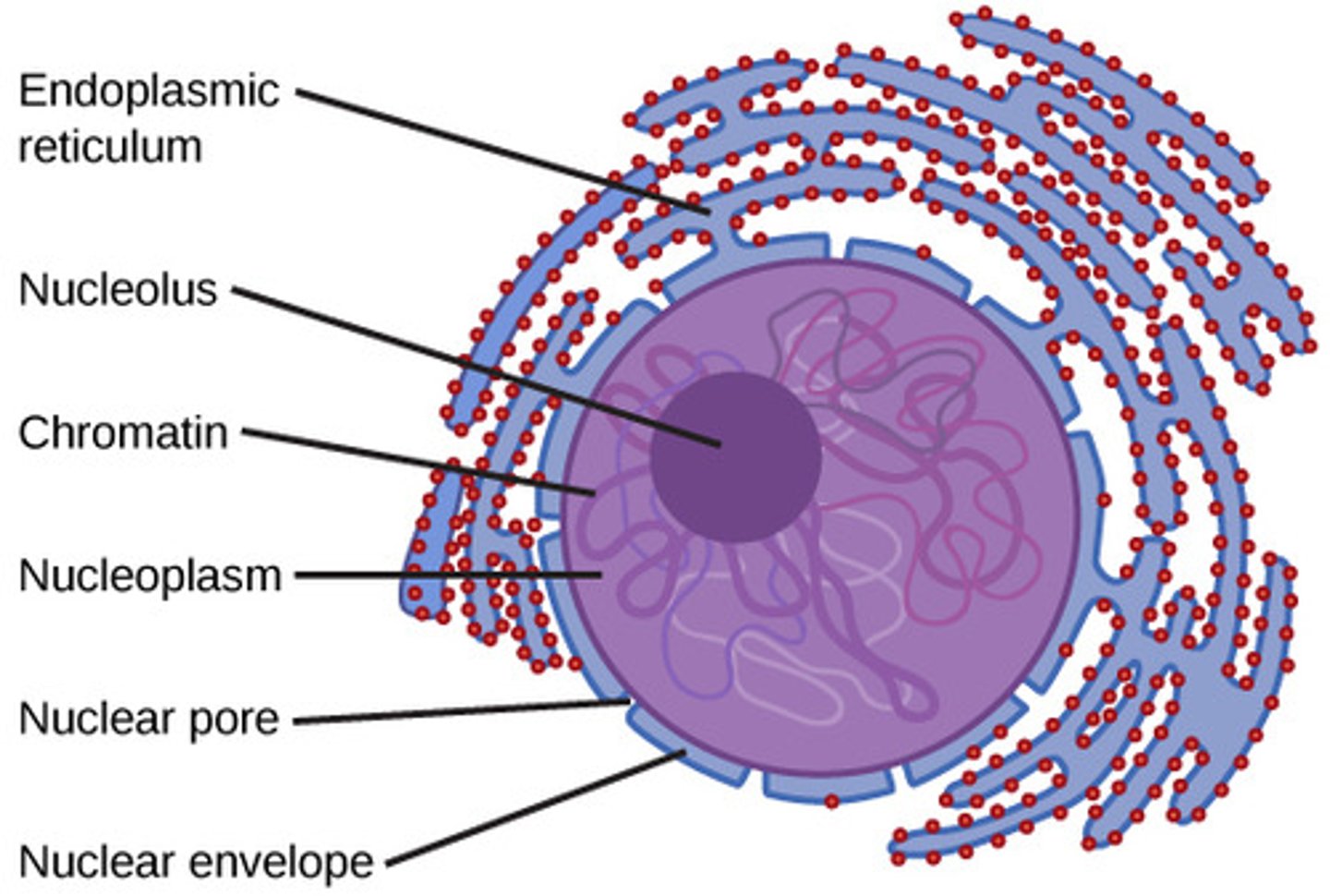
Nucleus
Contains the cell’s DNA. Controls gene expression. The structure of the nucleus includes:
Most cells have one nucleus, but some can have…
multiple (osteoclasts and skeletal muscle cells), or none (red blood cells and platelets).
Components of Nucleus
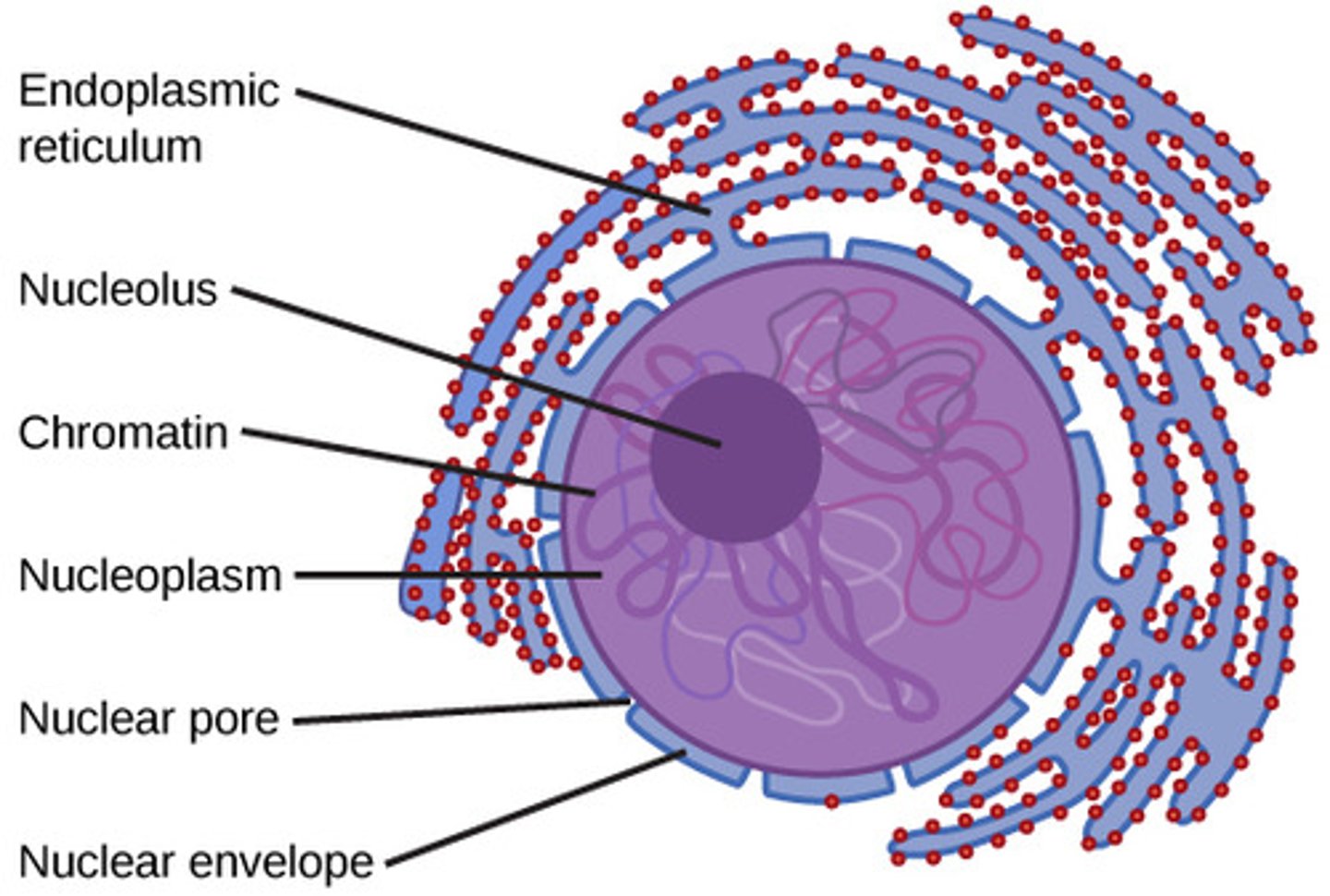
Nuclear Envelope
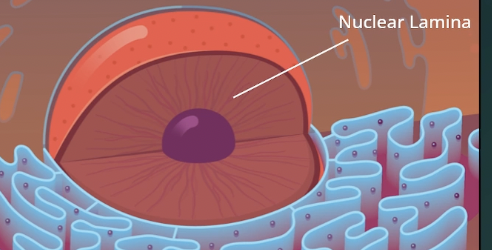
Nuclear Lamina
Nucleolus
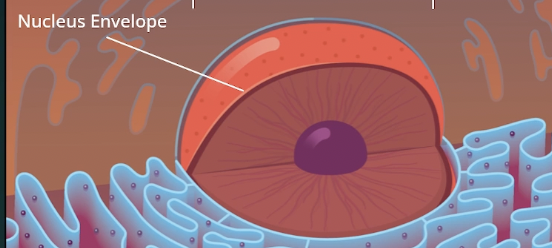
Nuclear envelope
double membrane (two phospholipid bilayers) with pores allowing molecules to enter and exit.
Nuclear lamina
protein network that maintains the shape of the nucleus.
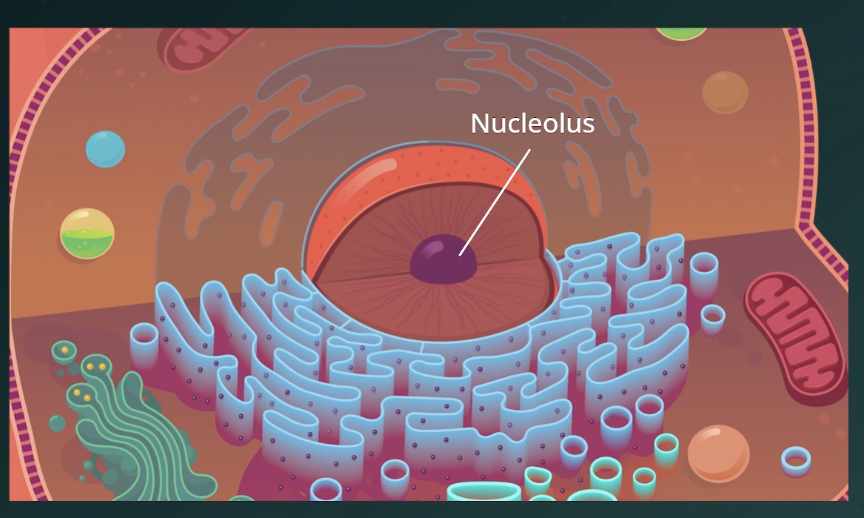
Nucleolus
region inside the nucleus where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is made.
Ribosomal proteins are imported from the
cytoplasm to the nucleolus and combined with
rRNA to form ribosomal subunits. The subunits
are exported to the cytoplasm for final
assembly into complete ribosome.
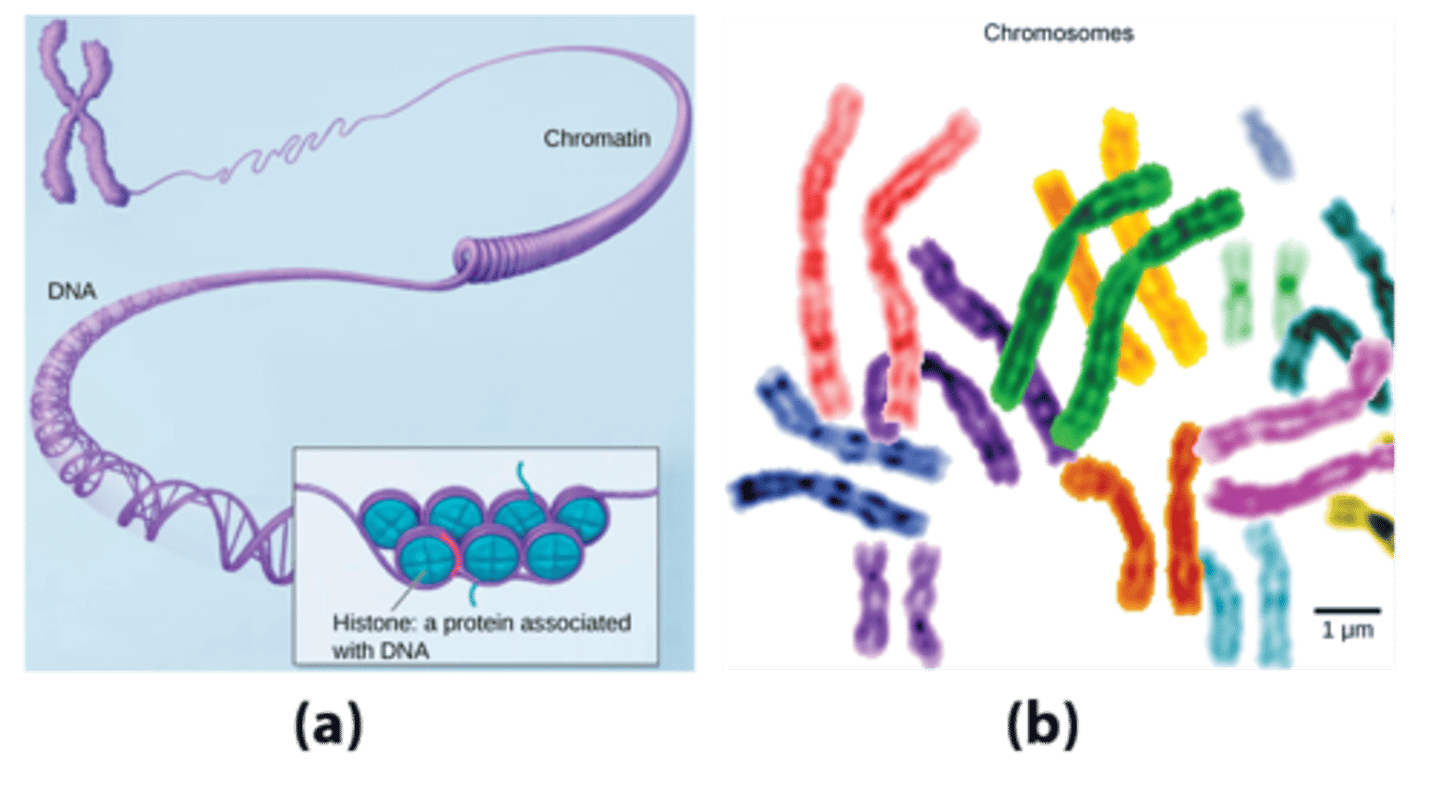
Nucleosome
a bundle of 8 histones with DNA coiled around them.
