Unit 4 Chemistry Study Set
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
What are orbitals?
Probability maps of where the electron will be 90% of the time
How many parts are orbitals made up of?
3
What is the first part of orbitals?
The principle quantum number
The higher the principal quantum number,
the more energy is held by electrons in that level
What is the second part of orbitals?
The subshell
How many types of subshells are there?
4
What are the subshell types (the letter)?
s, p, d, and f
T of F: Each type of subshell has a unique shape
True
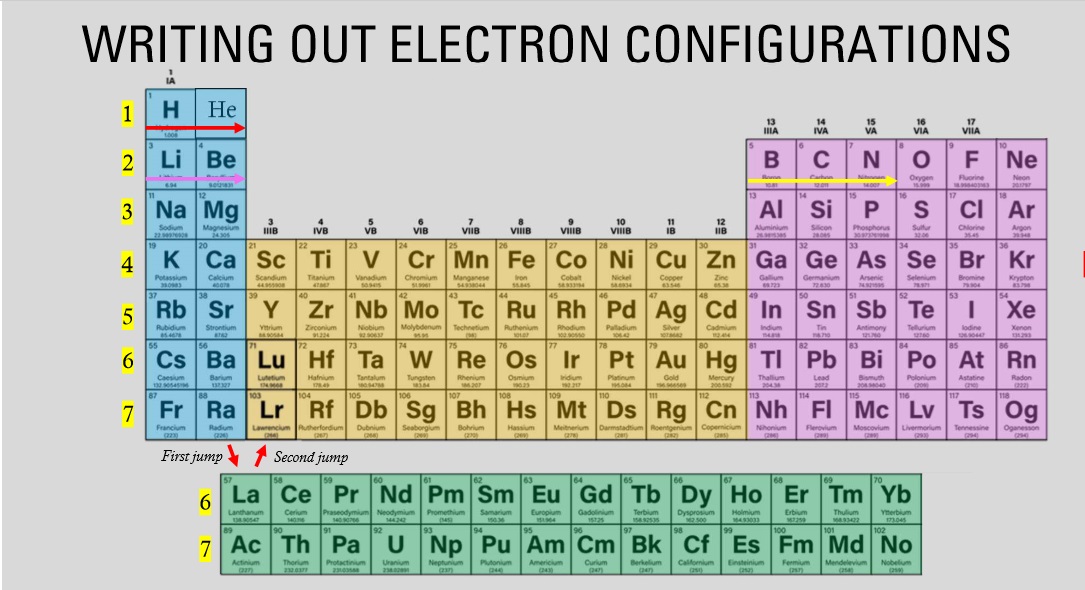
The elements highlighted in the blue fall under which block?
S block
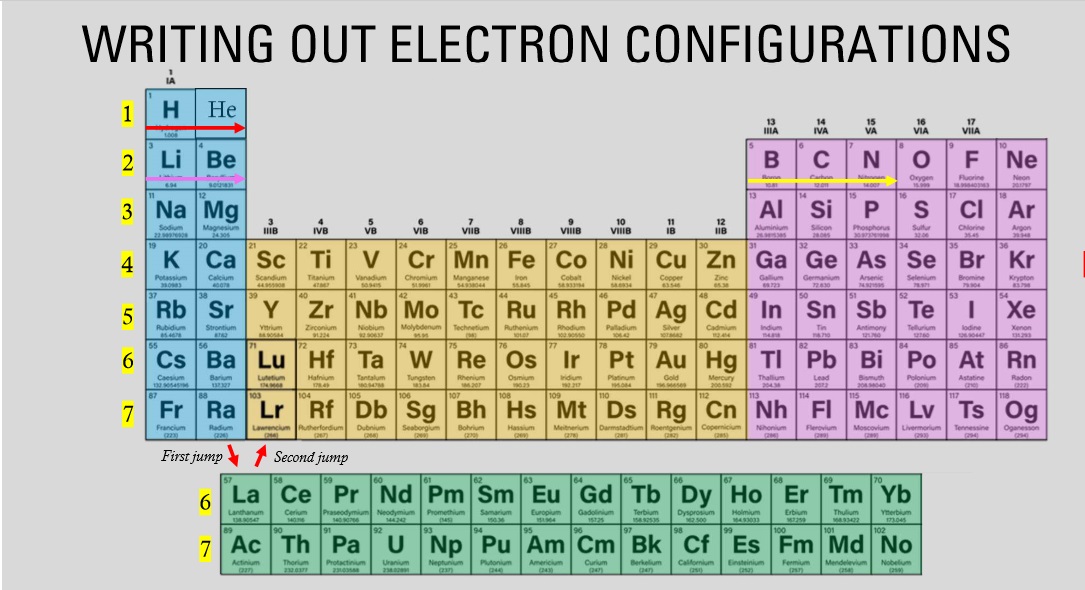
The elements highlighted in the yellow fall under which block?