Chromosome
tightly condensed chromatin which is visible when the cell is ready to divide.
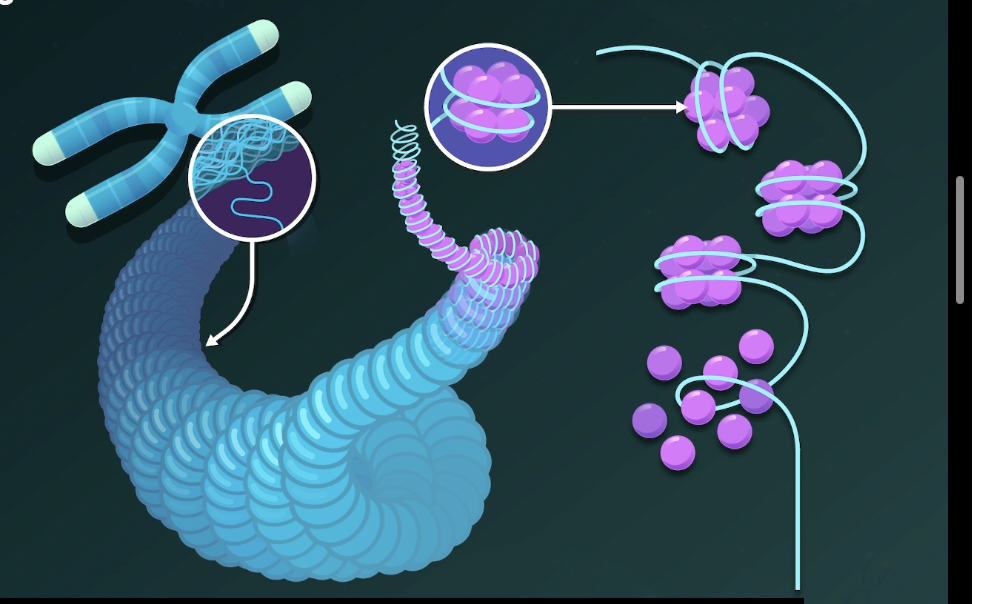
DNA Inside the Nucleus
Chromosome- Organized, compact form of DNA
Chromatins- General Packaging of DNA and proteins
Histones- Allows for structures to be bundled into nucleosomes
Cytosol vs Cytoplasm
Cytosol
Only the gel-like fluid inside the cell; does not include the components suspended within the gel substance
Cytoplasm
Area in which the cell’s metabolic processes occur. Includes cytosol and organelles suspended in the cytosol
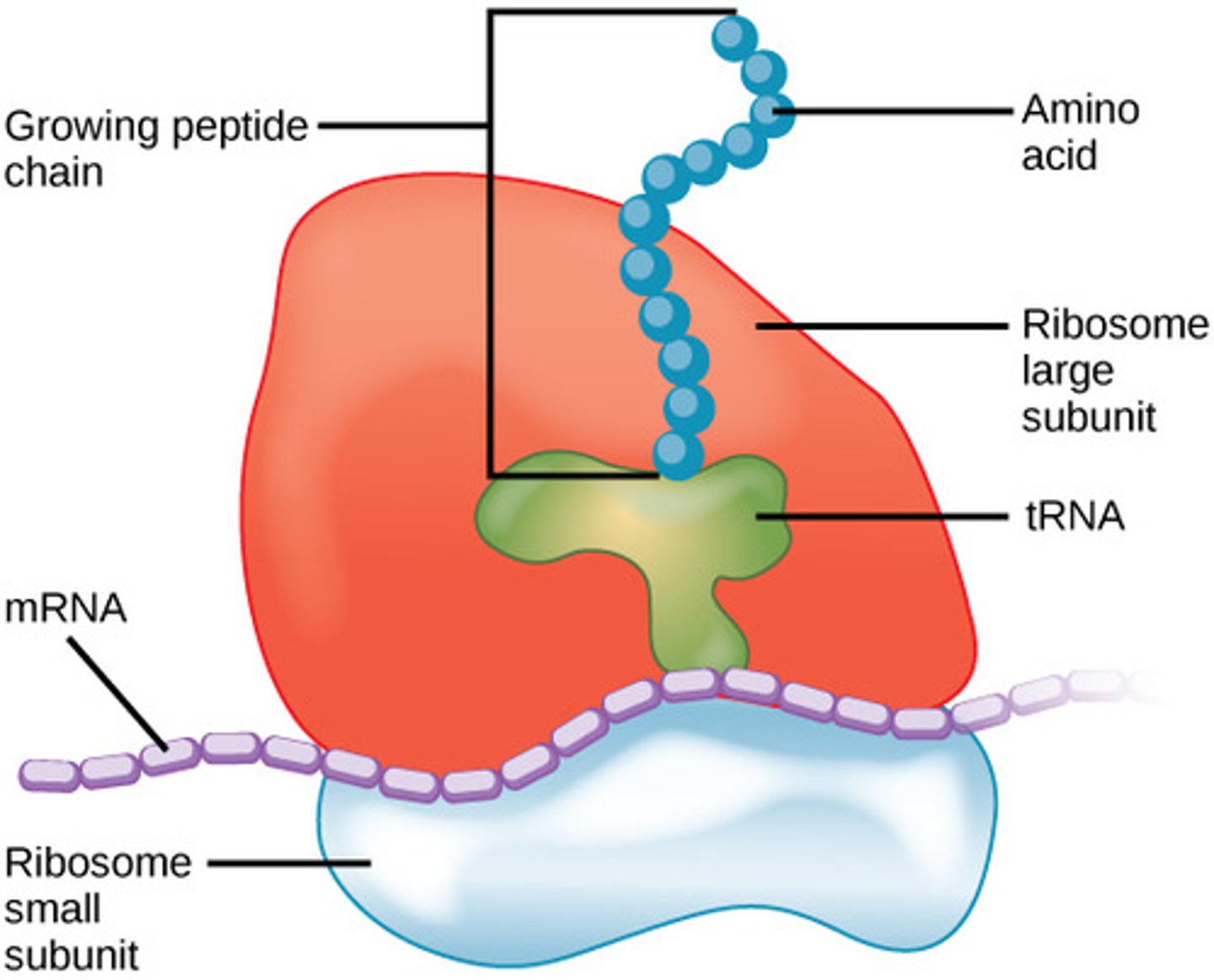
Ribosomes
non-membrane-bound organelles found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Responsible for protein synthesis (translation).
composed of 2 subunits containing rRNA and proteins (euk subunits bigger than prokaryotic subunits)
Can be found free floating (make proteins that function that inside the cell) or bound to the rough ER (make proteins exported outside of the cell)
Rough ER (RER)
synthesizes and modifies proteins before they are exported. Close to the nucleus and studded with ribosomes.
Capable of post-translational modifications of protein (e.g. attaching carbohydrates to make glycoproteins).
Smooth ER (SER)
synthesizes lipids and steroid hormones for export. Has no ribosomes.
In liver cells, it functions in breakdown of toxins, drugs, and toxic by-products.
Muscle cells have a specialized SER called the sarcoplasmic reticulum that stores and releases Ca2+ ions.
Golgi Apparatus:
series of flattened membrane sacs (cisternae) that sort, modify, and transport proteins after synthesis.
Also produces lysosomes and transports lipids.
Directionality: the golgi has a cis end (accepts incoming vesicles) and a trans end (exports vesicles).
Route of Golgi Apparatus
Proteins made by rough ER
Lipids and steroid hormones made by smooth ER
Cis face of golgi receives transport vesicles from ER
Golgi modifies and packages the substances
Trans face of golgi secretes vesicles for substances to exit
Lysosomes and its functions
Made by golgi, Contains digestive enzymes with a low pH
Apoptosis
Autophagy
Break down nutrients, pathogens, and cell debris
Peroxisomes
Commonly found in liver
Breakdown substances, fatty acids, and amino acids
Generate hydrogen peroxides (H2O2) to oxidize substrates
Vacuoles
Vesicles inside cells that store and move materials and are membrane bound
4 types of vacuoles
Transport- move materials between organelles
Food- transport food and fuses with lysosomes
Central- Tonoplasts in plant cells
Contractile- Collect and pump excess water out of the cell (in protists)
Cytoskeleton
Maintain cell shape and provide mechanical support
Move components within the cell
Cell motility
Anchors membrane proteins
3 Components of the Cytoskeleton and their functions
Microfilaments- Made of actin involved in cell motility
Intermediate Filaments- Support for maintaining cell shape
Microtubules- Made of tubulin for support and motility
Bundles of microtubules form the following…
Cilia- Short hair like extensions from cell for movement
Flagella- Thread-like extensions for cell movement
Centrioles- Development of spindle fibers for cell division
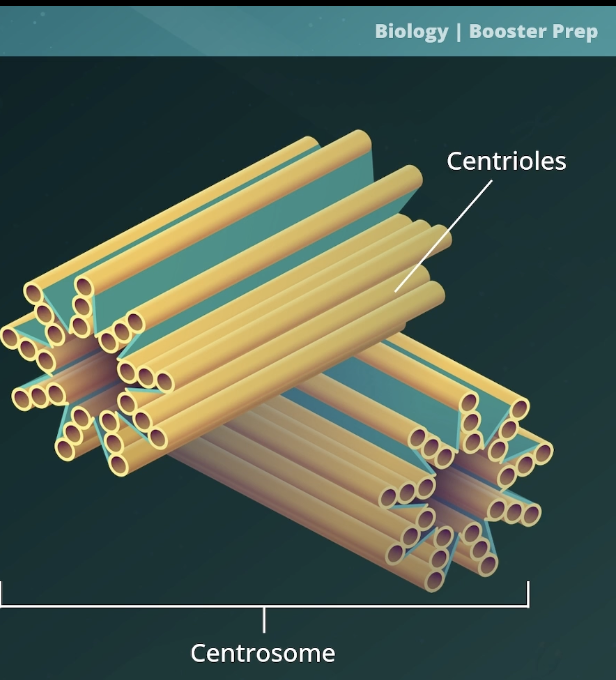
Microtubules organizing centers (MTOCs)
arrange microtubule structures within the cell (e.g. centrioles and basal bodies).
Form the spindle apparatus during cell division
Are structures that include centrosomes and basal bodies
Are found at the base of flagellum and cilium
Structure- 9×3 array
Mitochondria
Creates ATP and breaks down fatty acids (beta-oxidation)
inner membrane highly folded (cristae) to increase SA, contained within the inner membrane in mitochondrial matrix
Chloroplasts
Double membrane bound organelle that is the site of photosynthesis in plants and algae
Uses light energy to produce sugar
Absorbs red and blue and reflects green light
Evolved from photosynthetic cyanobacteria
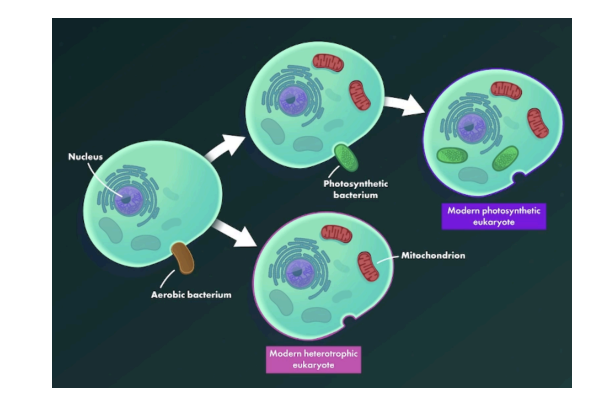
Endosymbiotic Theory
certain organelles (mitochondria and chloroplasts) in eukaryotic cells were once independent prokaryotic organisms that later formed a symbiotic relationship with a larger cell, leading to their presence as organelles in eukaryotic cells today. Mitochondria and chloroplasts:
1. Have their own circular DNA genome.
2. Are similar in size to prokaryotic cells.
3. Replicate similarly to prokaryotic cells (binary fission).
4. Contain small, prokaryotic-like ribosomes.
Components of Plant cells
Contains cell walls
Spindle pole bodies
Unique organelle- Plastids, storage vacuoles
Plastids
Chloroplasts (site of photosynthesis), leucoplasts (store nutrients) and chromoplasts
(store pigments).