D block
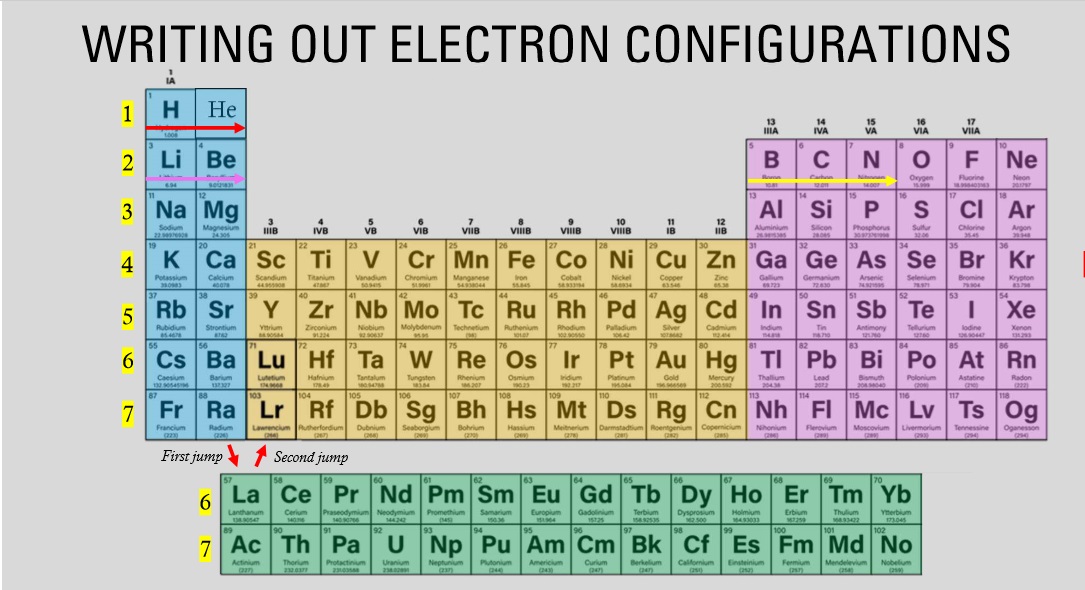
The elements highlighted in the pink fall under which block?
P block
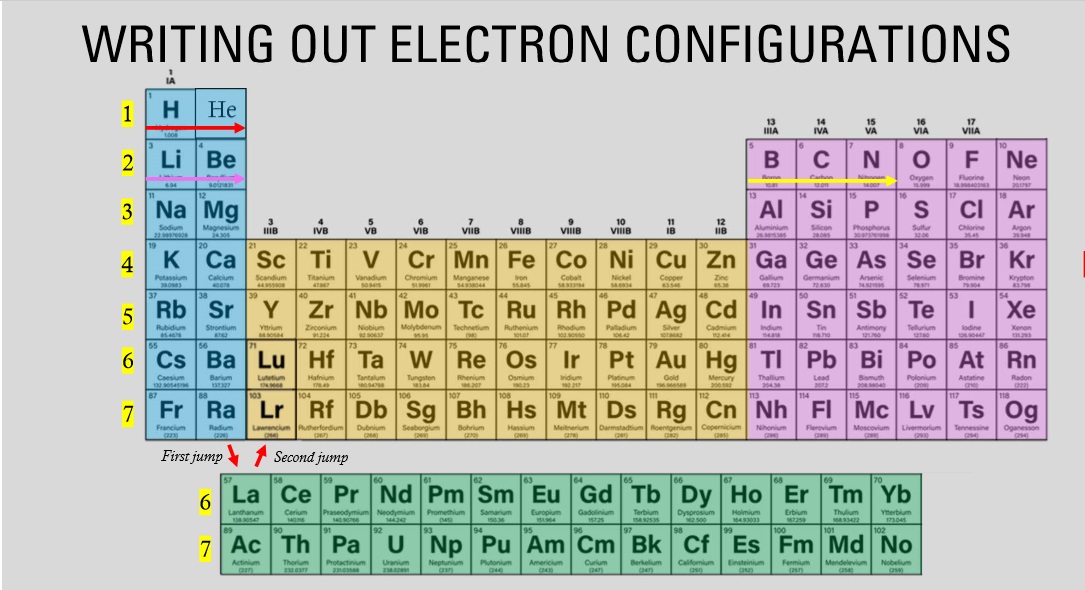
The elements highlighted in the green fall under which block?
F block
What is the third part of an orbital?
The number of electrons in the orbital
How is the number of electrons in an orbital shown?
With exponents
Each period on the Periodic Table corresponds to the _______________.
quantum number
How you should you read the Periodic Table to find any element’s electron configuration?
Left to right, top to bottom
When crossing into the d-block when writing electron configurations, what happens to the principal quantum number?
It becomes one less than the actual period the element is in
When crossing into the f-block when writing electron configurations, what happens to the principal quantum number?
It becomes two less than the actual period the element is in
Which family/group on the periodic table can you use as a shortcut for writing electron configurations?
Noble Gases (Group 18)
How do Noble Gas Electron Configurations work?
Place the pervious noble gas in brackets to signify all the electrons up to that point, then write out normally until you reach your desired element
What does an element’s electron configuration show us?
Which electrons are stable and which electrons are most likely to react
Why are noble gases chemically stable?
All their electrons completely fill up their orbitals
In chemical reactions, which electrons are the only electrons lost or gained?
Valence electrons
T or F: Valence electrons are the electrons found within the highest principal quantum number.
True
What is the electron configuration for Nitrogen?
1s²2s²2p³
What is the electron configuration of Gallium?
1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰4p¹
What is the Noble Gas electron configuration of Tin?
[Kr]5s²4d¹⁰5p²
What is the Noble Gas electron configuration of Lead?
[Xe]6s²4f¹⁴5d¹⁰6p²
What is atomic size?
The distance between an atom’s outermost electron and its nucleus
What is ionization energy?
The energy required to remove an electron from the atom in the gaseous state
What is metallic character?
How much an element behaves like a metal and loses electrons in chemical reactions
What is electronegativity?
The likelihood of an element to gain an electron
From Helium (very top right corner of Periodic Table) to Francium (very bottom left corner), what direction does Atomic Size’s trend go?
Down
From Helium (very top right corner of Periodic Table) to Francium (very bottom left corner), what direction does Metallic Character’s trend go?
Down
From Helium (very top right corner of Periodic Table) to Francium (very bottom left corner), what direction does Ionization Energy’s trend go?
Up
From Helium (very top right corner of Periodic Table) to Francium (very bottom left corner), what direction does Electronegativity’s trend go?
Up
How can the valence electrons of an element be represented visually (think of structures)?
Lewis structure
What is the Octet Rule?
In chemical bonding, atoms transfer or share electrons to obtain outer shells with eight electrons
Which group/family does the Octet Rule apply to?
Noble Gases/Group 18
What is ionic bonding?
Chemical bonding where electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another
What kind of elements does ionic bonding always occur between?
Metals and nonmetals
What must the overall charge of an ionic formula equal?
0
How do you name ionic formulas?
Positively-charged ion [SPACE] negatively-charged ion + “IDE” ending
What is the formula for aluminum fluoride?
AlF₃
What is the formula for lead (II) bromide?
PbBr₂
What is the formula for scandium (III) oxide?
Sd₂O₃
What is the formula for zinc sulfide?
ZnS
What is the name of the given formula?: FeCl₃
Iron (III) chloride
What is the name of the given formula?: MnBr₂
Manganese bromide
What is the name of the given formula?: Cu₂S
Copper (I) sulfide
What is the name of the given formula?: SnF₄
Tin (IV) fluoride
What is the name of the given formula?: AgH
Silver hydride
What is the name of the given formula?: BaF₂
Barium fluoride
What are some properties of ionic compounds?
High melting point, dissolves in water, conducts electricity
What is covalent bonding?
Chemical bonding where electrons are shared between atoms
What are some properties of covalent compounds?
Low melting point, dissolves in alcohol, does not conduct electricity
What kind of elements does covalent bonding always occur between?
Two or more nonmetals
How do you name covalent compounds?
(PREFIX) Positively-charged ion name [SPACE] (PREFIX) Negatively-charged ion + “IDE” ending
What is the prefix for one?
Mono
What is the prefix of two?
Di
What is the prefix of three?
Tri
What is the prefix of four?
Tetra
What is the prefix of five?
Penta
What is the prefix of six?
Hexa
What is the prefix of seven?
Hepta
What is the prefix of eight?
Octa
What is the prefix of nine?
Nona
What is the prefix of ten?
Deca
What acid name format do elemental anions have?
Hydro______Acid
What acid name format do “ate” polyatomic ions have?
____________ic Acid
What acid name format do “ous” polyatomic ions have?
_____________ous Acid
What is the name for the formula S₆O₂?
Hexasulfur dioxide
What is the name for the formula B₇Cl₅?
Heptaboron pentachloride
What is the name of the formula BCl₃?
Boron trichloride
What is the name of the formula ClO?
Chloride monooxide
What is the formula for the given name?: Nonaphosphorus octachloride
P₉Cl₈
What is the formula for the given name?: Dinitrogen tetroxide
N₂O₄
What is the formula for the given name?: Sodium pentachloride
NaCl₅
What is the formula for the given name?: Trinitrogen monoxide
N₃O
What is the name for the given formula?: Mg(ClO₃)₂
Magnesium chlorate
What is the name for the given formula?: CuC₂H₃O₂
Copper (I) acetate
What is the name for the given formula?: (NH₄)₃PO₄
Ammonium phosphate
What is the formula for scadium (III) carbonate?
SdCO3
What is the formula for potassium phosphate?
K₃PO₄
What is the formula for tin (IV) sulfate?
Sn(SO₄)₂
Name the following acid: HI
Hydroiodic acid
Name the following acid: H₂SO₃
Sulfurousacid
Name the following acid: H₃PO₄
Phosphoric acid