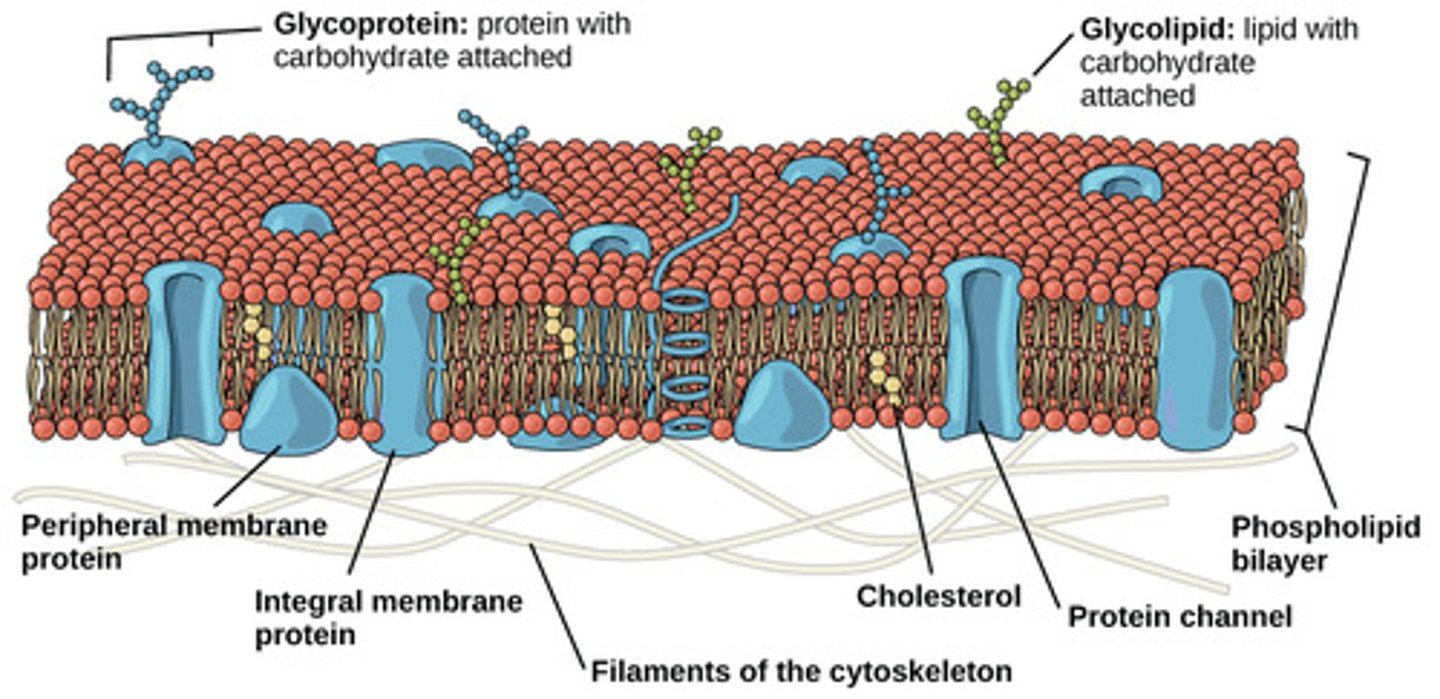
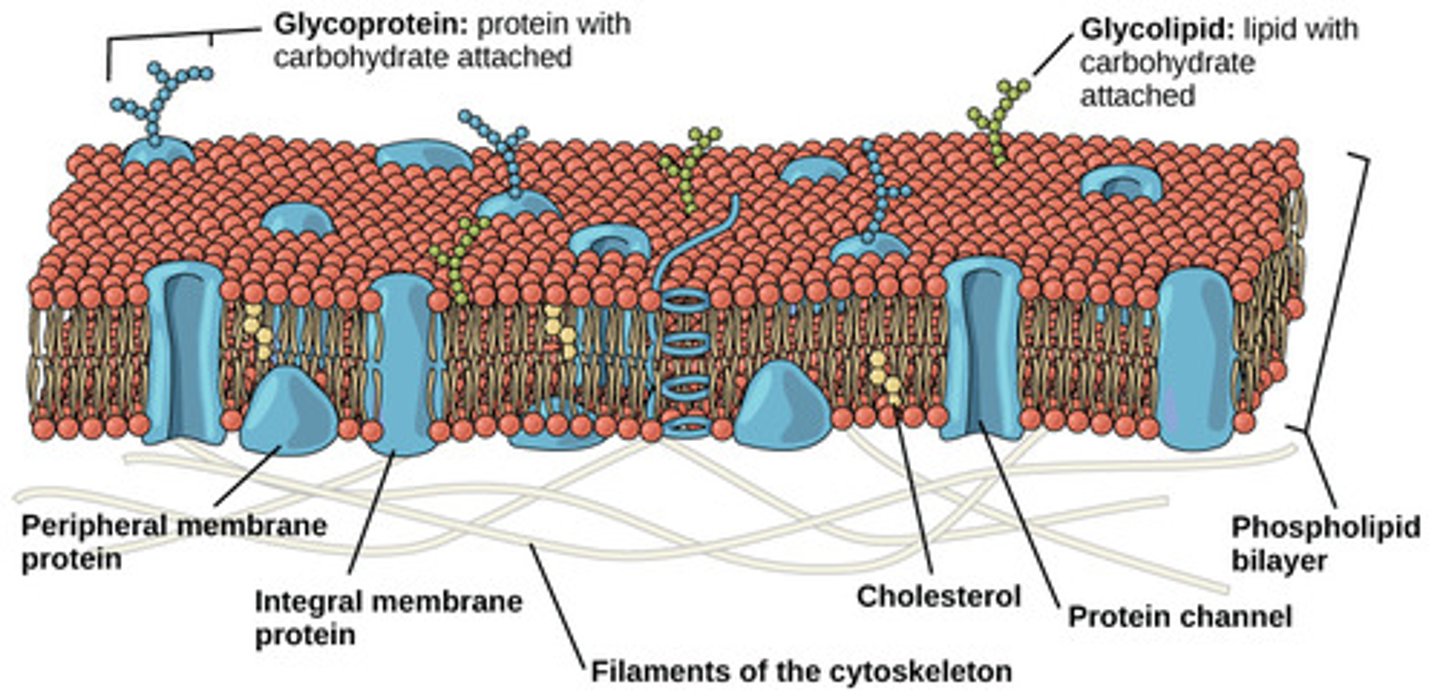
Peripheral Membrane
Attached to membrane surface
Hydrophilic and bound to the membrane by H-bonds and electrostatic interactions. Removable with high salt concentration or extreme pH
Integral Proteins
Extend into the membrane and have hydrophobic regions. Removable with a detergent which destroys the membrane
Transmembrane Proteins
Integral Proteins that pass completely through the membrane, connecting the interior and exterior of the cell
Transport Proteins
Transport Materials across the membrane
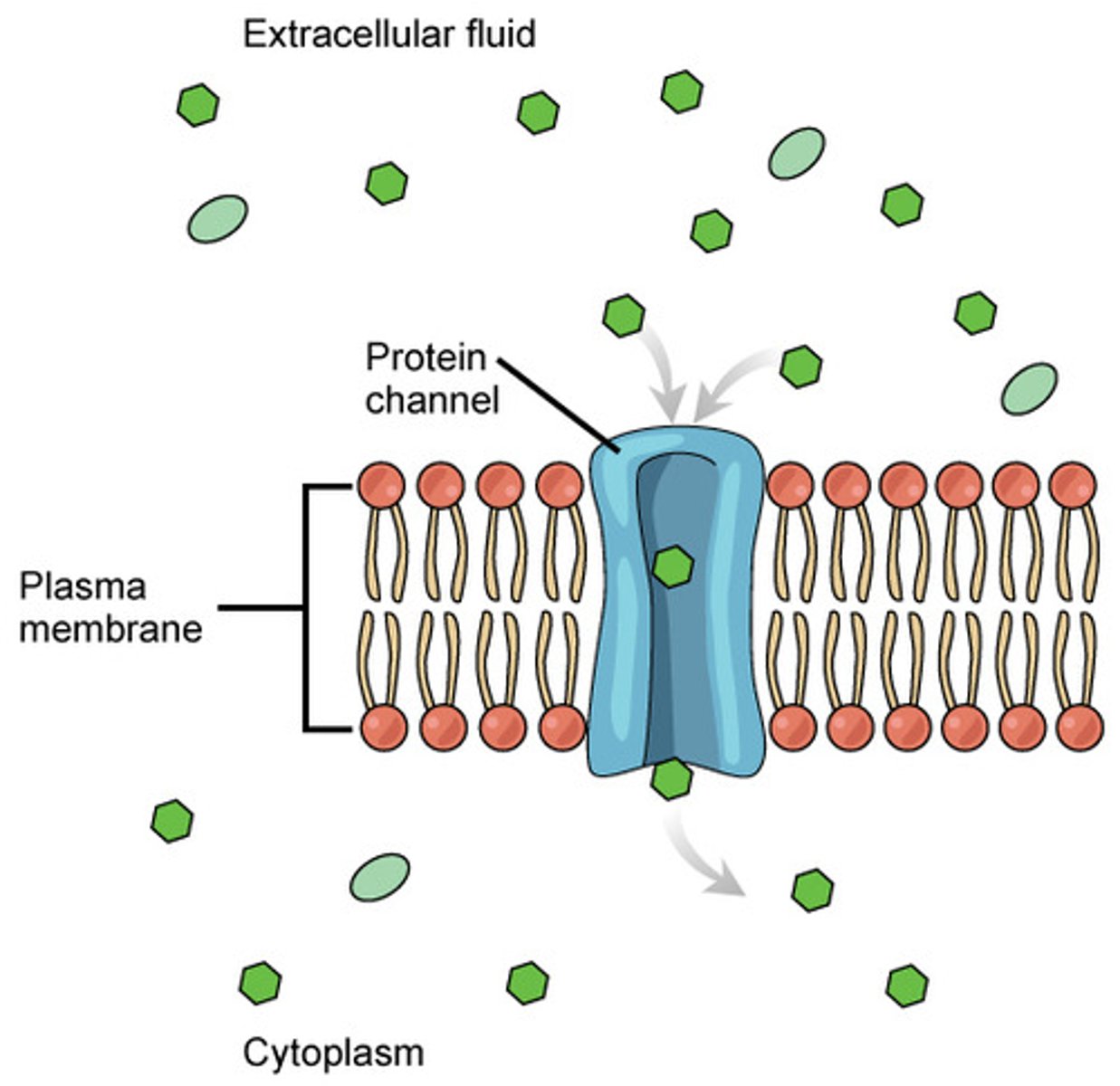
Channel Proteins
Hollow tubes substances can move through ( e.g aquaporins allowinf for quick movement of water across the membrane)
Ion Channels
Allow the passage of ions across the membrane of water across the membrane
Voltage gated ions
Opens or closes in response to a difference in membrane potential
Mechanically-gated ions
opens in response to pressure, vibration, temperature, etc.
Ligand-gated ions
Open or closes in response to molecule binding
Carrier Proteins
Pass molecules across the membrane by changing shape
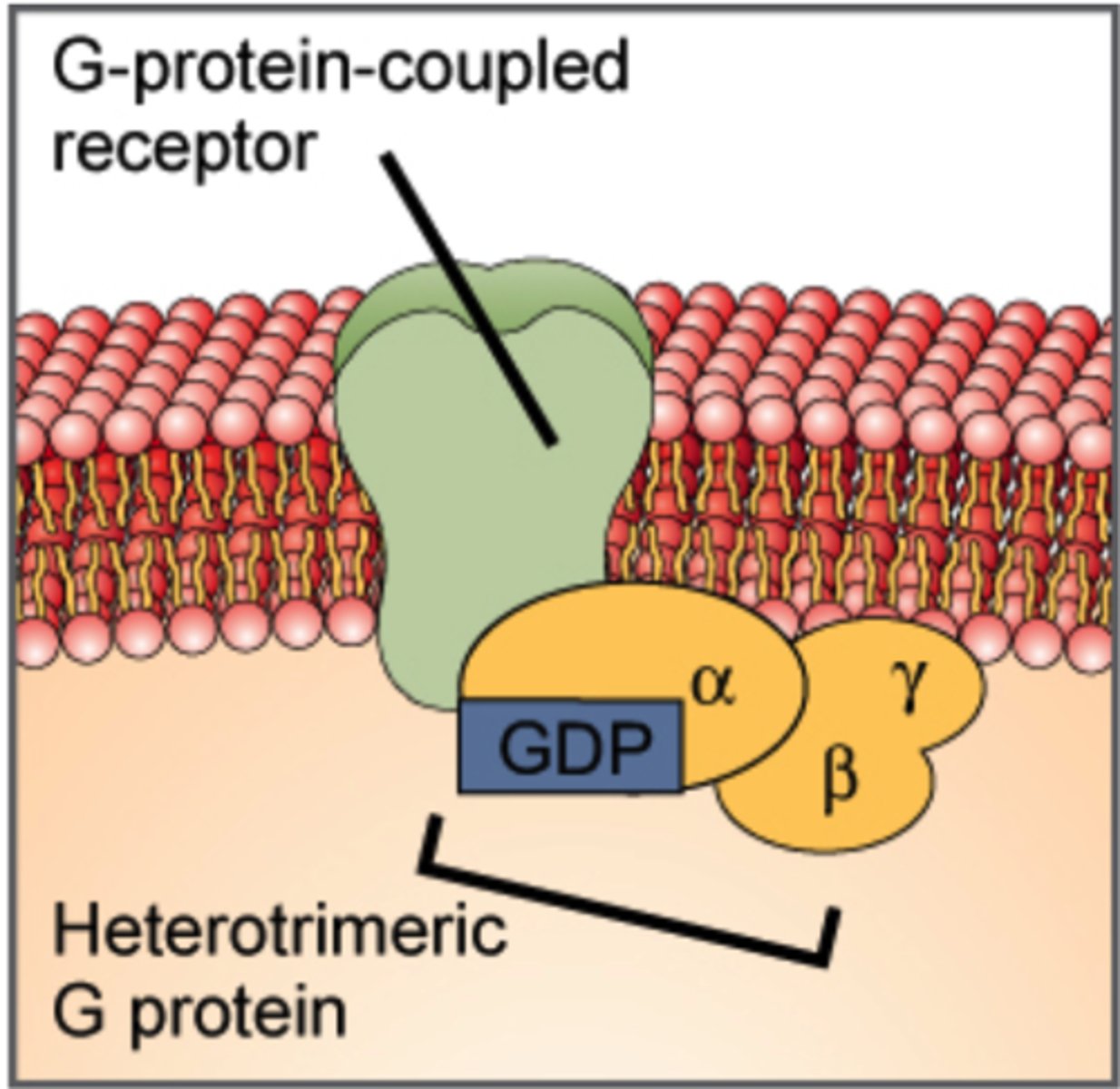
Receptor Proteins
Binding site for hormones and other signaling molecules that triggers changes inside of the cell when activated
Glycoproteins
Proteins with carbohydrates attached
Important for cell to cell recognition, signaling, and adhesion
Immune cells check membrane glycoproteins to determine if a cell is foreign
Can function as receptor proteins
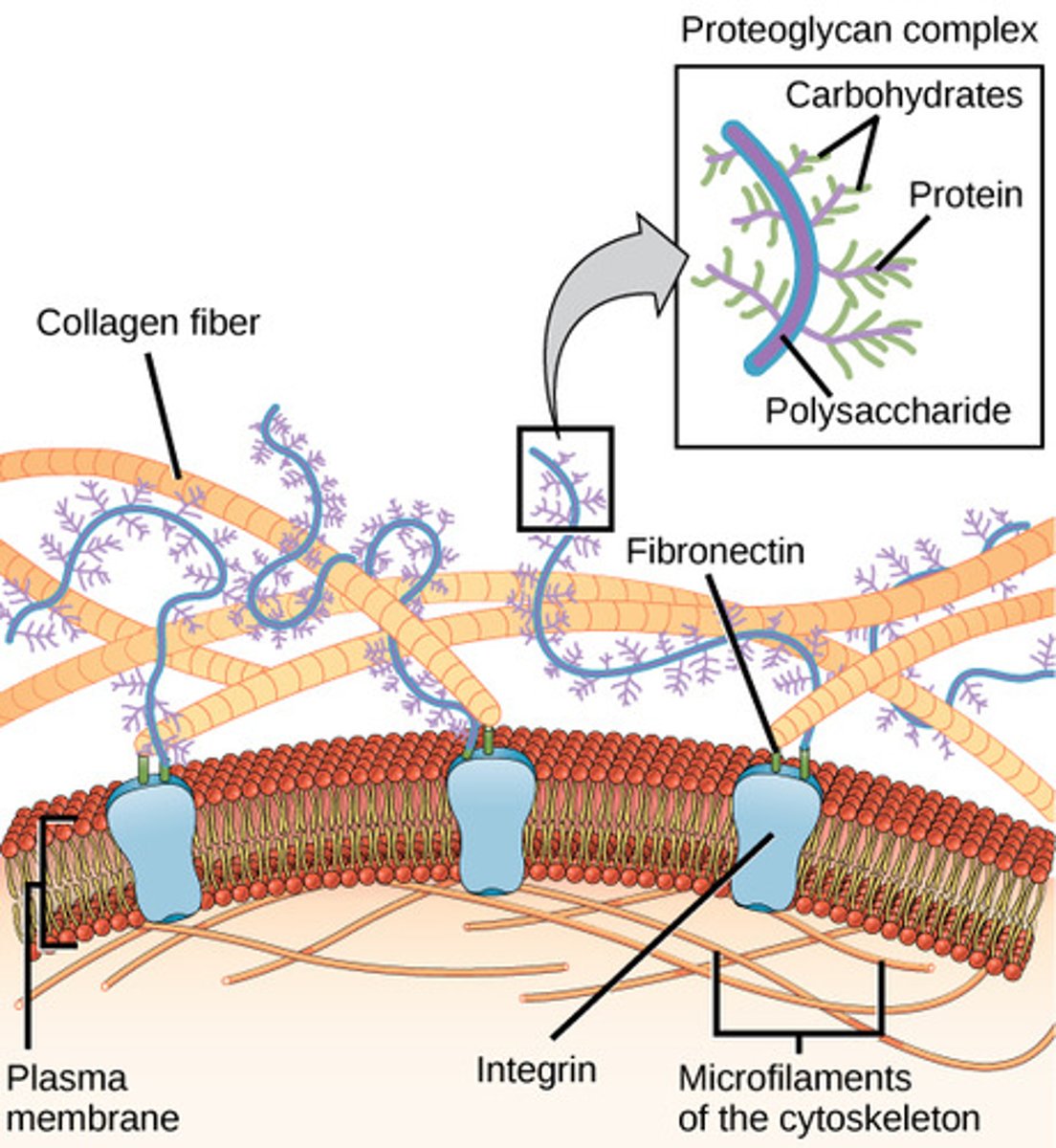
Adhesion/ Anchor Proteins
Attach cells to adjust cells and other extracellular/ intracellular proteins for stability and communication
Tight Junctions
form a seal between adjacent cells, preventing the passage or leakage of material between them (e.g. in the digestive tract and blood brain barrier).
Adherens Junctions:
firmly attaches adjacent cells together, allowing organization into tissues (e.g. cells lining blood vessels).
Stabilized by attachment to intracellular actin filaments.
Desmosomes
Similar to adherens junctions, but stronger. Found in tissues prone to mechanical stress (e.g. cardiac muscle, epidermis).
Stabilized by attachment to intracellular intermediate filaments (keratin).
Hemidesmosomes
attach cells to the extracellular matrix (at the basement membrane) to hold them in place to underlying tissues.
Found in epidermis of skin.
Gap Junctions
narrow tunnels between cells which allow for cell-to-cell communication.
Allow ions and small molecules to flow directly from one cell to another.
Can conduct electrical signals smoothly between cells (e.g. cardiac muscle cells).
Basement Membrane:
part of the extracellular matrix that anchors and supports cells attached to it.
Cell orientation
the apical (top) surface points outward
lateral surfaces are on the side, and the basal surface forms the bottom of the cell.
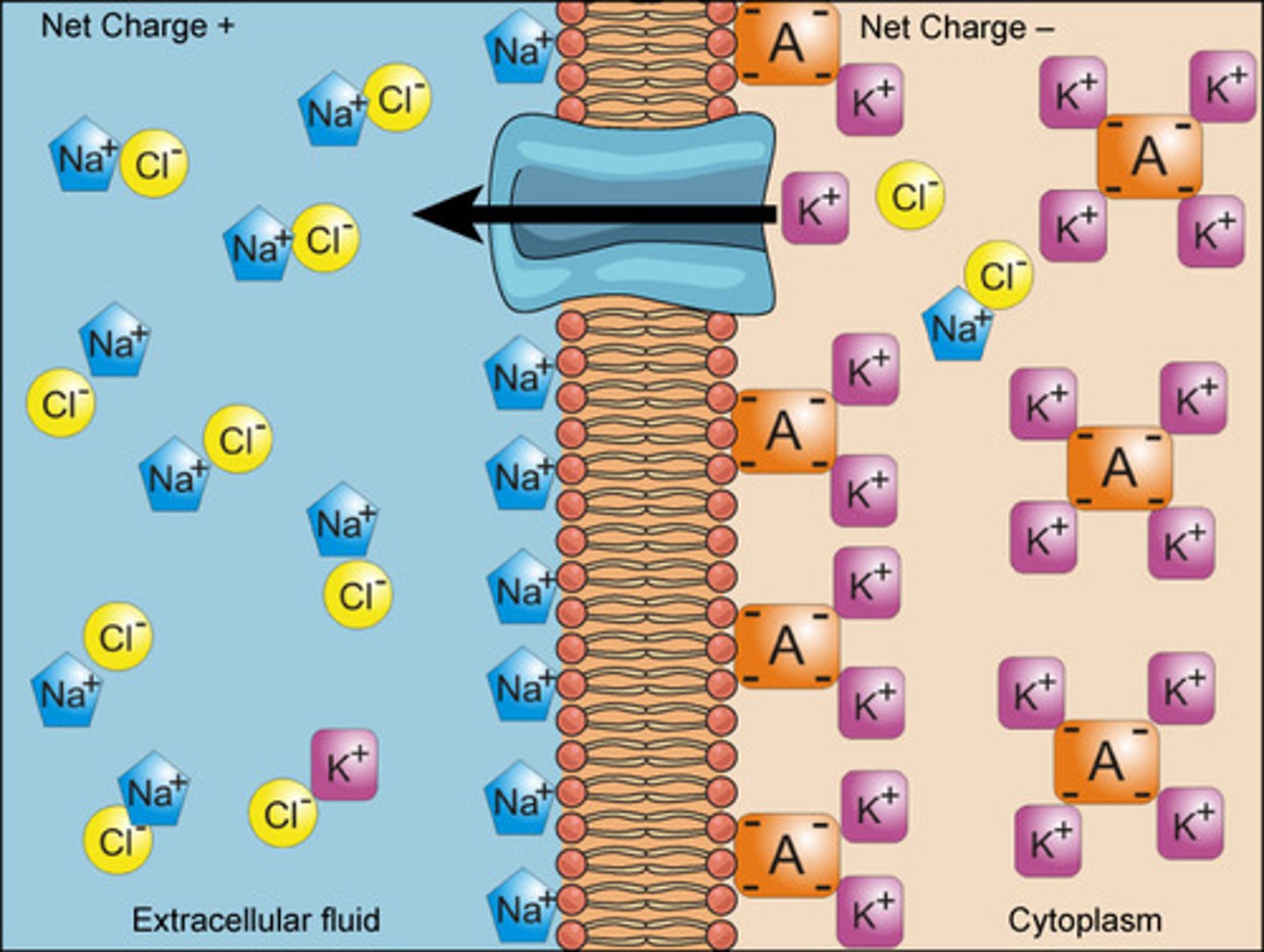
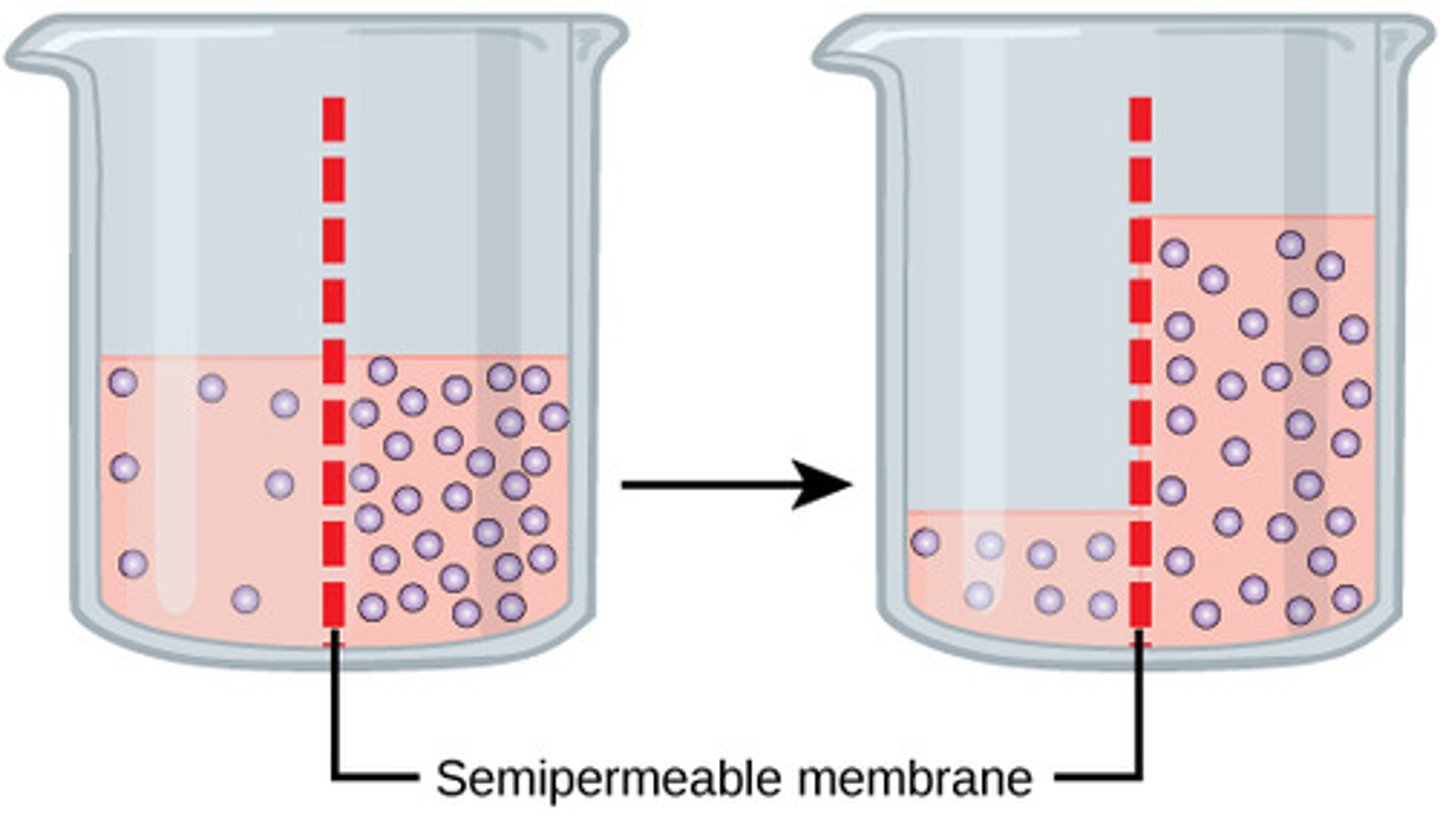
Hypotonic
More solutes inside the cell than outside
Causes H20 to rush into cell and causes cell to swell
Isotonic
Balanced H2O entry and exit at equal rate
Hypertonic
H2O rushes out of cell because more solutes outside than inside
Bacterial Cell wall contains…
Peptidoglycan
Plant cell wall contains…
Cellulose
Fungal cell wall contains
Fungi
Which membrane proteins provide a passageway through the membrane for hydrophilic, polar, and charged substances?
channel proteins
Which membrane proteins are a type of glycoprotein that distinguish between self and foreign substances?
recognition proteins
(Note: MHC on macrophage)
Which membrane proteins are used to pass ions across the membrane and referred to as gated channels in nerve and muscle cells?
ion channels
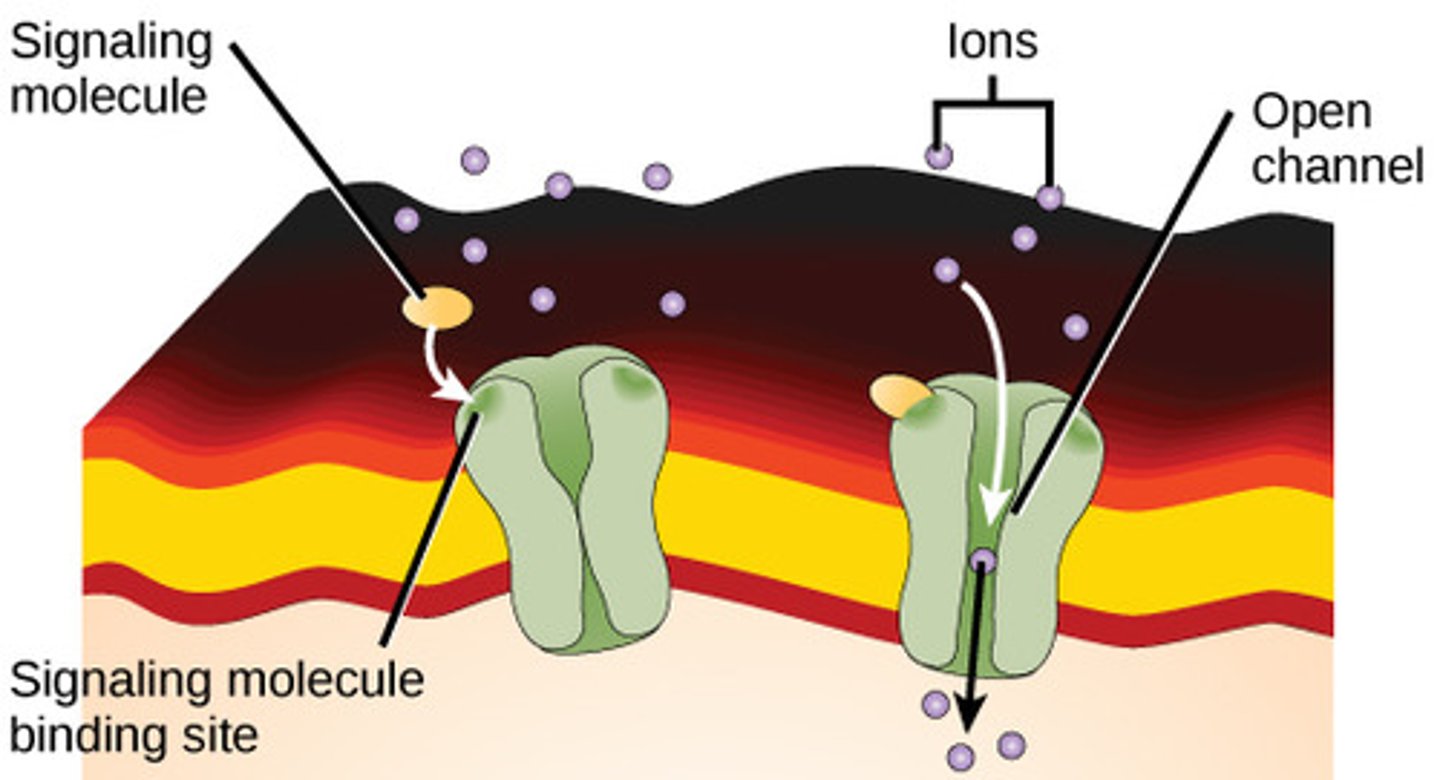
What are the types of ion channels?
1. voltage-gated
2. ligand-gated
3. mechanically gated
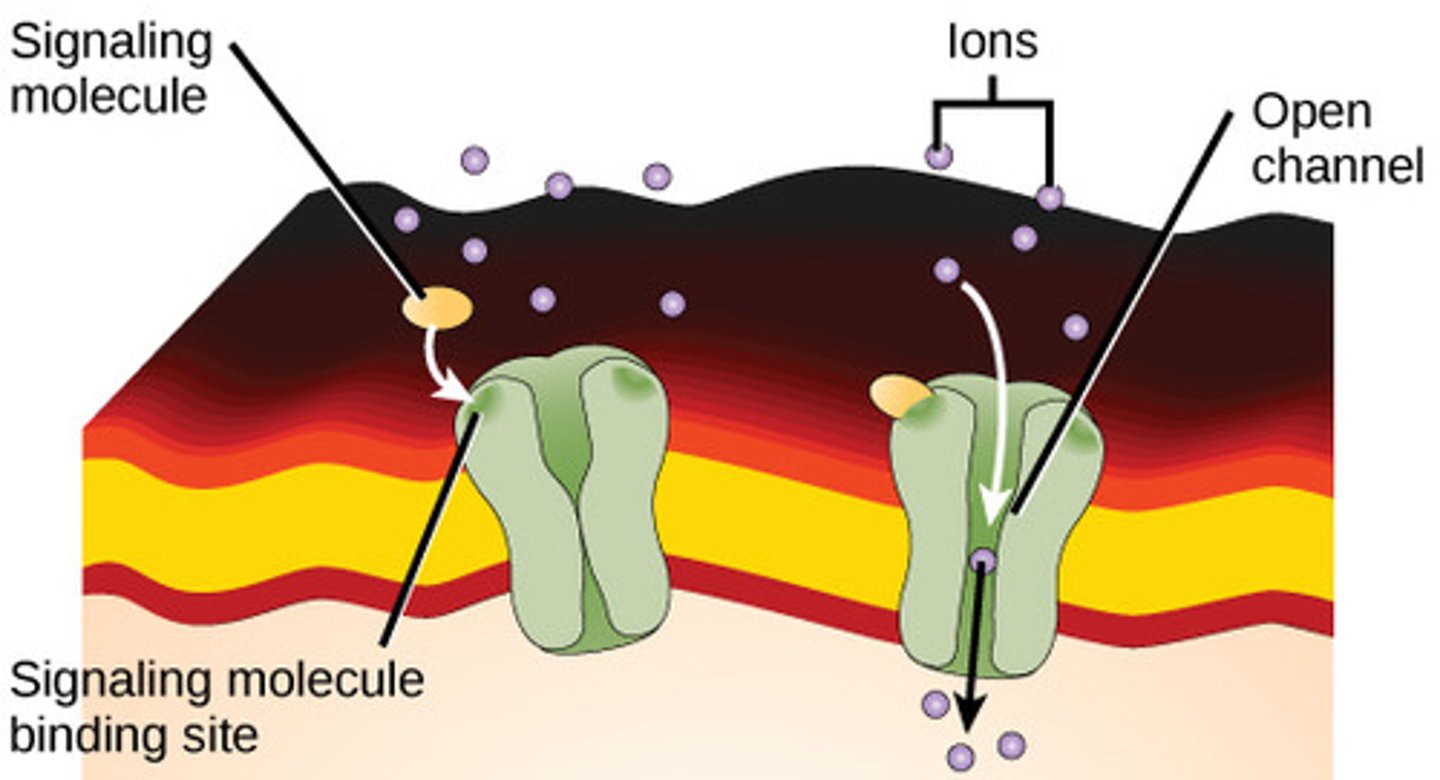
Which membrane proteins allow the passage of certain ions and small polar molecules, are less specific, and create relatively large openings?
porins
Which membrane proteins are specific to movement across the membrane via integral membrane proteins?
carrier proteins
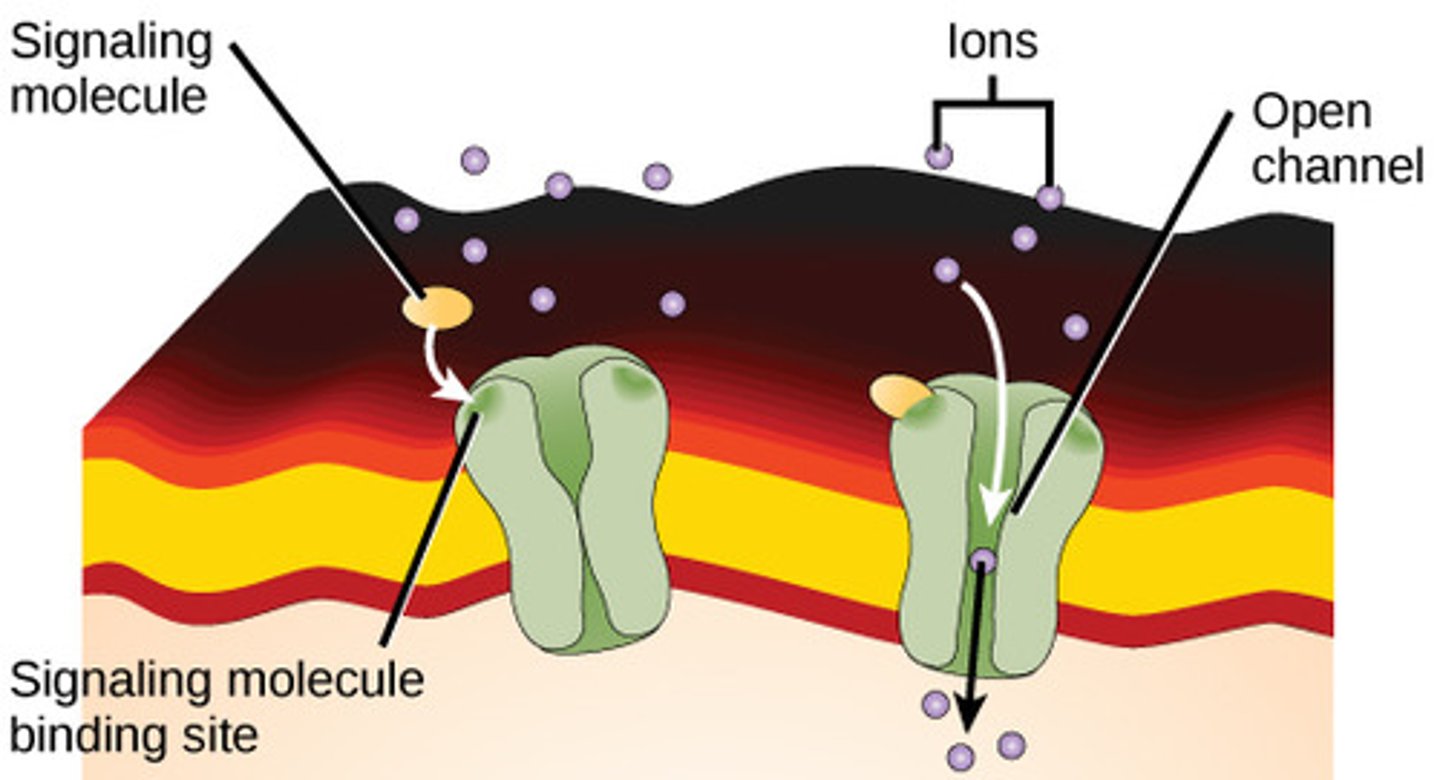
How do carrier proteins allow specific molecules to pass across the membrane?
changes shape after
binding to specific molecule
Which membrane proteins can use ATP to transport materials across the membrane?
transport proteins
(Note: includes active
transport and facilitated
transport)
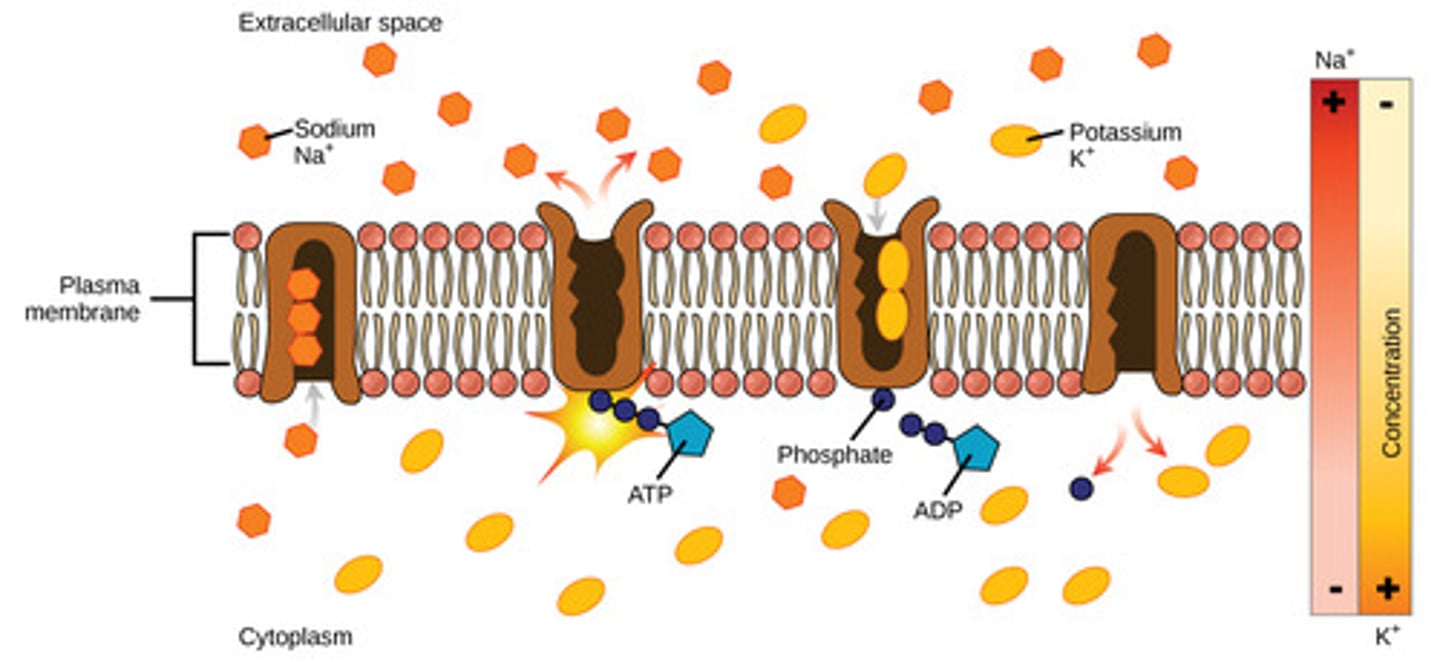
What is the difference between active transport and facilitated diffusion?
active transport requires energy and facilitated diffusion does not
Which membrane proteins attach cells to neighboring cells and provide anchors for stability via internal filaments and tubules?
adhesion proteins
Which membrane proteins serve as binding sites for hormones and other trigger molecules?
receptor proteins
Which membrane property allows small uncharged molecules to cross the cell membrane?
phospholipid membrane
semi permeability
(Note: all other substances
require a transporter)
Which membrane component maintains membrane integrity over a range of temperatures?
cholesterol
(Note: sterols perform
similar functions in plants)
What do prokaryotic cells use instead of cholesterol in their membrane?
hopanoids
Which membrane component makes a carbohydrate coat that covers the cell wall of some bacteria and the plasma membrane of some animal cells?
glycocalyx
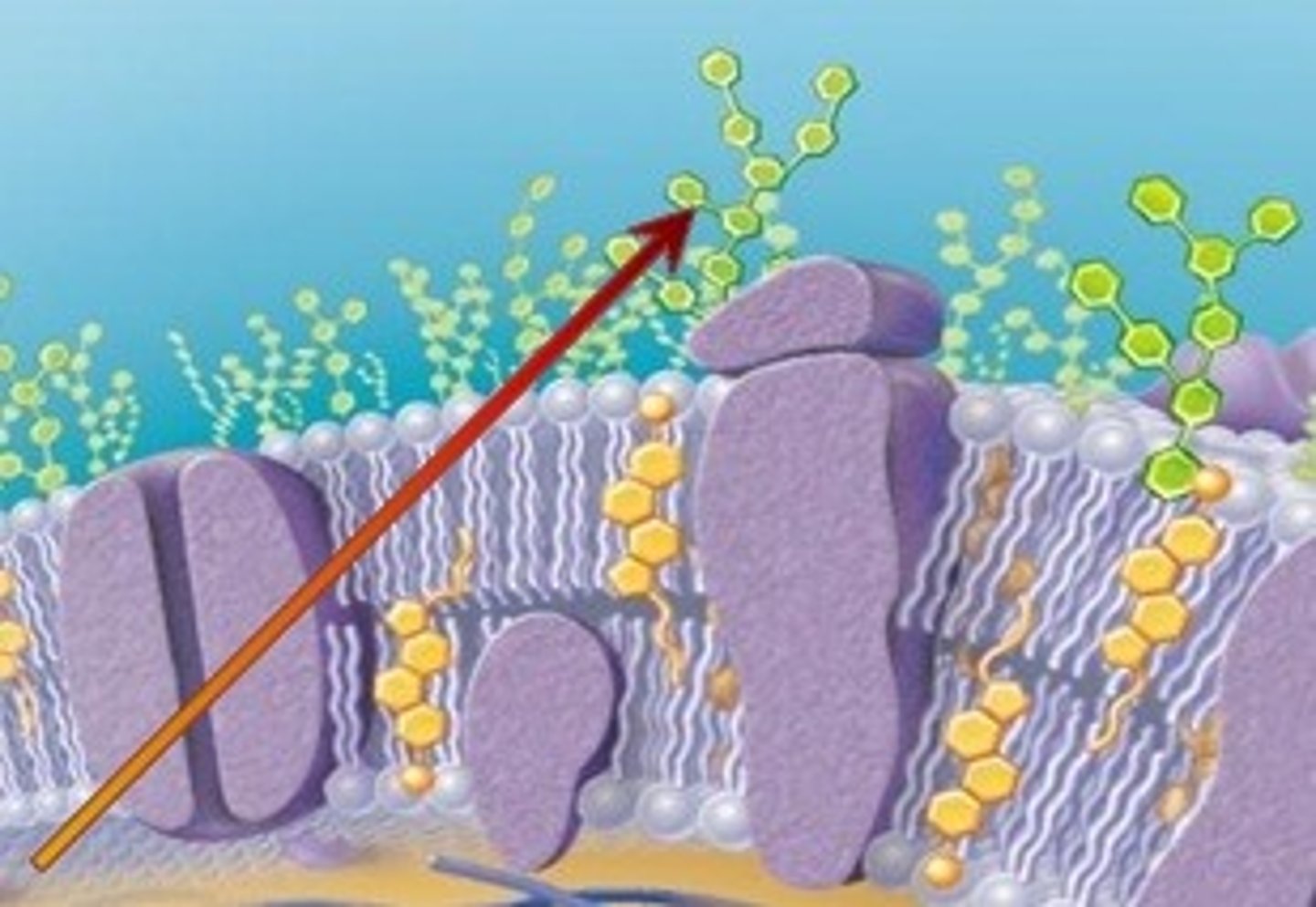
What are the components of the glycocalyx?
1. glycolipids attached
to the plasma membrane
2. glycoproteins serving
as recognition proteins
What are the functions of the glycocalyx?
1. adhesion
2. barrier to infection
3. markers for
cell-cell recognition
Which organelle contains chromatin, which is the general packaging structure of DNA around proteins in eukaryotes?
nucleus
(Note: tightness in
packaging depends
on cell stage)
What are tightly condensed chromatin when the cell is ready to divide?
chromosomes
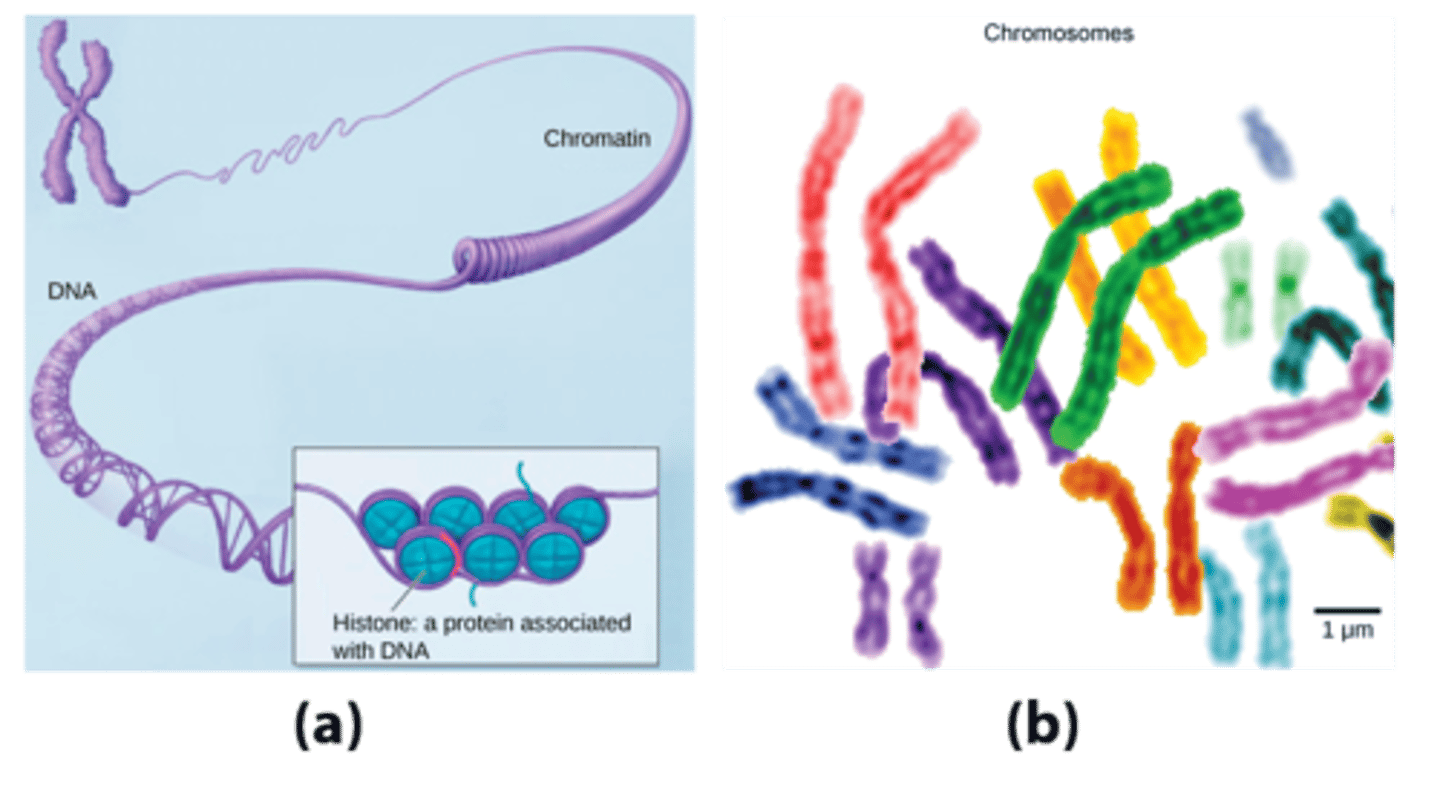
What structures serve to organize DNA which coil around it into bundles called nucleosomes?
histones
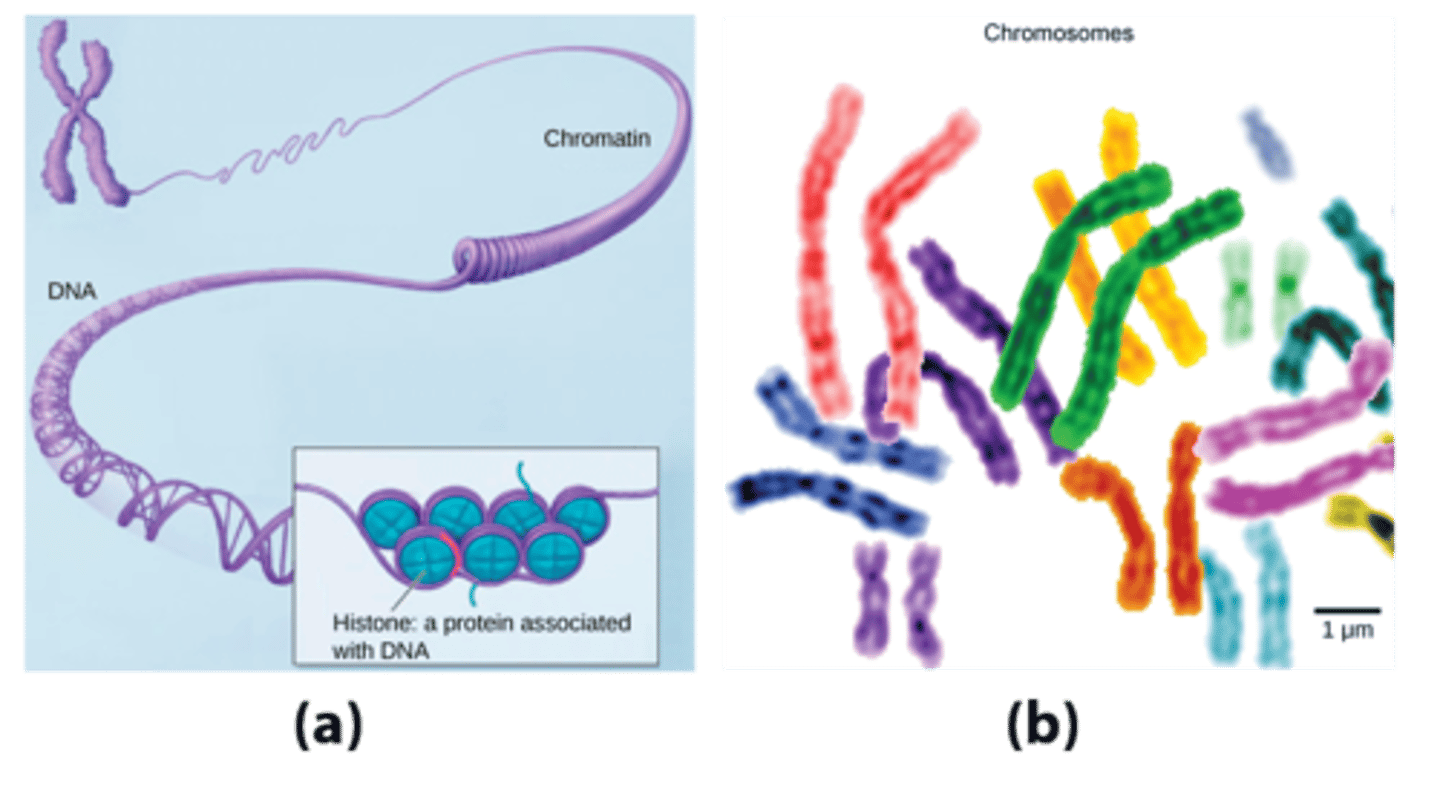
Nucleosomes are wrapped around what number of histone proteins?
8
Which structure is located inside the nucleus and serves as the site of ribosome synthesis?
nucleolus
What organelles are synthesized using rRNA and proteins which are imported from the cytoplasm?
ribosomes
(Note: Once ribosomal
subunits form, they are
exported to the
cytoplasm for final
assembly into a
complete ribosome)
What is the double-layered boundary that binds the nucleus?
nuclear envelope
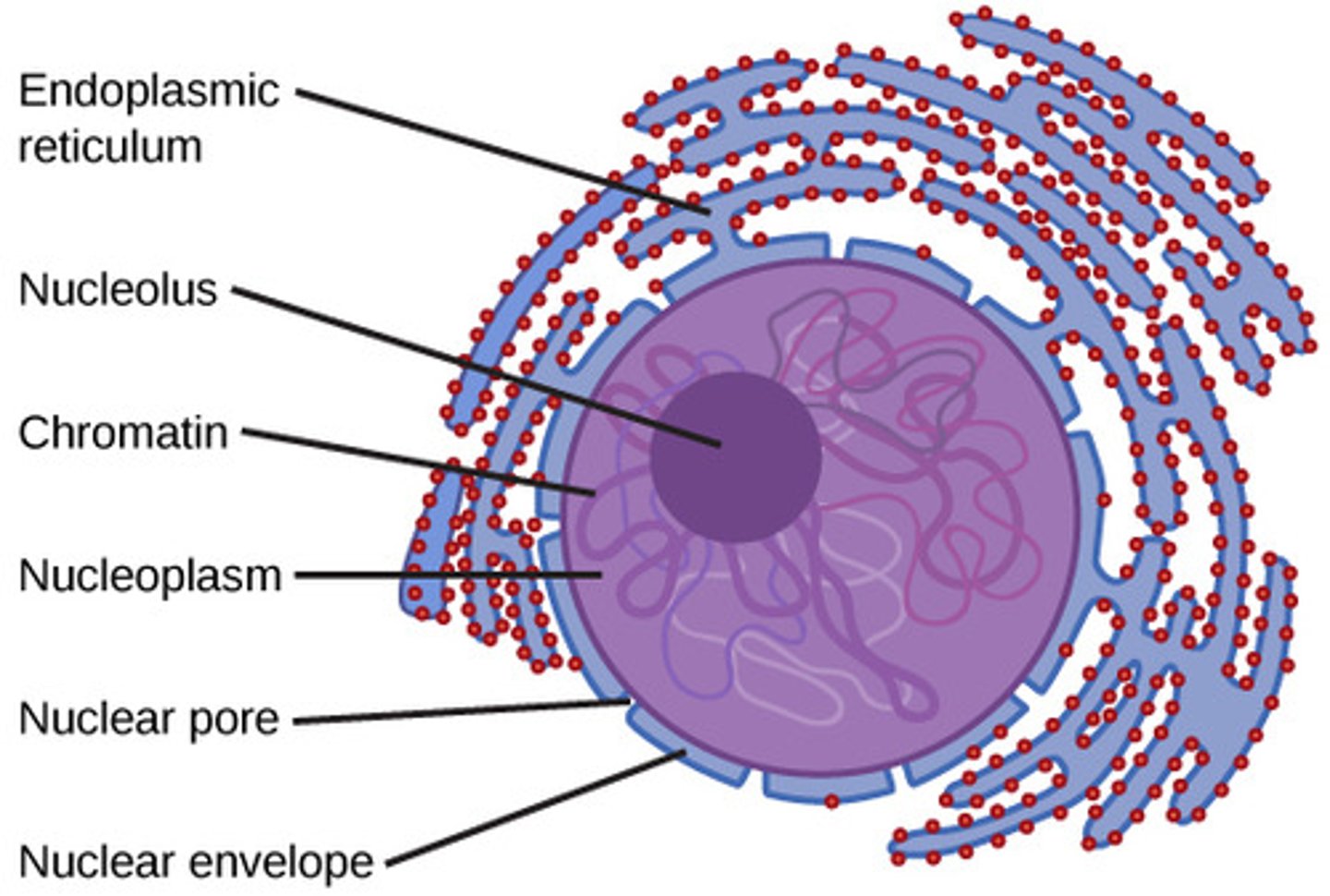
What structures allow transport across the nuclear envelope?
nuclear pores
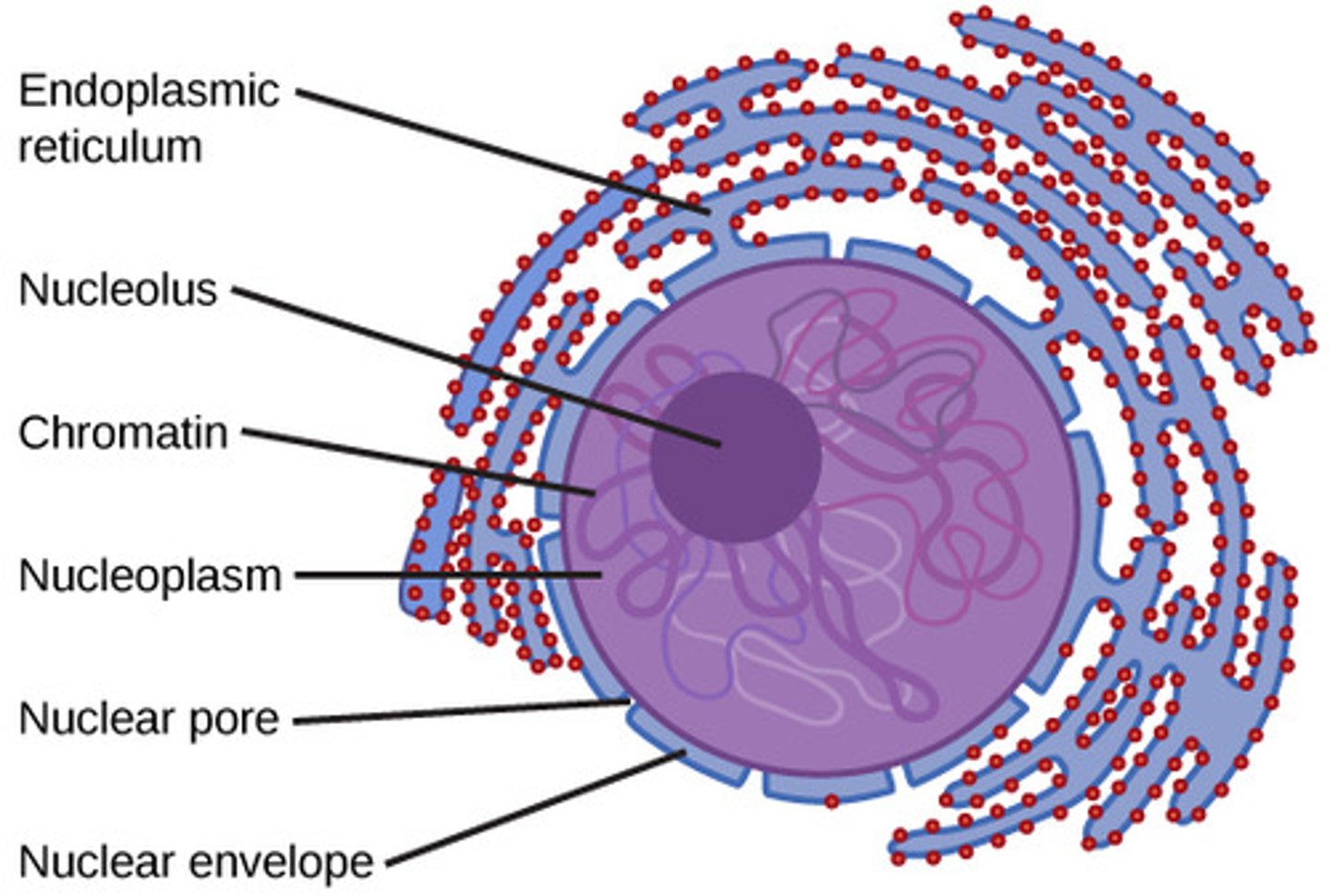
What is the cytoplasm-like substance within the nucleus?
nucleoplasm
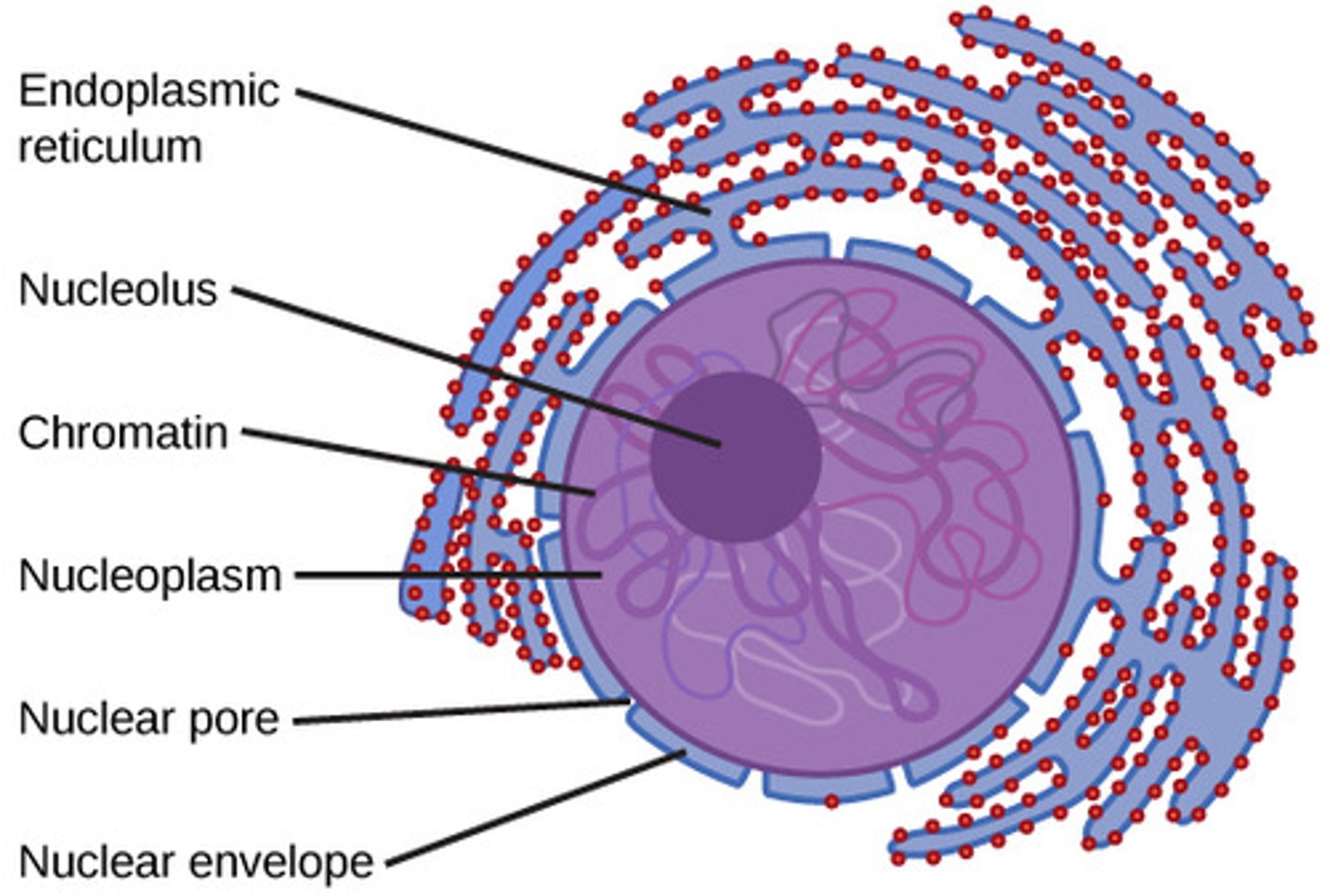
What is a dense fibrillar network inside of the nucleus of eukaryotic cells?
nuclear lamina
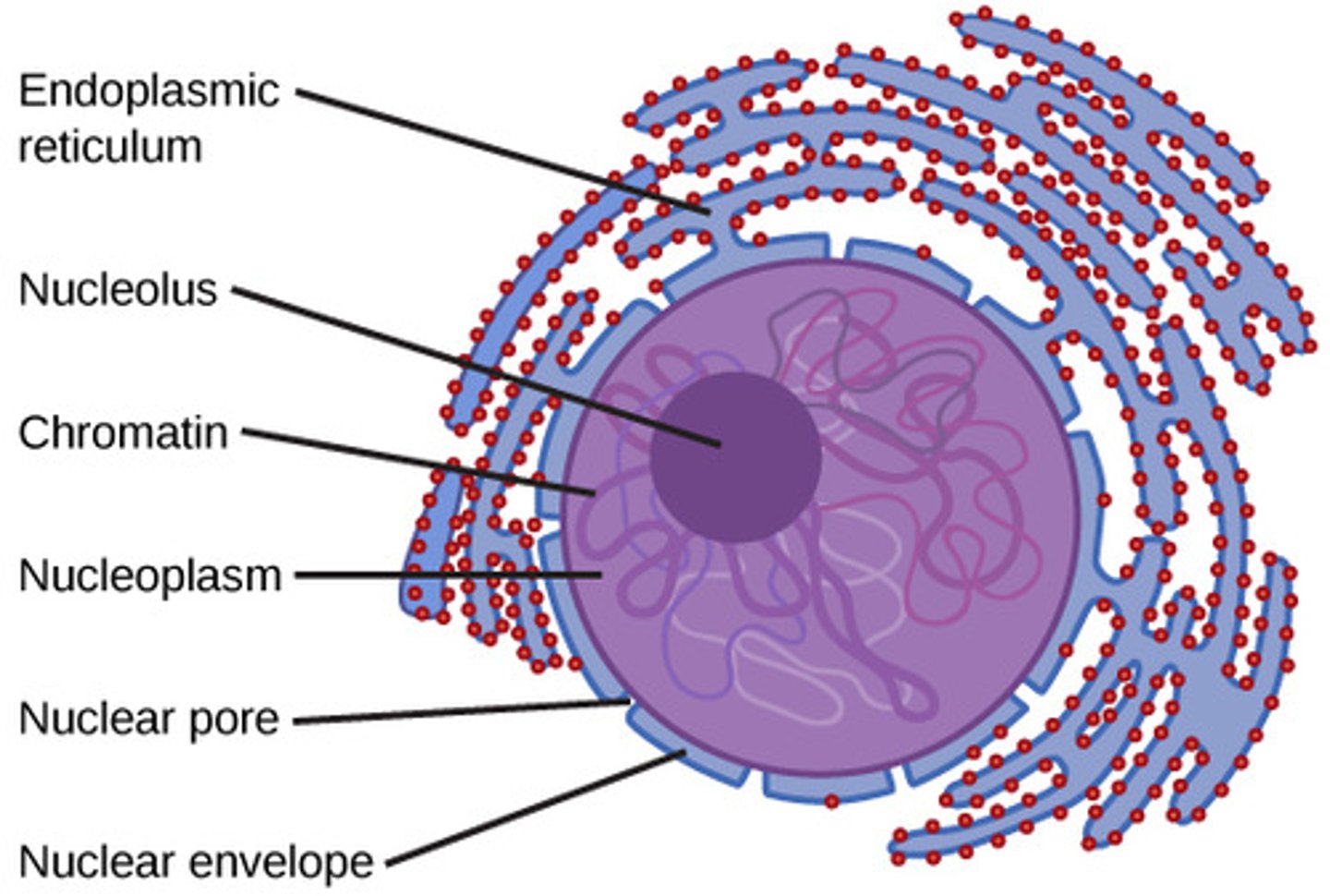
What are the components of the nuclear lamina?
1. intermediate filaments
2. membrane-associated proteins
What are the functions of the nuclear lamina?
1. mechanical support
2. regulation of DNA replication, cell division, and chromatin organization
Which organelle is the irregular shaped region within prokaryote cells that contains all or most of the cell’s genetic material?
nucleoid
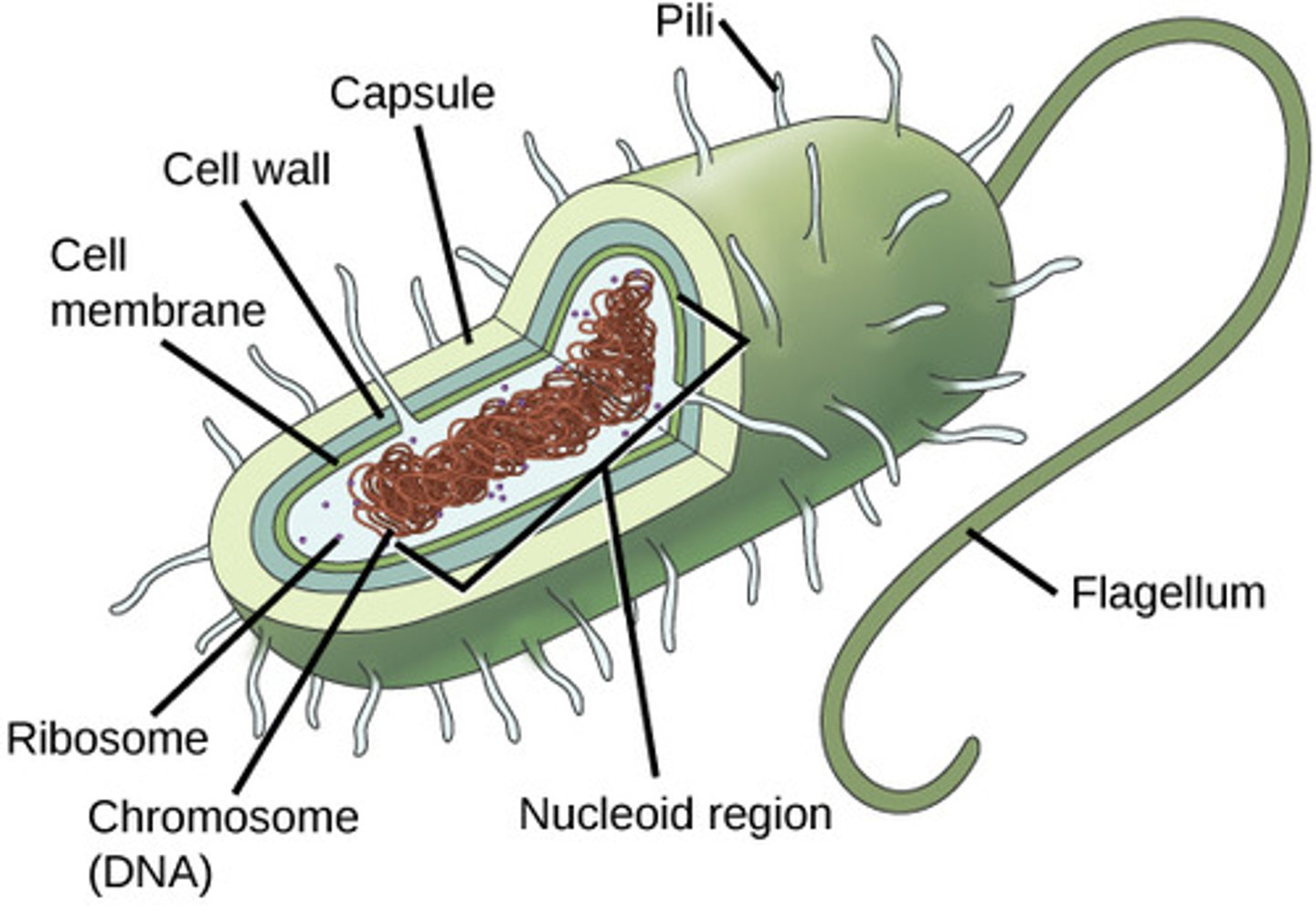
What is the area that contains the cell’s metabolic activity and transportation (cytosol and organelles)?
cytoplasm